A Mobile-Side-Dominant Method for Querying Present and Future Velocity on Urban Roads
-
摘要: 城市智能交通管理中经常查询路段的当前和未来交通速度,该文提出一种车载边缘为主(VED)的城市路段速度查询和预测方法:车载端在速度低于一定阈值时,与其它车载端交换收集到的数据,并在本地构建轻量级的当前和历史速度索引,以支持当前速度查询。为了用尽可能少的模型支持速度预测,提出根据路段拓扑同构将路网划分成若干路段等价类,根据周期性时窗和路段等价类将整个时空划分成若干模型等价类,同一个模型等价类的路段在给定时窗呈现相似的交通运行模式。针对每个模型等价类,车载端和数据中心配合进行联邦学习,训练长短期记忆模型(LSTMs)并存储在车载端,以响应车载端对附近未来交通状况的查询。每个车载端本地索引数据、本地响应查询,避免了查询响应延迟和通信拥塞;数据保存在车载端,而非集中存放,避免了安全攻击导致的隐私泄漏。Abstract: Querying present and future traffic velocities of road segments is a routine task in urban intelligence transportation management, and a Vehicle-equipped-Edge Dominant (VED) method is proposed to answer the querying of present and future velocity of urban road segments. The collected data is exchanged with the other mobile sides by every vehicle-equipped mobile side when the mobile side’s speed falls below a given threshold, and the light-weighted present and history velocity indexes are constructed locally to support the querying of present velocity. To train as few models as possible to predict future velocities, a road network is proposed to be partitioned into a set of road-segment clusters based on the segments’ topological morphism and the spatio-temporal space is proposed to be partitioned into a set of model-equivalence classes according to the periodic time windows and road-segment clusters. The similar traffic patterns are exhibited by the road segments in the same model-equivalence class within the given time window. For every model-equivalence class, the federated learning is performed between the mobile sides and the data center to train the Long Short-Term Memories (LSTMs) which are stored at the mobile sides to answer the querying of future velocities of nearby areas. Data is indexed by every mobile side and queries are answered locally, thus the query response latency and possible communication congestion can be avoided. Further, data is stored at the mobile sides, rather than at one data center, so as to prevent the privacy leakage due to security attacks.
-
Key words:
- Intelligence transportation /
- Query /
- Prediction /
- Index /
- Federated learning
-
2 inSphere
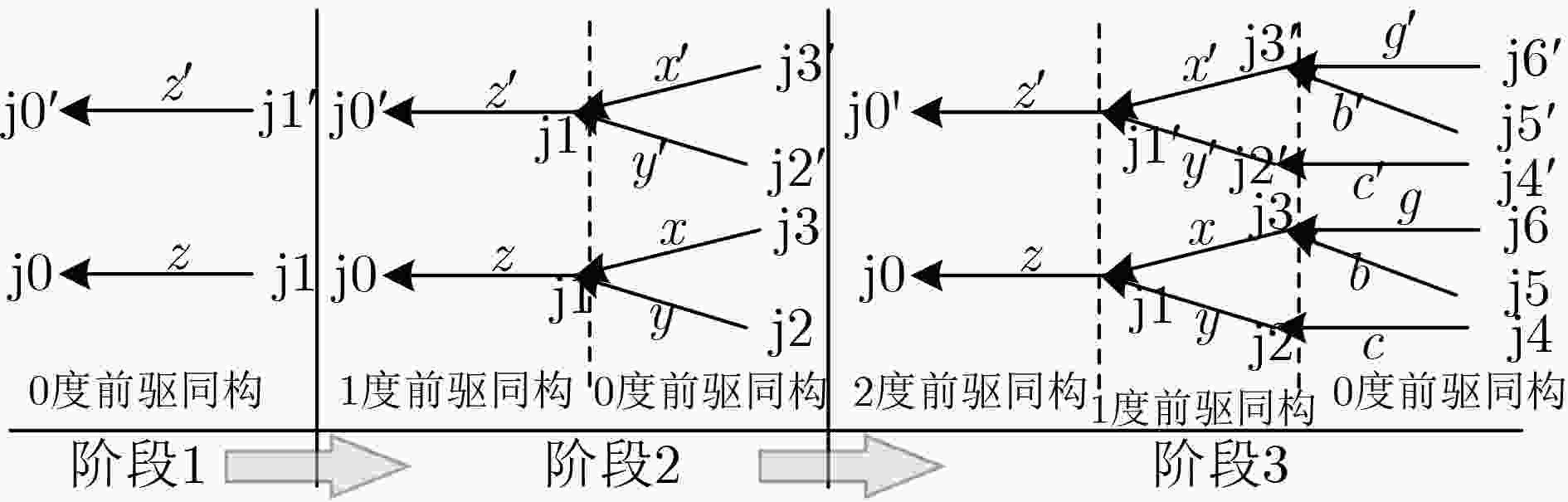
输入:路网$ \mathrm{D}\mathrm{N} $,进入同构参数$ m $,目标路段$ \mathrm{t}\mathrm{s}\mathrm{g} $ 输出:路段$ \mathrm{t}\mathrm{s}\mathrm{g} $的$ m $跳距内的进入路段 (1) 初始化队列$ Q $并将$ \mathrm{t}\mathrm{s}\mathrm{g} $入队 (2) $ \mathrm{v}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{s}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{t}\left(\mathrm{t}\mathrm{s}\mathrm{g}\right),\mathrm{ }\mathrm{r}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{t}\leftarrow \varnothing $ (3) while $ Q $非空 do (4) $ \mathrm{s}\mathrm{g}\leftarrow {Q}.\mathrm{p}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{p}\left(\cdot\right) $, $ \mathrm{r}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{t}\leftarrow \mathrm{r}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{t}\cup \left\{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{g}\right\} $ (5) if $ \left|\mathrm{s}\mathrm{g}\right| < m $ then (6) 获取$ \mathrm{s}\mathrm{g} $的所有直接前驱并将它们送入队列$ Q $ (7) end (8) end 1 同构路段划分
输入:路网$ \mathrm{D}\mathrm{N} $,同构参数$ m $和$ n $,特征标签集合$ L $ 输出:路段的同构分组 (1) 将$ \mathrm{D}\mathrm{N} $的第1个路段$ \mathrm{s}\mathrm{g} $压入栈$ \mathrm{S}\mathrm{K} $中 (2) while $ \mathrm{S}\mathrm{K} $非空 do (3) $ \mathrm{s}\mathrm{g}\leftarrow \mathrm{S}\mathrm{K}.\mathrm{p}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{p}\left(\cdot\right) $ (4) if $ \mathrm{s}\mathrm{g} $未被处理过 then (5) $ \mathrm{v}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{s}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{t}\left(\mathrm{s}\mathrm{g}\right) $ (6) $ \mathrm{s}\mathrm{g}\mathrm{的}\mathrm{前}\mathrm{驱}\mathrm{路}\mathrm{段}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{s}\mathrm{g}\mathrm{s}\leftarrow \mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{S}\mathrm{p}\mathrm{h}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{e}\left(\mathrm{D}\mathrm{N},\mathrm{s}\mathrm{g},m\right) $ (7) $ \mathrm{s}\mathrm{g}\mathrm{的}\mathrm{后}\mathrm{继}\mathrm{路}\mathrm{段}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{u}\mathrm{t}\mathrm{s}\mathrm{g}\mathrm{s}\leftarrow \mathrm{o}\mathrm{u}\mathrm{t}\mathrm{S}\mathrm{p}\mathrm{h}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{e}\left(\mathrm{D}\mathrm{N},\mathrm{s}\mathrm{g},n\right) $ (8) $ \mathrm{h}\mathrm{c}\leftarrow \mathrm{f}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{t}\mathrm{u}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{C}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{d}\mathrm{e}\left(\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{s}\mathrm{g}\mathrm{s},\mathrm{o}\mathrm{u}\mathrm{t}\mathrm{s}\mathrm{g}\mathrm{s},L\right) $ (9) 根据$ \mathrm{h}\mathrm{c} $将$ \mathrm{s}\mathrm{g} $归类 (10) end (11) if $ \mathrm{s}\mathrm{g} $的邻接路段$ w $未被分类过 then (12) push$ \left(w\right) $ (13) end (14) else (15) $ \mathrm{s}\mathrm{g}=\mathrm{S}\mathrm{K}.\mathrm{p}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{p}\left(\cdot\right) $ (16) end 3 响应未来交通查询
输入:车载端的LSTM模型,对未来交通的查询$ \mathrm{f}\mathrm{q}\left(\mathrm{r}\mathrm{s},\mathrm{t}\mathrm{s}\right) $,当前
速度索引PVI,恢复矩阵$ \bf{A}\bf{V} $输出:对应的时空单元$ \mathrm{S}\mathrm{G}\left(\mathrm{r}\mathrm{s},\mathrm{t}\mathrm{s}\right) $的预测速度 (1) $ \mathrm{l}\mathrm{s}\mathrm{t}\mathrm{m}\leftarrow \mathrm{车}\mathrm{载}\mathrm{端}\mathrm{对}\mathrm{应}\mathrm{于}\mathrm{S}\mathrm{G}\left(\mathrm{r}\mathrm{s},\mathrm{t}\mathrm{s}\right)\mathrm{的}\mathrm{L}\mathrm{S}\mathrm{T}\mathrm{M}\mathrm{模}\mathrm{型} $ (2) $ \mathrm{s}\mathrm{h}\leftarrow \mathrm{P}\mathrm{V}\mathrm{I}\mathrm{中}\mathrm{对}\mathrm{应}\mathrm{于} $mn(k–1)–SH(rs,ts–1)时空范围的样本概况 (3) 预测集$ \mathrm{p}\mathrm{v}\leftarrow \varnothing $ (4) for $ \mathrm{c}\mathrm{l}\in \mathrm{s}\mathrm{h} $ do (5) $ \mathrm{v}\mathrm{v}\leftarrow \mathrm{计}\mathrm{算}\mathrm{c}\mathrm{l}\mathrm{中}\mathrm{的}\mathrm{速}\mathrm{度} $ (6) if $ \mathrm{c}\mathrm{l} $ 为空 then (7) $ \mathrm{v}\mathrm{v}\leftarrow \bf{A}\bf{V}\left[\mathrm{r}\mathrm{s},\mathrm{t}\mathrm{s}\right]\mathrm{中}\mathrm{的}\mathrm{数}\mathrm{据} $ (8) end (9) $ \mathrm{将}\mathrm{v}\mathrm{v}\mathrm{加}\mathrm{入}\mathrm{p}\mathrm{v} $ (10) end (11) $ \mathrm{r}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{t}\leftarrow \mathrm{l}\mathrm{s}\mathrm{t}\mathrm{m}\left(\mathrm{p}\mathrm{v}\right) $ (12) return ret -
[1] PELANIS M, ŠALTENIS S, and JENSEN C S. Indexing the past, present, and anticipated future positions of moving objects[J]. ACM Transactions on Database Systems, 2006, 31(1): 255–298. doi: 10.1145/1132863.1132870. [2] PFOSER D, BRAKATSOULAS S, BROSCH P, et al. Dynamic travel time provision for road networks[C]. The 16th ACM SIGSPATIAL International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems, Irvine, USA, 2008: 68. doi: 10.1145/1463434.1463513. [3] CHANG Jundong. Spatial-temporal based traffic speed imputation for GPS probe vehicles[C]. The Fifth International Conference on Network, Communication and Computing, Kyoto, Japan, 2016: 326–330. doi: 10.1145/3033288.3033339. [4] CHEN Rongsheng and LEVIN M W. Traffic state estimation based on Kalman filter technique using connected vehicle V2V basic safety messages[C]. 2019 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference, Auckland, New Zealand, 2019: 4380–4385. doi: 10.1109/ITSC.2019.8917343. [5] 崔艳玲, 金蓓弘, 张扶桑. 基于数据融合的高速公路交通状况检测[J]. 计算机学报, 2017, 40(8): 1798–1812. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2017.01798.CUI Yanling, JIN Beihong, and ZHANG Fusang. Highway traffic condition detection with data fusion[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2017, 40(8): 1798–1812. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2017.01798. [6] BEI Pan, DEMIRYUREK U, and SHAHABI C. Utilizing real-world transportation data for accurate traffic prediction[C]. IEEE 12th International Conference on Data Mining, Brussels, Belgium, 2012: 595–604. doi: 10.1109/ICDM.2012.52. [7] HE Zhixiang, CHOW C Y, and ZHANG Jiadong. STCNN: A spatio-temporal convolutional neural network for long-term traffic prediction[C]. The 20th IEEE International Conference on Mobile Data Management, Hong Kong, China, 2019: 226–233. doi: 10.1109/MDM.2019.00-53. [8] TANG Keshuang, CHEN Siqu, CAO Yumin, et al. Short-term travel speed prediction for urban expressways: Hybrid convolutional neural network models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(3): 1829–1840. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2020.3027628. [9] TONG Guan, PENG Jiaheng, and LIANG Jun. Spatial-temporal graph multi-gate mixture-of-expert model for traffic prediction[C]. IEEE 26th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, Bilbao, Spain, 2023: 36–41. doi: 10.1109/ITSC57777.2023.10422031. [10] LI Maosen, CHEN Siheng, SHEN Yanning, et al. Online multi-agent forecasting with interpretable collaborative graph neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2024, 35(4): 4768–4782. doi: 10.1109/tnnls.2022.3152251. [11] 岳猛, 王怀远, 吴志军, 等. 云计算中DDoS攻防技术研究综述[J]. 计算机学报, 2020, 43(12): 2315–2336. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2020.02315.YUE Meng, WANG Huaiyuan, WU Zhijun, et al. A survey of DDoS attack and defense technologies in cloud computing[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2020, 43(12): 2315–2336. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2020.02315. [12] QI Bozhao, KANG Lei, and BANERJEE S. A vehicle-based edge computing platform for transit and human mobility analytics[C]. The Second ACM/IEEE Symposium on Edge Computing, San Jose, USA, 2017: 1. doi: 10.1145/3132211.3134446. [13] 吴洪越, 陈志伟, 石博文, 等. 一种面向边缘计算环境的去中心化服务请求分发方法[J]. 计算机学报, 2023, 46(5): 987–1002. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2023.00987.WU Hongyue, CHEN Zhiwei, SHI Bowen, et al. Decentralized service request dispatching for edge computing systems[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2023, 46(5): 987–1002. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2023.00987. [14] 张晓东, 张朝昆, 赵继军. 边缘智能研究进展[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2023, 60(12): 2749–2769. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.202220192.ZHANG Xiaodong, ZHANG Chaokun, and ZHAO Jijun. State-of-the-art survey on edge intelligence[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2023, 60(12): 2749–2769. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.202220192. [15] WANG Tian, LUO Hao, ZHENG Xi, et al. Crowdsourcing mechanism for trust evaluation in CPCS based on intelligent mobile edge computing[J]. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology, 2019, 10(6): 62. doi: 10.1145/3324926. [16] FELDMAN M, LAI K, STOICA I, et al. May. Robust incentive techniques for peer-to-peer networks[C]. The 5th ACM Conference on Electronic Commerce, New York, USA, 2004: 102–111. doi: 10.1145/988772.988788. [17] 陈山枝, 葛雨明, 时岩. 蜂窝车联网(C-V2X)技术发展、应用及展望[J]. 电信科学, 2022, 38(1): 1–12. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-0801.2022007.CHEN Shanzhi, GE Yuming, and SHI Yan. Technology development, application and prospect of cellular vehicle-to-everything (C-V2X)[J]. Telecommunications Science, 2022, 38(1): 1–12. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-0801.2022007. [18] HOCHREITER S and SCHMIDHUBER J. Long short-term memory[J]. Neural Computation, 1997, 9(8): 1735–1780. doi: 10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735. [19] RAMSAK F, MARKL V, FENK R, et al. Integrating the UB-tree into a database system kernel[C]. The 26th International Conference on Very Large Data Bases, Cairo, Egypt, 2000: 263–272. [20] NIELSEN F. On a generalization of the Jensen–Shannon divergence and the Jensen–Shannon centroid[J]. Entropy, 2020, 22(2): 221. doi: 10.3390/e22020221. [21] MCMAHAN B, MOORE E, RAMAGE D, et al. Communication-efficient learning of deep networks from decentralized data[C]. The 20th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Fort Lauderdale, USA, 2017: 1273–1282. -






 下载:
下载:















 下载:
下载:
