Text-to-video Generation: Research Status, Progress and Challenges
-
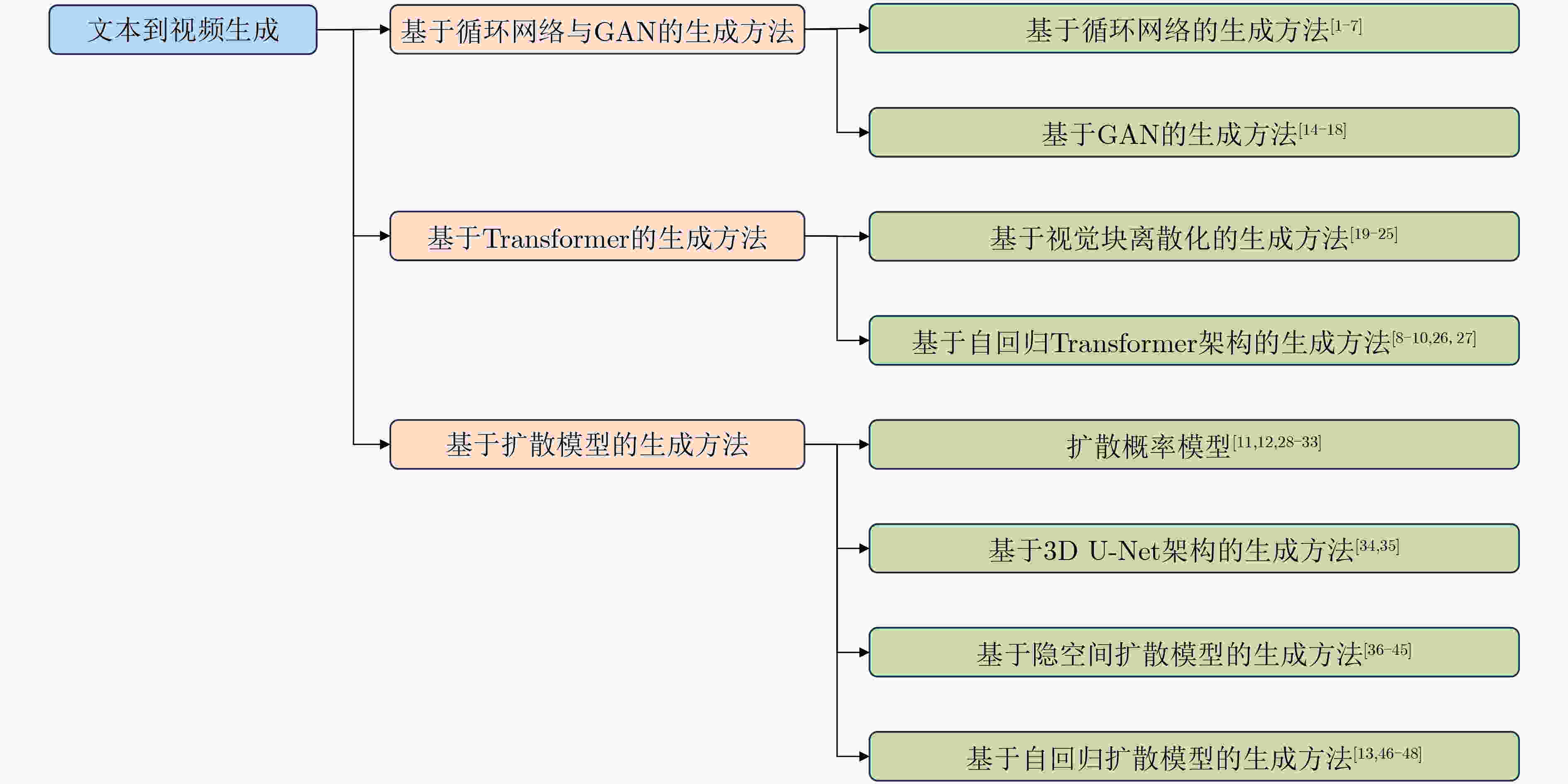
摘要: 文本到视频生成旨在根据用户给定的文本描述生成语义一致、内容真实、时序连贯且符合逻辑的视频。该文首先介绍了文本到视频生成领域的研究现状,详细介绍了3类主流的文本到视频生成方法:基于循环网络与生成对抗网络(GAN)的生成方法,基于Transformer的生成方法和基于扩散模型的生成方法。这3类生成方法在视频生成任务上各有优劣:基于循环网络与生成对抗网络的生成方法能生成较高分辨率和时长的视频,但难以生成复杂的开放域视频;基于Transformer的生成方法有能力生成复杂的开放域视频,但受限于Transformer模型单向偏置、累计误差等问题,难以生成高保真视频;扩散模型具有很好的泛化性,但受制于推理速度和高昂的内存消耗,难以生成高清的长视频。然后,该文介绍了文本到视频生成领域的评测基准和指标,并分析比较了现有主流方法的性能。最后,展望了未来可能的研究方向。Abstract: The generation of video from text aims to produce semantically consistent, photo-realistic, temporal consistent, and logically coherent videos based on provided textual descriptions. Firstly, the current state of research in the field of text-to-video generation is elucidated in this paper, providing a detailed overview of three mainstream approaches: methods based on recurrent networks and Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN), methods based on Transformers, and methods based on diffusion models. Each of these models has its strengths and weaknesses in video generation. The recurrent networks and GAN-based methods can generate videos with higher resolution and duration but struggle with generating complex open-domain videos. Transformer-based methods show proficiency in generating open-domain videos but face challenges related to unidirectional biases and accumulated errors, making it difficult to produce high-fidelity videos. Diffusion models exhibit good generalization but are constrained by inference speed and high memory consumption, making it challenging to generate high-definition and lengthy videos. Subsequently, evaluation benchmarks and metrics in the text-to-video generation domain are explored, and the performance of existing methods is compared. Finally, potential future research directions in the field is outlined.
-
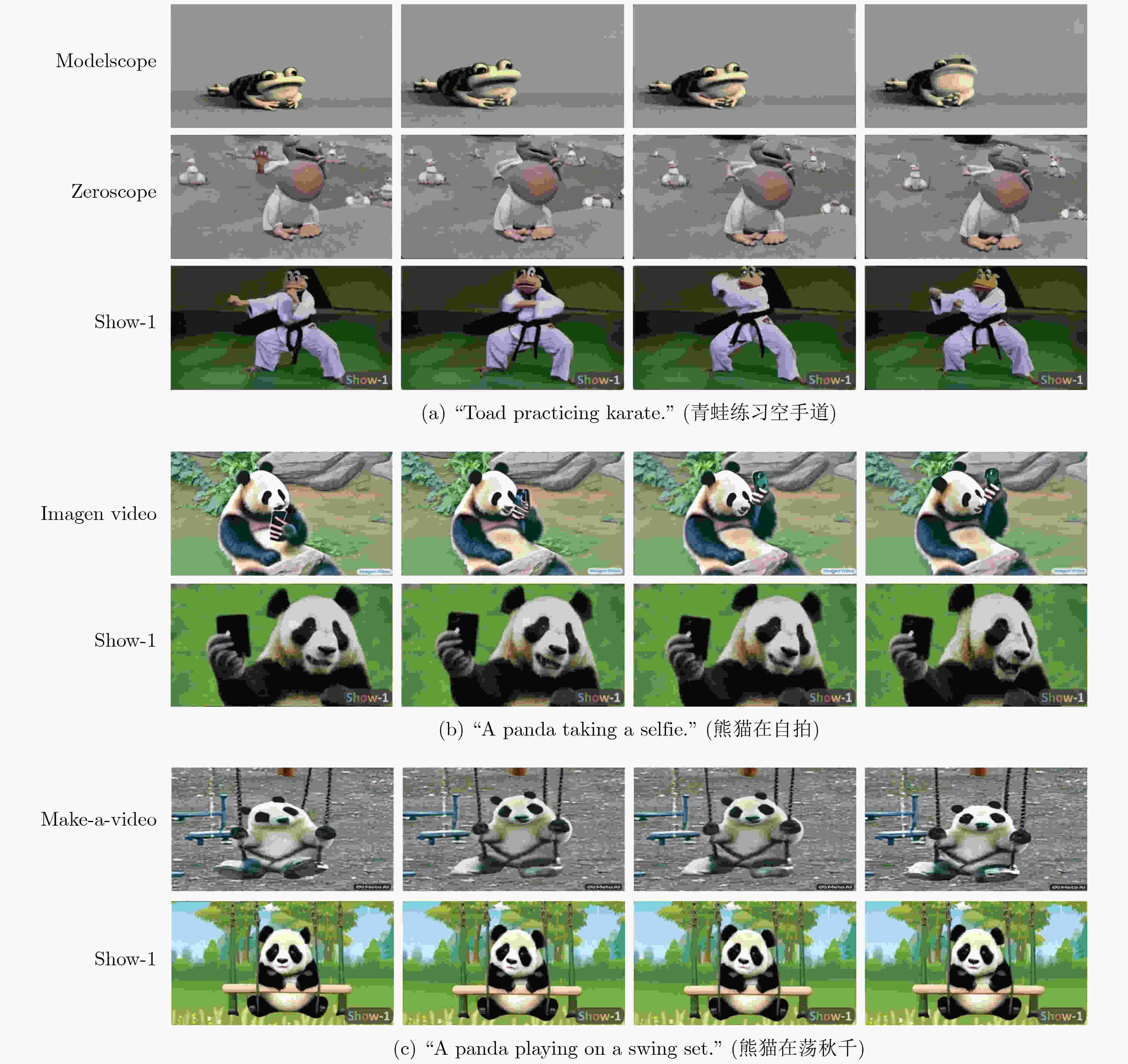
图 3 一些现有方法的可视化比较[53]
表 1 UCF-101数据集上的比较
表 2 MSR-VTT数据集上的比较
-
[1] FINN C, GOODFELLOW I J, and LEVINE S. Unsupervised learning for physical interaction through video prediction[C]. The 29th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 64–72. [2] RANZATO M, SZLAM A, BRUNA J, et al. Video (language) modeling: A baseline for generative models of natural videos[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1412.6604, 2014. [3] SRIVASTAVA N, MANSIMOV E, and SALAKHUTDINOV R. Unsupervised learning of video representations using LSTMs[C]. The 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 2015: 843–852. [4] AKAN A K, ERDEM E, ERDEM A, et al. SLAMP: Stochastic latent appearance and motion prediction[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 14728–14737. doi: 10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.01446. [5] BABAEIZADEH M, FINN C, ERHAN D, et al. Stochastic variational video prediction[C]. The 6th International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, Canada, 2018: 1–14. [6] DENTON E and FERGUS R. Stochastic video generation with a learned prior[C]. The 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholmsmässan, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 1174–1183. [7] FRANCESCHI J Y, DELASALLES E, CHEN M, et al. Stochastic latent residual video prediction[C]. The 37th International Conference on Machine Learning, 2020: 303. [8] VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 6000–6010. [9] RAKHIMOV R, VOLKHONSKIY D, ARTEMOV A, et al. Latent video transformer[C]. The 16th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications, 2021: 101–112. [10] YAN W, ZHANG Yunzhi, ABBEEL P, et al. VideoGPT: Video generation using VQ-VAE and transformers[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2104.10157, 2021. [11] SOHL-DICKSTEIN J, WEISS E A, MAHESWARANATHAN N, et al. Deep unsupervised learning using nonequilibrium thermodynamics[C]. The 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 2015: 2256–2265. [12] HO J, SALIMANS T, GRITSENKO A, et al. Video diffusion models[C]. The 36th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 628. [13] VOLETI V, JOLICOEUR-MARTINEAU A, and PAL C. MCVD: Masked conditional video diffusion for prediction, generation, and interpolation[C]. The 36th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 1698. [14] TULYAKOV S, LIU Mingyu, YANG Xiaodong, et al. MoCoGAN: Decomposing motion and content for video generation[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 1526–1535. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00165. [15] YU S, TACK J, MO S, et al. Generating videos with dynamics-aware implicit generative adversarial networks[C]. The 10th International Conference on Learning Representations, 2022: 1–15. [16] SAITO M, SAITO S, KOYAMA M, et al. Train sparsely, generate densely: Memory-efficient unsupervised training of high-resolution temporal GAN[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2020, 128(10/11): 2586–2606. doi: 10.1007/s11263-020-01333-y. [17] SKOROKHODOV I, TULYAKOV S, and ELHOSEINY M. StyleGAN-V: A continuous video generator with the price, image quality and perks of StyleGAN2[C]. 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 3626–3636. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00361. [18] KARRAS T, LAINE S, AITTALA M, et al. Analyzing and improving the image quality of StyleGAN[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 8110–8119. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00813. [19] RUMELHART D E, HINTON G E, and WILLIAMS R J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors[J]. Nature, 1986, 323(6088): 533–536. doi: 10.1038/323533a0. [20] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. The 26th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, USA, 2012: 1106–1114. [21] DEVLIN J, CHANG M W, LEE K, et al. BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding[C]. The 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Minneapolis, USA, 2019: 4171–4186. doi: 10.18653/v1/N19-1423. [22] RADFORD A, WU J, CHILD R, et al. Language models are unsupervised multitask learners[J]. OpenAI, 2019, 1(8): 9. [23] VAN DEN OORD A, VINYALS O, and KAVUKCUOGLU K. Neural discrete representation learning[C]. The 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 6306–6315. [24] DOSOVITSKIY A, BEYER L, KOLESNIKOV A, et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale[C]. The 9th International Conference on Learning Representations, Austria, 2021: 1–12. [25] WU Chenfei, LIANG Jian, JI Lei, et al. NÜWA: Visual synthesis pre-training for neural visual world creation[C]. The 17th European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 2022: 720–736. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-19787-1_41. [26] HONG Wenyi, DING Ming, ZHENG Wendi, et al. CogVideo: Large-scale pretraining for text-to-video generation via transformers[C]. The Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations, Kigali, Rwanda, 2023: 1–13. [27] DING Ming, ZHENG Wendi, HONG Wenyi, et al. CogView2: Faster and better text-to-image generation via hierarchical transformers[C]. The 36th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 16890–16902. [28] ROMBACH R, BLATTMANN A, LORENZ D, et al. High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models[C]. 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 10684–10695. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01042. [29] HO J, JAIN A, and ABBEEL P. Denoising diffusion probabilistic models[C]. The 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2020: 6840–6851. [30] KARRAS T, AILA T, LAINE S, et al. Progressive growing of GANs for improved quality, stability, and variation[C]. The 6th International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, Canada, 2018: 1–12. [31] NICHOL A Q, DHARIWAL P, RAMESH A, et al. GLIDE: Towards photorealistic image generation and editing with text-guided diffusion models[C]. The 39th International Conference on Machine Learning, Baltimore, USA, 2022: 16784–16804. [32] RAMESH A, DHARIWAL P, NICHOL A, et al. Hierarchical text-conditional image generation with CLIP latents[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2204.06125, 2022. [33] GAFNI O, POLYAK A, ASHUAL O, et al. Make-a-scene: Scene-based text-to-image generation with human priors[C]. The 17th European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 2022: 89–106. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-19784-0_6. [34] HO J, CHAN W, SAHARIA C, et al. Imagen video: High definition video generation with diffusion models[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2210.02303, 2022. [35] SINGER U, POLYAK A, HAYES T, et al. Make-a-video: Text-to-video generation without text-video data[C]. The Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations, Kigali, Rwanda, 2023. [36] NI Haomiao, SHI Changhao, LI Kai, et al. Conditional image-to-video generation with latent flow diffusion models[C]. 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, Canada, 2023: 18444–18455. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.01769. [37] LUO Zhengxiong, CHEN Dayou, ZHANG Yingya, et al. Notice of Removal: VideoFusion: Decomposed diffusion models for high-quality video generation[C]. 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, Canada, 2023: 10209–10218. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.00984. [38] WANG Jiuniu, YUAN Hangjie, CHEN Dayou, et al. ModelScope text-to-video technical report[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2308.06571, 2023. [39] https://research.runwayml.com/gen2. [40] https://pika.art/. [41] https://huggingface.co/cerspense/zeroscope_v2_576w. [42] WANG Xiang, YUAN Hangjie, ZHANG Shiwei, et al. VideoComposer: Compositional video synthesis with motion controllability[C]. The 37th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, USA, 2023. [43] https://openai.com/research/video-generation-models-as-world-simulators. [44] PEEBLES W and XIE Saining. Scalable diffusion models with transformers[C]. 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2023: 4195–4205. doi: 10.1109/ICCV51070.2023.00387. [45] MEI Kangfu and PATEL V. VIDM: Video implicit diffusion models[C]. The 37th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, USA, 2023: 9117–9125. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v37i8.26094. [46] DENG Zijun, HE Xiangteng, PENG Yuxin, et al. MV-Diffusion: Motion-aware video diffusion model[C]. The 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Ottawa, Canada, 2023: 7255–7263. doi: 10.1145/3581783.3612405. [47] DENG Zijun, HE Xiangteng, and PENG Yuxin. Efficiency-optimized video diffusion models[C]. The 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Ottawa, Canada, 2023: 7295–7303. doi: 10.1145/3581783.3612406. [48] SOOMRO K, ZAMIR A R, and SHAH M. UCF101: A dataset of 101 human actions classes from videos in the wild[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1212.0402, 2012. [49] XU Jun, MEI Tao, YAO Ting, et al. MSR-VTT: A large video description dataset for bridging video and language[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 5288–5296. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.571. [50] UNTERTHINER T, VAN STEENKISTE S, KURACH K, et al. Towards accurate generative models of video: A new metric & challenges[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1812.01717, 2018. [51] SALIMANS T, GOODFELLOW I, ZAREMBA W, et al. Improved techniques for training GANs[C]. The 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 2234–2242. [52] BLATTMANN A, DOCKHORN T, KULAL S, et al. Stable video diffusion: Scaling latent video diffusion models to large datasets[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2311.15127, 2023. [53] ZHANG D J, WU J Z, LIU Jiawei, et al. Show-1: Marrying pixel and latent diffusion models for text-to-video generation[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2309.15818, 2023. [54] YIN Shengming, WU Chenfei, YANG Huan, et al. NUWA-XL: Diffusion over diffusion for eXtremely long video generation[C]. The 61st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Toronto, Canada, 2023: 1309–1320. doi: 10.18653/v1/2023.acl-long.73. [55] VILLEGAS R, BABAEIZADEH M, KINDERMANS P J, et al. Phenaki: Variable length video generation from open domain textual descriptions[C]. The 11th International Conference on Learning Representations, Kigali, Rwanda, 2023. [56] ZHANG Yabo, WEI Yuxiang, JIANG Dongsheng, et al. ControlVideo: Training-free controllable text-to-video generation[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2305.13077, 2023. -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
