General Low-complexity Beamforming Designs for Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface-aided Multi-user Systems
-
摘要: 针对可重构智能超表面(RIS)辅助多用户系统中基站和RIS联合波束成形设计问题,该文提出通用低复杂度联合波束成形设计方案。首先,分析RIS辅助多用户系统以最大化和数据速率为目标的联合波束成形非凸优化问题。其次,利用波束导向矢量近似正交性设计RIS反射矩阵,进一步利用迫零方法设计基站发射波束成形,并对多用户进行功率分配优化。最后,讨论该方案适用性并对比该方案的计算复杂度相比现有方案降低了一个数量级。仿真结果表明,所提通用低复杂度波束成形设计可以获得较高和数据速率,并且采用最优功率分配可以进一步提高和数据速率。此外,仿真结果和理论分析都表明系统和数据速率随RIS位置的变化而变化,该结论为RIS位置的选择提供参考依据。Abstract:
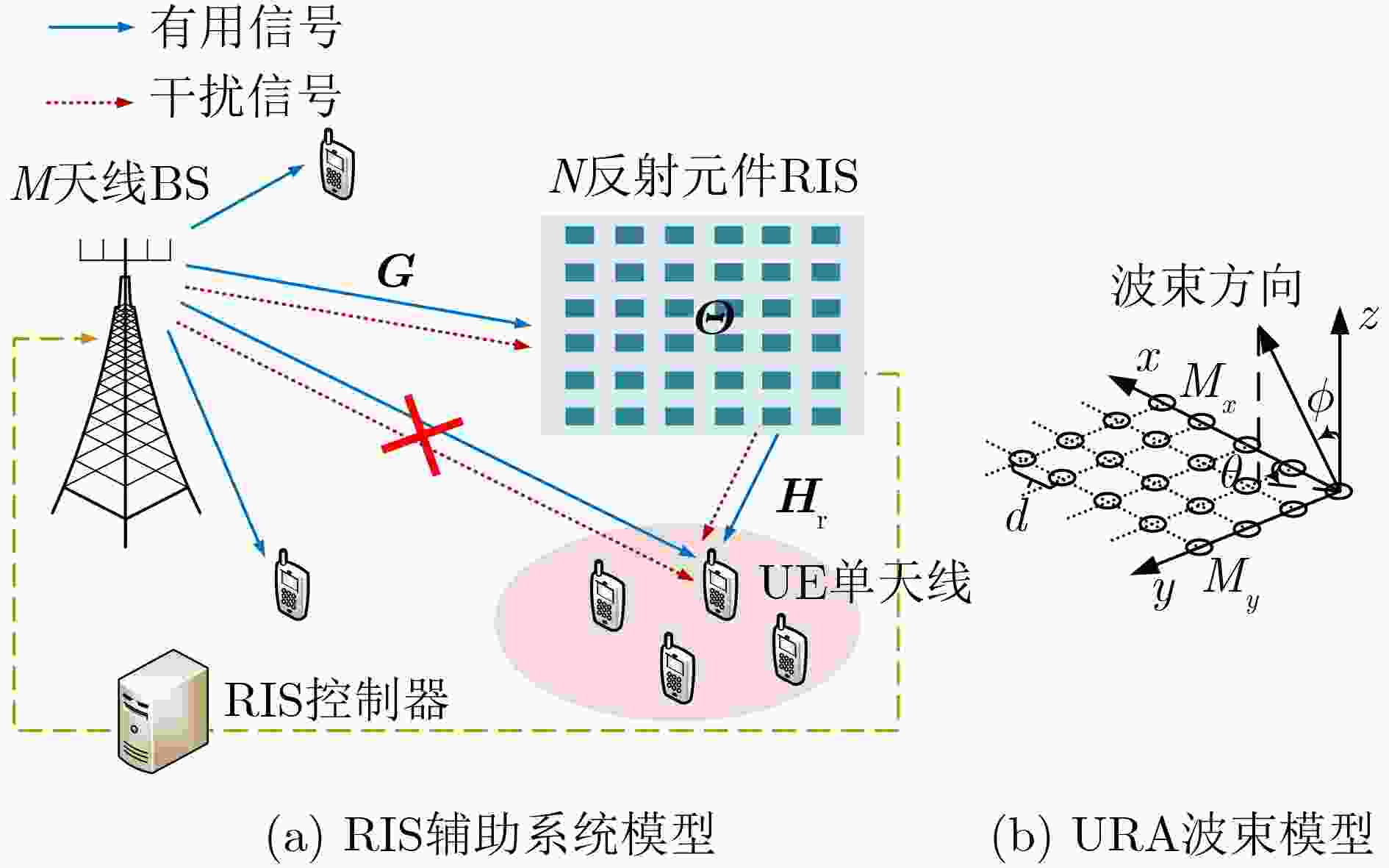
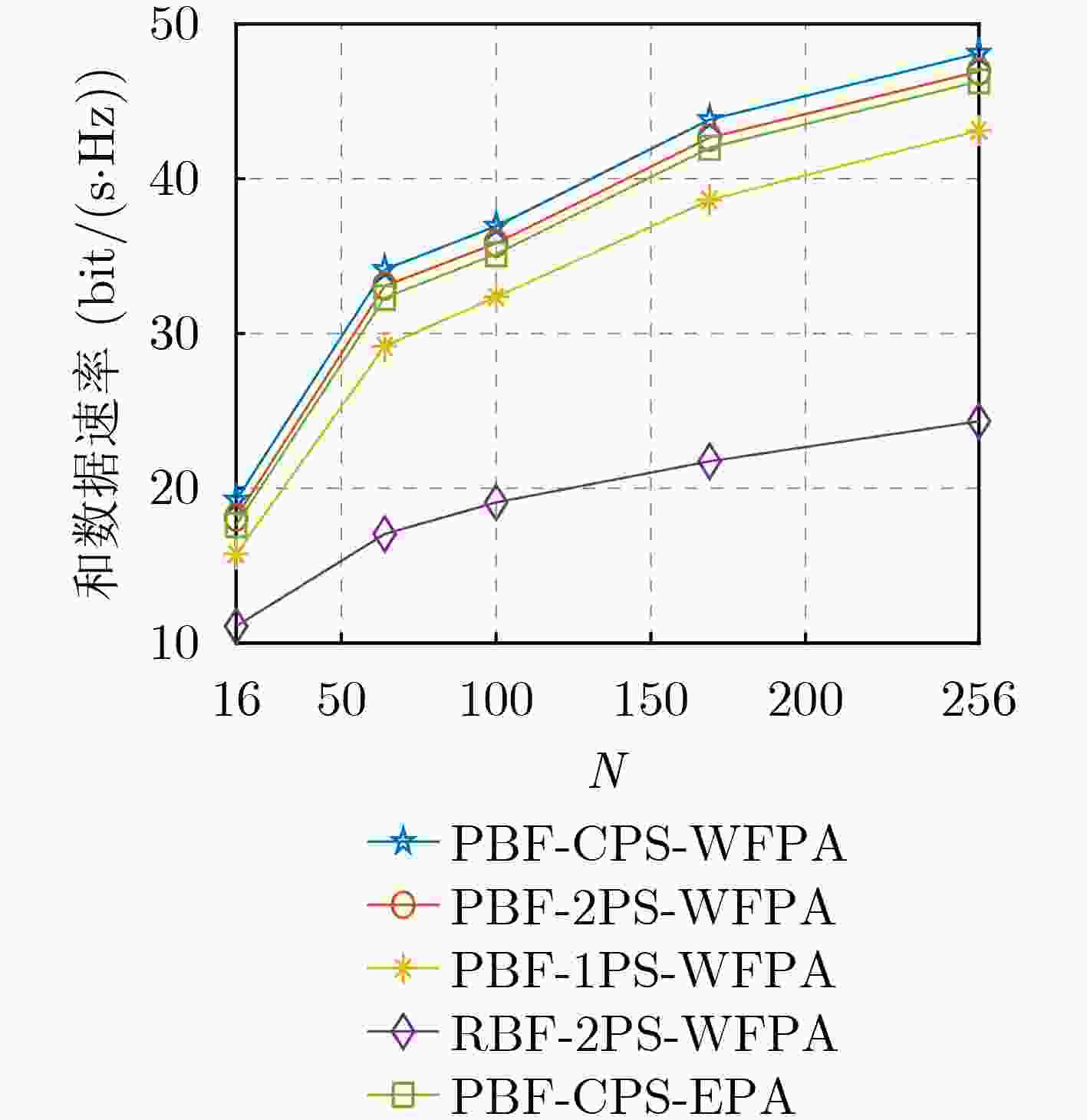
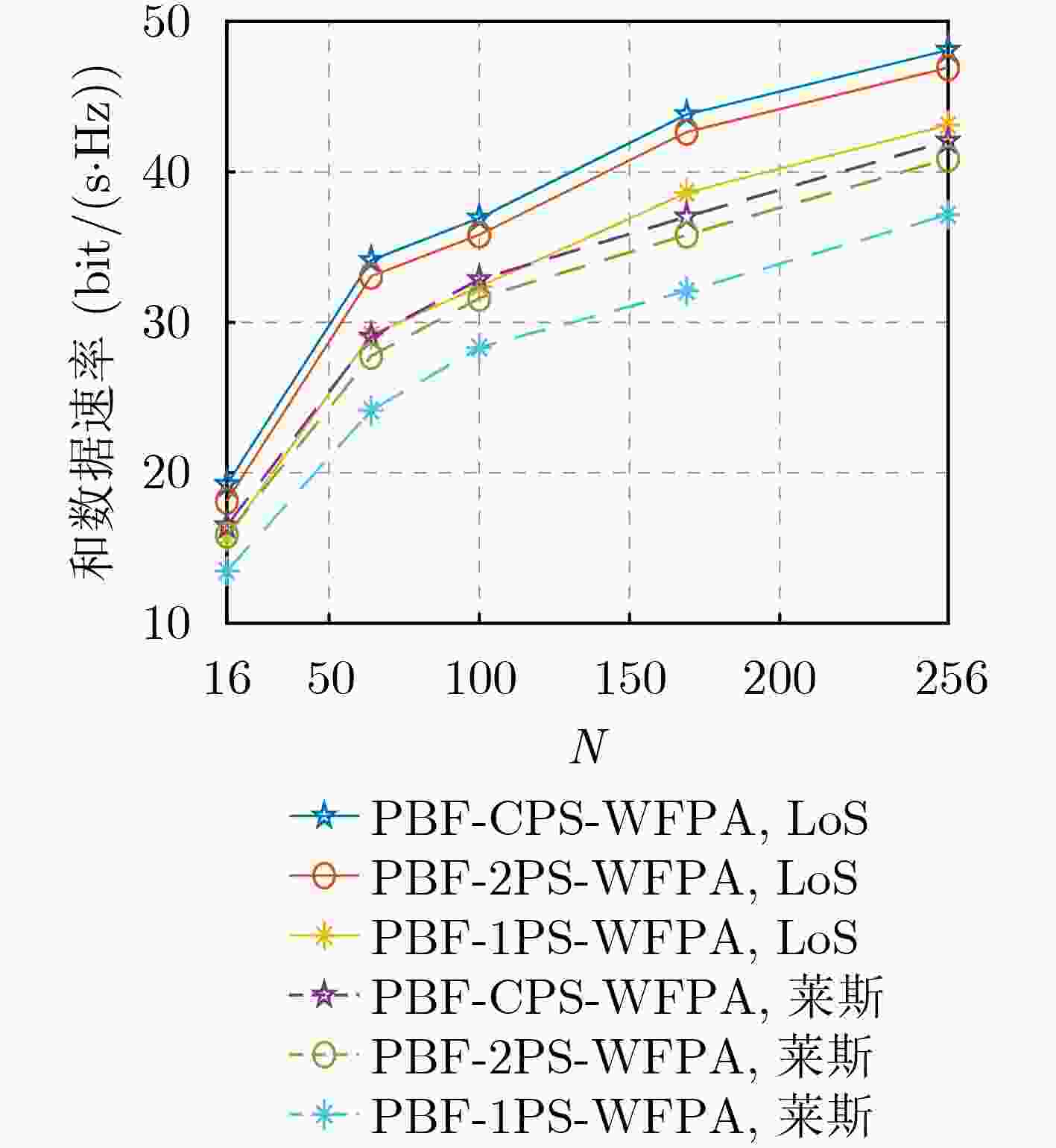
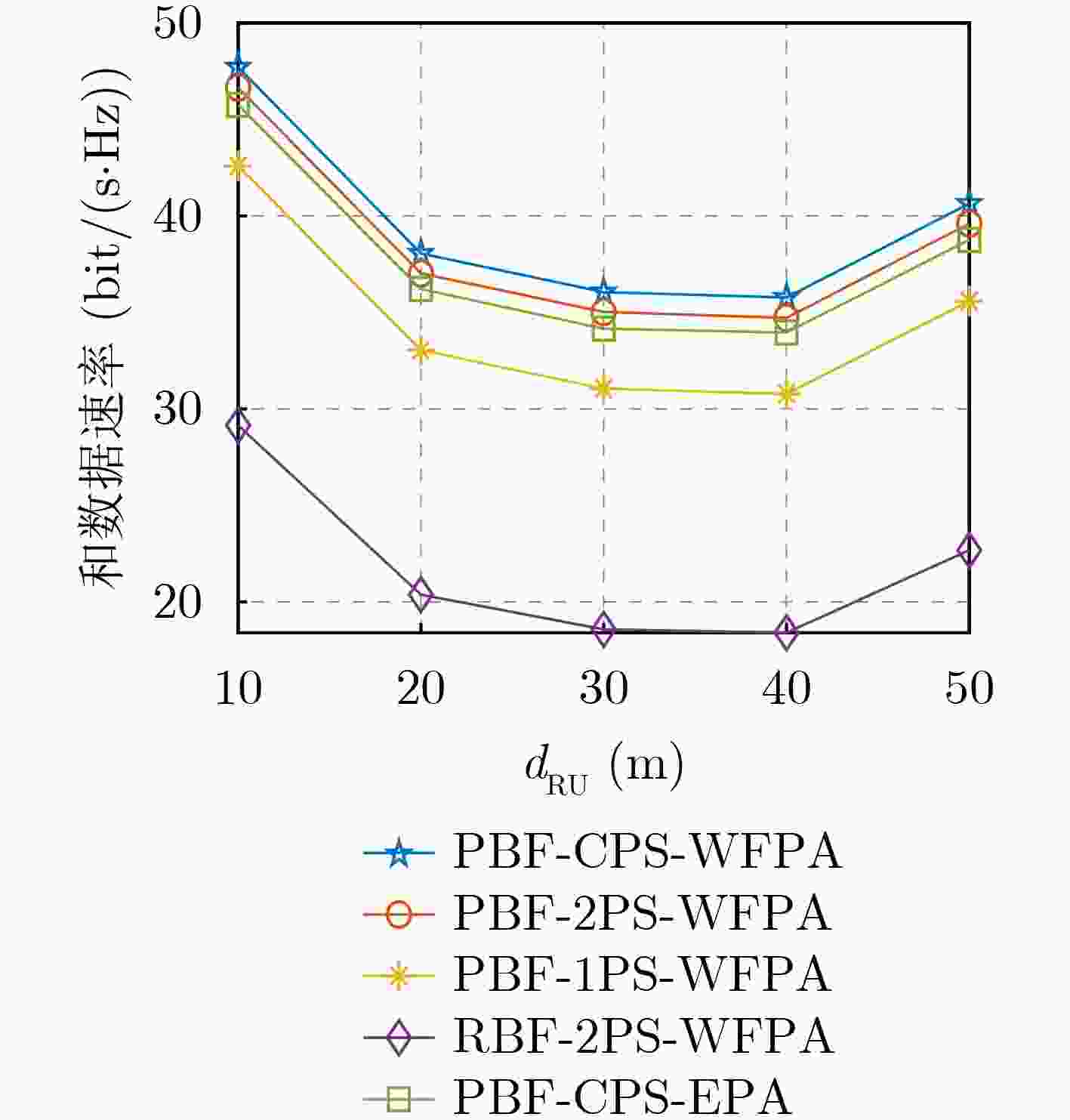
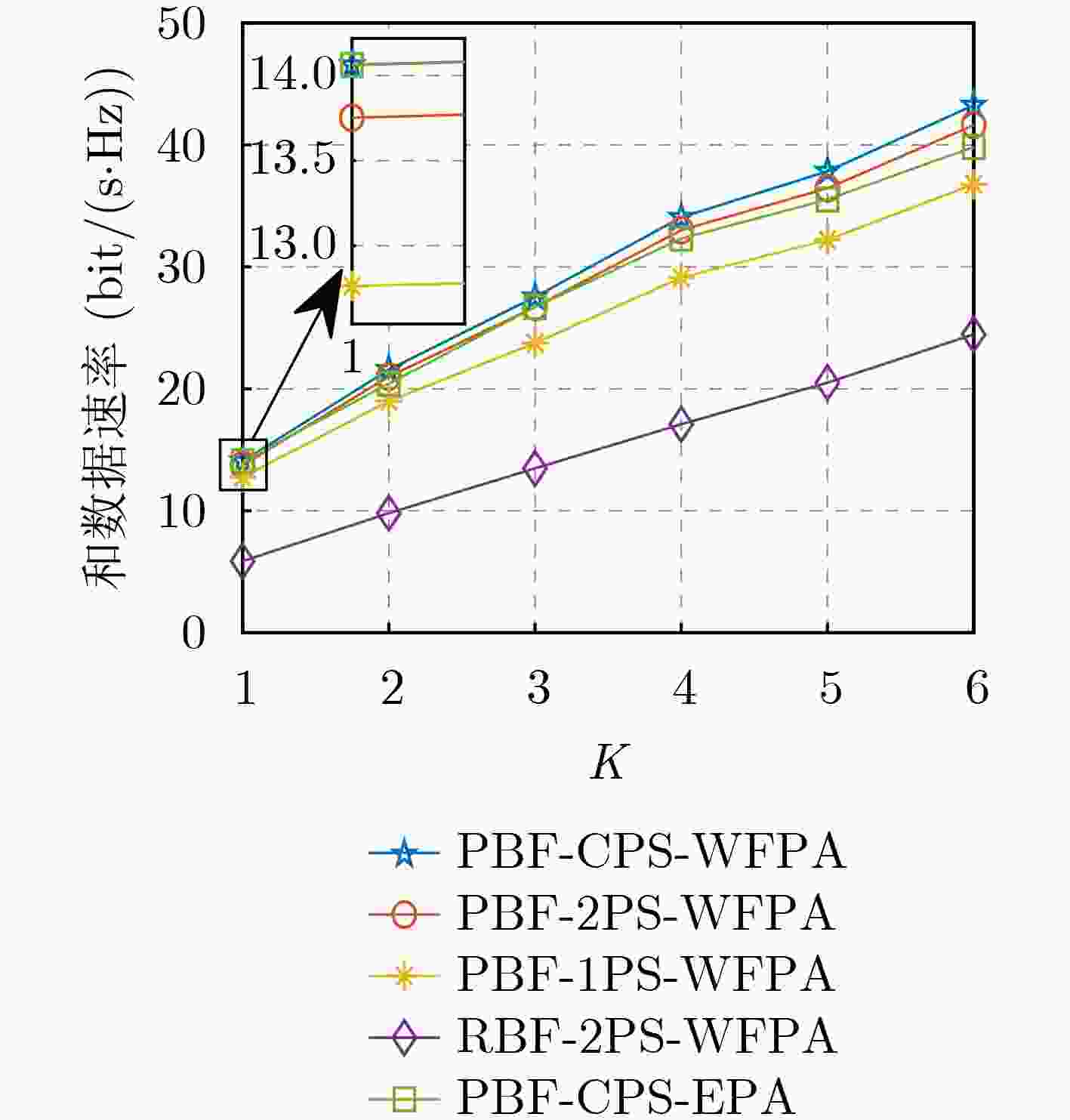
Objective Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS), an innovative technology for 6G communication, can effectively reduce hardware costs and energy consumption. Most researchers examine the joint BeamForming (BF) design problem in RIS-assisted Multiple-Input Single-Output (MISO) systems or single-user Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) systems. However, few investigate the non-convex joint BF optimization problem for RIS-assisted multi-user MISO systems. The existing joint BF design approaches for these systems primarily rely on iterative algorithms that are complex, and some methods have a limited application range. Methods To address the issue, general low-complexity joint BF designs for RIS-assisted multi-user systems are considered. The communication system consists of a Base Station (BS) with an M -antenna configuration utilizing a Uniform Rectangular Array (URA), a RIS with N reflecting elements also arranged in a URA, and K single-antenna User Equipment (UEs). It is assumed that the transmission channel between the BS and UEs experiences blocking due to fading and potential obstacles in a dynamic wireless environment. The non-convex optimization challenge of joint BF design is analyzed, with the goal of maximizing the sum data rate for RIS-aided multi-user systems. The design process involves three main steps: First, the RIS reflection matrix ${\boldsymbol{\varTheta}} $ is designed based on the perfect channel state information obtained from both the BS-RIS and RIS-UE links. This design exploits the approximate orthogonality of the beam steering vectors for all transmitters and receivers using the URA (as detailed in Lemma 1). Second, the transmit BF matrix W at the BS is derived using the zero-forcing method. Third, the power allocation at the BS for multiple users is optimized using the Water-Filling (WF) algorithm. The proposed scheme is applicable to both single-user and multi-user scenarios, accommodating Line-of-Sight (LoS) paths, Rician channels with LoS paths, as well as Non-LoS (NLoS) paths. The computational complexity of the proposed joint BF design is quantified at a total complexity of ${\mathcal{O}}(N+K^2M+K^3) $. Compared with existing schemes, the computational complexity of the proposed design is reduced by at least an order of magnitude. Results and Discussions To verify the performance of the proposed joint BF scheme, simulation tests were conducted using the MATLAB platform. Five different schemes were considered for comparison: Scheme 1: BF design and Water-Filling Power Allocation (WFPA) proposed in this paper, utilizing Continuous Phase Shift (CPS) design without accounting for the limitations of the RIS phase shifter’s accuracy. Scheme 2: Proposed Beamforming (PBF) and WFPA with 2-bit Phase Shift (2PS) design, taking phase shift accuracy limitations into consideration. Scheme 3: 1-bit Phase Shift (1PS) design under PBF and WFPA. Scheme 4: 2PS design under Random BeamForming (RBF) and WFPA. Scheme 5: Equal Power Allocation (EPA) design under PBF and CPS. Initial numerical results demonstrate that the proposed BF design can achieve a high sum data rate, which can be further enhanced by employing optimal power allocation. Furthermore, under identical simulation conditions, the LoS scenario exhibited superior sum data rate performance compared to the Rician channel scenario, with a performance advantage of approximately 6 bit/(s∙Hz). This difference can be attributed to the presence of multiple paths in the Rician channel, which increases interference and decreases the signal-to-noise ratio, thereby reducing the sum data rate. Additionally, when the distance between BS and UEs is fixed, and the RIS is positioned on the straight line between the BS and the UEs, the system sum data rate initially decreases and then increases as the distance between the RIS and UEs increases due to path loss. The simulation results confirm that when the RIS is situated near the UEs (i.e., further from the BS), improved data rate performance can be achieved. This improvement arises because the path loss of the RIS-UE link is greater than that of the BS-RIS link. Therefore, optimal data rate performance is attained when the RIS is closer to the UEs. Moreover, both the simulation results and theoretical analysis indicate that the sum data rate is influenced by the RIS location, offering valuable insights for the selection of RIS positioning. Conclusions This paper proposes a general low-complexity BF design for RIS-assisted multi-user communication systems. Closed-form solutions for transmit BF, power distribution of the BS, and the reflection matrix of the RIS are provided to maximize the system’s sum data rate. Simulation results indicate that the proposed BF design achieves higher data rates than alternative schemes. Additionally, both the simulation findings and theoretical analysis demonstrate that the sum data rate varies with the RIS’s location, providing a reference criterion for optimizing RIS placement. -
Key words:
- Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS) /
- Beamforming /
- Sum data rate /
- Low complexity
-
1 低复杂度联合波束成形设计算法
输入:初始化$ \left( {{{\boldsymbol{W}}}{\text{,}}{ {\boldsymbol{\varTheta }}}{\text{,}}{ {\boldsymbol{P}}}} \right) $ 步骤1 基于已知BS-RIS信道$ {{\boldsymbol{G}}} $和RIS-UEs信道$ {{{\boldsymbol{H}}}_{\text{r}}} $和引理1,根
据式(14)计算RIS反射矩阵$ {{\boldsymbol{\varTheta}} } $;步骤2 基于ZF理论,根据式(19)计算BS发射波束成形$ {{\boldsymbol{W}}} $; 步骤3 基于WF理论,根据式(23)计算功率分配矢量$ {{\boldsymbol{P}}} $; 步骤4 输出优化得到的$ \left( {{{\boldsymbol{W}}}{\text{,}}{ {\boldsymbol{\varTheta}} }{\text{,}}{ {\boldsymbol{P}}}} \right) $。 表 1 波束成形方案计算复杂度对比
文献 复杂度 参数 文献 [3] $ \mathcal{O}\left( {{N^6}} \right) $ N:RIS反射元件数 文献[18] $ \mathcal{O}\left( {{I_{\text{o}}}\left( {{I_{\text{a}}}{M^2}{K^2} + {I_{\text{p}}}{N^2}} \right)} \right) $ M:基站发射天线数 文献[16] $ \mathcal{O}\left( {Q\left( {{M^3} + M{N^2} + N!} \right)} \right) $ K:用户数 文献[17] $ \mathcal{O}\left( {NI\left( {K{M^2}} \right)} \right) $ $ {I_{\text{o}}} $,$ {I_{\text{a}}} $,$ {I_{\text{p}}} $,$ I $:迭代次数 本文 $ \mathcal{O}\left( {N + {K^2}M + {K^3}} \right) $ Q:预设训练集数目 -
[1] YOU Xiaohu, WANG Chengxiang, HUANG Jie, et al. Towards 6G wireless communication networks: Vision, enabling technologies, and new paradigm shifts[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2021, 64(1): 110301. doi: 10.1007/s11432-020-2955-6. [2] ZHANG Zhengquan, XIAO Yue, MA Zheng, et al. 6G wireless networks: Vision, requirements, architecture, and key technologies[J]. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 2019, 14(3): 28–41. doi: 10.1109/MVT.2019.2921208. [3] WU Qingqing and ZHANG Rui. Intelligent reflecting surface enhanced wireless network via joint active and passive beamforming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(11): 5394–5409. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2936025. [4] HUANG Chongwen, ZAPPONE A, ALEXANDROPOULOS G C, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for energy efficiency in wireless communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(8): 4157–4170. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2922609. [5] JIANG Hao, RUAN Chengyao, ZHANG Zaichen, et al. A general wideband non-stationary stochastic channel model for intelligent reflecting surface-assisted MIMO communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(8): 5314–5328. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3066806. [6] WU Qingqing, ZHANG Shuowen, ZHENG Beixiong, et al. Intelligent reflecting surface-aided wireless communications: A tutorial[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(5): 3313–3351. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3051897. [7] 李兴旺, 田志发, 张建华, 等. IRS辅助NOMA网络下隐蔽性能研究[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2023. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2023-0174.LI Xingwang, TIAN Zhifa, ZHANG Jianhua, et al. Performance analysis of covert communication in IRS-assisted NOMA networks[J]. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2023. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2023-0174. [8] LIU Yuanwei, LIU Xiao, MU Xidong, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces: Principles and opportunities[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2021, 23(3): 1546–1577. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2021.3077737. [9] YAN Wenjing, YUAN Xiaojun, HE Zhenqing, et al. Passive beamforming and information transfer design for reconfigurable intelligent surfaces aided multiuser MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2020, 38(8): 1793–1808. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2020.3000811. [10] GUO Huayan, LIANG Yingchang, CHEN Jie, et al. Weighted sum-rate maximization for reconfigurable intelligent surface aided wireless networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(5): 3064–3076. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.2970061. [11] PAN Cunhua, REN Hong, WANG Kezhi, et al. Multicell MIMO communications relying on intelligent reflecting surfaces[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(8): 5218–5233. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.2990766. [12] LIU Sifan, LIU Rang, LI Ming, et al. Joint BS-RIS-user association and beamforming design for RIS-assisted cellular networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(5): 6113–6128. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3231347. [13] 李国权, 党刚, 林金朝, 等. RIS辅助的MISO系统安全鲁棒波束赋形算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(8): 2867–2875. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220894.LI Guoquan, DANG Gang, LIN Jinzhao, et al. Secure and robust beamforming algorithm for RIS assisted MISO systems[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(8): 2867–2875. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220894. [14] WANG Peilan, FANG Jun, DAI Linglong, et al. Joint transceiver and large intelligent surface design for massive MIMO mmWave systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(2): 1052–1064. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3030570. [15] HE Zhenyao, SHEN Hong, XU Wei, et al. Low-cost passive beamforming for RIS-aided wideband OFDM systems[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2022, 11(2): 318–322. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2021.3126852. [16] AN Jiancheng, XU Chao, GAN Lu, et al. Low-complexity channel estimation and passive beamforming for RIS-assisted MIMO systems relying on discrete phase shifts[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2022, 70(2): 1245–1260. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3127924. [17] ALMEKHLAFI M, ARFAOUI M A, ASSI C, et al. A low complexity passive beamforming design for reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) in 6G networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(5): 6309–6321. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3233469. [18] SU Ruochen, DAI Linglong, and NG D W K. Wideband precoding for RIS-aided THz communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2023, 71(6): 3592–3604. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2023.3263230. [19] ZHANG Zijian and DAI Linglong. A joint precoding framework for wideband reconfigurable intelligent surface-aided cell-free network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2021, 69: 4085–4101. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2021.3088755. [20] WU Qingqing and ZHANG Rui. Towards smart and reconfigurable environment: Intelligent reflecting surface aided wireless network[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2020, 58(1): 106–112. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.1900107. [21] LI Xingwang, GAO Xuesong, LIU Yingting, et al. Overlay CR-NOMA assisted intelligent transportation system networks with imperfect SIC and CEEs[J]. Chinese Journal of Electronics, 2023, 32(6): 1258–1270. doi: 10.23919/cje.2022.00.071. [22] TANG Wankai, CHEN Mingzheng, CHEN Xiangyu, et al. Wireless communications with reconfigurable intelligent surface: Path loss modeling and experimental measurement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(1): 421–439. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3024887. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
