Deepfake Video Detection on Social Networks Using Multi-domain Aware Driven by Common Mechanism Analysis Between Artifacts
-
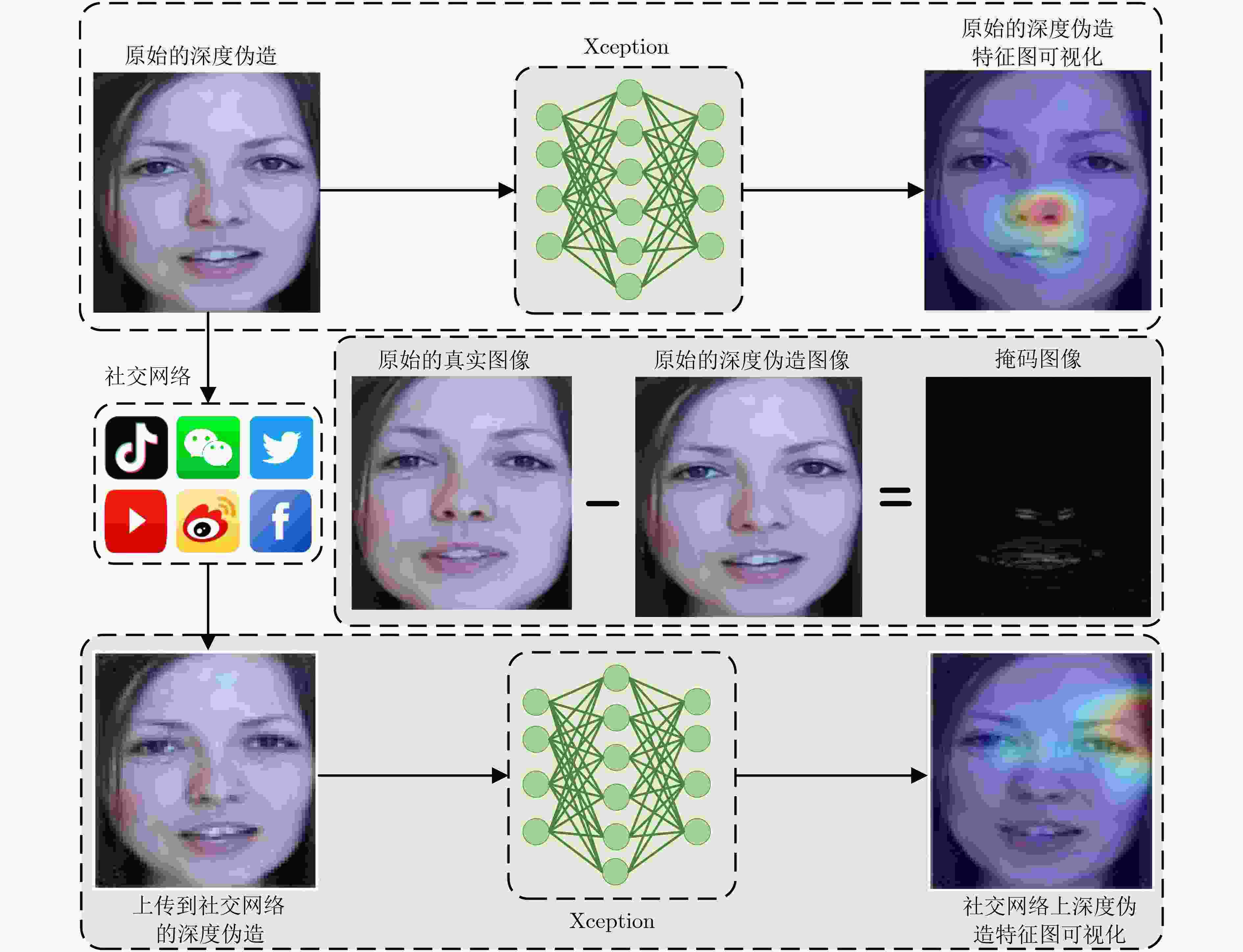
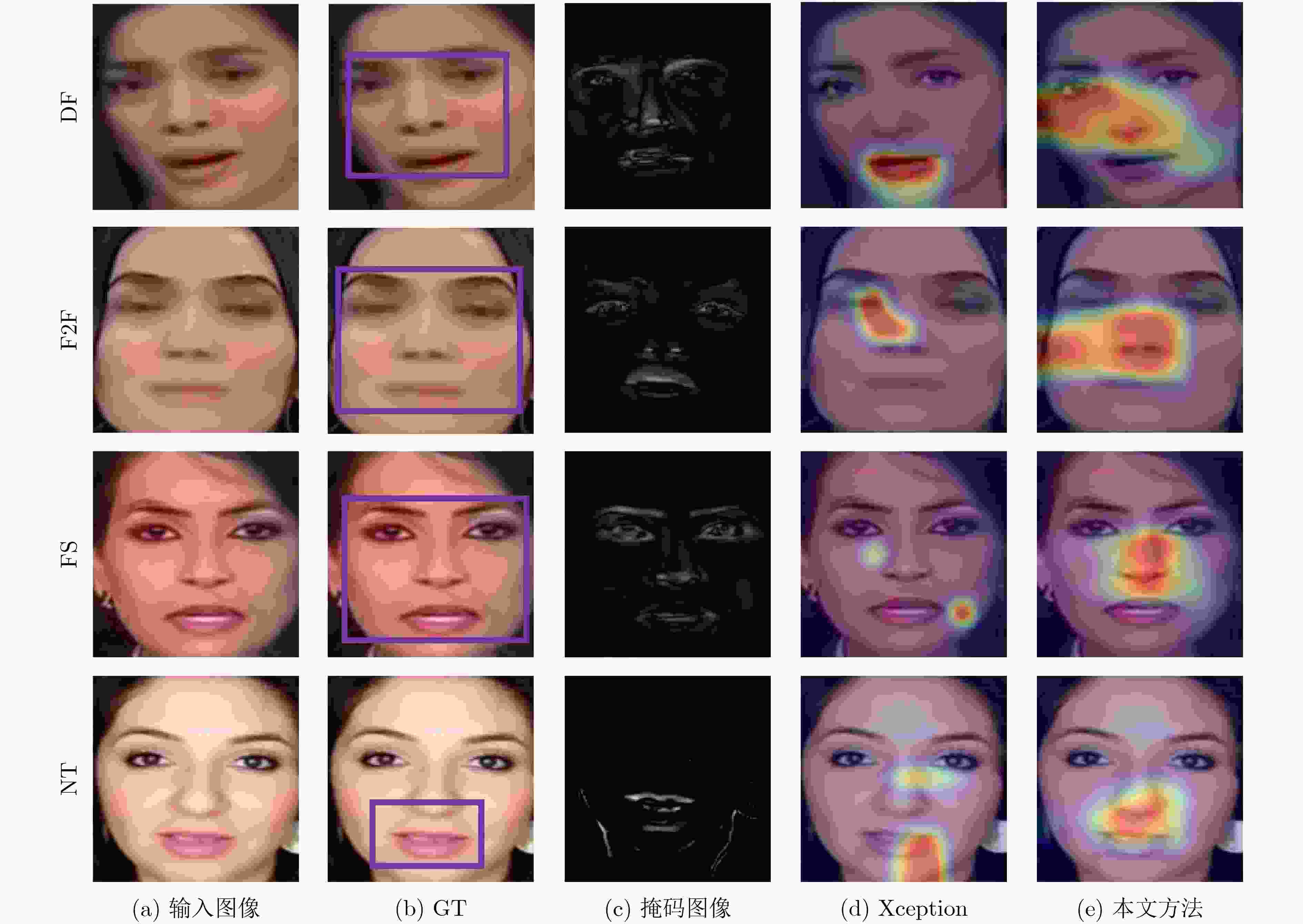
摘要: 深度伪造技术在社交网络上的滥用引发了人们对视觉内容真实性与可靠性的严重担忧。已有检测算法未充分考虑社交网络上深度伪造视频的退化现象,导致深度伪造检测性能受以压缩为主的伪影信息干扰与上下文相关信息缺失等挑战性问题的限制。压缩编码与深度伪造生成算法上采样操作会在视频上留下伪影,这些伪影可导致真实视频与深度伪造视频间的细粒度差异。该文通过分析压缩伪影与深度伪造伪影的共性机理,揭示了二者间的结构相似性,为深度伪造检测模型抗压缩鲁棒性的增强提供了可靠理论依据。首先,针对压缩噪声对深度伪造特征的干扰,基于压缩伪影与深度伪造伪影频域表示的结构相似性,设计了频域自适应陷波滤波器以消除特定频带上压缩伪影的干扰。其次,为削弱深度伪造检测模型对未知噪声的敏感,设计了基于残差学习的去噪分支。采用基于注意力机制的特征融合方法增强深度伪造判别特征,结合度量学习策略优化网络模型,实现了具有抗压缩鲁棒性的深度伪造检测。理论分析与实验结果表明,与基线方法相比,该文算法在压缩深度伪造视频上的检测性能具有明显提升,并可作为一种即插即用模型与现有检测方法结合以提高其抗压缩鲁棒性。Abstract: The misuse of deepfake technology on social networks has raised serious concerns about the authenticity and reliability of visual content. The degradation phenomenon of deepfake videos on social networks has not been adequately considered in existing detection algorithms, resulting in deepfake detection performance being limited by challenging issues such as compression artifacts interference and lack of context-related information. Compression encoding and up-sampling operations in deepfake generation algorithms can leave artifacts on videos, which can result in fine-grained differences between real videos and deepfake videos. The common mechanisms between compression artifacts and deepfake artifacts are analyzed to reveal the structural similarities between them, which provides a reliable theoretical basis for enhancing the robustness of deepfake detection models against compression. Firstly, to address the interference of compression noise on deepfake features, the frequency-domain adaptive notch filter is designed based on the structural similarity of compression artifacts and deepfake artifacts to eliminate the interference of compression artifacts on specific frequency bands. Secondly, the denoising branch based on residual learning is designed to reduce the sensitivity of the deepfake detection model to unknown noise. Additionally, the attention-based feature fusion method is adopted to enhance the discriminative features of deepfakes. Metric learning strategies are adopted to optimize network models, achieving deepfake detection with resistance to compression. Theoretical analysis and experimental results indicate that the detection performance of compressed deepfake videos is significantly enhanced by using the algorithm proposed in this paper. It can be used as a plug-and-play model combined with existing detection methods to enhance their robustness against compression.
-
表 1 本文算法与基线算法在4个数据集C23上性能的比较(%)
方法 DF F2F FS NT ACC AUC ACC AUC ACC AUC ACC AUC Xception[5] 97.90 99.45 95.54 99.46 95.81 99.02 88.92 95.59 Capsule[21] 98.25 99.32 98.34 98.96 98.46 99.71 88.90 94.46 RFM[22] 89.56 98.42 94.09 98.63 90.15 99.23 87.31 94.60 F3-Net[14] 97.34 99.68 97.71 99.44 98.18 99.78 89.12 95.64 本文 99.02 99.94 98.58 99.63 99.21 99.89 91.79 97.12 表 2 本文算法与基线算法在4个数据集C40上性能的比较(%)
方法 DF F2F FS NT ACC AUC ACC AUC ACC AUC ACC AUC Xception[5] 90.11 96.46 79.81 89.53 86.00 93.89 51.30 54.04 Capsule[21] 89.37 94.81 81.97 89.52 83.66 90.36 55.31 58.12 RFM[22] 86.91 93.78 73.75 82.65 78.06 89.42 61.25 63.05 F3-Net[14] 92.12 97.78 84.72 92.84 88.84 95.13 58.28 63.28 本文 95.17 98.73 86.87 93.84 90.19 96.47 59.42 66.97 表 3 本文算法与基线算法在各数据集的C40上训练C23上测试的性能比较(%)
方法 DF F2F FS NT ACC AUC ACC AUC ACC AUC ACC AUC Xception[5] 89.78 96.95 82.95 95.16 89.81 95.97 58.28 63.15 Capsule[21] 87.56 95.17 88.37 93.84 89.78 95.00 55.87 60.91 RFM[22] 89.56 95.76 77.15 86.00 82.71 91.39 65.18 69.53 F3-Net[14] 92.81 98.71 89.56 97.04 89.96 97.56 62.09 70.72 本文 95.65 99.31 90.42 95.71 93.01 98.01 66.89 71.61 表 4 本文算法与基线算法在各数据集的C23上训练C40上测试的性能比较(%)
方法 DF F2F FS NT ACC AUC ACC AUC ACC AUC ACC AUC Xception[5] 76.54 94.87 55.23 84.30 79.42 86.00 50.21 51.29 Capsule[21] 79.87 90.68 58.78 77.11 73.68 82.63 58.40 67.84 RFM[22] 75.90 90.07 73.75 84.86 69.15 82.67 56.09 62.88 F3-Net[14] 77.12 94.45 57.18 82.45 78.87 88.48 54.31 68.61 本文 88.86 95.85 75.92 86.04 84.57 92.90 54.74 67.96 -
[1] IGLESIAS G, TALAVERA E, and DÍAZ-ÁLVAREZ A. A survey on GANs for computer vision: Recent research, analysis and taxonomy[J]. Computer Science Review, 2023, 48: 100553. doi: 10.1016/j.cosrev.2023.100553. [2] ZANARDELLI M, GUERRINI F, LEONARDI R, et al. Image forgery detection: A survey of recent deep-learning approaches[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2023, 82(12): 17521–17566. doi: 10.1007/s11042-022-13797-w. [3] 牛淑芬, 戈鹏, 宋蜜, 等. 移动社交网络中基于属性加密的隐私保护方案[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(3): 847–855. doi: 10.11999/JEIT221174.NIU Shufen, GE Peng, SONG Mi, et al. A privacy protection scheme based on attribute encryption in mobile social networks[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(3): 847–855. doi: 10.11999/JEIT221174. [4] KINGRA S, AGGARWAL N, and KAUR N. Emergence of deepfakes and video tampering detection approaches: A survey[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2023, 82(7): 10165–10209. doi: 10.1007/s11042-022-13100-x. [5] CHOLLET F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 1800–1807. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.195. [6] BINH L M and WOO S. ADD: Frequency attention and multi-view based knowledge distillation to detect low-quality compressed deepfake images[C]. The 36th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2022: 122–130. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v36i1.19886. [7] LEE S, AN J, and WOO S S. BZNet: Unsupervised multi-scale branch zooming network for detecting low-quality deepfake videos[C]. The ACM Web Conference 2022, Lyon, France, 2022: 3500–3510. doi: 10.1145/3485447.3512245. [8] LIN Liqun, ZHENG Yang, CHEN Weiling, et al. Saliency-aware spatio-temporal artifact detection for compressed video quality assessment[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2023, 30: 693–697. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2023.3283541. [9] FRANK J, EISENHOFER T, SCHÖNHERR L, et al. Leveraging frequency analysis for deep fake image recognition[C]. The 37th International Conference on Machine Learning, 2020: 3247–3258. [10] LI Yuezun, CHANG M C, and LYU Siwei. In ictu oculi: Exposing AI created fake videos by detecting eye blinking[C]. 2018 IEEE International Workshop on Information Forensics and Security (WIFS), Hong Kong, China, 2018: 1–7. doi: 10.1109/WIFS.2018.8630787. [11] CIFTCI U A, DEMIR I, and YIN Lijun. Fakecatcher: Detection of synthetic portrait videos using biological signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020: 1. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2020.3009287. [12] COZZOLINO D, THIES J, RÖSSLER A, et al. ForensicTransfer: Weakly-supervised domain adaptation for forgery detection[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1812.02510, 2018. [13] AFCHAR D, NOZICK V, YAMAGISHI J, et al. MesoNet: A compact facial video forgery detection network[C]. 2018 IEEE International Workshop on Information Forensics and Security (WIFS), Hong Kong, China, 2018: 1–7. doi: 10.1109/WIFS.2018.8630761. [14] QIAN Yuyang, YIN Guojun, SHENG Lu, et al. Thinking in frequency: Face forgery detection by mining frequency-aware clues[C]. 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 86–103. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-58610-2_6. [15] LIU Honggu, LI Xiaodan, ZHOU Wenbo, et al. Spatial-phase shallow learning: Rethinking face forgery detection in frequency domain[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, USA, 2021: 772–781. doi: 10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00083. [16] LI Ying, BIAN Shan, WANG Chuntao, et al. Exposing low-quality deepfake videos of social network service using spatial restored detection framework[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2023, 231: 120646. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.120646. [17] ZHANG Yun, ZHU Linwei, JIANG Gangyi, et al. A survey on perceptually optimized video coding[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2023, 55(12): 245. doi: 10.1145/3571727. [18] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module[C]. 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 3–19. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_1. [19] RÖSSLER A, COZZOLINO D, VERDOLIVA L, et al. FaceForensics++: Learning to detect manipulated facial images[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea, 2019: 1–11. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2019.00009. [20] ZHANG Kaipeng, ZHANG Zhanpeng, LI Zhifeng, et al. Joint face detection and alignment using multitask cascaded convolutional networks[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2016, 23(10): 1499–1503. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2016.2603342. [21] NGUYEN H H, YAMAGISHI J, and ECHIZEN I. Capsule-forensics: Using capsule networks to detect forged images and videos[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 2019: 2307–2311. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2019.8682602. [22] WANG Chengrui and DENG Weihong. Representative forgery mining for fake face detection[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, USA, 2021: 14918–14927. doi: 10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.01468. [23] SELVARAJU R R, COGSWELL M, DAS A, et al. Grad-CAM: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 2017: 618–626. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.74. -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
