Method of Maximizing Sum Rate for Dual STAR-RIS Assisted Downlink NOMA Systems
-
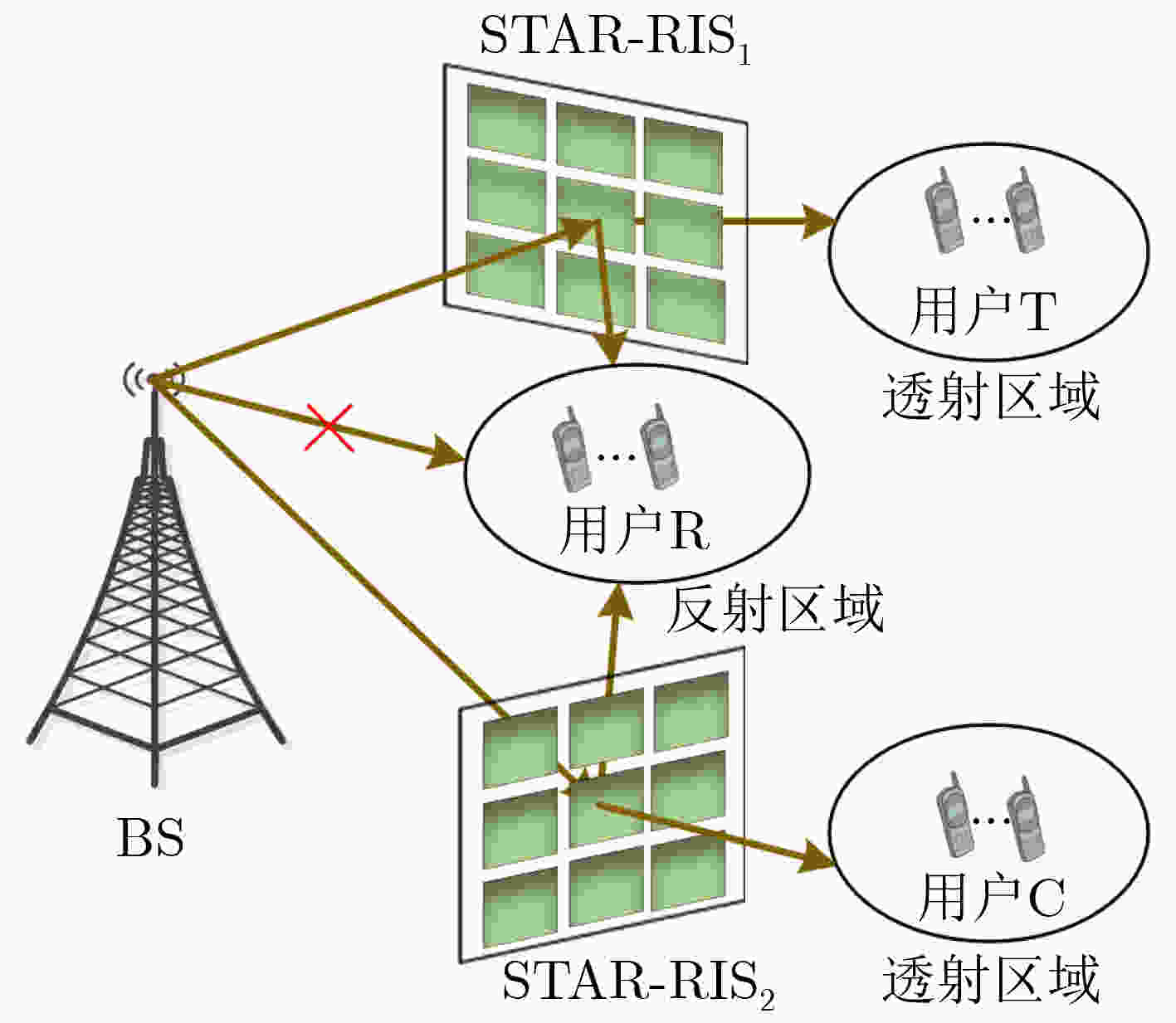
摘要: 对于两个同时透射和反射的智能可重构表面(STAR-RIS)辅助的下行非正交多址接入(NOMA)系统,该文提出一种最大化和速率的方法。首先构建最大化和速率的优化问题,优化参数为STAR-RIS相移、功率分配和时间分配;然后用半正定规划法(SDP)优化双STAR-RIS相移;最后,用迭代的方法交替优化功率分配和时间分配,在每次迭代过程中分别用拉格朗日对偶分解法优化功率分配和函数极值法优化时间分配。仿真结果显示,双STAR-RIS辅助的NOMA系统的和速率高于单STAR-RIS辅助的NOMA系统。
-
关键词:
- 非正交多址接入 /
- 同时透射和反射的智能可重构表面 /
- 和速率 /
- 功率 /
- 相移
Abstract: A sum-rate maximization method is proposed for two Simultaneously Transmitting And Reflecting Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (STAR-RIS) assisted downlink Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access (NOMA) systems. Firstly, the optimization problem for maximizing sum rate is constructed, with STAR-RIS phase shifts, power allocation and time allocation as optimization parameters. Then the Semi-Definite Programming method (SDP) is used to optimize the phase shifts of these two STAR-RISs. Finally, the power allocation and time allocation are optimized alternately by iterative method. In each iteration, Lagrange dual decomposition method is used to optimize power allocation and function extremum method is used to optimize time allocation. Simulation results show that the sum rate of the dual STAR-RIS-assisted NOMA system is higher than that of the single STAR-RIS-assisted NOMA system. -
表 1 仿真参数
参数 数值 BS与STAR-RIS1路径损耗指数 2 BS与STAR-RIS2路径损耗指数 2 STAR-RIS1与用户T/R路径损耗指数 2 STAR-RIS2与用户C/R路径损耗指数 2 莱斯因子(dB) 5 用户R、用户T、用户C数目 2,2,2 BS与两个STAR-RIS距离(m) 50,50 STAR-RIS1与用户T/R距离(m) 10 STAR-RIS2与用户C/R距离(m) 10 噪声功率$ {\sigma ^2} $(dBm) –99 $ {R_{\min}} $(bit/(s·Hz)) 0.1 -
[1] GAN Xu, ZHONG Caijun, HUANG Chongwen, et al. Multiple RISs assisted cell-free networks with two-timescale CSI: Performance analysis and system design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2022, 70(11): 7696–7710. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2022.3208629. [2] 张诚, 王鸿. 智能反射面辅助的非正交多址系统高能效传输方案研究[J]. 重庆邮电大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 35(1): 16–22. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.202110130355.ZHANG Cheng and WANG Hong. Research on energy-efficient transmission scheme for IRS-assisted NOMA systems[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications (Natural Science Edition), 2023, 35(1): 16–22. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.202110130355. [3] LIU Yuanwei, LIU Xiao, MU Xidong, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces: Principles and opportunities[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2021, 23(3): 1546–1577. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2021.3077737. [4] XIE Zhen, LI Xingwang, ZENG Ming, et al. Resource allocation for double IRSs assisted wireless powered NOMA networks[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2023, 12(5): 823–827. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2023.3244997. [5] WANG Peiyu, WANG Hong, MA Haochun, et al. Sum rate maximization for STAR-RIS aided NOMA system with two-way communication[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2023, 27(10): 2857–2861. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2023.3306557. [6] WANG Kaijie, ZHOU Ting, XU Tianheng, et al. Asymmetric adaptive modulation for uplink NOMA systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(11): 7222–7235. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3102152. [7] ZUO Jiakuo, LIU Yuanwei, DING Zhiguo, et al. Uplink NOMA for STAR-RIS networks[EB/OL]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2110.05686, 2021. [8] FU Shen, WANG Hong, ZHAO Haitao, et al. On STAR-RIS-aided NOMA with multi-group detection[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2023, 12(11): 1971–1975. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2023.3303414. [9] WANG Peiyu, WANG Hong, and FU Yibo. Average rate maximization for mobile STAR-RIS-aided NOMA system[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2023, 27(5): 1362–1366. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2023.3261442. [10] 王培宇, 王鸿, 马昊淳. 多通道STAR-IRS辅助的NOMA系统用户分组方案研究[J]. 南京邮电大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 42(5): 47–53. doi: 10.14132/j.cnki.1673-5439.2022.05.007.WANG Peiyu, WANG Hong, and MA Haochun. On user grouping for multi-carrier STAR-IRS-aided NOMA systems[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications (Natural Science), 2022, 42(5): 47–53. doi: 10.14132/j.cnki.1673-5439.2022.05.007. [11] FANG Fang, WU Bibo, FU Shu, et al. Energy-efficient design of STAR-RIS Aided MIMO-NOMA networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2023, 71(1): 498–511. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2022.3223706. [12] GUO Yi, FANG Fang, CAI Donghong, et al. Energy-efficient design for a NOMA assisted STAR-RIS network with deep reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(4): 5424–5428. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3224926. [13] WU Chenyu, MU Xidong, LIU Yuanwei, et al. Resource allocation in STAR-RIS-aided networks: OMA and NOMA[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(9): 7653–7667. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2022.3160151. [14] ZUO Jiakuo, LIU Yuanwei, DING Zhiguo, et al. Joint design for simultaneously transmitting and reflecting (STAR) RIS assisted NOMA systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2023, 22(1): 611–626. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2022.3197079. [15] GRANT M and BOYD S P. CVX: MATLAB software for disciplined convex programming[EB/OL]. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/229058225_CVX_MATLAB_software_for_disciplined_convex_programming, 2014. -





 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:
