Research on Localization Algorithm with 5G Opportunistic Signals in Co-channel Interference Environments
-
摘要: 针对全球导航卫星系统(GNSS)拒止环境下定位精度难以保证的问题,该文设计了一种基于新无线电(NR)机会信号的定位方案,并提出一种基于干扰消除子空间追踪(ICSP)算法,解决超密集网络(UDNs)和异构网络(HetNets)环境中同频干扰对定位观测量提取精度不足的问题。通过仿真实验和通用软件无线电外设(USRP)半实物仿真,验证了ICSP算法在复杂网络环境中优化5G机会信号接收机性能、提高定位精度上的有效性。Abstract: In response to the challenge of ensuring positioning accuracy in environments where the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) is denied, a positioning scheme based on opportunistic New Radio (NR) signals is devised and an Interference Cancellation Subspace Pursuit (ICSP) algorithm is proposed in this paper. This algorithm aims to resolve the issue of inadequate precision in the extraction of positioning observations due to co-channel interference within Ultra-Dense Networks (UDNs) and Heterogeneous Networks (HetNets). The effectiveness of the ICSP algorithm in optimizing the performance of 5G opportunistic signal receivers and enhancing positioning accuracy in complex network environments has been validated through simulation experiments and semi-physical simulations utilizing the Universal Software Radio Peripheral (USRP).
-
表 1 算法复杂度
算法 所需乘法次数 SIC $ KCNL{\text{ + }}K{N^2} $ SCP $ KCNL{\text{ + }}N({K^3}{L^2} + {K^2}L) + O({L^3}) $ ICSP $ KCNL{\text{ + }}N({K^3}{L^2} + {K^2}L{\text{ + }}N){\text{ + }}O({L^3}) $ 表 2 基站基本参数
基站ID号 纬度(°) 经度(°) 高度(m) 中心频率(MHz) 运营商 418 45.769 187 53 126.674 699 26 181.371 3 509.76 中国联通 348 45.771 155 50 126.678 329 04 152.963 3 509.76 中国联通 47 45.771 806 62 126.674 012 97 150.758 3 509.76 中国联通 11 45.770 464 10 126.676 657 18 132.231 3 509.76 虚拟基站 表 3 实验接收参数
参数名称 参数值 USRP接收带宽 10 ${\text{MHz}}$ 采样率 30.72 $ {\text{MSps}} $ 晶振类型 温补晶振(Temperature Compensated Crystal Oscillator, TCXO) 同步精度 30 $ {\text{ns}} $ 中心频率 3509.76 $ {\text{MHz}} $ -
[1] Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA). Adaptable navigation systems[EB/OL]. https://www.darpa.mil/program/adaptable-navigation-systems, 2023. [2] EL-SHEIMY N and LI You. Indoor navigation: State of the art and future trends[J]. Satellite Navigation, 2021, 2(1): 7. doi: 10.1186/S43020-021-00041-3. [3] OBEIDAT H, SHUAIEB W, OBEIDAT O, et al. A review of indoor localization techniques and wireless technologies[J]. Wireless Personal Communications, 2021, 119(1): 289–327. doi: 10.1007/s11277-021-08209-5. [4] SHARMA N and KUMAR K. Resource allocation trends for ultra dense networks in 5G and beyond networks: A classification and comprehensive survey[J]. Physical Communication, 2021, 48: 101415. doi: 10.1016/j.phycom.2021.101415. [5] STOYNOV V, POULKOV V, VALKOVA-JARVIS Z, et al. Ultra-dense networks: Taxonomy and key performance indicators[J]. Symmetry, 2023, 15(1): 2. doi: 10.3390/sym15010002. [6] RAJAMOHAN N and KANNU A P. Downlink synchronization techniques for heterogeneous cellular networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2015, 63(11): 4448–4460. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2015.2474381. [7] GOWDA N M and KANNU A P. Compressive sensing framework for signal processing in heterogeneous cellular networks[C]. 2012 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Anaheim, USA, 2012: 3610–3615. doi: 10.1109/GLOCOM.2012.6503676. [8] 王旭东, 刘帅, 吴楠. CAEFi: 基于卷积自编码器降维的信道状态信息指纹室内定位方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(8): 2757–2766. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210663.WANG Xudong, LIU Shuai, and WU Nan. CAEFI: Channel state information fingerprint indoor location method using convolutional autoencoder for dimension reduction[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(8): 2757–2766. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210663. [9] 刘凯凯, 田增山, 李泽, 等. 仓储场景中基于无线标签的三维定位方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(12): 4218–4227. doi: 10.11999/JEIT221269.LIU Kaikai, TIAN Zengshan, LI Ze, et al. 3-D localization method based on wireless tags in warehouse scenarios[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(12): 4218–4227. doi: 10.11999/JEIT221269. [10] JIANG Feng, ZHANG Zhenkai, and NAJAFABADI H E. Deep sea TDOA localization method based on improved OMP algorithm[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 168151–168161. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2954330. [11] SHAMAEI K and KASSAS Z M. Receiver design and time of arrival estimation for opportunistic localization with 5G signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(7): 4716–4731. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3061985. [12] CHEN Liang, ZHOU Xin, CHEN Feifei, et al. Carrier phase ranging for indoor positioning with 5G NR signals[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 9(13): 10908–10919. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3125373. [13] GOWDA N M and KANNU A P. Interferer identification in hetnets using compressive sensing framework[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2013, 61(11): 4780–4787. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2013.092813.130196. [14] RAJAMOHAN N, JOSHI A, and KANNU A P. Joint block sparse signal recovery problem and applications in LTE cell search[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(2): 1130–1143. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2016.2552247. [15] SHAMAEI K. Exploiting cellular signals for navigation: 4G to 5G[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of California, 2020. -





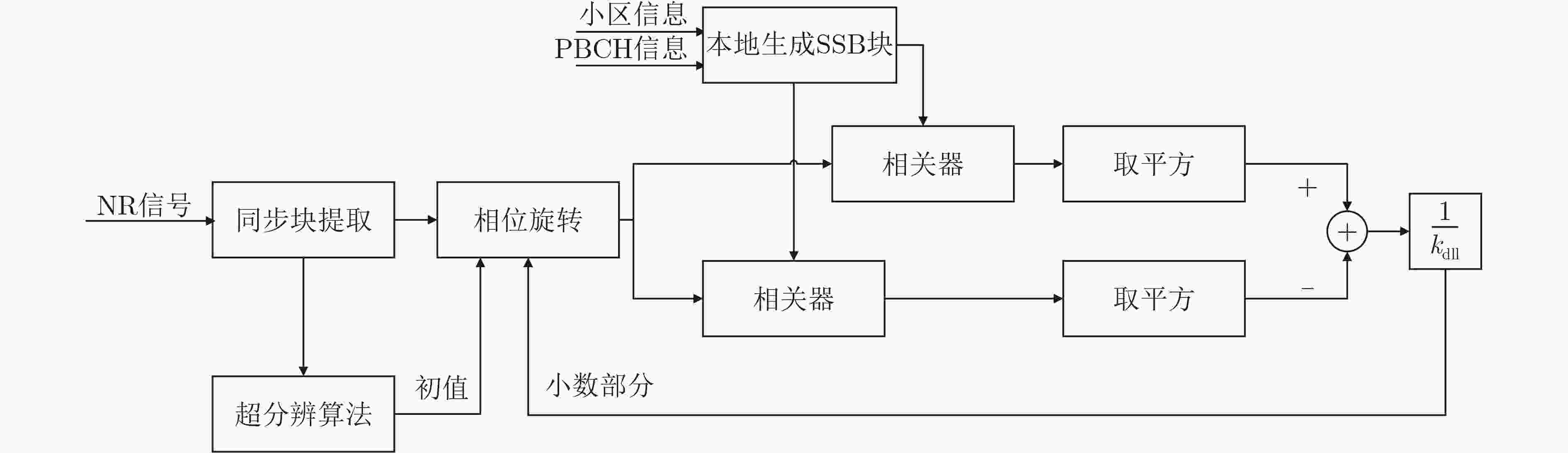
 下载:
下载:
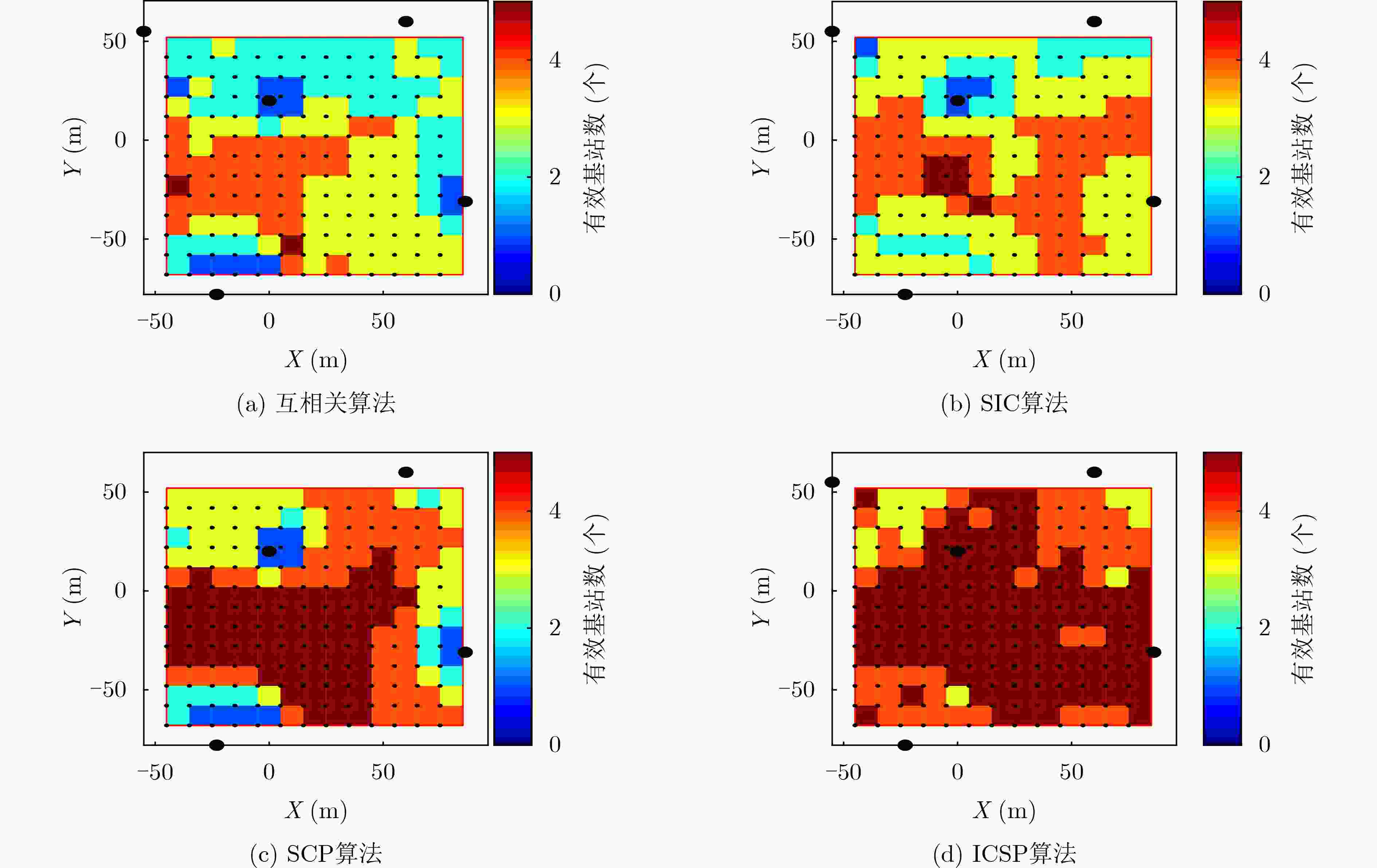
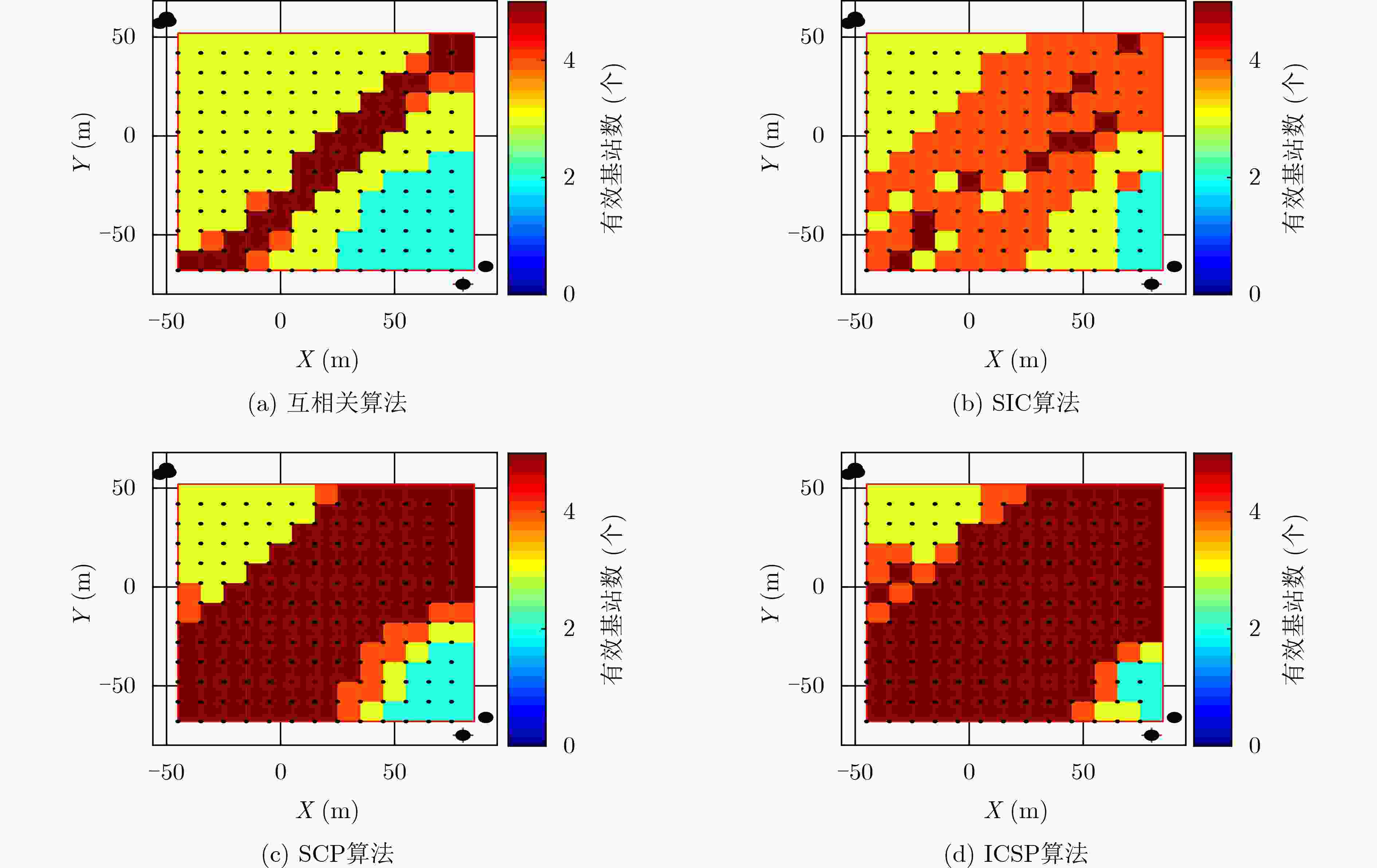
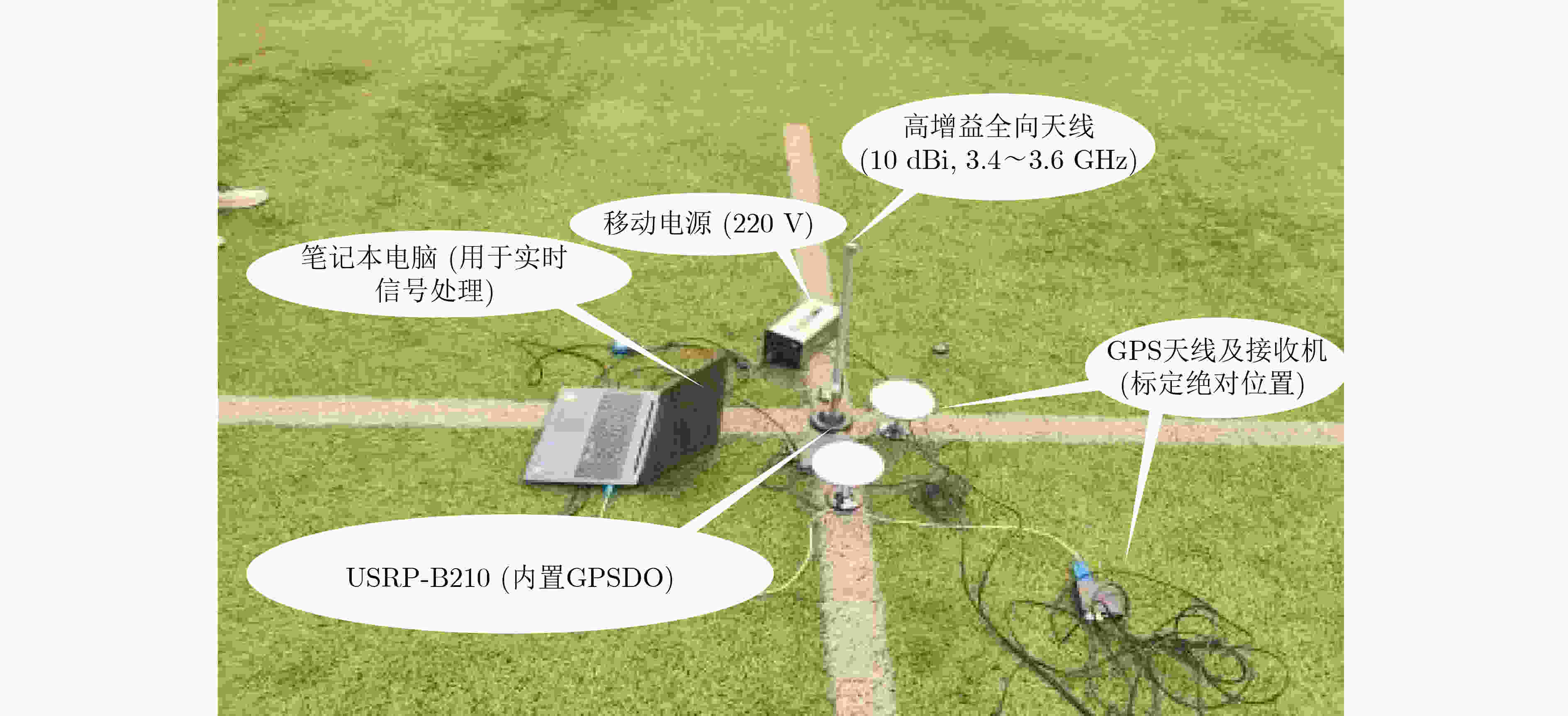
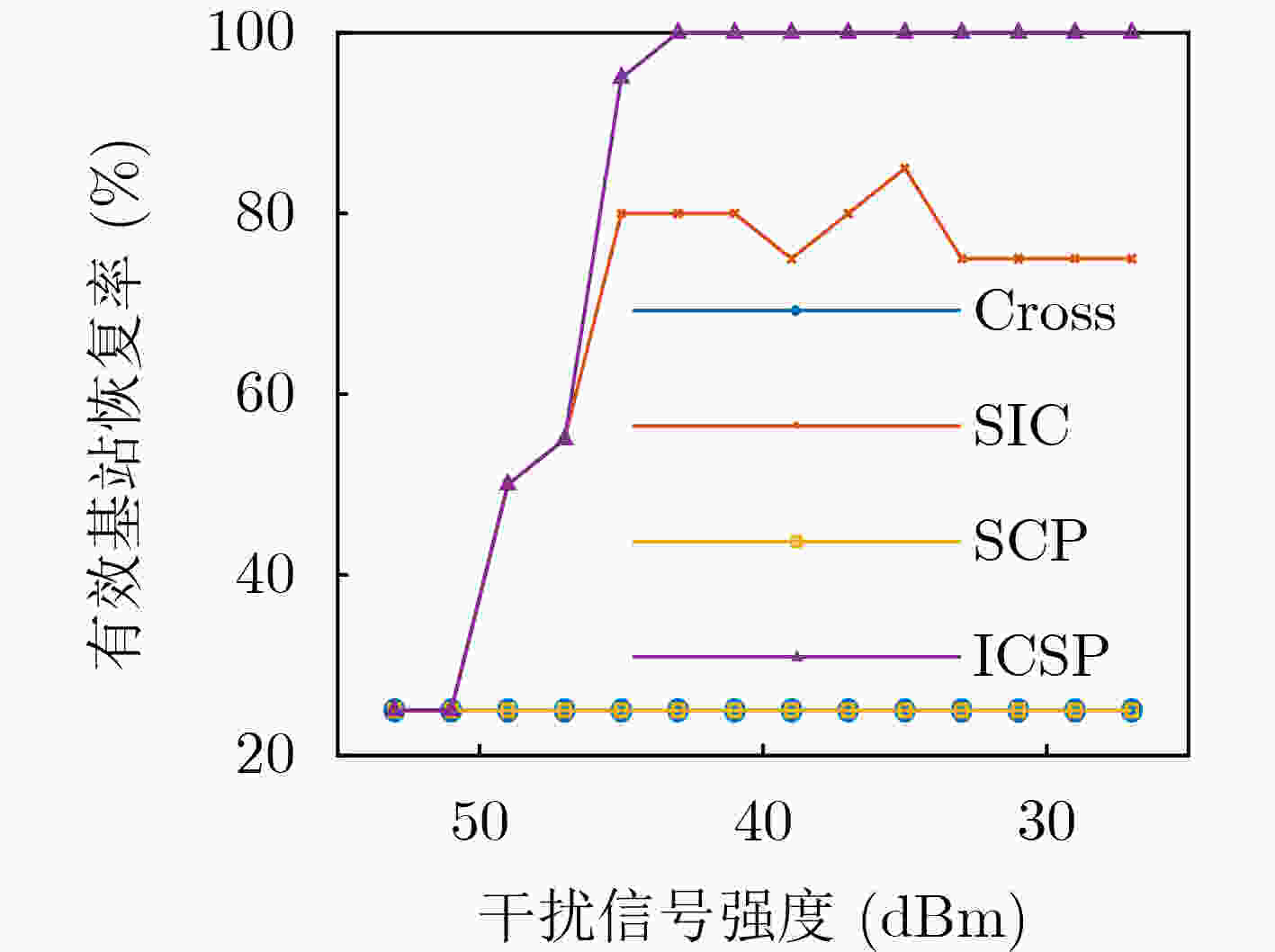

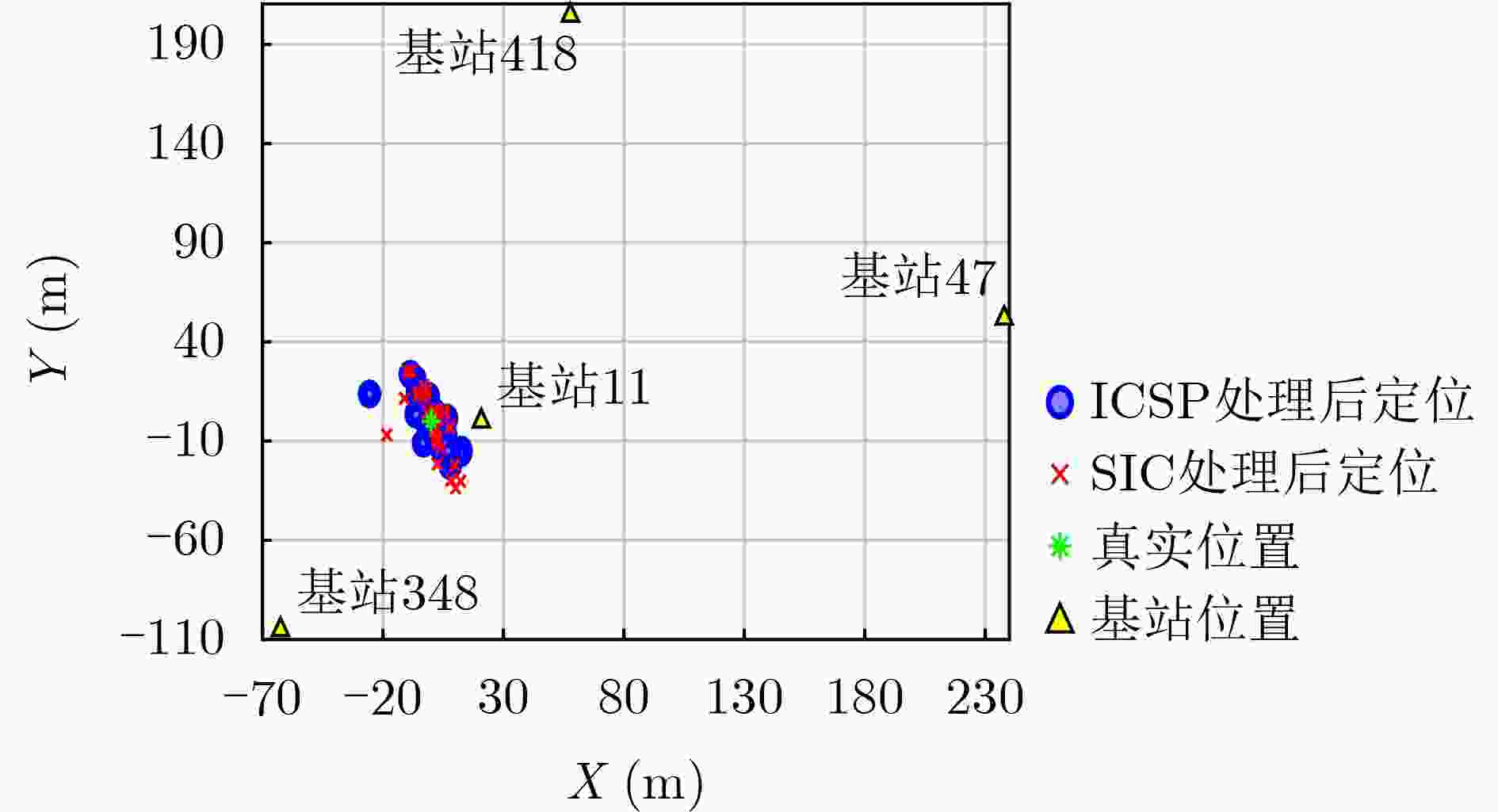


 下载:
下载:
