Radio Environment Map Construction Method for Complex Scenes Based on Inverse Obstacle Distance Weighted
-
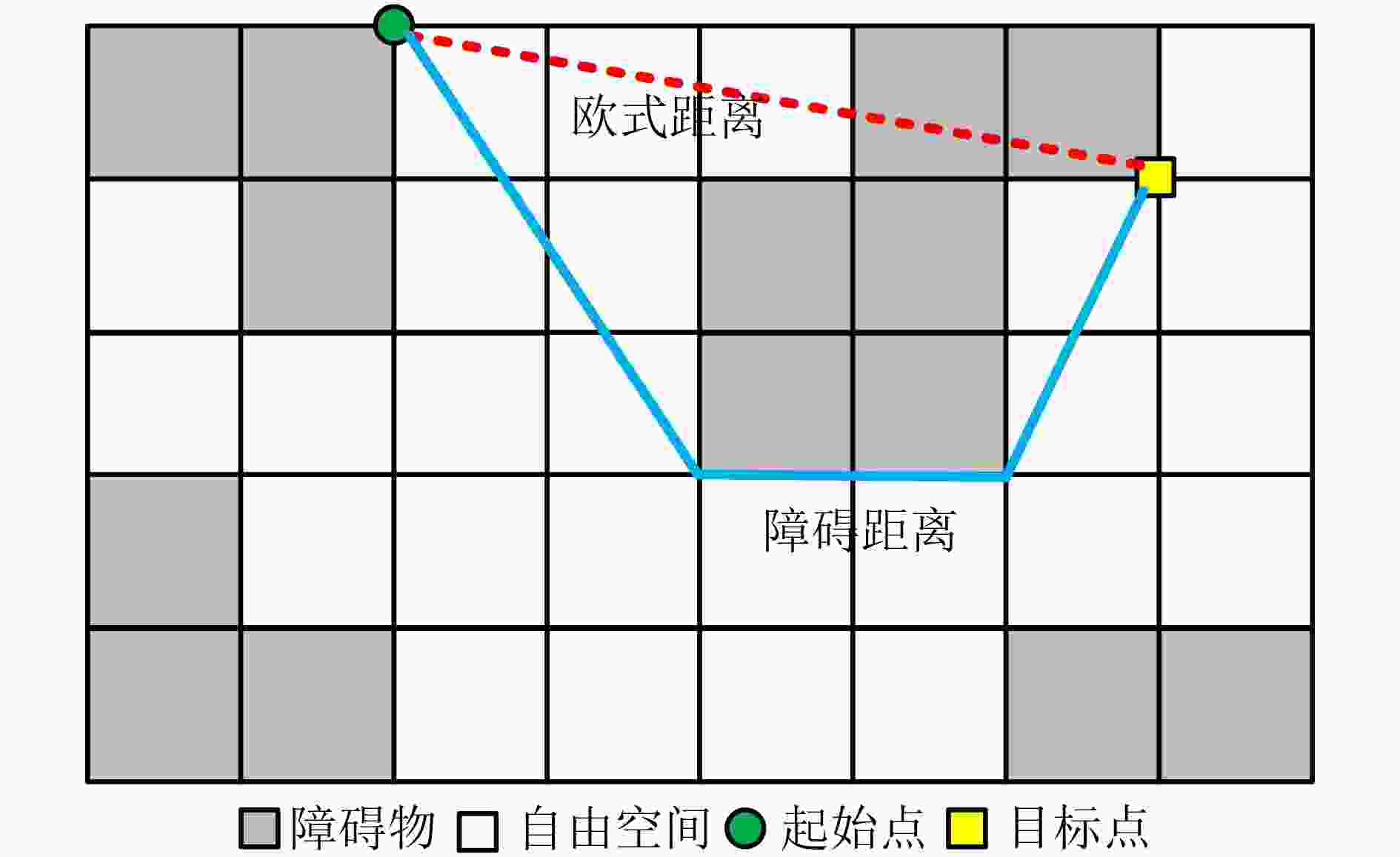
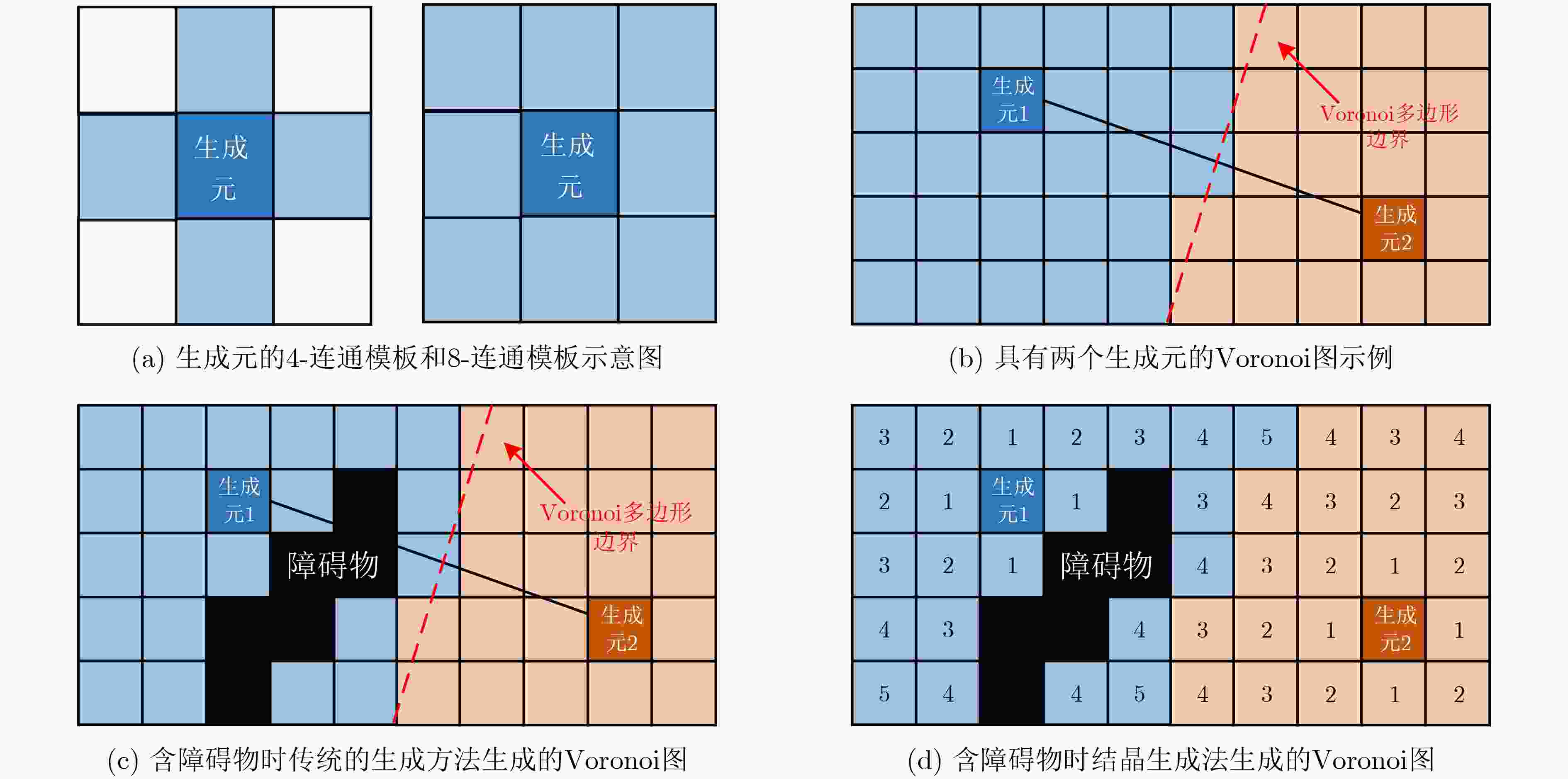
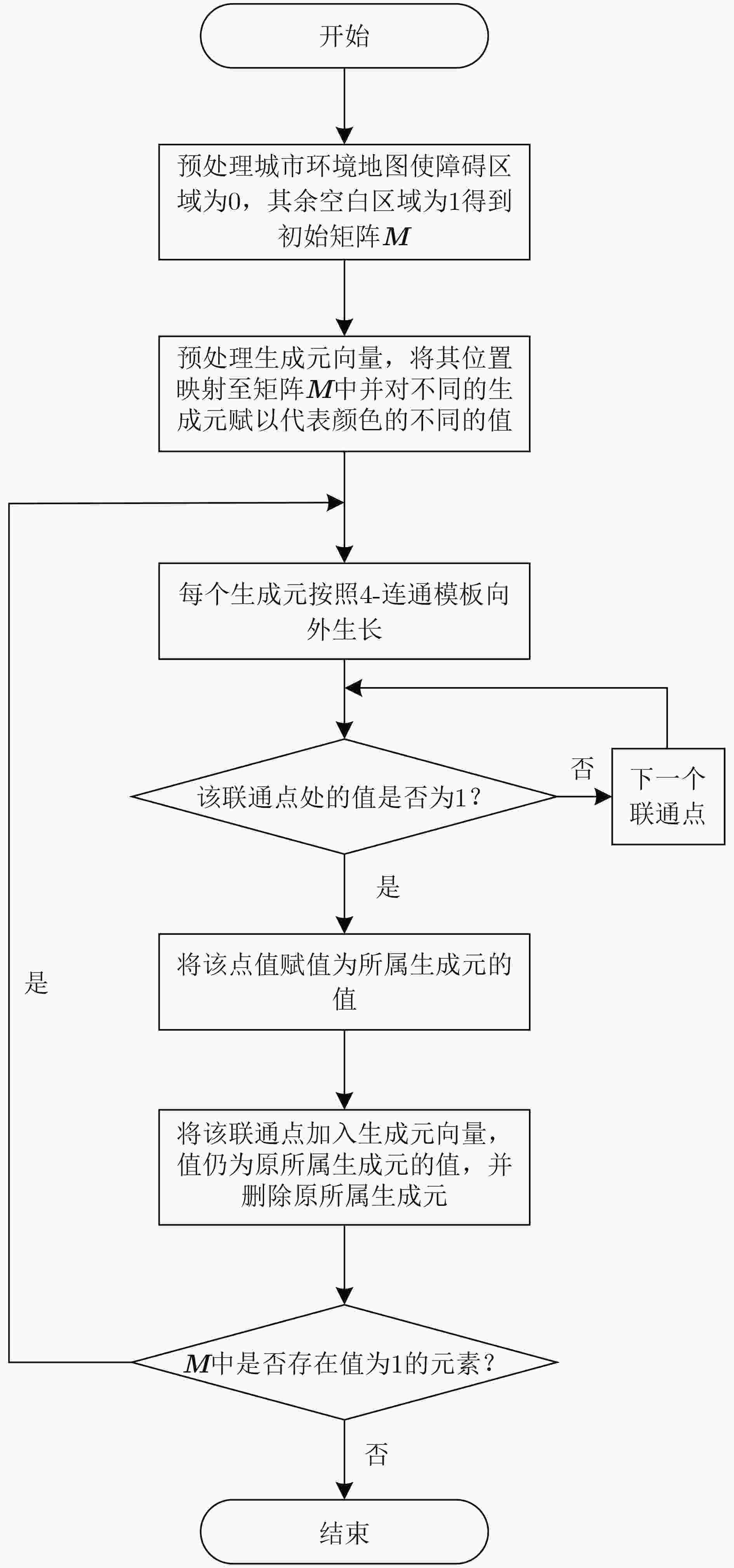
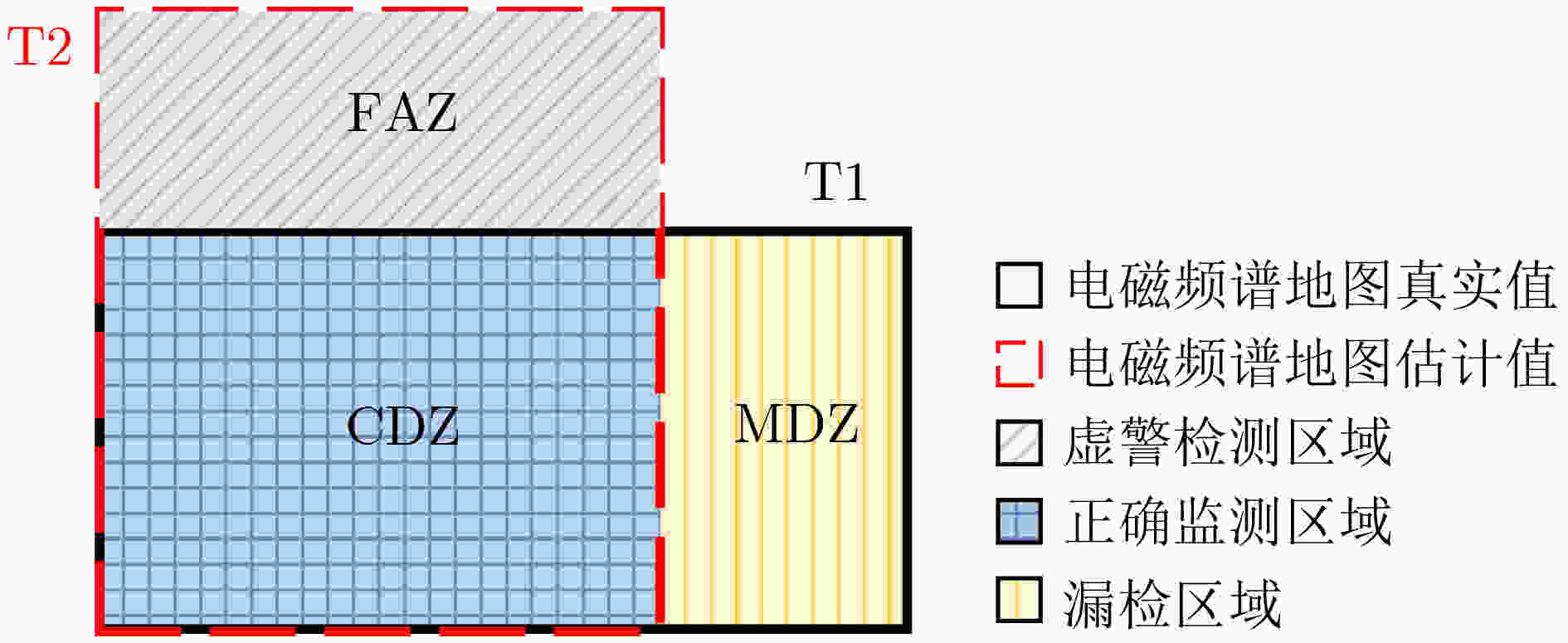
摘要: 针对复杂场景中存在电磁波不可穿透的障碍物导致电磁频谱地图(REMs)构建性能不佳、反距离加权(IDW)算法受限于插值邻域的人工选择等问题,该文提出一种基于Voronoi图的反障碍距离加权(VIODW)的复杂场景电磁频谱地图构建算法。该算法通过创建包含障碍物的Voronoi图,为每一个待插值点自适应选定插值邻域用于电磁频谱数据构建,并利用任意角度路径寻优(ANYA)算法计算得到待插值点与插值邻域内每个监测站点之间的障碍距离,最后以障碍距离的反幂次作为权重加权获得待插值点处的电磁频谱数据,实现高精度的复杂场景电磁频谱地图构建。理论分析和仿真结果表明,该方法具有良好的构建精度,能够准确拟合出电磁波在复杂场景中的功率分布情况,为复杂场景下电磁频谱地图高精度构建提供了一种有效方法。Abstract: Addressing the issues of inadequate performance in constructing Radio Environment Maps (REMs) in complex scenarios due to non-penetrable obstacles for electromagnetic waves, and the arbitrary selection of interpolation neighborhoods imposed by Inverse Distance Weighted (IDW), a Voronoi-based Inverse Obstacle Distance Weighted algorithm (VIODW) is proposed in this paper. This algorithm adaptively defines interpolation neighborhoods for each interpolation point by creating Voronoi diagrams incorporating obstacles for numerical computation. Then, using the ANY-Angle (ANYA) Algorithm to calculate the obstacle distance between the interpolation point and each monitoring station within the interpolation neighborhood. Finally, by calculating the weighted mean with the inverse power of the obstacle distance as the weight, the value at the point is obtained, achieving high-precision construction of REMs in complex scenarios. Both theoretical analysis and simulation results demonstrate that this method offers excellent construction accuracy and can accurately model the power distribution of electromagnetic waves in complex scenarios. Hence, it provides an effective approach for high-precision REM construction in complex scenarios.
-
表 1 不同数量电磁监测站点下各算法的RMSE对比
算法 50 100 200 500 1 000 2 000 3 000 IDW1 9.235 6 8.386 5 8.436 8 8.350 7 7.840 8 7.471 4 6.665 9 IDW2 6.662 7 4.748 4 4.513 7 4.053 2 3.458 2 3.268 8 2.773 6 IDW3 5.619 2 3.625 4 3.279 7 2.362 6 1.784 6 1.258 6 0.961 8 MSM 6.295 3 3.610 5 3.441 1 2.137 6 1.663 8 0.973 1 0.653 1 VIODW 4.761 9 3.185 5 2.518 8 1.689 5 1.332 0 0.846 7 0.623 1 -
[1] YILMAZ H B, TUGCU T, ALAGÖZ F, et al. Radio environment map as enabler for practical cognitive radio networks[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2013, 51(12): 162–169. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2013.6685772. [2] ROMERO D and KIM S J. Radio map estimation: A data-driven approach to spectrum cartography[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2022, 39(6): 53–72. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2022.3200175. [3] PESKO M, JAVORNIK T, KOŠIR A, et al. Radio environment maps: The survey of construction methods[J]. KSII Transactions on Internet and Information Systems, 2014, 8(11): 3789–3809. doi: 10.3837/tiis.2014.11.008. [4] 陈智博, 胡景明, 张邦宁, 等. 基于张量Tucker分解的频谱地图构建算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(11): 4161–4169. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230796.CHEN Zhibo, HU Jingming, ZHANG Bangning, et al. Spectrum map construction algorithm based on tensor Tucker decomposition[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(11): 4161–4169. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230796. [5] XING Yue, SONG Qifan, and CHENG Guang. Benefit of interpolation in nearest neighbor algorithms[J]. SIAM Journal on Mathematics of Data Science, 2022, 4(2): 935–956. doi: 10.1137/21M1437457. [6] AZPURUA M A and DOS RAMOS K. A comparison of spatial interpolation methods for estimation of average electromagnetic field magnitude[J]. Progress in Electromagnetics Research M, 2010, 14: 135–145. doi: 10.2528/PIERM10083103. [7] SHEPARD D. A two-dimensional interpolation function for irregularly-spaced data[C]//The 1968 23rd ACM National Conference, 1968: 517–524. doi: 10.1145/800186.810616. [8] MAITI P and MITRA D. Ordinary kriging interpolation for indoor 3D REM[J]. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 2023, 14(10): 13285–13299. doi: 10.1007/s12652-022-03784-2. [9] XIE Yunfeng, CHEN Tongbin, LEI Mei, et al. Spatial distribution of soil heavy metal pollution estimated by different interpolation methods: Accuracy and uncertainty analysis[J]. Chemosphere, 2011, 82(3): 468–476. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.09.053. [10] MERWADE V M, MAIDMENT D R, and GOFF J A. Anisotropic considerations while interpolating river channel bathymetry[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2006, 331(3/4): 731–741. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2006.06.018. [11] MUELLER T G, PUSULURI N B, MATHIAS K K, et al. Map quality for ordinary kriging and inverse distance weighted interpolation[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2004, 68(6): 2042–2047. doi: 10.2136/sssaj2004.2042. [12] LU G Y and WONG D W. An adaptive inverse-distance weighting spatial interpolation technique[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2008, 34(9): 1044–1055. doi: 10.1016/j.cageo.2007.07.010. [13] 史利民, 王仁宏. 几种基于散乱数据拟合的局部插值方法[J]. 数学研究与评论, 2006, 26(2): 283–291. doi: 10.3770/j.issn:1000-341X.2006.02.014.SHI Limin and WANG Renhong. Some local methods for scattered data interpolation[J]. Journal of Mathematical Research and Exposition, 2006, 26(2): 283–291. doi: 10.3770/j.issn:1000-341X.2006.02.014. [14] RENKA R J. Multivariate interpolation of large sets of scattered data[J]. ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software, 1988, 14(2): 139–148. doi: 10.1145/45054.45055. [15] 段平, 盛业华, 李佳, 等. 自适应的IDW插值方法及其在气温场中的应用[J]. 地理研究, 2014, 33(8): 1417–1426. doi: 10.11821/dlyj201408003.DUAN Ping, SHENG Yehua, LI Jia, et al. Adaptive IDW interpolation method and its application in the temperature field[J]. Geographical Research, 2014, 33(8): 1417–1426. doi: 10.11821/dlyj201408003. [16] CAO Yu, TANG Xiaobo, LI Jie, et al. Flow field distribution and structural strength performance evaluation of fixed offshore wind turbine based on digital twin technology[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 288: 116156. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.116156. [17] 夏海洋, 查淞, 黄纪军, 等. 电磁频谱地图构建方法研究综述及展望[J]. 电波科学学报, 2020, 35(4): 445–456. doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.2020040801.XIA Haiyang, ZHA Song, HUANG Jijun, et al. Survey on the construction methods of spectrum map[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2020, 35(4): 445–456. doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.2020040801. [18] MCGARVEY R G and CAVALIER T M. A global optimal approach to facility location in the presence of forbidden regions[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2003, 45(1): 1–15. doi: 10.1016/S0360-8352(03)00028-7. [19] HARABOR D D, GRASTIEN A, ÖZ D, et al. Optimal any-angle pathfinding in practice[J]. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 2016, 56: 89–118. doi: 10.1613/jair.5007. [20] 曹清洁. 障碍Voronoi图的结晶生成及其应用[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2007, 24(8): 147–149, 197. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386X.2007.08.055.CAO Qingjie. The crystal growth of Voronoi diagrams with obstacles and its application[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2007, 24(8): 147–149, 197. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386X.2007.08.055. [21] 周璧华, 陈彬, 高成, 等. 钢筋网及钢筋混凝土电磁脉冲屏蔽效能研究[J]. 电波科学学报, 2000, 15(3): 251–259. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0388.2000.03.001.ZHOU Bihua, CHEN Bin, GAO Cheng, et al. Study on EMP shielding effectiveness of wire-mesh reinforcement and reinforced-concrete[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2000, 15(3): 251–259. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0388.2000.03.001. [22] YAPAR Ç, LEVIE R, KUTYNIOK G, et al. Real-time outdoor localization using radio maps: A deep learning approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2023, 22(12): 9703–9717. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2023.3273202. -






 下载:
下载:
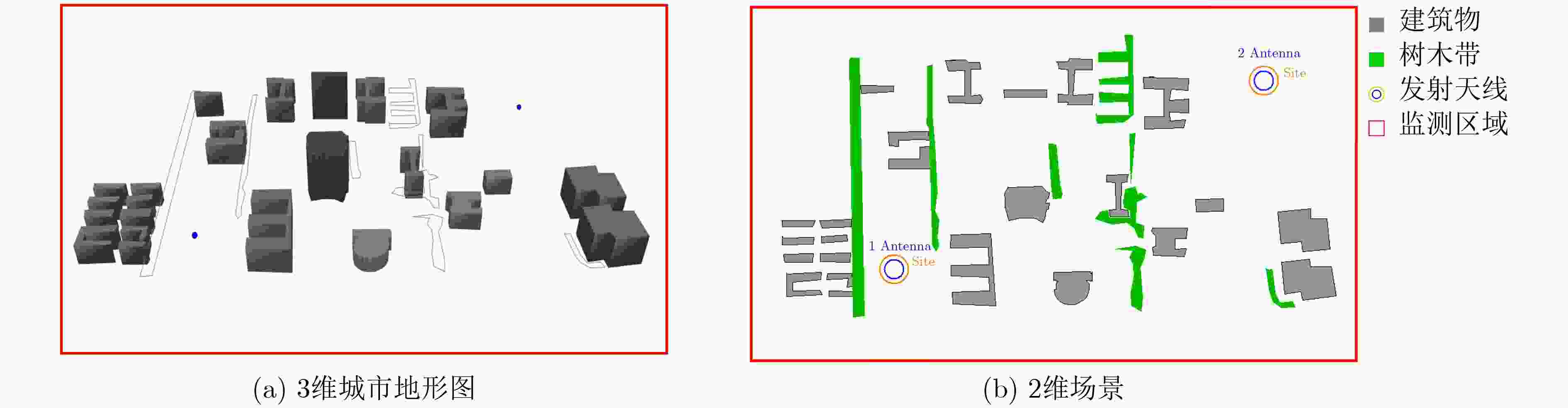

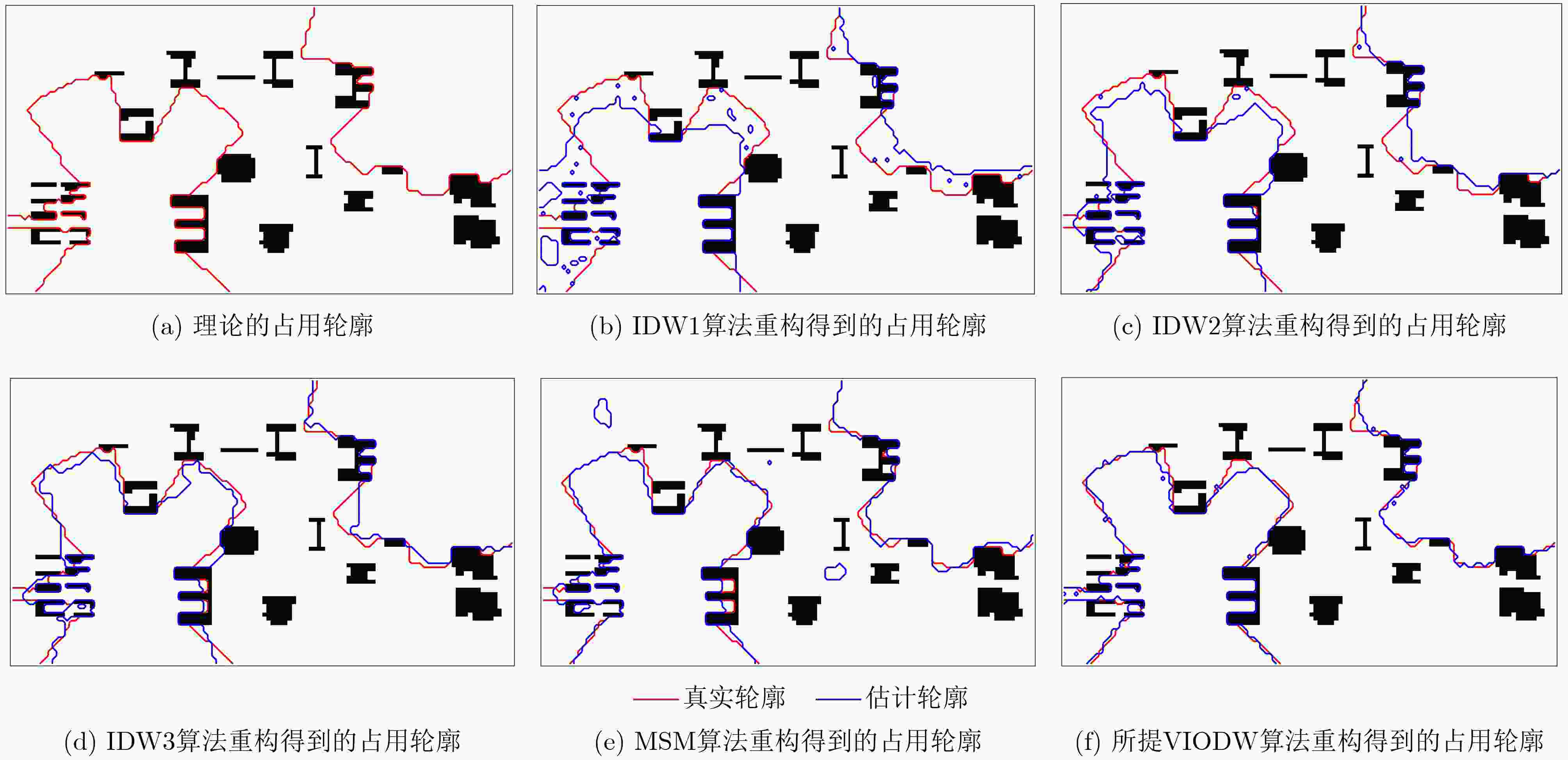
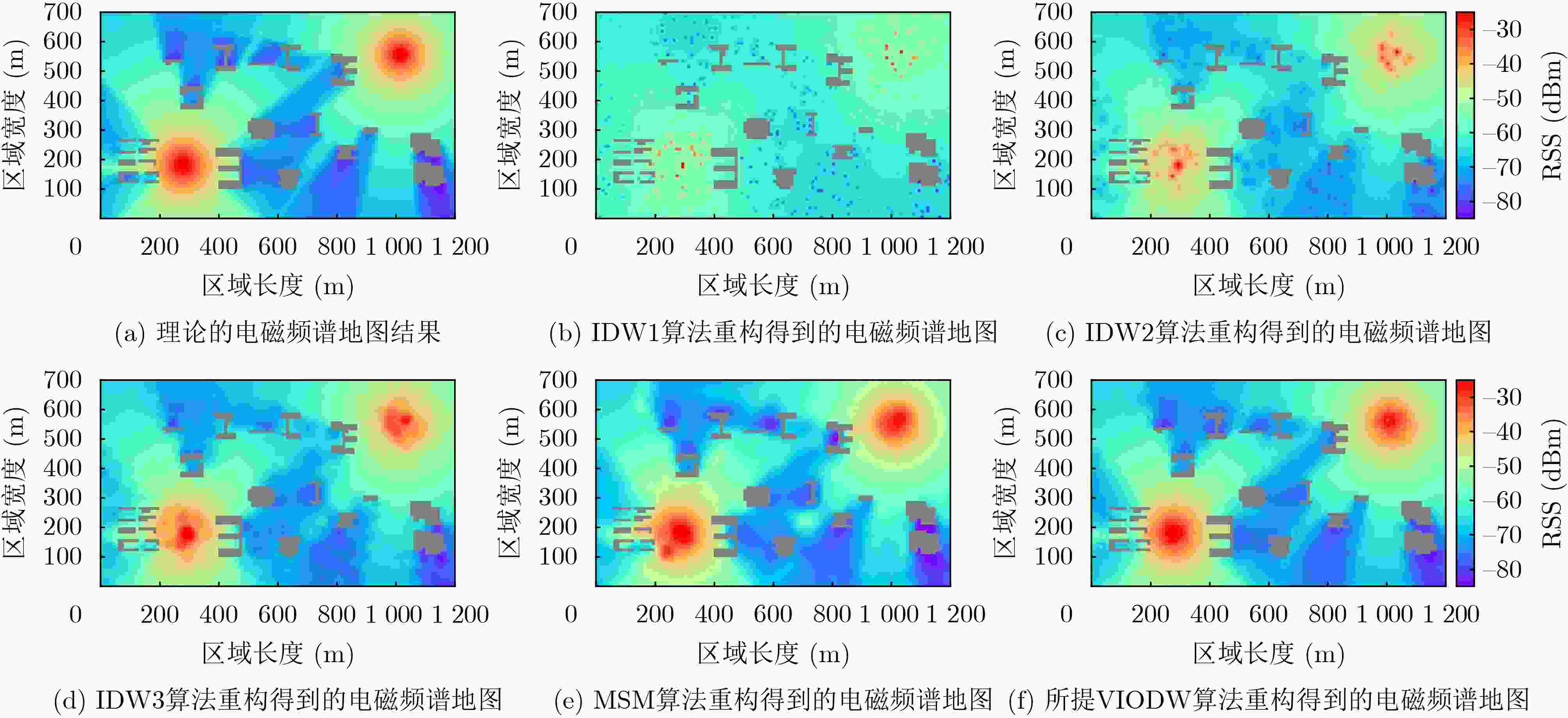


 下载:
下载:
