A Method for Radio Frequency Interference Space Angle Sparse Bayesian Estimating in Synthetic Aperture Microwave Radiometer
-
摘要: 该文提出一种综合孔径微波辐射计射频干扰源(RFI)空间稀疏贝叶斯估计方法。首先建立了综合孔径微波辐射计可见度函数干涉测量模型,观测数据表示为综合孔径天线基线对相关导向矢量观测矩阵与视场亮温的乘积,由于相关导向矢量观测矩阵的正交性和RFI空间角度分布的稀疏性,亮温在基线对相关导向矢量观测矩阵正交基所构成的支撑域中的变换系数是稀疏的。该文在稀疏贝叶斯学习(SBL)框架下对亮温进行稀疏重构。该方法在无需稀疏度和正则化参数等先验信息前提下也能获得较高的重构性能。计算机仿真验证了该方法的有效性。Abstract: A sparse Bayesian estimation for spatial Radio Frequency Interference (RFI) of synthetic aperture microwave radiometers is proposed in this paper. Firstly, an interferometry measurement model of the visibility function for synthetic aperture microwave radiometers is established. The observed data are expressed as the product of the observation matrix of the aperture synthesis antenna baseline correlation steering vector and the brightness temperature of the field of view. Due to the orthogonality of the observation matrix and the sparsity of the RFI spatial angle distribution, the transformation coefficients of brightness temperature in the support domain are sparse. Under the Sparse Bayesian Learning (SBL) framework, brightness temperature is sparsely reconstructed. Notably, this method can obtain high reconstruction performance without the prior information of sparsity and regularization parameters. The effectiveness of this method is verified through computer simulations.
-
表 1 陆地背景定位结果
算法 400 K 1 000 K MUSIC (0.406 5,0.208 6) (0.406 5,0.208 6) SBL (0.406 5,0.208 6) (0.406 5,0.208 6) 表 2 海陆交替背景定位结果
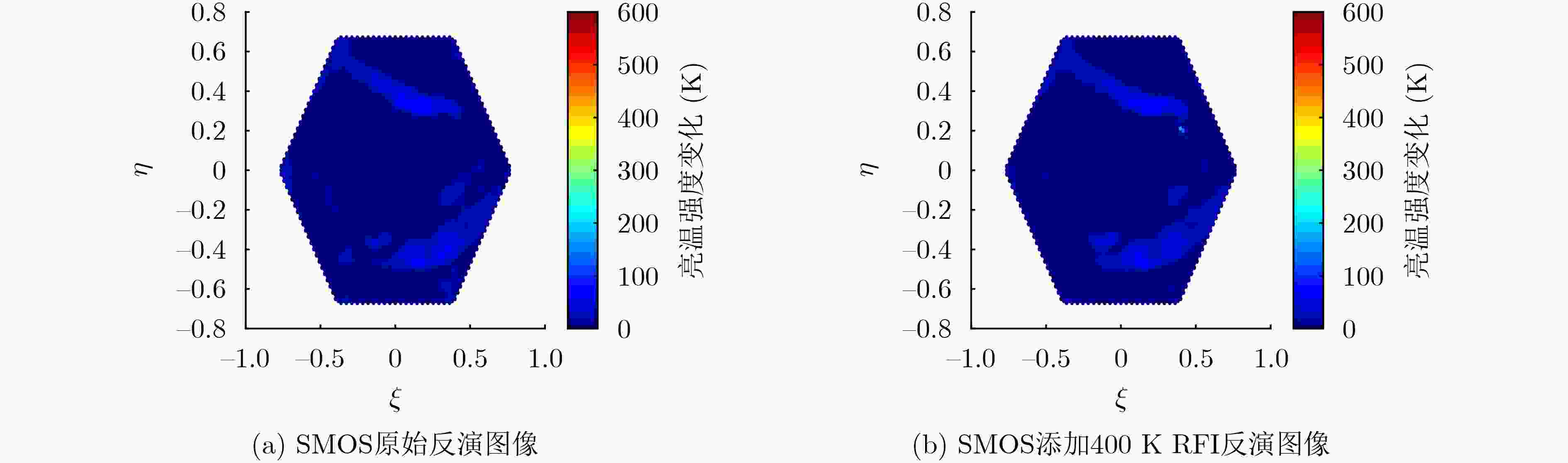
算法 400 K 1 000 K MUSIC (0.361 3,0.260 8) (0.383 9,0.195 6) SBL (0.406 5,0.208 6) (0.406 5,0.208 6) 表 3 SMOS背景定位结果
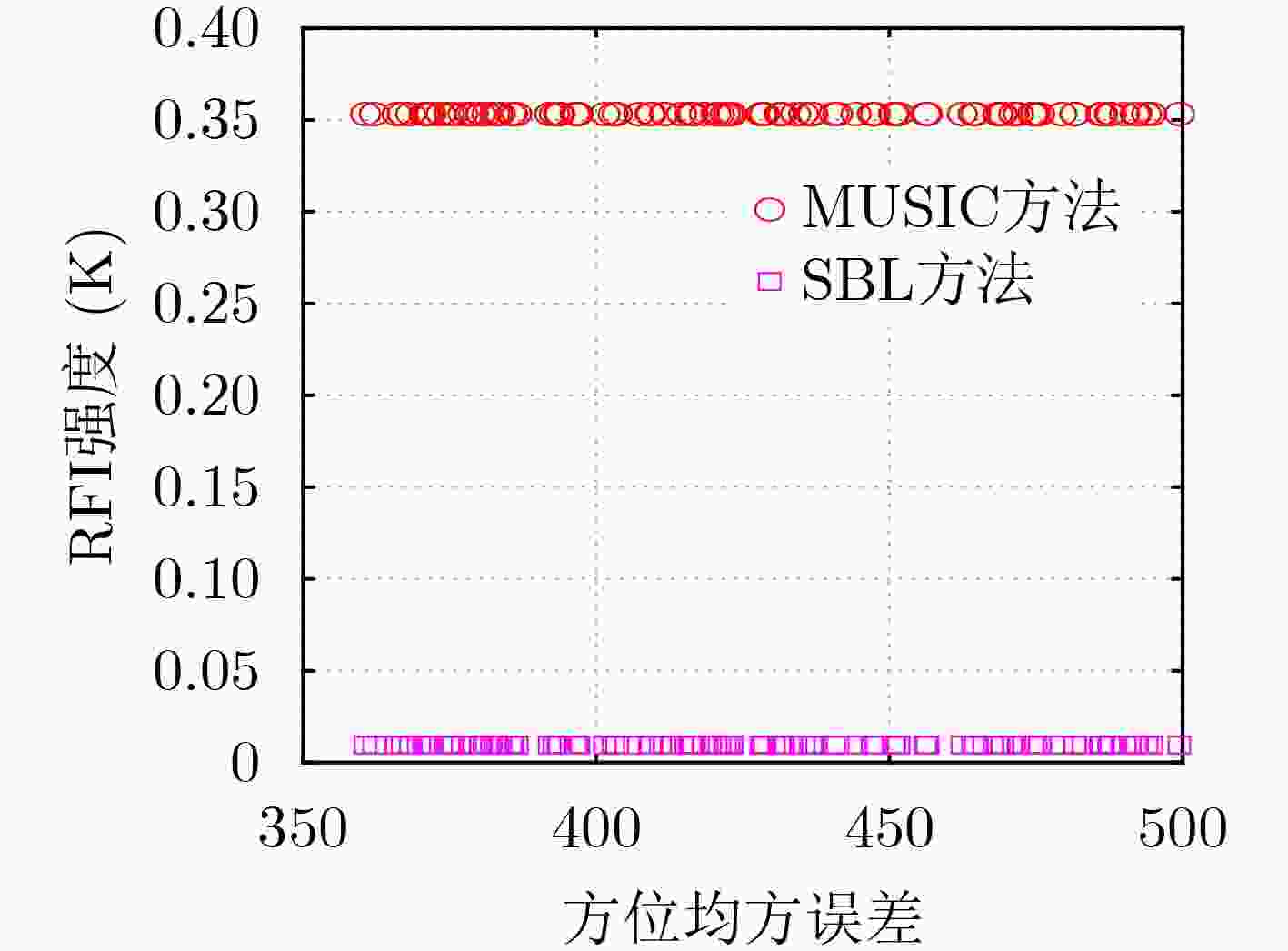
算法 (0.4,0.2) 方位均方误差 MUSIC (0.199 5,0.303 7) 0.353 2 SBL (0.399 1,0.209 5) 0.009 5 表 4 SMOS数据定位结果
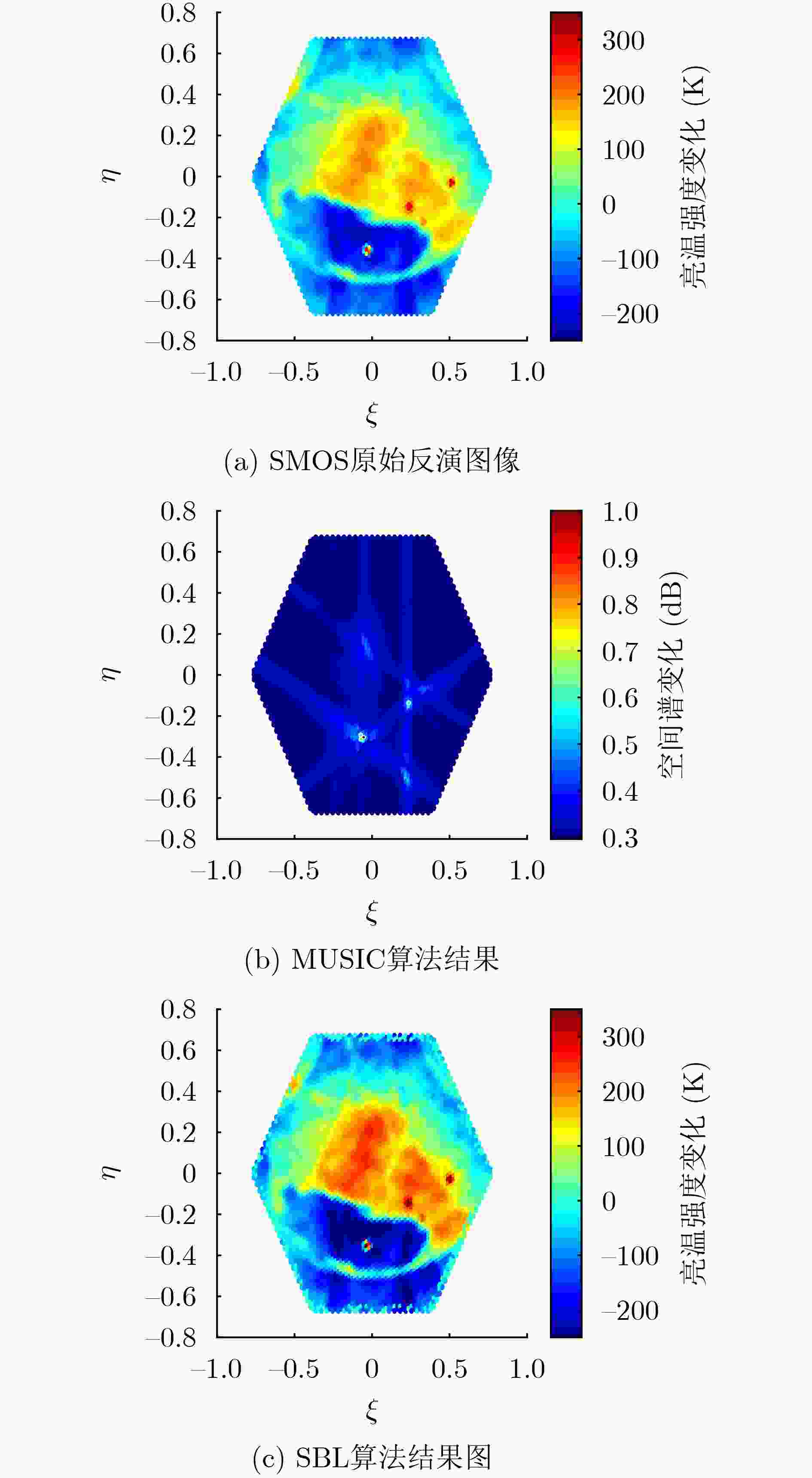
算法 1 2 3 4 MUSIC (– 0.0544 , –0.3037 )(– 0.0726 , –0.3142 )(– 0.0726 , –0.2933 )( 0.2358 , –0.1362 )SBL (– 0.0363 , –0.3561 )( 0.2358 , –0.1362 )( 0.2358 , –0.1571 )( 0.5079 , –0.0209 ) -
[1] 何越, 田晓明, 祝颂, 等. 基于GNSS/MET和微波辐射计资料的合肥地区大气可降水量变化特征分析[J]. 气象水文海洋仪器, 2023, 40(3): 15–19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-009X.2023.03.005.HE Yue, TIAN Xiaoming, ZHU Song, et al. Analysis on variation characteristics of atmospheric precipitable water in Hefei based on GNSS/MET and microwave radiometer data[J]. Meteorological, Hydrological and Marine Instruments, 2023, 40(3): 15–19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-009X.2023.03.005. [2] 伍晋. 基于综合孔径辐射计的海洋盐度遥感外部源校正方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 华中科技大学, 2022. doi: 10.27157/d.cnki.ghzku.2022.004416.WU Jin. Research on foreign sources correction method for sea surface salinity remote sensing based on synthetic aperture radiometer[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2022. doi: 10.27157/d.cnki.ghzku.2022.004416. [3] 党张利, 穆建华, 闫军, 等. 六盘山区两类雾物理结构的初步观测研究[J]. 干旱区地理, 2023, 46(4): 574–582. doi: 10.12118/j.issn.1000-6060.2022.382.DANG Zhangli, MU Jianhua, YAN Jun, et al. Preliminary observations study of physical structures of two types of fog in Liupan Mountain areas[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2023, 46(4): 574–582. doi: 10.12118/j.issn.1000-6060.2022.382. [4] CAMPS A J, CORBELLA I, TORRES F, et al. RF interference analysis in aperture synthesis interferometric radiometers: Application to L-band MIRAS instrument[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(2): 942–950. doi: 10.1109/36.841976. [5] NJOKU E G, ASHCROFT P, CHAN T K, et al. Global survey and statistics of radio-frequency interference in AMSR-E land observations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2005, 43(5): 938–947. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2004.837507. [6] MARTÍN-NEIRA M, LEVINE D M, KERR Y, et al. Microwave interferometric radiometry in remote sensing: An invited historical review[J]. Radio Science, 2014, 49(6): 415–449. doi: 10.1002/2013RS005230. [7] OLIVA R, NIETO S, and FÉLIX-REDONDO F. RFI detection algorithm: Accurate geolocation of the interfering sources in SMOS images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(10): 4993–4998. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2262721. [8] CASTRO R, GUTIERREZ A, and BARBOSA J. A first set of techniques to detect radio frequency interferences and mitigate their impact on SMOS data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(5): 1440–1447. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2179304. [9] PARK H, CAMPS A, and GONZÁLEZ-GAMBAU V. Accurate geolocation of RFI sources in SMOS imagery based on superresolution algorithms[C]. 2014 13th Specialist Meeting on Microwave Radiometry and Remote Sensing of the Environment (MicroRad), Pasadena, USA, 2014: 29–32. doi: 10.1109/MicroRad.2014.6878902. [10] PARK H, GONZÁLEZ-GAMBAU V, and CAMPS A. High angular resolution RFI localization in synthetic aperture interferometric radiometers using direction-of-arrival estimation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(1): 102–106. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2327006. [11] MALIOUTOV D, CETIN M, and WILLSKY A S. A sparse signal reconstruction perspective for source localization with sensor arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2005, 53(8): 3010–3022. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2005.850882. [12] ANTERRIEU E, KHAZAAL A, CABOT F, et al. Geolocation of RFI sources with sub-kilometric accuracy from SMOS interferometric data[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2016, 180: 76–84. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2016.02.007. [13] 杨磊, 夏亚波, 廖仙华, 等. 双层稀疏贝叶斯学习ISAR超分辨成像算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2023, 45(5): 1371–1379. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.05.13.YANG Lei, XIA Yabo, LIAO Xianhua, et al. Super-resolution ISAR imagery algorithm based on bi-sparsity Bayesian learning[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(5): 1371–1379. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.05.13. [14] 许煜辉. 基于贝叶斯学习的阵列天线故障诊断方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 南京邮电大学, 2022. doi: 10.27251/d.cnki.gnjdc.2022.000977.XU Yuhui. Research on fault diagnosis of antenna arrays based on Bayesian learning[D]. [Master dissertation], Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2022. doi: 10.27251/d.cnki.gnjdc.2022.000977. [15] 章涛, 张亚娟, 孙刚, 等. 稀疏贝叶斯字典学习空时机动目标参数估计算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(8): 2884–2892. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210567.ZHANG Tao, ZHANG Yajuan, SUN Gang, et al. Maneuvering target parameter estimation based on sparse Bayesian dictionary learning in space-time adaptive processing[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(8): 2884–2892. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210567. [16] CORBELLA I, TORRES F, BLANCH S, et al. Inter-element phase calibration in interferometric radiometers[C]. 2006 IEEE International Symposium on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Denver, USA, 2006: 3976–3979. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2006.1020. [17] CORBELLA I, DUFFO N, VALL-LLOSSERA M, et al. The visibility function in interferometric aperture synthesis radiometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2004, 42(8): 1677–1682. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2004.830641. [18] WU Qisong, ZHANG Y D, AMIN M G, et al. Complex multitask Bayesian compressive sensing[C]. 2014 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Florence, Italy, 2014: 3375–3379. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2014.6854226. [19] 李军. 基于虚拟天线阵的综合孔径辐射计成像方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 华中科技大学, 2017.LI Jun. Research on imaging method of synthetic aperture interferometric radiometry based on virtual antenna arrays[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2017. -






 下载:
下载:







 下载:
下载:
