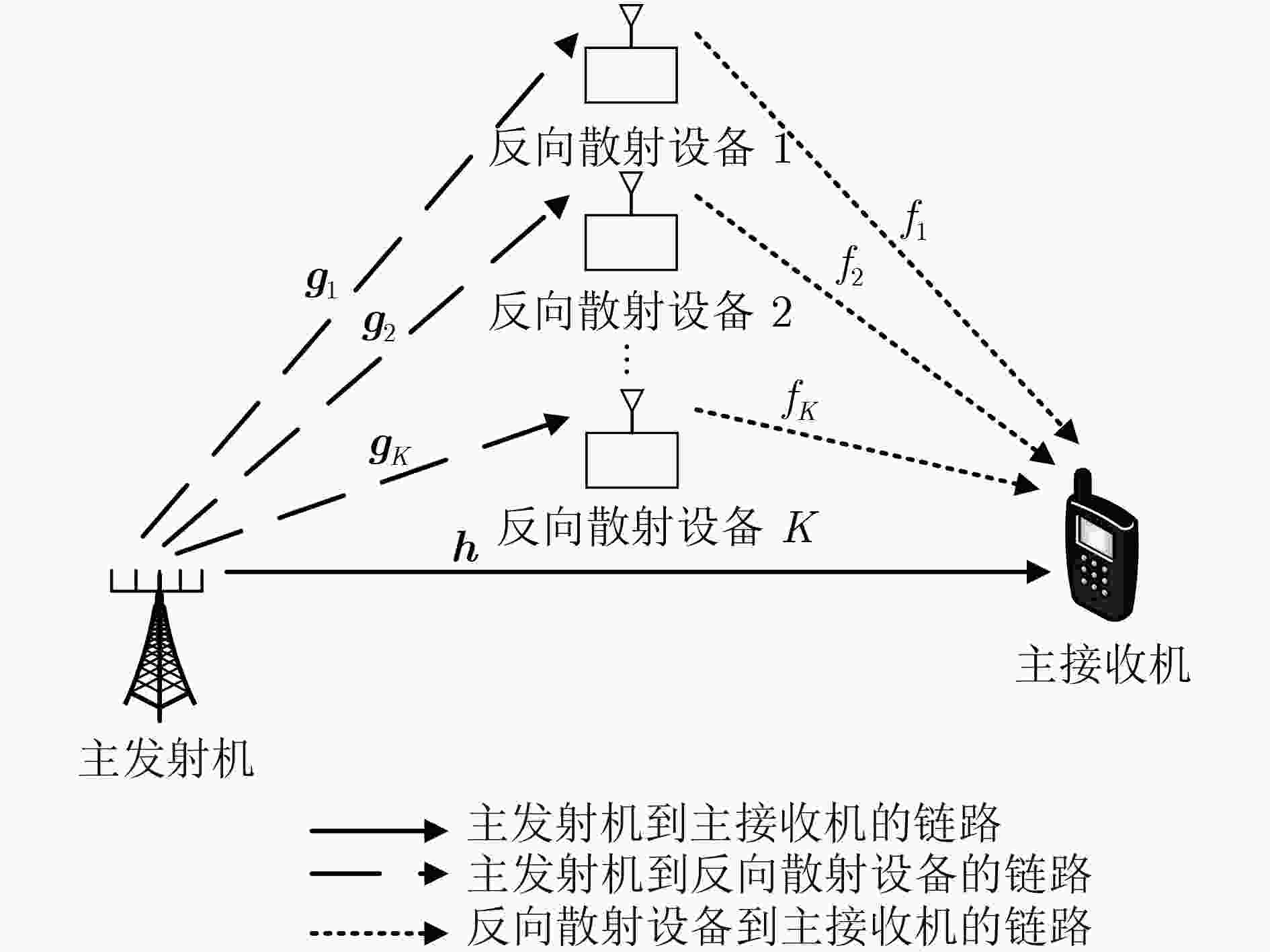
Resource Allocation Algorithm for Multiple-Input Single-Output Symbiotic Radio with Imperfect Channel State Information
-
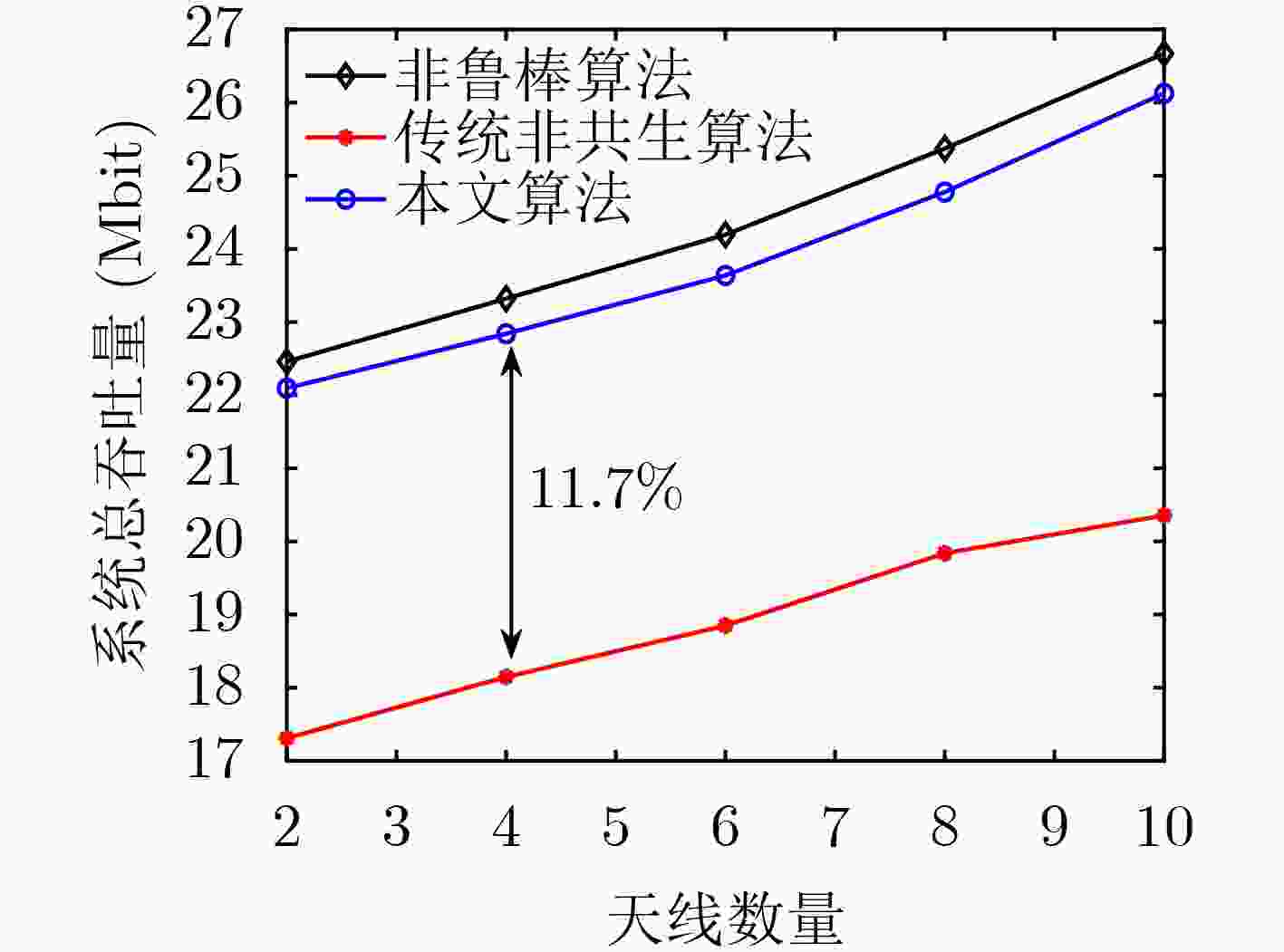
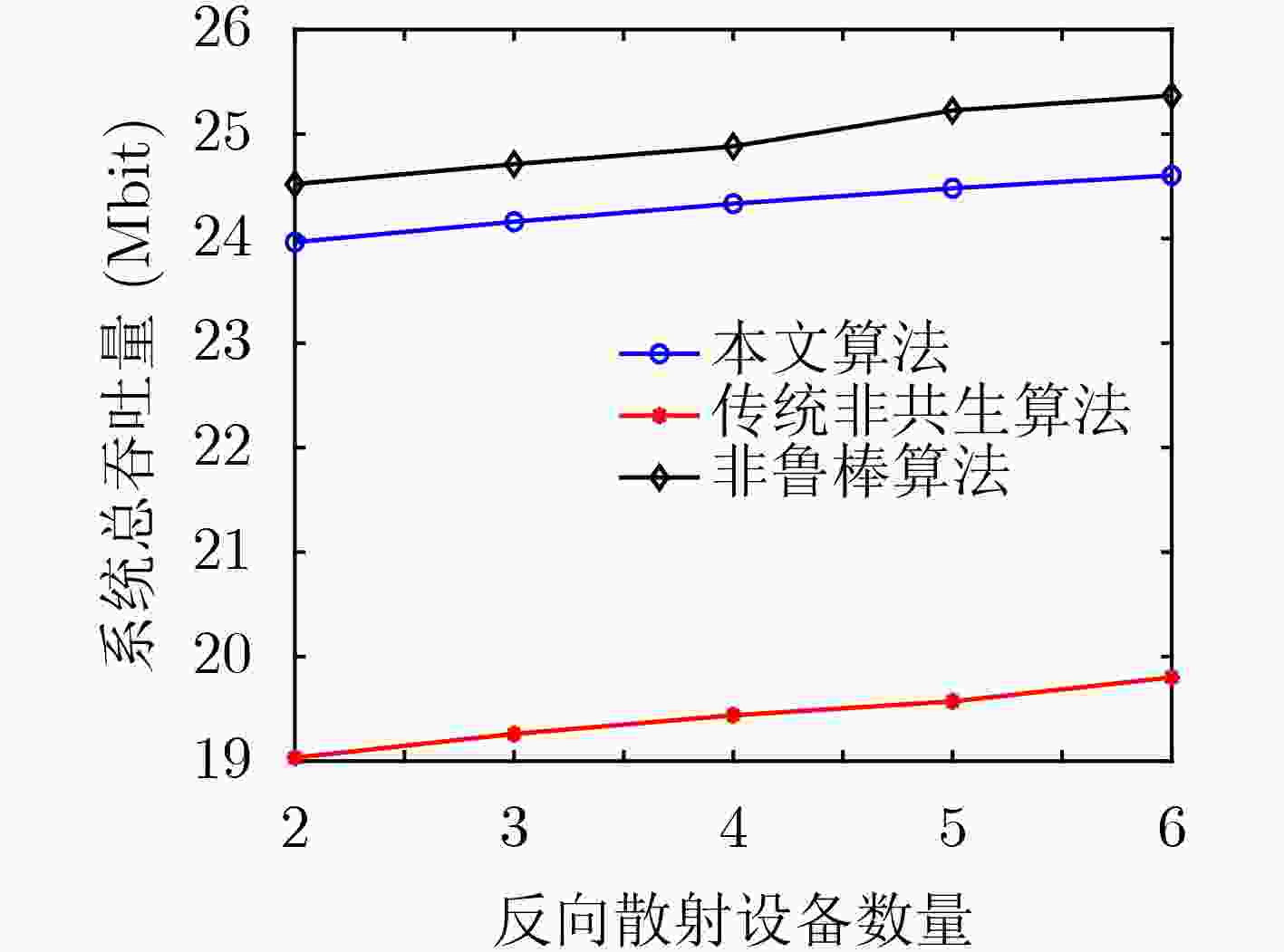
摘要: 针对信道估计误差会导致传统最优资源分配算法失效的问题,该文提出一种基于不完美信道状态信息(CSI)的多输入单输出(MISO)共生无线电系统鲁棒资源分配算法。考虑每个用户最小吞吐量约束、传输时间约束、基站最大发射功率约束和用户反射系数约束,基于有界信道不确定性模型,建立了一个传输时间、波束成形向量和反射系数联合优化的鲁棒吞吐量最大化资源分配问题。利用拉格朗日对偶、变量替换和交替优化方法将原问题转换成凸优化问题求解。仿真结果表明,与传统非共生资源分配算法相比,所提算法的吞吐量提升11.7%,中断概率减小5.31%。Abstract: To overcome the effect of channel estimation errors on the ineffectiveness of conventional optimal resource allocation algorithms, a robust resource allocation algorithm with imperfect Channel State Information(CSI) is proposed in Multiple-Input Single-Output(MISO) symbiotic radio systems. Considering the constraints of the minimum throughput of users, transmission time, maximum transmit power of the base station, and the reflection coefficients of users, based on bounded channel uncertainties, a robust throughput-maximization resource allocation problem is formulated by jointly optimizing transmission time, beamforming vectors, and reflection coefficients. The original problem is transformed into a convex problem by applying the Lagrange dual theory, the variable substitution, and the alternating optimizing methods. Simulation results verified that the throughput of the proposed algorithm is improved by 11.7% and the outage probability is reduced by 5.31% by comparing it with the non-robust resource allocation algorithm.
-
Key words:
- Symbiotic Radio(SR) /
- Robust resource allocation /
- Throughput maximization
-
表 1 相关工作总结
文献 网络类型 用户数 CSI 优化变量 目标函数 传输时间 反射系数 波束成形 [5] SISO SR 单用户 完美 × √ × Max:加权和速率 [6] MISO SR 单用户 完美 × × √ Min:传输功率,Max:能效 [7] MISO SR 多用户 完美 √ √ × Max:能效 [8] MISO NOMA-TDMA SR 多用户 完美 √ √ × Max:最小吞吐量 [9] MISO 全双工+NOMA-TDMA SR 多用户 完美 √ √ × Max:最小吞吐量 [10] SISO RIS+SR 多用户 完美 × √ × Max:能效 [11] MISO RIS+SR 单用户 完美 × √ √ Max:能效 [12] MISO RIS+SR+NOMA 多用户 完美 √ × × Max:资源效率 [13] SISO RIS+UAV+SR 单用户 完美 × × × Min:加权和误码率 [14] MISO SR 多用户 完美 × √ × Min: SNR [15] MISO SR+窃听者 单用户 完美 × √ × Max:保密速率 [16] MIMO RIS+SR 单用户 完美 × √ × Min:传输功率 [17] MISO RIS+SR 单用户 不完美 × × √ Min:传输功率 [18] MISO RIS+SR 单用户 不完美 × √ √ Min:传输功率 本文 MISO SR 多用户 不完美 √ √ √ Max:吞吐量 1 基于迭代的鲁棒吞吐量最大化算法
初始化系统参数:$K$, ${\delta ^2}$, $N$, $B$, $T$;初始化迭代次数$l = 0$;
定义最大迭代次数${L_{\max }}$和收敛精度$\varpi $;(1) WHILE
$ \left| {\displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{k = 1}^K {{{\left( {R_k^{\text{u}} + R_k^{\text{b}}} \right)}^{(l)}}} - \displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{k = 1}^K {{{\left( {R_k^{\text{u}} + R_k^{\text{b}}} \right)}^{(l - 1)}}} } \right| \ge \varpi $ 或
$l \le {L_{\max }}$ DO(2) 设置迭代次数$l = l + 1$; (3) 固定$t_k^{(l - 1)}$和$\theta _k^{(l - 1)}$,根据式(26)计算${{{\boldsymbol{W}}}^{(l)}}$;若${{{\boldsymbol{W}}}^{(l)}}$的秩
为1,则使用特征值分解法得到最优解;若${{{\boldsymbol{W}}}^{(l)}}$的秩大于1,
采用高斯随机化方法得到近似解;(4) 固定${{{\boldsymbol{W}}}^{(l)}}$,根据式(32)求解$t_k^{(l)}$和$\theta _k^{(l)}$; (5) 更新吞吐量$ \displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{k = 1}^K {\left( {R_k^{\text{u}} + R_k^{\text{b}}} \right)} $。 (6) END WHILE -
[1] ZHANG Qianqian, LIANG Yingchang, YANG Hongchuan, et al. Mutualistic mechanism in symbiotic radios: When can the primary and secondary transmissions be mutually beneficial?[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(10): 8036–8050. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2022.3163735. [2] HU Jinlin, LIANG Yingchang, and PEI Yiyang. Reconfigurable intelligent surface enhanced multi-user MISO symbiotic radio system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(4): 2359–2371. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2020.3047444. [3] 未来移动通信论坛. 未来IMT通信系统频谱研究白皮书(2024年)[R]. 2024. [4] LIANG Yingchang, ZHANG Qianqian, LARSSON E G, et al. Symbiotic radio: Cognitive backscattering communications for future wireless networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2020, 6(4): 1242–1255. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2020.3023139. [5] GUO Huayan, LIANG Yingchang, LONG Ruizhe, et al. Resource allocation for symbiotic radio system with fading channels[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 34333–34347. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2904612. [6] CHU Zheng, HAO Wanming, XIAO Pei, et al. Resource allocations for symbiotic radio with finite blocklength backscatter link[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(9): 8192–8207. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.2980928. [7] YANG Haohang, YE Yinghui, LIANG Kai, et al. Energy efficiency maximization for symbiotic radio networks with multiple backscatter devices[J]. IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society, 2021, 2: 1431–1444. doi: 10.1109/OJCOMS.2021.3090836. [8] ZHANG Ronghaixiang, KANG Xin, and LIANG Yingchang. Minimum throughput maximization for peer-assisted NOMA-plus-TDMA symbiotic radio networks[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2021, 10(9): 1847–1851. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2021.3083841. [9] LIAO Yating, YANG Gang, and LIANG Yingchang. Resource allocation in NOMA-enhanced full-duplex symbiotic radio networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 22709–22720. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2967153. [10] LI Jing, LI Xin, BI Yanjun, et al. Energy-efficient joint resource allocation with reconfigurable intelligent surfaces in symbiotic radio networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2022, 8(4): 1816–1827. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2022.3188986. [11] ZHOU Chunyu, XU Yongjun, LI Dong, et al. Energy-efficient maximization for RIS-aided MISO symbiotic radio systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(10): 13689–13694. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2023.3274796. [12] WU Mingjiang, LEI Xianfu, ZHOU Xiangyun, et al. RIS-assisted energy- and spectrum-efficient symbiotic transmission in NOMA systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2023, 71(5): 2801–2815. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2023.3241355. [13] HUA Meng, YANG Luxi, WU Qingqing, et al. UAV-assisted intelligent reflecting surface symbiotic radio system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(9): 5769–5785. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3070014. [14] HAN Shiying, LIANG Yingchang, and SUN Guiling. The design and optimization of random code assisted Multi-BD symbiotic radio system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(8): 5159–5170. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3065941. [15] AL-NAHARI A, JÄNTTI R, ZHENG Gan, et al. Ergodic secrecy rate analysis and optimal power allocation for symbiotic radio networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2023, 11: 82327–82337. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3301186. [16] ZHANG Qianqian, LIANG Yingchang, and POOR H V. Reconfigurable intelligent surface assisted MIMO symbiotic radio networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(7): 4832–4846. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3070043. [17] ZHOU Hu, KANG Xin, LIANG Yingchang, et al. Cooperative beamforming for reconfigurable intelligent surface-assisted symbiotic radios[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71(11): 11677–11692. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3190515. [18] 吴翠先, 周春宇, 徐勇军, 等. 智能反射面辅助的多入单出共生无线电鲁棒安全资源分配算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(4): 1203–1211. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230426.WU Cuixian, ZHOU Chunyu, XU Yongjun, et al. Robust secure resource allocation algorithm for multiple input single output symbiotic radio with reconfigurable intelligent surface assistance[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(4): 1203–1211. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230426. [19] 徐勇军, 姜思巧, 王公仆, 等. 基于不完美CSI的认知反向散射通信吞吐量最大化算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(7): 2325–2333. doi: 10.11999/JEIT221483.XU Yongjun, JIANG Siqiao, WANG Gongpu, et al. Throughput maximization algorithm for cognitive backscatter communication with imperfect CSI[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(7): 2325–2333. doi: 10.11999/JEIT221483. [20] BOYD S and VANDENBERGHE L. Convex Optimization[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2004. [21] WU Tuo, JIANG Miao, ZHANG Qi, et al. Beamforming design in multiple-input-multiple-output symbiotic radio backscatter systems[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2021, 25(6): 1949–1953. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2021.3060468. [22] HEIDARPOUR A R, ARDAKANI M, TELLAMBURA C, et al. Network-coded cooperative systems in cognitive radio networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(12): 11011–11023. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2022.3188729. -





 下载:
下载:







 下载:
下载:
