Collaborative Electromagnetic Suppression Method for Electromagnetic Security Control of Major Events
-
摘要: 该文研究了复杂环境条件下重大活动安保区域的电磁安全协同压制技术问题。首先采用了城市环境电波传播模型,建模分析了城市复杂电磁环境的特征。其次,针对高效电磁压制与有效避免有害干扰问题,利用势博弈方法设计电磁压制设备协同部署算法,基于此,提出了基于遗传算法的压制设备功率优化方法,实现了电磁压制设备协同工作下干扰功率的高效投送。仿真结果表明,所提出的电磁压制设备位置部署算法可获得与理论最优方法(即遍历算法)近似的优异性能,且运算复杂度更低;在保证相同干扰效果下,所提功率优化算法相较于传统干扰功率分配方法的传输功率降低了50%以上,实现了精准协同管控。Abstract: The electromagnetic security cooperative suppression technology in the security area of major events under the complex urban environment is presented in this paper. Firstly, the complex urban electromagnetic environment is modeled by using the radio wave propagation model suitable for dense urban environment. Secondly, aiming at the problem of efficient electromagnetic suppression and effective avoidance of harmful interference, the potential game method is used to design the cooperative deployment algorithm of electromagnetic suppression equipment. Building upon this, the power optimization method of suppression equipment based on genetic algorithm is proposed to achieve the efficient delivery of interference power under the cooperative work of electromagnetic suppression equipment. The simulation results indicate that the proposed electromagnetic suppression equipment deployment algorithm can obtain outstanding performance similar to the theoretical optimal method (i.e., traversal algorithm), with lower computational complexity. Moreover, under identical interference effectiveness, the proposed power optimization algorithm reduces transmission power by over 50% compared to the traditional interference power allocation methods, thereby achieving precise collaborative control.
-
表 1 符号的定义
符号 定义 $i$ 可部署设备点索引$,i \in [1,M]$ $j$ 典型点索引$,j \in [1,N]$ $k$ 白名单索引$,k \in [1,P]$ $q$ 管制台站索引$,q \in \left[ {1,Q} \right]$ $ P_{{t_j}}^{{\text{Th}}} $ 典型点$ {t_j} $接收机正常工作的阈值 $ P_{{w_k}}^{{\text{Th}}} $ 白名单设备$ {w_k} $能允许的最大压制强度 $ P_{{c_q}}^{{\text{Th}}} $ 管制台站$ {c_q} $接收机正常工作的阈值 $ d_{{s_i},{t_j}}^{{\text{2D}}} $ 设备点${s_i}$到典型点${t_j}$的2维距离 $ {d_{{s_i},{t_j}}} $ 设备点${s_i}$到典型点${t_j}$的3维距离 1 基于势博弈的压制设备位置部署算法
输入:${{\mathbf{P}}_{{\text{rx}}}}$, $ {\bf{P}}{{\bf{C}}_{{\text{rx}}}} $, ${\bf{P}}{{\bf{W}}_{{\text{rx}}}}$, $P_{{t_j}}^{{\text{th}}}$, $P_{{c_q}}^{{\text{th}}}$, $ P_{{w_k}}^{{\text{th}}} $ 初始化: (1) 设置收敛阈值$\varepsilon $ (2) 初始化效用函数最小值$ {U_{\min }} = \infty $,迭代变量$r = 1$ Repeat 随机产生一组可部署设备方案${V^r} = \{ v_{{d_1}}^r,v_{{d_2}}^r, \cdots ,v_{{d_I}}^r\} $ $P_{{t_j}}^{{\text{sum}},r} \leftarrow $利用式(22)计算叠加在典型点的接收干扰功率 $P_{{c_q}}^{{\text{sum}},r} \leftarrow $利用式(23)计算叠加在管制台站的接收干扰功率 for $t = 1:N,q = 1:Q$ do if $P_{{t_j}}^{{\text{sum}},r} \ge P_{{t_j}}^{{\text{th}}}$,$P_{{c_q}}^{{\text{sum}}} \ge P_{{c_q}}^{{\text{th}}}$ then ${U^r} \leftarrow $利用式(18),式(19),式(20),式(24),式(25)计算
效用函数$ {U_{\min }} \leftarrow $更新效用函数最小值 else $r = r + 1$ end if end for Until $\left| {{U^r} - {U_{\min }}} \right| < \varepsilon $ 输出:${V^*} \leftarrow $根据最小效用函数得到最优设备方案 2 基于遗传算法的协同压制功率优化方法
输入:${{\mathbf{P}}_{{\text{rx}}}}$, $ {\bf{P}}{{\bf{C}}_{{\text{rx}}}} $, ${\bf{P}}{{\bf{W}}_{{\text{rx}}}}$, $P_{{t_j}}^{{\text{th}}}$, $P_{{c_q}}^{{\text{th}}}$, $ P_{{w_k}}^{{\text{th}}} $ 初始化: (1) 设置最大进化代数$T$,交叉概率${P_{\text{c}}}$,变异概率${P_{\text{m}}}$,种群规模$M$ (2) 初始化种群${P_0}$并计算当前种群中各个体的适应度,迭代变量$t = 0$ while $t < T$ do $t = t + 1$ ${P_{\text{s}}} \leftarrow $利用式(29),式(30)计算适应度得到每个个体的选择概率 ${\mathrm{chroms}} \leftarrow $根据${P_s}$随机选择个体 $({{\mathrm{chrom}}_1},{{\mathrm{chrom}}_2}) \leftarrow $根据交叉概率${P_{\text{c}}}$随机生成需要交叉的个体 $({{\mathrm{child}}_1},{{\mathrm{child}}_2}) \leftarrow $利用式(31)生成新的交叉子代个体 ${\mathrm{chrom}} \leftarrow $根据变异概率${P_{\text{m}}}$随机生成需要变异的个体 ${\mathrm{child}} \leftarrow $利用式(32)生成新的变异子代个体 end while 输出:${P_{{T_{{\text{opt}}}}}} \leftarrow $最大适应度个体 -
[1] KONG Deqiang, YANG Baoping, and LI Fei. Research on prototype system for electromagnetic spectrum management and control based on GIS[C]. Proceedings of the 8th Annual International Conference on Network and Information Systems for Computers, Hangzhou, China, 2022. doi: 10.1109/ICNISC57059.2022.00156. [2] HAR D, WATSON A M, and CHADNEY A G. Comment on diffraction loss of rooftop-to-street in COST 231-Walfisch-Ikegami model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 1999, 48(5): 1451–1452. doi: 10.1109/25.790519. [3] WALFISCH J and BERTONI H L. A theoretical model of UHF propagation in urban environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1988, 36(12): 1788–1796. doi: 10.1109/8.14401. [4] MEDEISIS A and KAJACKAS A. On the use of the universal Okumura-Hata propagation prediction model in rural areas[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE 51st Vehicular Technology Conference Proceedings, Tokyo, Japan, 2000: 1815–1818. doi: 10.1109/VETECS.2000.851585. [5] 杨鸿杰. 基于强化学习的智能通信干扰决策技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 中国电子科技集团公司电子科学研究院, 2019. doi: 10.27728/d.cnki.gdzkx.2019.000061.YANG Hongjie. Research on intelligent communication jamming decision-making technology based on reinforcement learning[D]. [Master dissertation], China Academic of Electronics and Information Technology, 2019. doi: 10.27728/d.cnki.gdzkx.2019.000061. [6] 韩鹏, 卢俊道, 王晓丽. 利用于博弈论的雷达有源干扰资源分配算法[J]. 现代防御技术, 2018, 46(4): 53–59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2018.04.009.HAN Peng, LU Jundao, and WANG Xiaoli. Radar active jamming resource assignment algorithm based on game theory[J]. Modern Defence Technology, 2018, 46(4): 53–59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2018.04.009. [7] 李冯敬, 姚佩阳, 张杰勇, 等. 基于多Agent的分布式通信对抗目标分配系统[J]. 计算机工程, 2012, 38(12): 283–286,290. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3428.2012.12.083.LI Fengjing, YAO Peiyang, ZHANG Jieyong, et al. Distributed communication countermeasures target assignment system based on multi-agent[J]. Computer Engineering, 2012, 38(12): 283–286,290. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3428.2012.12.083. [8] 薛羽, 庄毅, 朱浩, 等. 求解协同干扰问题的高效免疫遗传算法[J]. 电子科技大学学报, 2013, 42(3): 453–458. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2013.03.026.XUE Yu, ZHUANG Yi, ZHU Hao, et al. Efficiently immune genetic algorithm for solving cooperative jamming problem[J]. Journal of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2013, 42(3): 453–458. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2013.03.026. [9] TAN Junjie, LIANG Yingchang, ZHANG Lin, et al. Deep reinforcement learning for joint channel selection and power control in D2D networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(2): 1363–1378. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3032991. [10] 白琦. 基于多干扰源环境下动态功率分配的电磁压制系统设计[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2012.BAI Qi. The designment of electromagnetic compaction system based on dynamic power allocation in the environment of multiple interference sources[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2012. [11] 彭翔, 许华, 蒋磊, 等. 一种基于深度强化学习的动态自适应干扰功率分配方法[J]. 电子学报, 2023, 51(5): 1223–1234. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20220391.PENG Xiang, XU Hua, JIANG Lei, et al. A dynamic adaptive jamming power allocation method based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2023, 51(5): 1223–1234. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20220391. [12] FRIIS H T. A note on a simple transmission formula[J]. Proceedings of the IRE, 1946, 34(5): 254–256. doi: 10.1109/JRPROC.1946.234568. [13] ETSI. ETSI TR 138 901-2020 5G; Study on channel model for frequencies from 0.5 to 100 GHz[S]. ETSI, 2020. [14] VENNILA N L, KUMAR S, and KUMAR J R R. Game theory based method for spectrum management in cognitive radio-WSN applications[C]. Proceedings of the 2nd Asian Conference on Innovation in Technology, Ravet, India, 2022: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ASIANCON55314.2022.9909191. [15] MONDERER D and SHAPLEY L S. Potential games[J]. Games and Economic Behavior, 1996, 14(1): 124–143. doi: 10.1006/game.1996.0044. [16] SAMPSON J R. Adaptation in natural and artificial systems (John H. Holland)[J]. SIAM Review, 1976, 18(3): 529–530. doi: 10.1137/1018105. [17] ANWAAR A, ASHRAF A, BANGYAL W H K, et al. Genetic algorithms: Brief review on genetic algorithms for global optimization problems[C]. Proceedings of the 2022 Human-Centered Cognitive Systems, Shanghai, China, 2022: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/HCCS55241.2022.10090327. -





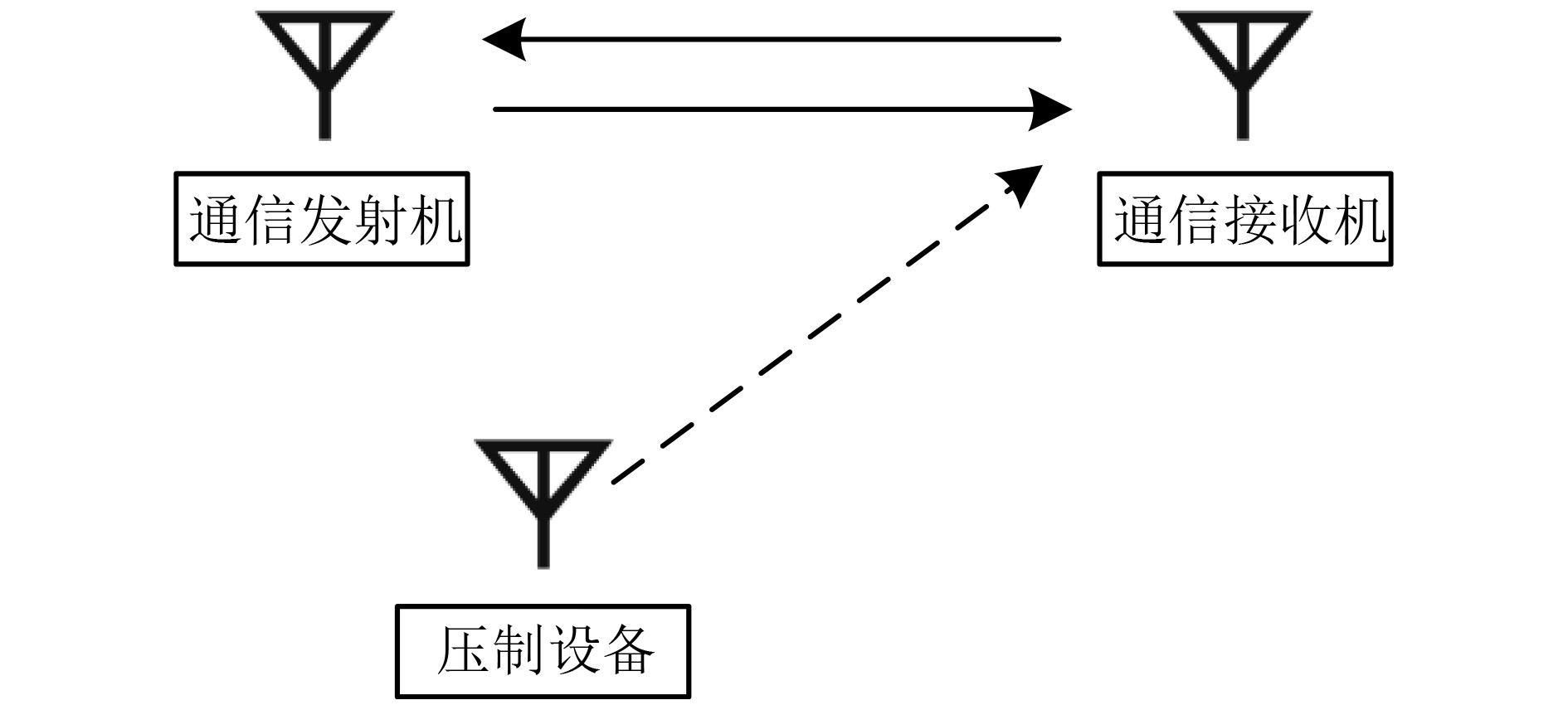
 下载:
下载:
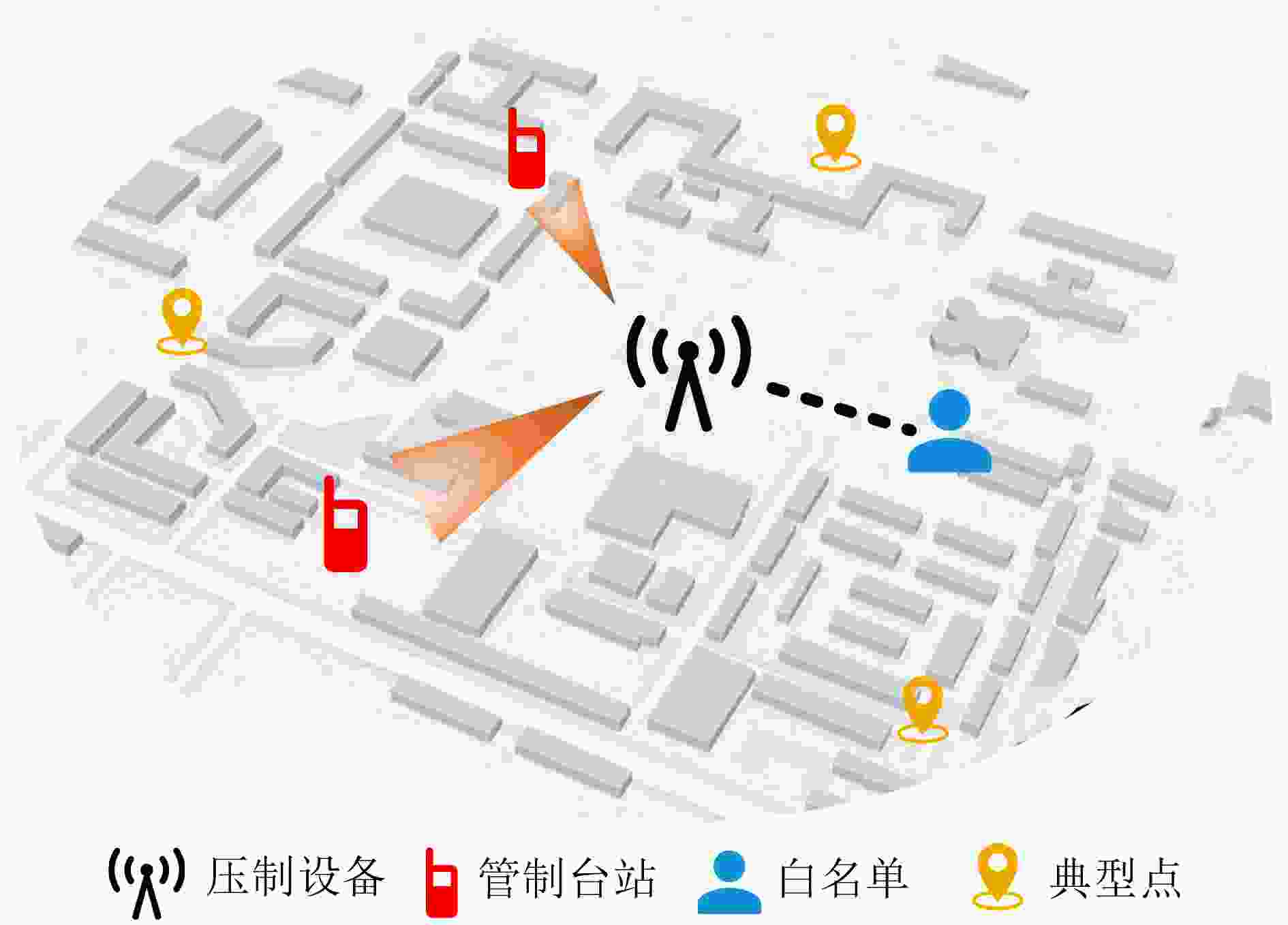
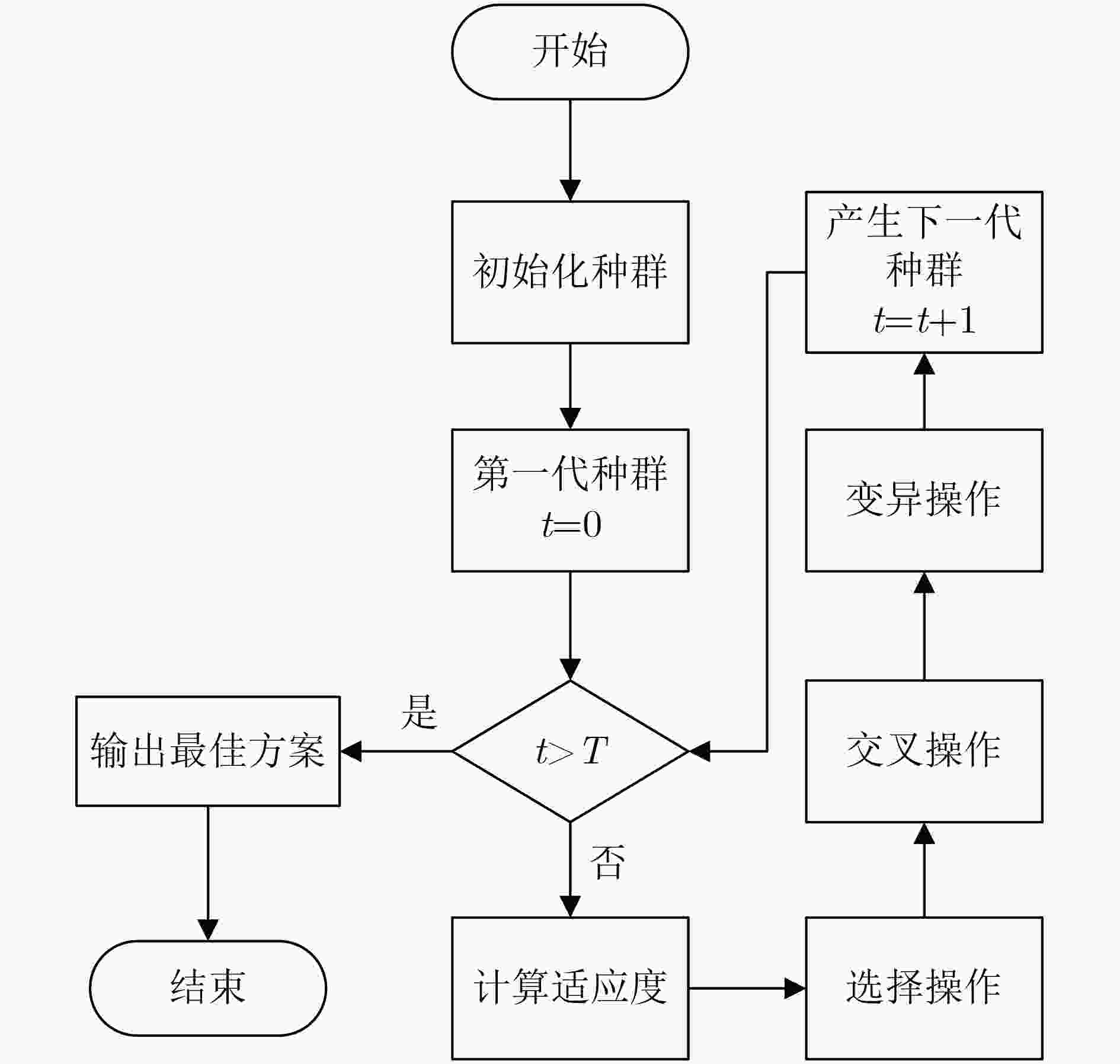
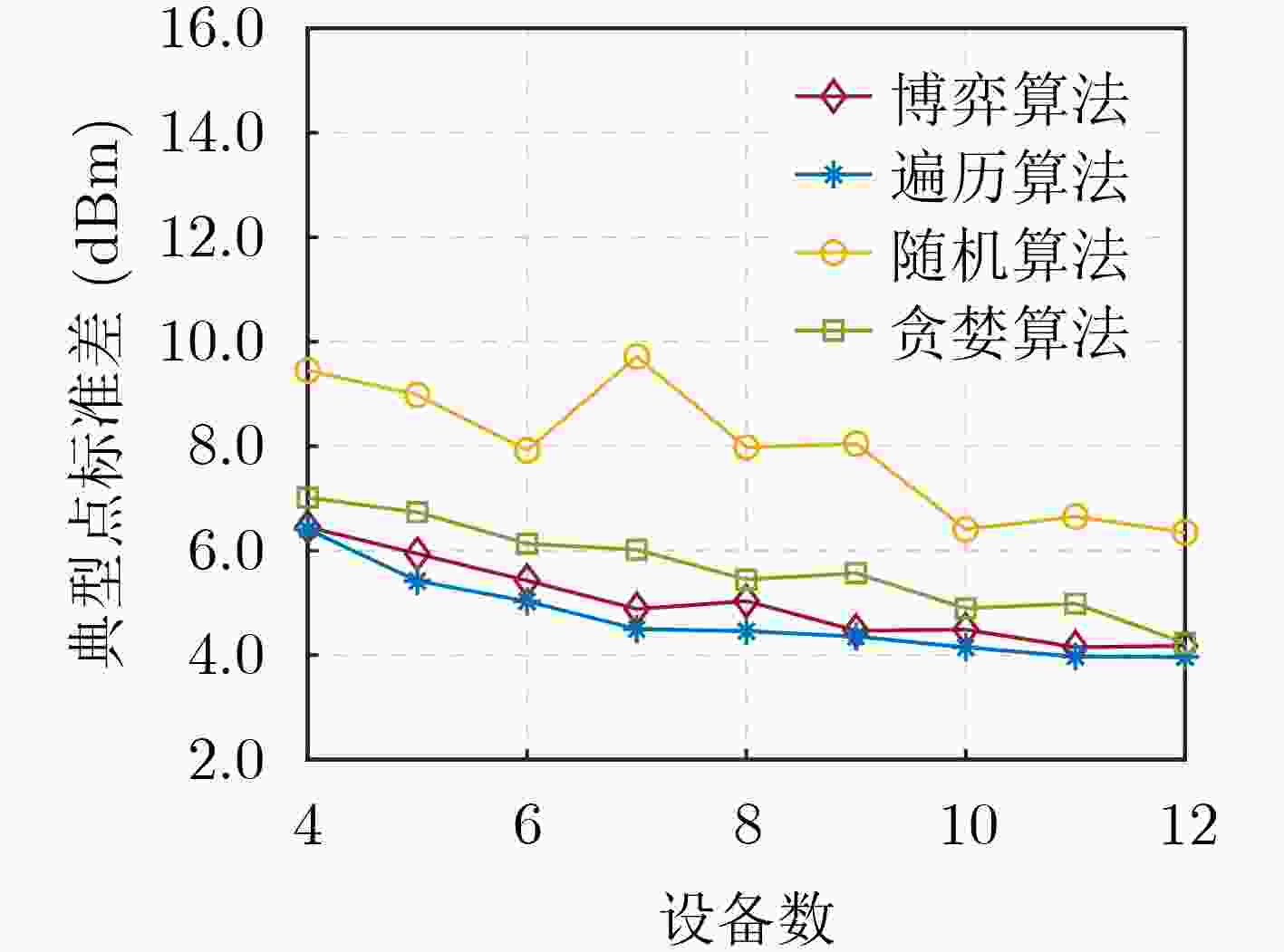
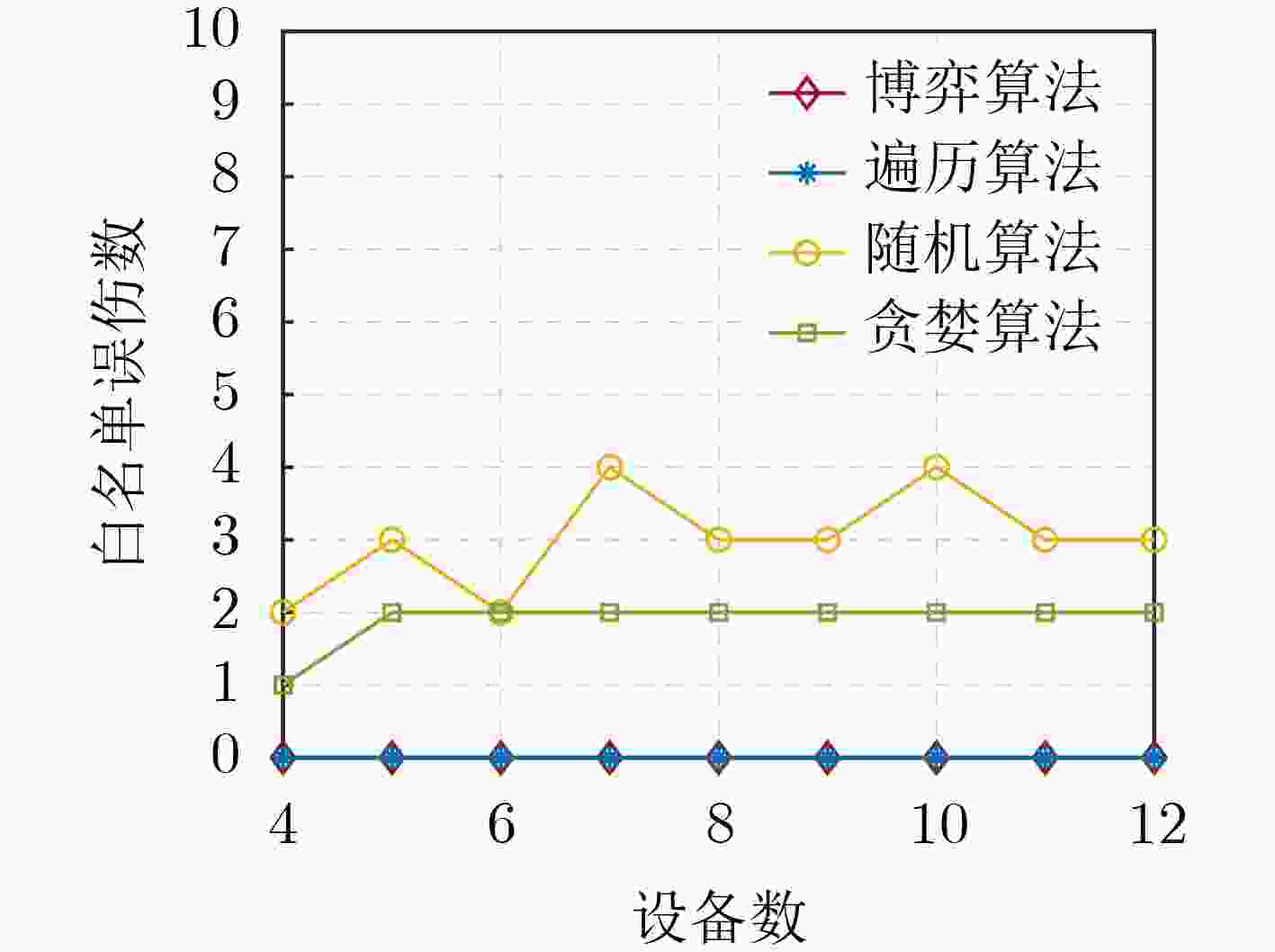
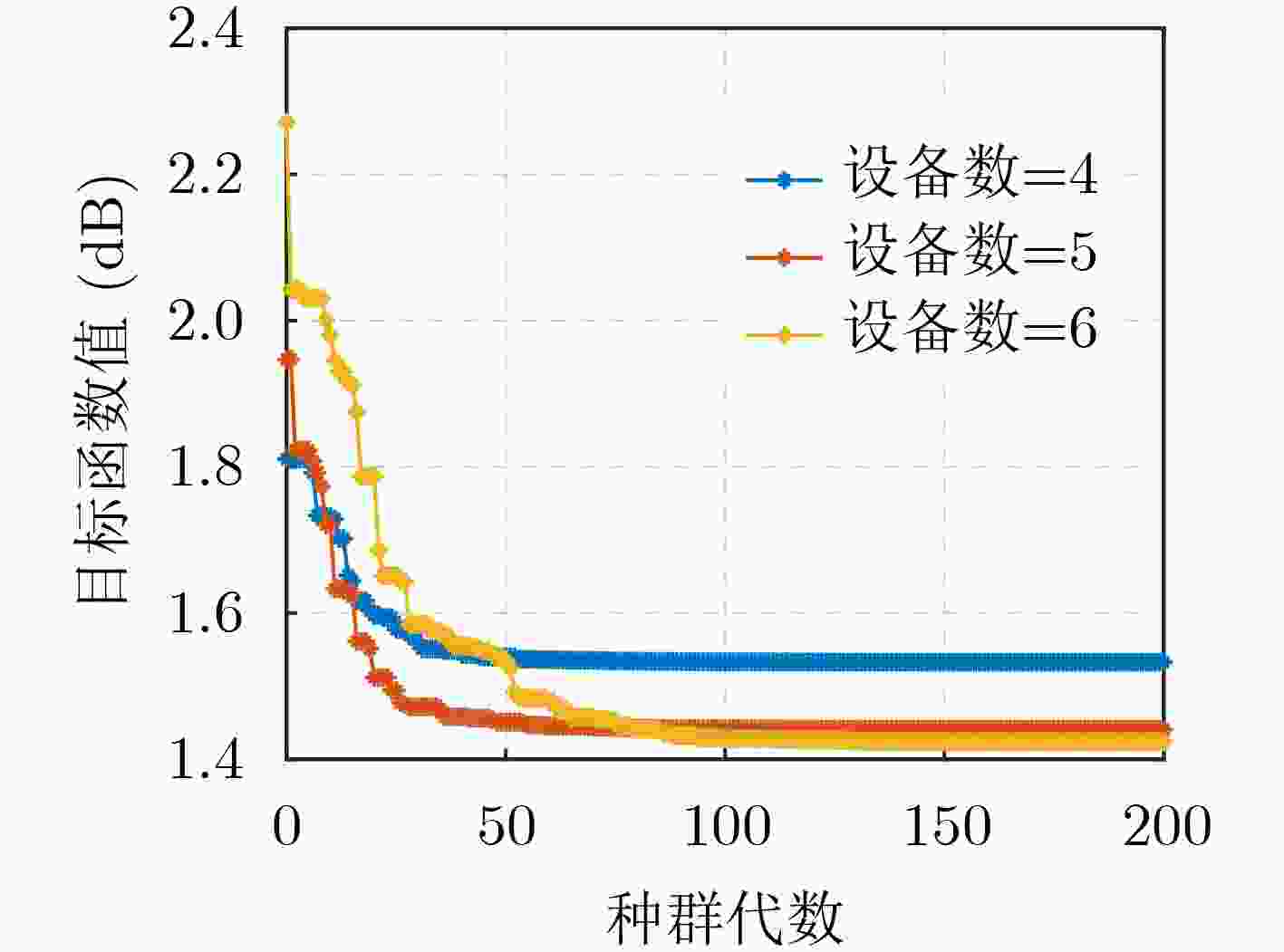
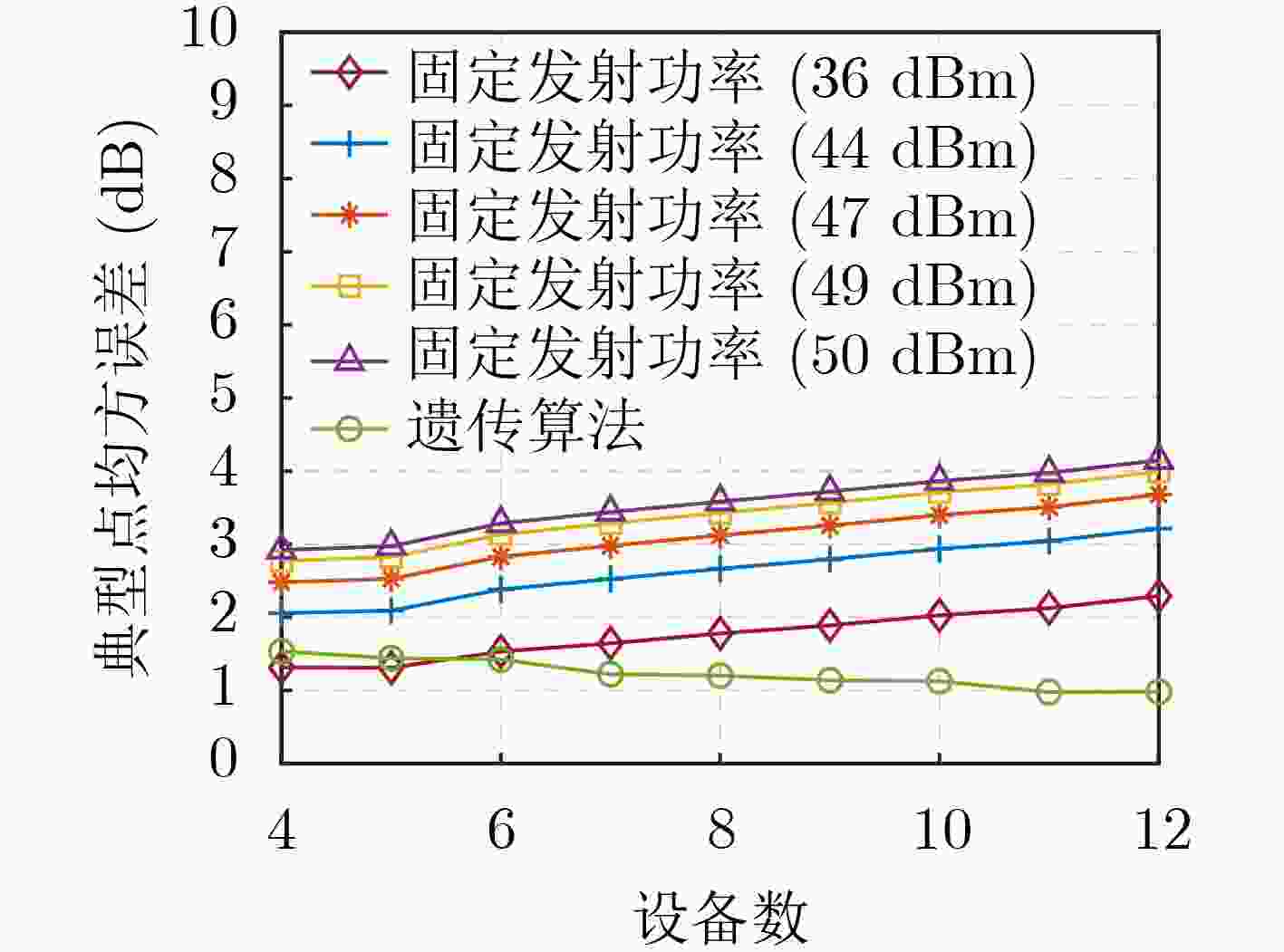


 下载:
下载:
