Broadband Fusion of Multiband Radar Signals Based on Optimal Dictionary Selection
-
摘要: 多频段雷达带宽融合外推是一种提升雷达带宽、解决小目标高分辨成像的有效手段。然而,现有多频段融合算法仍面临运算慢、精度低等问题。为此,该文提出基于最优字典选择正交匹配追踪的多频段融合外推雷达超分辨距离成像方法。首先,对多频段信号进行参数化建模,提出基于蛇优化的信号相参配准方法,实现多频段信号高精度相位对齐;然后,利用几何绕射模型,提出基于最优字典选择正交匹配追踪的多频段信号模型估计方法,实现多频段信号融合外推,估计未知频段频谱,获取大带宽信号;最后,通过仿真和实测数据,验证了该方法的可行性。该方法在保障高精度的前提下,通过简化模型粗估计与完整模型精估计结合,有效降低了运算量,实现了快速精确多频段融合外推处理。Abstract: Multiband Fusion is an effective way to broaden bandwidth of radar, which plays a key role in the detection and recognition of small-scale target. However, the existing multiband fusion algorithms still face the problems of slow operation and low precision. Therefore, a super-resolution technique of multiband fusion based on optimal dictionary selection and orthogonal matching pursuit is proposed in this paper. Firstly, the parametric model of multiband radar signal is conducted. Next, Snake Optimizer (SO) is applied to the coherent processing. Then, an Orthogonal Matching Pursuit (OMP) algorithm based on the optimal Geometrical Theory of Diffraction (GTD) dictionary selection is used to extrapolate the vacant spectrum. Experiment results of simulated and measured data are given. Experimental results show that the proposed method can effectively achieve super-resolution. This method combines simplified model rough estimation with complete model fine estimation, effectively reducing the amount of computation and realizing fast and accurate multiband fusion extrapolation processing.
-
表 1 频率依赖因子取值表
散射机理类型 频率依赖因子取值 平板、二面角、三面角的反射 1 单弯曲曲面的反射 0.5 双弯曲曲面的反射、直边的绕射 0 曲边的绕射 –0.5 尖顶、角的绕射 –1 1 蛇优化算法
初始化:设置基本参数:参数维度dim,设定自变量取值范围 ,种群中个体数量为N,最大迭代次数T,当前迭代次数t,初始t=1。在定
义域内随机建立初始种群。种群划分:将完整种群中个体划分为两个种群。 迭代流程: (1) 参量计算:按式(6)计算温度temp,按式(7)计算食物位置P。 (2) 更新判断:首先判断P情况:当P< 0.25时,执行步骤3;当P > 0.6时,执行步骤4;其余情况,执行步骤5。 (3) 情景1(P< 0.25):按式(8)–式(11)执行更新。跳转到步骤6,执行判断。 (4) 情景2(P > 0.6):按式(12)–式(13)执行更新。跳转到步骤6,执行判断。 (5) 情景3(P的其余取值情况):当随机数rand 大于0.6,按式(14)–式(15)执行更新;反之,按式(16)–式(17)执行更新。执行步骤6。 (6) 判断:淘汰劣势个体,当迭代次数达到结束要求(或种群适应度变化小于设定阈值)时,迭代结束。 输出:最优相参估计值$ {X_{{\mathrm{food}}}} $。 表 2 仿真多频段参数设置
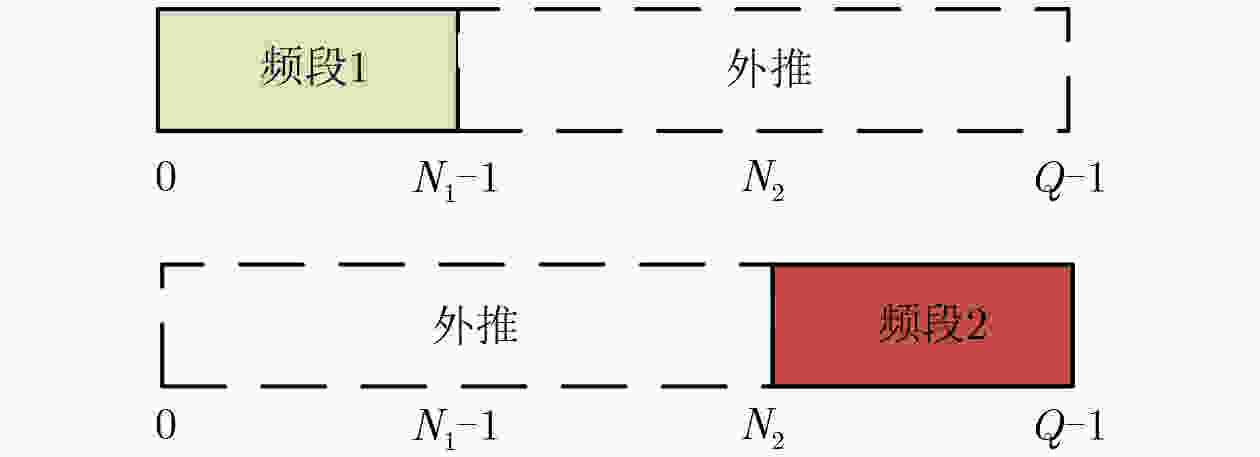
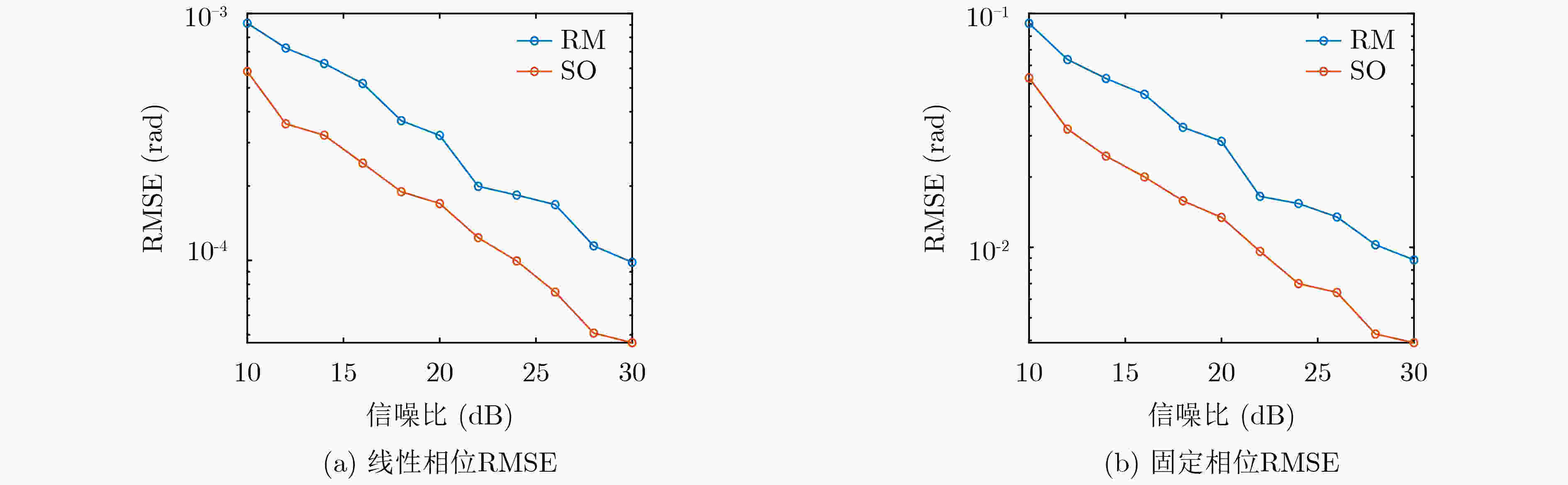
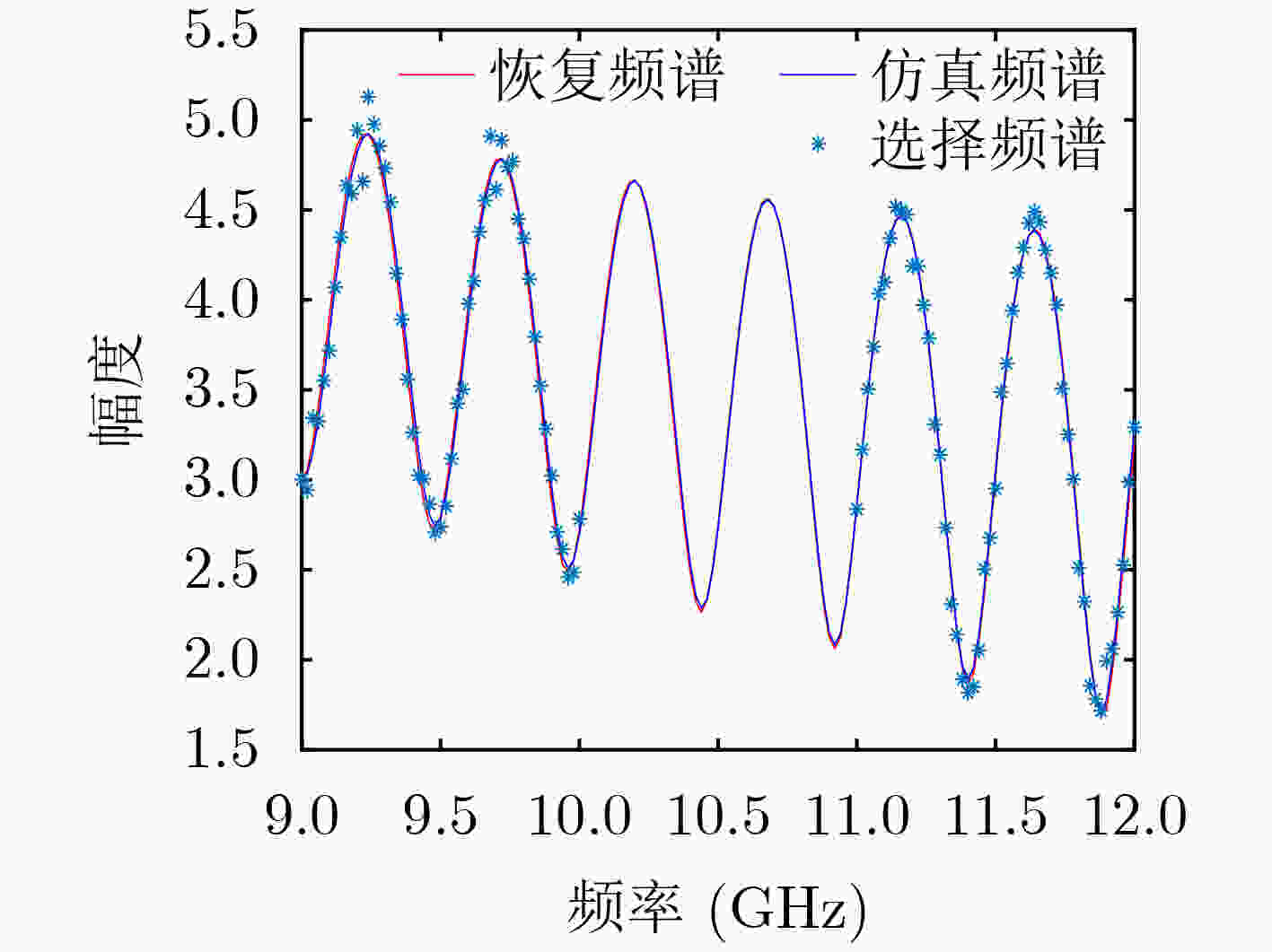
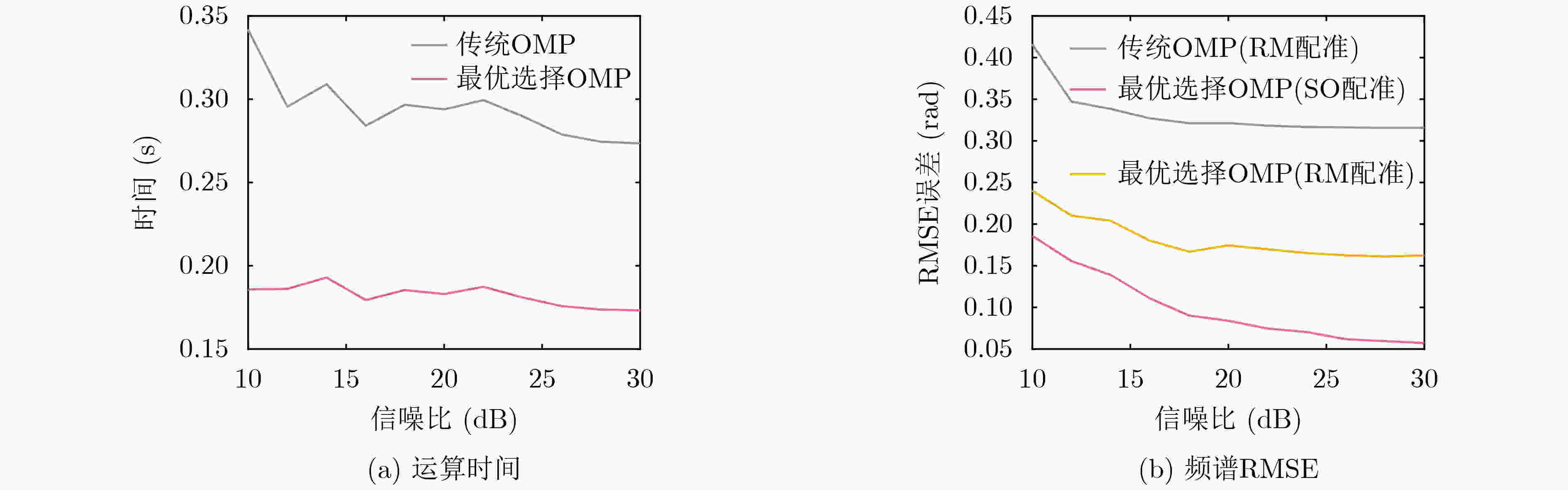
频段1 频段2 外推宽带 频段 (GHz) 9~10 11~12 9~12 频点间隔 (MHz) 20 20 20 频点个数 51 51 151 线性相位误差 (rad) / 0.3 / 固定相位误差 (rad) / 1.0 / 表 3 外场多频段处理参数设置
X1频段 X2频段 外推宽带 频段(GHz) 9~10 11~12 9~12 频点间隔(MHz) 5 5 5 频点个数 201 201 601 表 4 实测角反间距(cm)
X1频段(9~10 GHz) X2频段(11~12 GHz) 本文方法(9~12 GHz) 传统方法(9~12 GHz) 17.07 cm间距 角反射器测量间距 21.36 19.81 16.53 16.00 12.33 cm间距 角反射器测量间距 \ \ 13.86 14.40 -
[1] LI Weidong, HU Cheng, WANG Rui, et al. Comprehensive analysis of polarimetric radar cross-section parameters for insect body width and length estimation[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2021, 64(2): 122302. doi: 10.1007/s11432-020-3010-6. [2] 蔡炯, 王锐, 胡程. 基于最小熵的机动目标雷达检测[J]. 信号处理, 2022, 38(7): 1416–1423. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2022.07.007.CAI Jiong, WANG Rui, and HU Cheng. Maneuvering targets radar detection based on minimum entropy[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2022, 38(7): 1416–1423. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2022.07.007. [3] 王锐, 李卫东, 胡程, 等. 全极化昆虫雷达生物参数反演方法与外场定量试验验证[J]. 信号处理, 2021, 37(2): 199–208. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2021.02.005.WANG Rui, LI Weidong, HU Cheng, et al. Insect biological parameters estimation method and field quantitative experiment verification for fully polarimetric entomological radar[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2021, 37(2): 199–208. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2021.02.005. [4] TIAN Weiming, FANG Linlin, WANG Rui, et al. A robust tracking method focusing on target fluctuation and maneuver characteristics[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2022, 65(11): 212302. doi: 10.1007/s11432-021-3438-7. [5] 梁文哲, 冯阳凯, 王锐, 等. 低信噪比下基于YOLOv3的昆虫目标检测[J]. 信号处理, 2022, 38(1): 109–117. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2022.01.013.LIANG Wenzhe, FENG Yangkai, WANG Rui, et al. Insect target detection based on YOLOv3 under low SNR[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2022, 38(1): 109–117. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2022.01.013. [6] HU Cheng, ZHANG Fan, LI Weidong, et al. Estimating insect body size from radar observations using feature selection and machine learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5120511. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3224618. [7] 王成. 雷达信号层融合成像技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2006.WANG Cheng. A comprehensive study on tombs with single patio in Chang’an area of tang dynasty[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2006. [8] 刘承兰, 贺峰, 魏玺章, 等. 基于数据相关的多雷达融合成像相干配准研究[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2010, 32(6): 1266–1271. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2010.06.033.LIU Chenglan, HE Feng, WEI Xizhang, et al. Research on multiple radar fusion imaging coherence compensation based on data correlation[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2010, 32(6): 1266–1271. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2010.06.033. [9] WANG Tingjing, ZHANG Ying, ZHAO Hua, et al. Multiband radar signal coherent processing algorithm for motion target[J]. International Journal of Antennas and Propagation, 2017, 2017: 4060789. doi: 10.1155/2017/4060789. [10] 李涛. 基于频带合成的距离分辨率提高方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2020.LI Tao. Research on method of improving distance resolution based on band fusion[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2020. [11] TIAN Biao, CHEN Zengping, and XU Shiyou. Sparse subband fusion imaging based on parameter estimation of geometrical theory of diffraction model[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2014, 8(4): 318–326. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2013.0192. [12] HURST M P and MITTRA R. Scattering center analysis via Prony's method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1987, 35(8): 986–988. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1987.1144210. [13] CARRIERE R and MOSES R L. High resolution radar target modeling using a modified Prony estimator[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1992, 40(1): 13–18. doi: 10.1109/8.123348. [14] CUOMO K M, PION J E, and MAYHAN J T. Ultrawide-band coherent processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1999, 47(6): 1094–1107. doi: 10.1109/8.777137. [15] ROY R and KAILATH T. ESPRIT-estimation of signal parameters via rotational invariance techniques[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1989, 37(7): 984–995. doi: 10.1109/29.32276. [16] POTTER L C, CHIANG D M, CARRIERE R, et al. A GTD-based parametric model for radar scattering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1995, 43(10): 1058–1067. doi: 10.1109/8.467641. [17] 闫华, 张磊, 陆金文, 等. 任意多次散射机理的GTD散射中心模型频率依赖因子表达[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(3): 370–381. doi: 10.12000/JR21005.YAN Hua, ZHANG Lei, LU Jinwen, et al. Frequency-dependent factor expression of GTD scattering center model for the arbitrary multiple scattering mechanism[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(3): 370–381. doi: 10.12000/JR21005. [18] WIPF D P and RAO B D. Sparse Bayesian learning for basis selection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2004, 52(8): 2153–2164. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2004.831016. [19] ZHU Xiaoxiu, GUO Baofeng, HU Wenhua, et al. Scene segmentation of multi-band ISAR fusion imaging based on MB-PCSBL[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(3): 3520–3532. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3026109. [20] CHEN S S, DONOHO D L, and SAUNDERS M A. Atomic decomposition by basis pursuit[J]. SIAM Review, 2001, 43(1): 129–159. doi: 10.1137/S003614450037906X. [21] BAI Xueru, WANG Ge, LIU Siqi, et al. High-resolution radar imaging in low SNR environments based on expectation propagation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(2): 1275–1284. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3004006. [22] GHASEMI M, SHEIKHI A, and PISHROW M M. Multiple radar subbands fusion technique based on generalized likelihood ratio test[J]. Physical Communication, 2021, 46: 101331. doi: 10.1016/j.phycom.2021.101331. [23] TROPP J A and GILBERT A C. Signal recovery from random measurements via orthogonal matching pursuit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2007, 53(12): 4655–4666. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2007.909108. [24] 朱晓秀, 刘利民, 胡文华, 等. 基于GTD模型的多视角多频带ISAR融合成像[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2023, 45(3): 726–735. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.03.13.ZHU Xiaoxiu, LIU Limin, HU Wenhua, et al. Multi-angle and multi-band ISAR fusion imaging based on GTD model[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(3): 726–735. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.03.13. [25] HASHIM F A and HUSSIEN A G. Snake Optimizer: A novel meta-heuristic optimization algorithm[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2022, 242: 108320. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2022.108320. [26] SKOLNIK M I. Radar Handbook[M]. 3rd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2008: chapter 8, page5. [27] HU Cheng, YAN Yujia, WANG Rui, et al. High-resolution, multi-frequency and full-polarization radar database of small and group targets in clutter environment[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2023, 66(12): 227301. doi: 10.1007/s11432-023-3889-7. -





 下载:
下载:

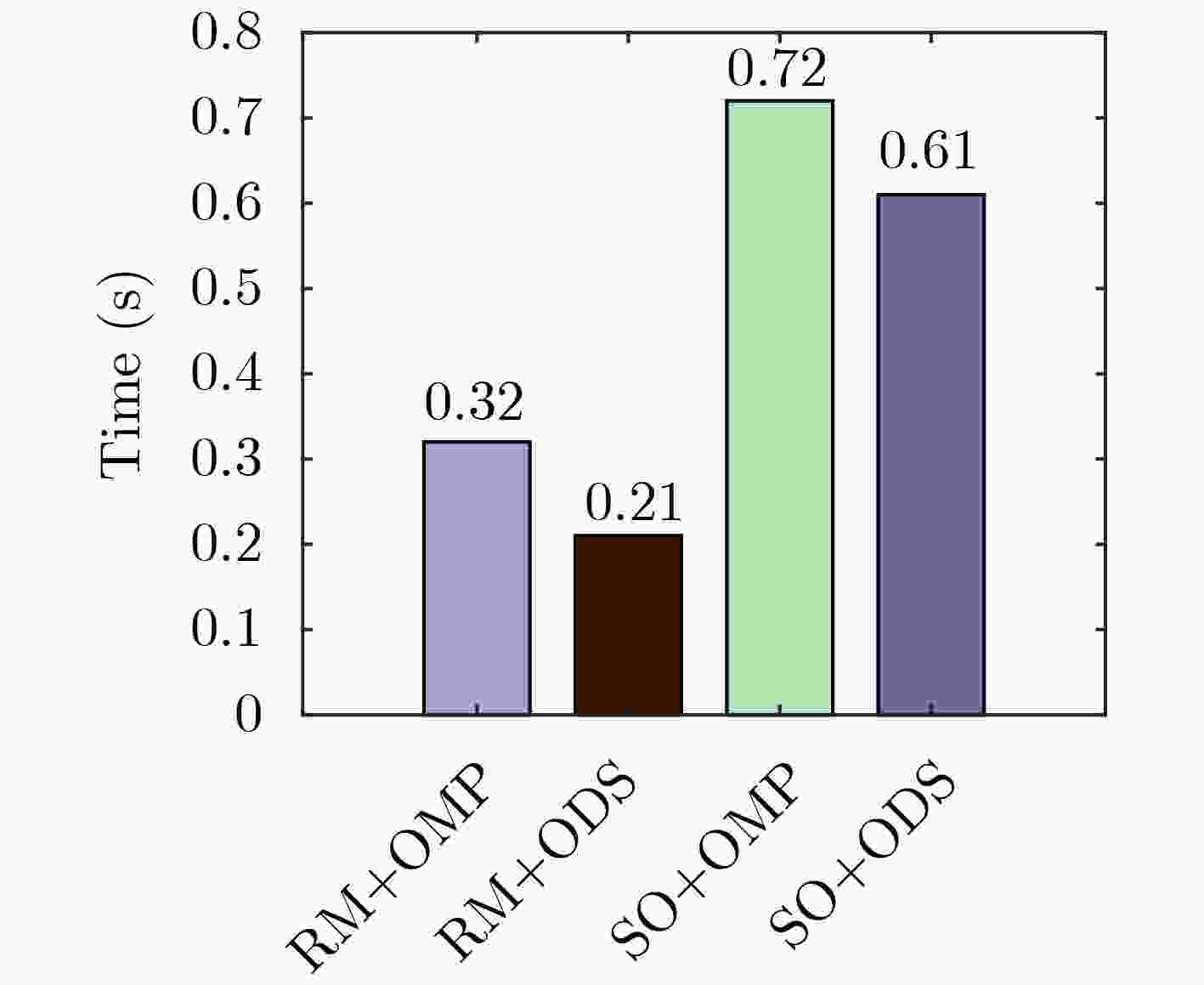
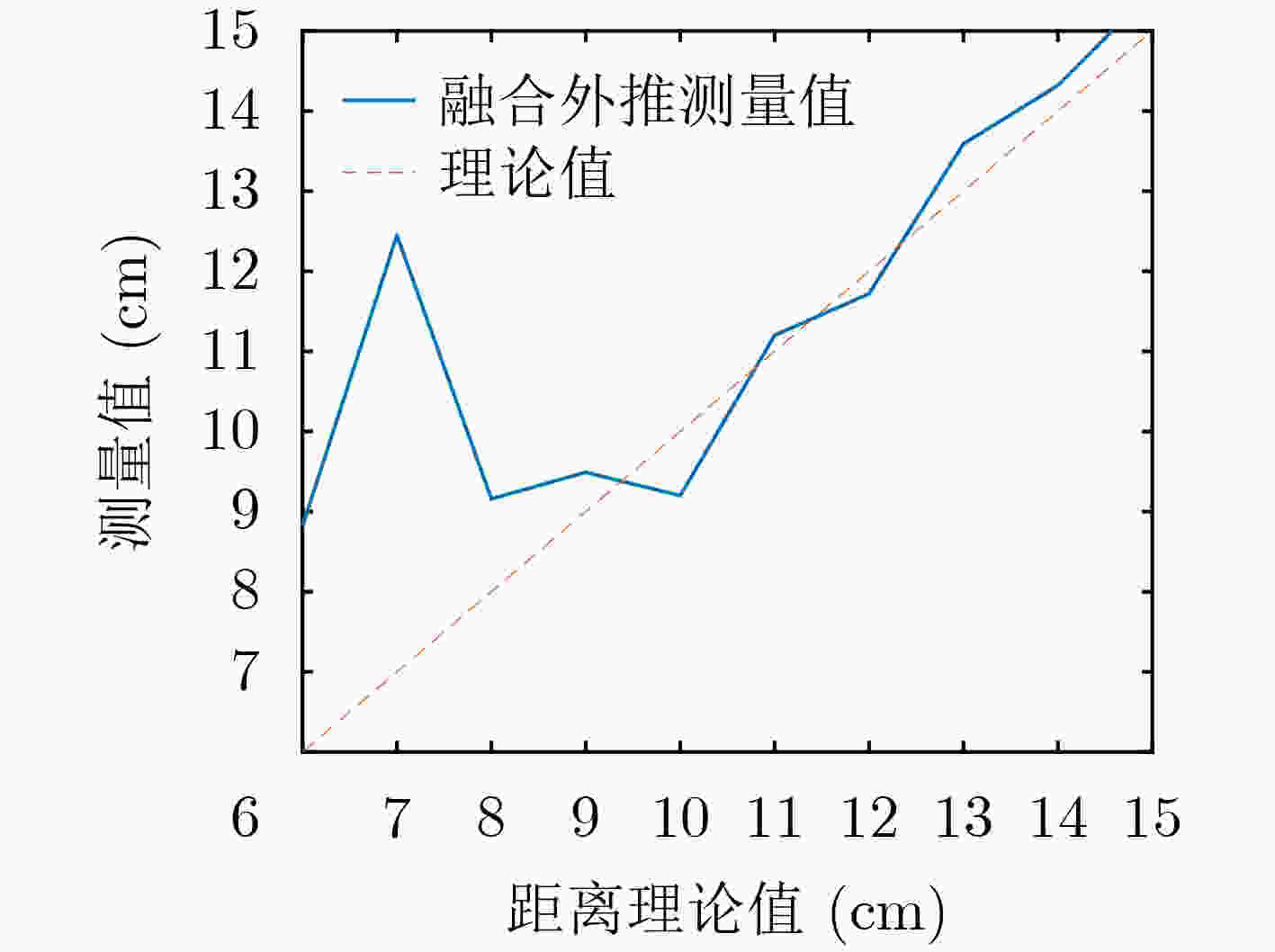

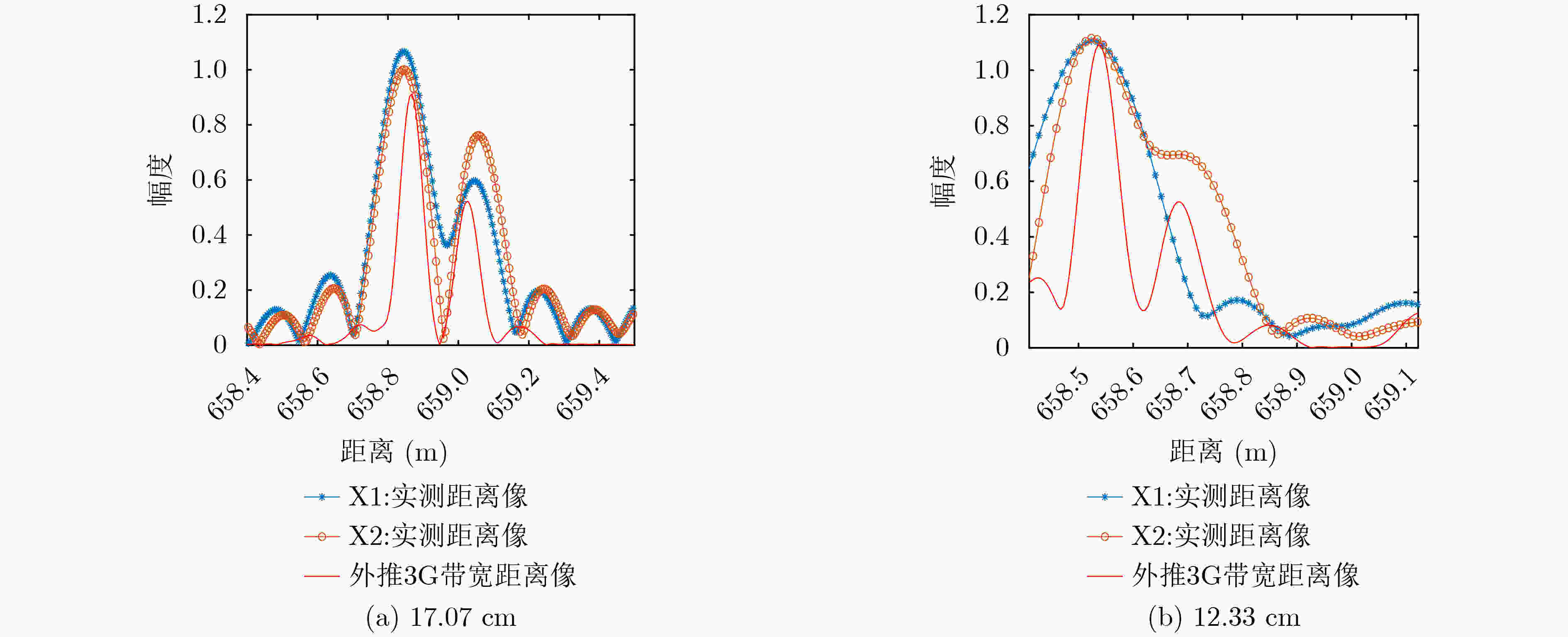


 下载:
下载:
