UAV Path Planning Method for Passive Radar Transmitter Localization
-
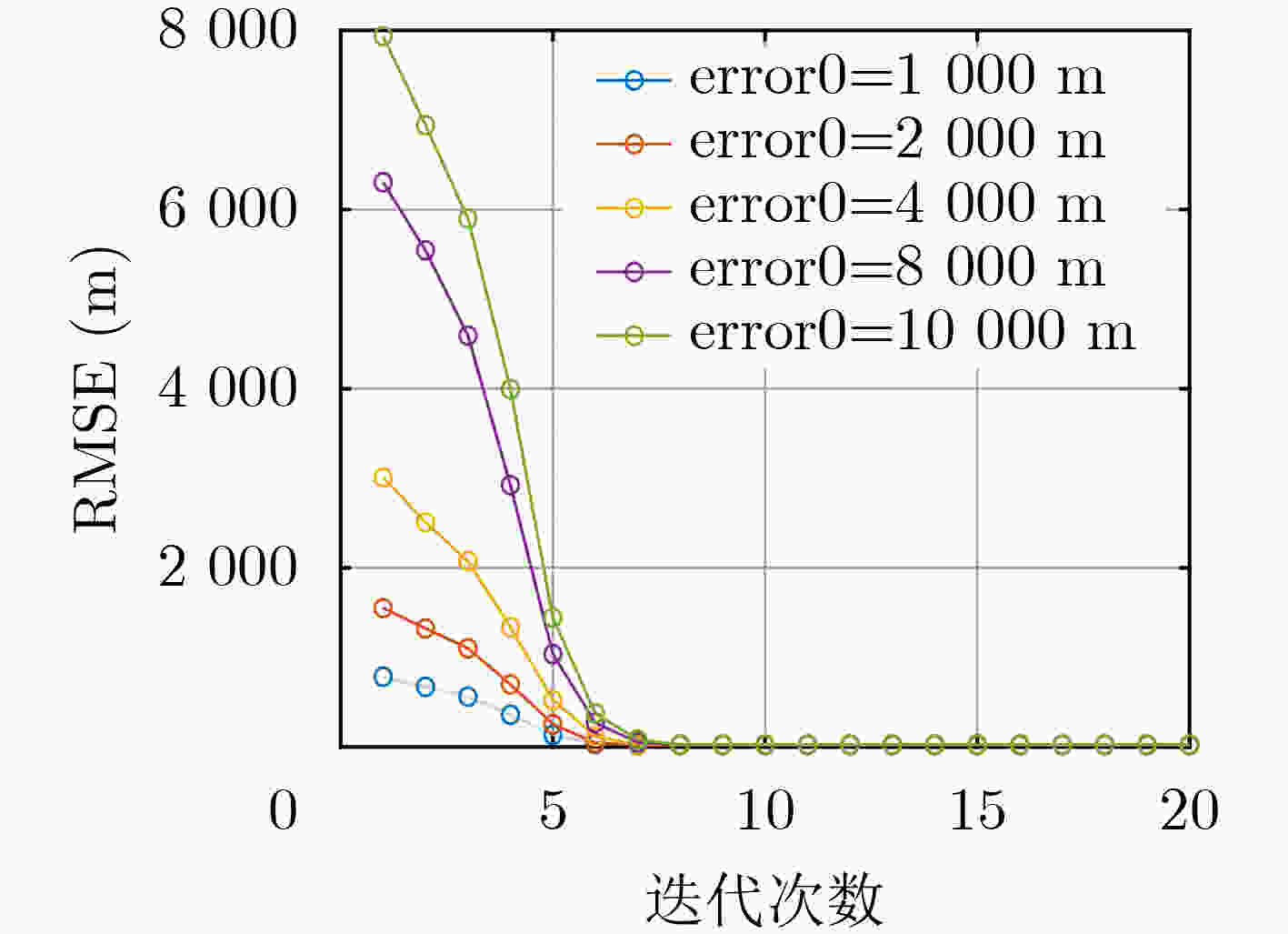
摘要: 在广域未知环境中,外辐射源雷达机动部署常面临难以及时获取第三方发射站精确位置信息的难题。为此,该文提出一种基于合作无人机航迹规划的发射站定位方法。首先,利用单个无人机作为合作目标,建立2维场景下的定位模型和量测方程,并采用列文伯格-马夸尔特(Levenberg-Marquardt, LM)算法进行解算。然后,构建融合Fisher信息和控制参数约束的优化函数,对无人机航迹进行动态规划,从而提高发射站定位的精度和方法的实用性。最后,仿真实验表明,在最大控制距离约束下,所提方法的定位结果优于直线航迹和经典优化航迹,最终发射站定位精度小于双基距离差量测标准差,能够满足外辐射源雷达系统目标探测定位的应用要求。Abstract: In the broad and unknown environments, mobile deployment of passive radar often faces challenges in promptly obtaining the precise location information of third-party transmitter stations. To address this issue, a transmitter localization method based on cooperative Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) path planning is proposed. Firstly, a single UAV is used as a cooperative target to establish the localization model and measurement equation in a two-dimensional scenario, and the Levenberg-Marquardt (LM) algorithm is employed for solution. Then, an optimization function is constructed by integrating Fisher information and control parameter constraints to dynamically plan the UAV trajectory, thereby improving the accuracy of transmitter localization and the practicality of this method. Finally, simulation experiments show that under the maximum control distance constraint, the positioning result of the proposed method is better than that of straight-line track and typical optimized track, and the final positioning accuracy is less than the standard deviation of the bistatic distance difference measurements, which can meet the application requirements of the passive radar system.
-
Key words:
- Passive radar /
- Transmitter localization /
- Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV) /
- Path planning
-
表 1 图2中不同航迹的发射站定位RMSE(m)
航迹点数 10 20 30 40 50 60 本文规划航迹 576.77 172.61 85.61 35.81 27.72 26.61 FIM优化航迹 525.80 176.27 78.52 38.29 – – 直线航迹 560.43 127.12 54.31 – – – -
[1] 万显荣, 易建新, 占伟杰, 等. 基于多照射源的被动雷达研究进展与发展趋势[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(6): 939–958. doi: 10.12000/JR20143.WAN Xianrong, YI Jianxin, ZHAN Weijie, et al. Research progress and development trend of the multi-illuminator-based passive radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(6): 939–958. doi: 10.12000/JR20143. [2] 万显荣. 基于低频段数字广播电视信号的外辐射源雷达发展现状与趋势[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(2): 109–123. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20027.WAN Xianrong. An overview on development of passive radar based on the low frequency band digital broadcasting and TV signals[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(2): 109–123. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20027. [3] PINE K C, PINE S, and CHENEY M. The geometry of far-field passive source localization with TDOA and FDOA[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(6): 3782–3790. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3087804. [4] ZHAO Sihao, ZHANG Xiaoping, CUI Xiaowei, et al. Optimal two-way TOA localization and synchronization for moving user devices with clock drift[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(8): 7778–7789. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3092255. [5] LI Qian, CHEN Baixiao, and YANG Minglei. Improved two-step constrained total least-squares TDOA localization algorithm based on the alternating direction method of multipliers[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(22): 13666–13673. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3004235. [6] ZHAO Yongsheng, HU Dexiu, ZHAO Yongjun, et al. Moving target localization for multistatic passive radar using delay, Doppler and Doppler rate measurements[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 31(5): 939–949. doi: 10.23919/JSEE.2020.000071. [7] XIANG Peng, WANG Gang, and HO K C. Bias reduced semidefinite relaxation method for AOA object localization in 3-D[C]. 2022 IEEE 12th Sensor Array and Multichannel Signal Processing Workshop (SAM), Trondheim, Norway, 2022: 91–95. doi: 10.1109/SAM53842.2022.9827814. [8] HU Shibo, YI Jianxin, WAN Xianrong, et al. Illuminator of opportunity localization for digital broadcast-based passive radar in moving platforms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(4): 3539–3549. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2022.3227526. [9] 赵洪立, 习建博. 一种基于多辐射源匹配的未知辐射源的定位方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2014, 3(6): 727–731. doi: 10.12000/JR14128.ZHAO Hongli and XI Jianbo. A method of unknown illuminator location based on matched multi-illuminators[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(6): 727–731. doi: 10.12000/JR14128. [10] CHENG Xin, SHU Feng, LI Yifan, et al. Optimal measurement of drone swarm in RSS-based passive localization with region constraints[J]. IEEE Open Journal of Vehicular Technology, 2023, 4: 1–11. doi: 10.1109/OJVT.2022.3213866. [11] HE Liang, GONG Pan, ZHANG Xiaofei, et al. The bearing-only target localization via the single UAV: Asymptotically unbiased closed-form solution and path planning[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 153592–153604. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2947455. [12] ZHANG Lu, YANG Jianbo, ZHANG Ziyan, et al. A cooperative localization algorithm based on UAV platform[C]. 2021 International Conference on Advanced Computing and Endogenous Security, Nanjing, China, 2022: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/IEEECONF52377.2022.10013095. [13] 孙仲康, 郭福成, 冯道旺, 等. 单站无源定位跟踪技术[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2008: 73–87.SUN Zhongkang, GUO Fucheng, FENG Daowang, et al. Passive Location and Tracking Technology by Single Observer[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2008: 73–87. [14] 陈宇航, 饶云华, 潘宇盈, 等. 分时多频外辐射源雷达发射站定位方法[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2022, 20(3): 335–341,354. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2022.03.013.CHEN Yuhang, RAO Yunhua, PAN Yuying, et al. Positioning method of transmitting station for time-division-multifrequency passive radar[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2022, 20(3): 335–341,354. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2022.03.013. [15] YI Jianxin, WAN Xianrong, FU Yan, et al. ADS-B information based transmitter localization in passive radar[C]. 2014 31th URSI General Assembly and Scientific Symposium (URSI GASS), Beijing, China, 2014: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/URSIGASS.2014.6929185. [16] MALANOWSKI M, KULPA K, ŻYWEK M, et al. Estimation of transmitter position based on known target trajectory in passive radar[C]. 2020 IEEE International Radar Conference (RADAR), Washington, USA, 2020: 506–511. doi: 10.1109/RADAR42522.2020.9114827. [17] KRUECKEMEIER M, SCHWARTAU F, PAUL S, et al. Passive radar transmitter localization using a planar approximation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(5): 3405–3415. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3074133. [18] 饶云华, 朱华梁, 郑志杰. 基于合作目标的外辐射源雷达发射站直接定位[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2023, 45(2): 394–400. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.02.09.RAO Yunhua, ZHU Hualiang, and ZHENG Zhijie. Direct position determination of transmitter based on cooperative target in passive radar[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(2): 394–400. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.02.09. [19] 关欣, 吕政君, 衣晓. 单站外辐射源定位误差分析与仿真优化[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2018, 16(2): 201–208,220. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2018.02.014.GUAN Xin, LYU Zhengjun, and YI Xiao. Simulation and analysis of errors in passive monostatic location[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2018, 16(2): 201–208,220. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2018.02.014. [20] XIONG Jiawei, YUAN Kai, TANG Rongxin, et al. An improved iterative algorithm utilized in data processing for incoherent scatter radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 3508405. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3109087. [21] GAVIN H P. The Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm for nonlinear least squares curve-fitting problems[EB/OL]. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:113404737, 2019. [22] OSHMAN Y and DAVIDSON P. Optimization of observer trajectories for bearings-only target localization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1999, 35(3): 892–902. doi: 10.1109/7.784059. [23] DOGANCAY K. UAV path planning for passive emitter localization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2012, 48(2): 1150–1166. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2012.6178054. [24] 李万春, 黄成峰. 基于角度和多普勒频率的外辐射源定位系统的接收器最优航迹分析[J]. 雷达学报, 2014, 3(6): 660–665. doi: 10.12000/JR14118.LI Wanchun and HUANG Chengfeng. Optimal trajectory analysis for the receiver of passive location systems using direction of arrival and doppler measurements[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(6): 660–665. doi: 10.12000/JR14118. [25] TZOREFF E and WEISS A J. Path design for best emitter location using two mobile sensors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(19): 5249–5261. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2728504. [26] 左燕, 刘雪娇, 彭冬亮. 距离相关噪声AOA协同定位下无人机路径优化方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(4): 1192–1198. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200078.ZUO Yan, LIU Xuejiao, and PENG Dongliang. UAV path planning for AOA-based source localization with distance-dependent noises[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2021, 43(4): 1192–1198. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200078. [27] 齐小刚, 李博, 范英盛, 等. 多约束下多无人机的任务规划研究综述[J]. 智能系统学报, 2020, 15(2): 204–217. doi: 10.11992/tis.201811018.QI Xiaogang, LI Bo, FAN Yingsheng, et al. A survey of mission planning on UAVs systems based on multiple constraints[J]. CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems, 2020, 15(2): 204–217. doi: 10.11992/tis.201811018. -





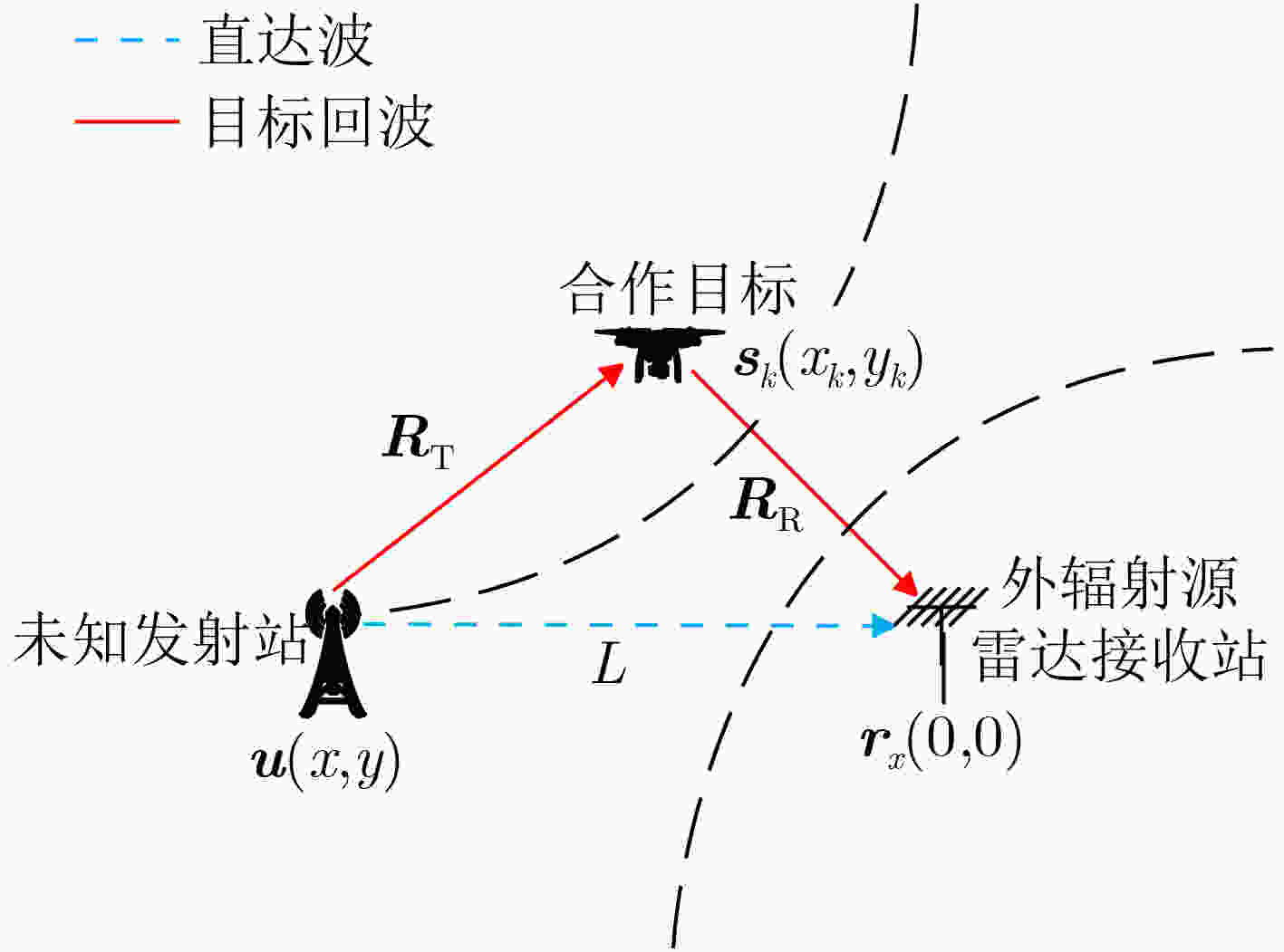
 下载:
下载:
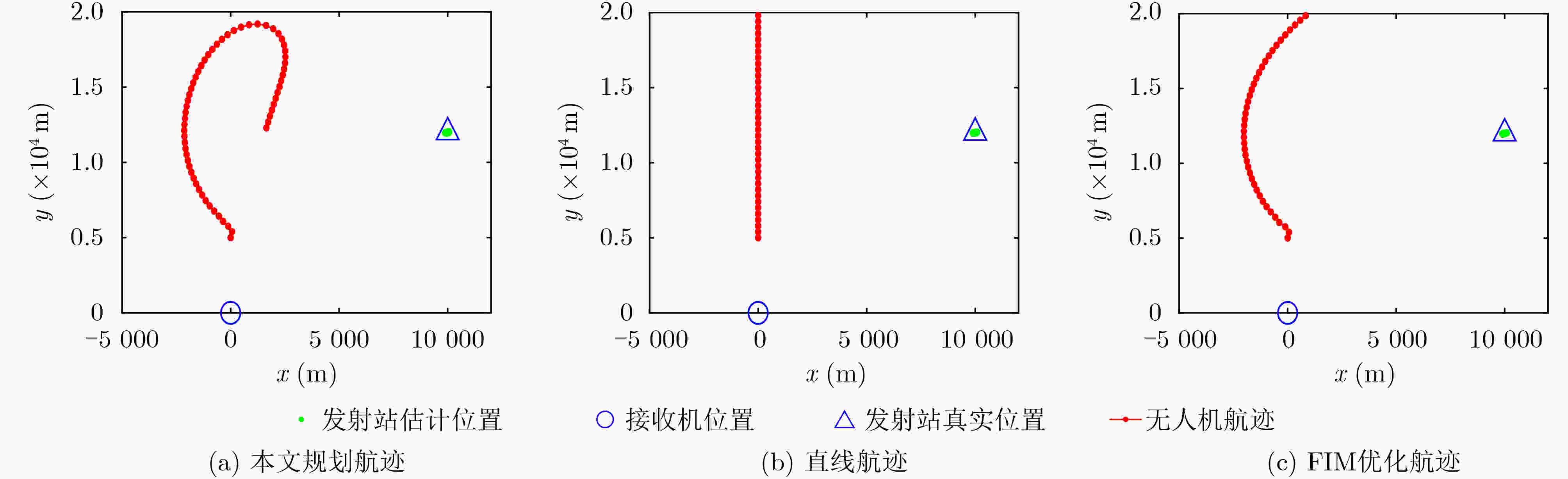
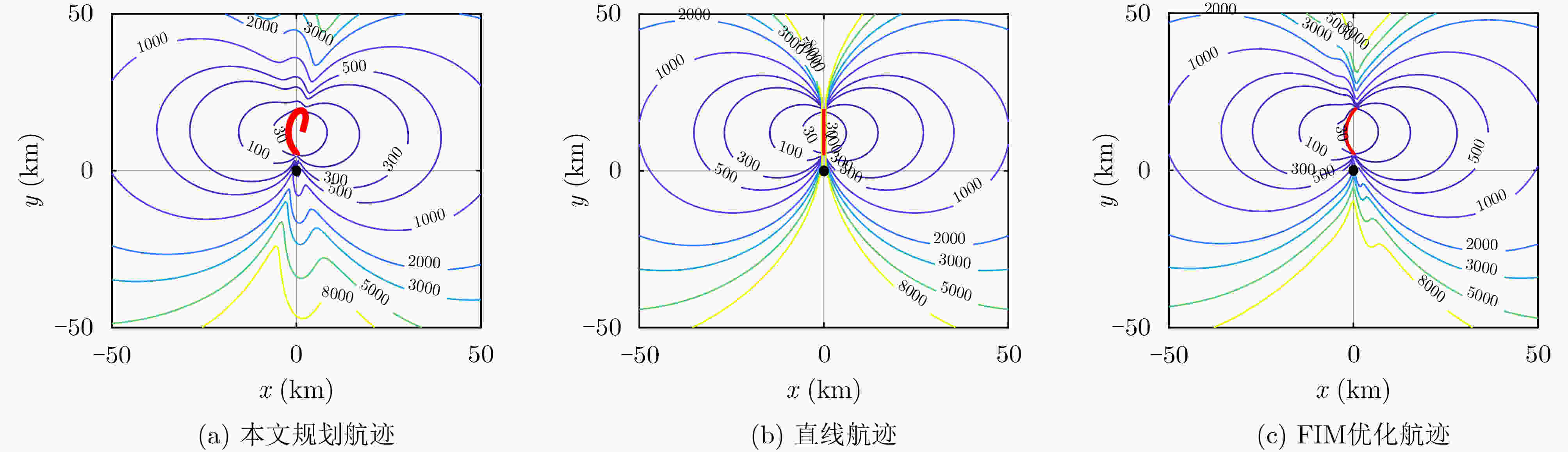
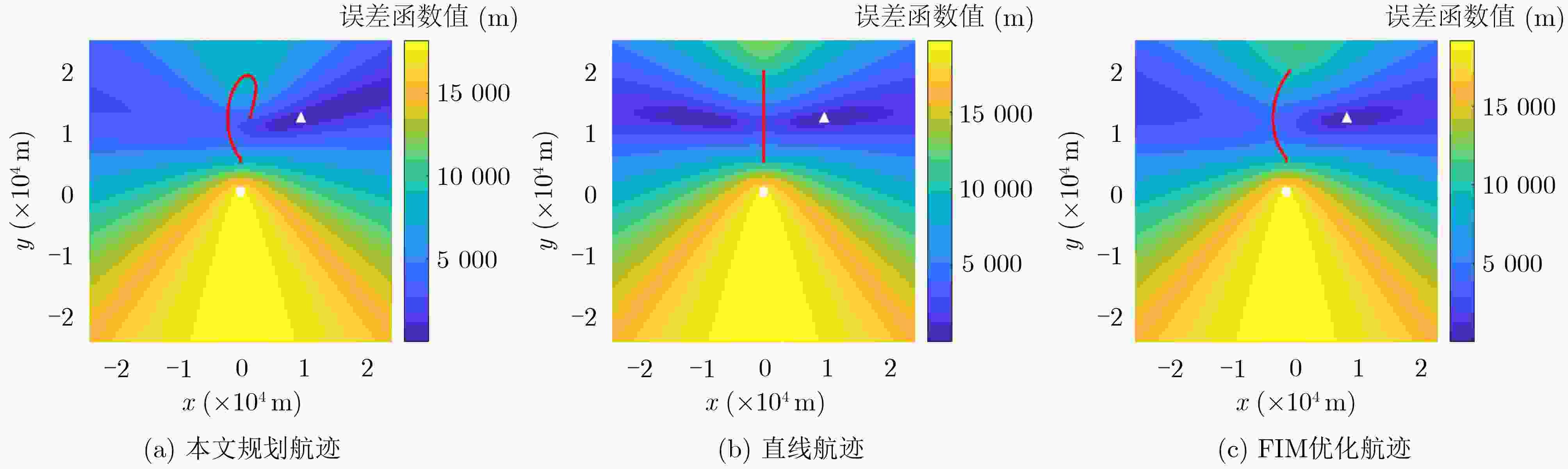


 下载:
下载:
