Research on the Double Layer Coupling Dynamic Information Propagation Model of the Internet of Things
-
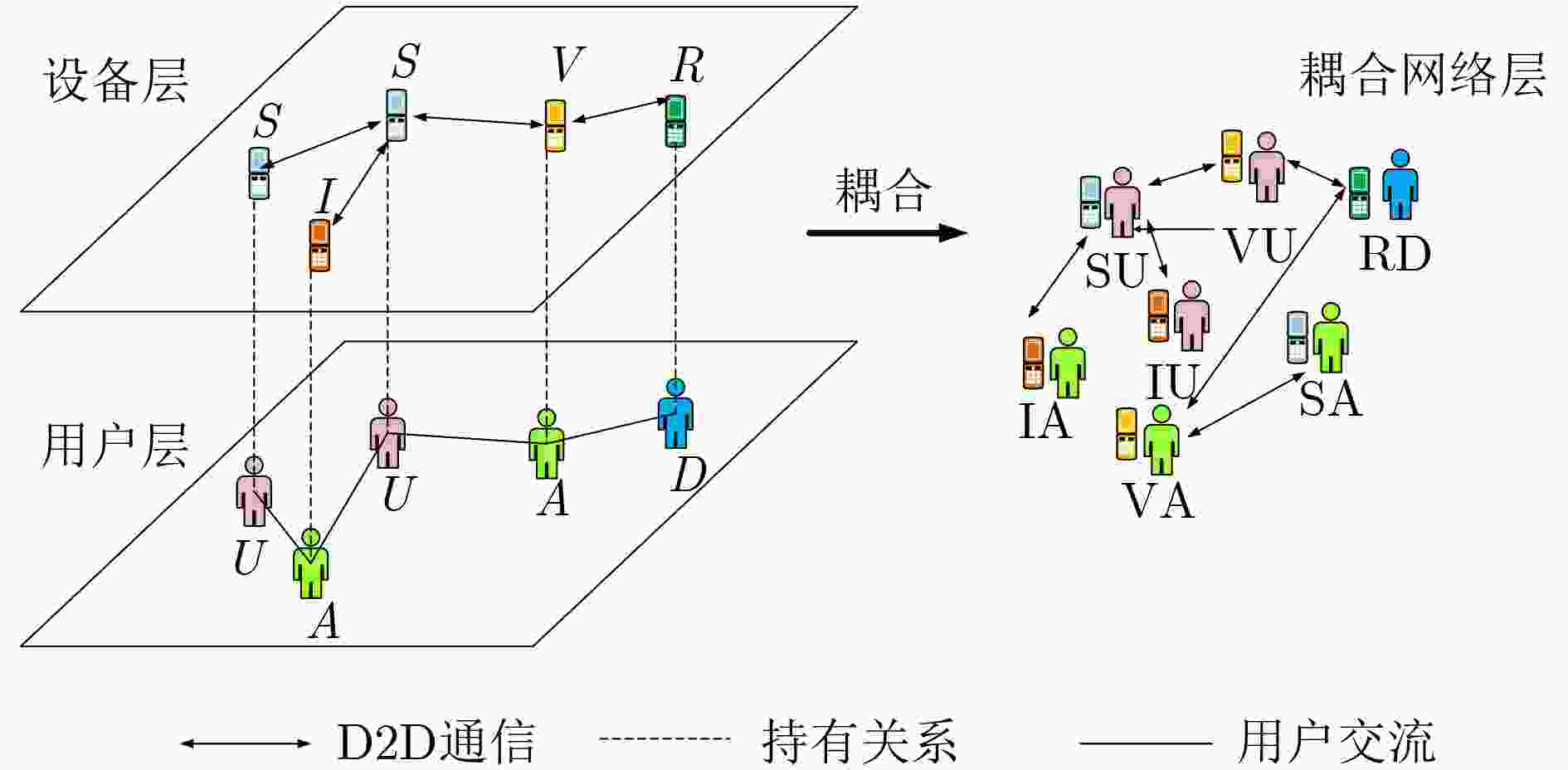
摘要: 信息传播模型的研究是物联网领域的重要组成部分,它有助于提高物联网系统的性能和效率,促进物联网技术的进一步发展,针对物联网通信中影响信息传播的因素复杂且不稳定的问题,该文提出一种双层耦合信息传播模型SIVR-UAD,通过分析物联网中不同状态的设备和用户对信息传播的影响,建立了6种耦合状态,并利用马尔科夫方法分析耦合节点的状态变化过程,找到信息传播平衡点,最后通过理论分析证明了模型的平衡点的唯一性以及稳定性。仿真结果表明,在3组不同的初始耦合节点数下,SIVR-UAD模型中的6种耦合节点数量变化始终趋向同一稳定水平,证明了该模型的平衡点和稳定性。
-
关键词:
- 物联网通信 /
- SIVR-UAD /
- 双层耦合信息传播模型 /
- 稳定性证明
Abstract: The study of information dissemination models is an important component of the Internet of Things field, which helps to improve the performance and efficiency of IoT systems, promote the further development of IoT technology. In response to the complex and unstable factors that affect information dissemination in IoT communication, a double-layer coupled information dissemination model SIVR-UAD (Susceptible, Infection, Variant, Recovered-Unknown, Aware, Disinterest) is proposed, which analyzes the impact of devices and users in different states on information dissemination in the Internet of Things, Six coupling states were established, and the Markov method was used to analyze the state change process of the coupling nodes, finding the information dissemination equilibrium point. Finally, the uniqueness and stability of the equilibrium point of the model were proved through theoretical analysis. The simulation results show that under three different initial coupling node numbers, the number of six coupling nodes in the SIVR-UAD model always tends to the same stable level, proving the equilibrium point and stability of the model. -
表 1 模型参数
参数 定义 S 未携带信息的设备 I 携带有效信息的设备 V 携带无效信息的设备 R 不再接收和传播信息的设备 U 不了解信息情况的用户 A 查看过信息且了解情况的用户 D 停止传播无效信息的用户 $ {\beta _1} $ 单位时间设备S接收到有效信息的概率 $ {\beta _2} $ 单位时间设备S接收到无效信息的概率 $ {\mu _1} $ 单位时间设备I不再传播有效信息的概率 $ {\mu _2} $ 单位时间设备V不再传播无效信息的概率 $ \lambda $ 单位时间用户知道信息的概率 $ \delta $ 单位时间用户不再传播无效信息的概率 $ \varphi $ 单位时间设备R不再占用资源的概率 -
[1] 徐瑶, 王玢. 物联网环境中的5G关键技术及产业化应用[J]. 数字通信世界, 2021(7): 53–54. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1672-7274.2021.07.025.XU Yao and WANG Fen. 5G key technologies and industrialization application in internet of things environment[J]. Digital Communication World, 2021(7): 53–54. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1672-7274.2021.07.025. [2] 宋晓虹. 物联网技术在智慧农业中的应用及发展模式创新探索[J]. 南方农机, 2022, 53(23): 163–165. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3872.2022.23.049.SONG Xiaohong. Exploration of the application and development model innovation of internet of things technology in smart agriculture[J]. Southern Agricultural Machinery, 2022, 53(23): 163–165. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3872.2022.23.049. [3] 王文斌. 城市综合管廊基于物联网融合通信系统应用分析[J]. 新型工业化, 2022, 12(9): 260–263. doi: 10.19335/j.cnki.2095-6649.2022.9.064.WANG Wenbin. Analysis of the application of integrated communication systems based on the internet of things in urban comprehensive pipe corridors[J]. The Journal of New Industrialization, 2022, 12(9): 260–263. doi: 10.19335/j.cnki.2095-6649.2022.9.064. [4] 陈章余. 物联网技术在电子通信领域的应用及其研究[J]. 信息与电脑, 2022, 34(12): 197–199. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9767.2022.12.062.CHEN Zhangyu. Application and research of internet of things technology in electronic communication[J]. Information & Computer, 2022, 34(12): 197–199. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9767.2022.12.062. [5] 闫思洁. 在物联网通信中应用计算机硬件及网络技术的实践途径[J]. 网络安全技术与应用, 2022(6): 31–33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6833.2022.06.018.YAN Sijie. Practical approaches to applying computer hardware and network technology in IoT communication[J]. Network Security Technology & Application, 2022(6): 31–33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6833.2022.06.018. [6] 杨青丰, 刘思雨, 唐丽萍. 5G网络下的物联网通信技术探讨[J]. 中国管理信息化, 2022, 25(9): 163–165.YANG Qingfeng, LIU Siyu, and TANG Liping. Exploration of IoT communication technology under 5G network[J]. China Management Informationization, 2022, 25(9): 163–165. [7] 贺英. 物联网通信服务平台保障系统的设计与实现研究[J]. 中国新通信, 2022, 24(17): 19–21.HE Ying. Research on the design and implementation of the internet of things communication service platform guarantee system[J]. China New Telecommunications, 2022, 24(17): 19–21. [8] 史国剑. 物联网技术在智慧交通中的应用分析[J]. 时代汽车, 2022(21): 193–195.SHI Guojian. Application analysis of internet of things technology in intelligent transportation[J]. Auto Time, 2022(21): 193–195. [9] 许晶晶. 人工智能与物联网在智慧城市中的应用研究[J]. 中国设备工程, 2023(4): 42–44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0711.2023.04.019.XU Jingjing. Research on the application of artificial intelligence and the internet of things in smart cities[J]. China Plant Engineering, 2023(4): 42–44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0711.2023.04.019. [10] 赵炬, 吴佩利, 孟然. 物联网在煤矿中的应用现状及展望[J]. 陕西煤炭, 2023, 42(1): 139–144. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-749X.2023.01.030.ZHAO Ju, WU Peili, and MENG Ran. Application status and prospect of internet of things in coal mines[J]. Shaanxi Coal, 2023, 42(1): 139–144. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-749X.2023.01.030. [11] 刘文孝, 李冰, 刘凯. 物联网技术在现代化农业发展中的应用[J]. 种子科技, 2023, 41(2): 123–125. doi: 10.19904/j.cnki.cn14-1160/s.2023.02.041.LIU Wenxiao, LI Bing, and LIU Kai. The application of internet of things technology in the development of modern agriculture[J]. Seed Science & Technology, 2023, 41(2): 123–125. doi: 10.19904/j.cnki.cn14-1160/s.2023.02.041. [12] 黄兴, 张文杰, 李曦, 等. 一种面向电力物联网的认知D2D网络能效资源分配算法[J]. 电测与仪表, 2023, 60(2): 97–103. doi: 10.19753/j.issn1001-1390.2023.02.014.HUANG Xing, ZHANG Wenjie, LI Xi, et al. Energy-efficient resource allocation algorithm for cognitive D2D networks for power IoT[J]. Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation, 2023, 60(2): 97–103. doi: 10.19753/j.issn1001-1390.2023.02.014. [13] 徐涵, 张庆. 复杂网络上传播动力学模型研究综述[J]. 情报科学, 2020, 38(10): 159–167. doi: 10.13833/j.issn.1007-7634.2020.10.024.XU Han and ZHANG Qing. A review of epidemic dynamics on complex networks[J]. Information Science, 2020, 38(10): 159–167. doi: 10.13833/j.issn.1007-7634.2020.10.024. [14] 王彦本. 传播动力学研究综述[J]. 通讯世界, 2015(3): 24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4222.2015.03.017.WANG Yanben. Overview of communication dynamics research[J]. Telecom World, 2015(3): 24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4222.2015.03.017. [15] 张鹏, 赵动员, 梅蕾. 移动社交网络信息传播研究述评与展望[J]. 情报科学, 2020, 38(2): 170–176. doi: 10.13833/j.issn.1007-7634.2020.02.025.ZHANG Peng, ZHAO Dongyuan, and MEI Lei. Review and prospect of information dissemination research on mobile social network[J]. Information Science, 2020, 38(2): 170–176. doi: 10.13833/j.issn.1007-7634.2020.02.025. [16] 汪意. 基于SEIR模型的复杂网络上的疾病传播动力学与隔离措施研究[D]. [硕士论文], 杭州师范大学, 2021. doi: 10.27076/d.cnki.ghzsc.2021.000728.WANG Yi. Research on dynamics of disease spreading and isolation measures in complex networks based on SEIR model[D]. [Master dissertation], Hangzhou Normal University, 2021. doi: 10.27076/d.cnki.ghzsc.2021.000728. [17] 许云霞, 雷学红. 具有Logistic增长的SIRS传染病模型的稳定性及最优控制分析[J]. 湖北民族大学学报: 自然科学版, 2020, 38(2): 200–205. doi: 10.13501/j.cnki.42-1908/n.2020.06.017.XU Yunxia and LEI Xuehong. Dynamic analysis and optimal control of an SIRS epidemic model with logistic growth[J]. Journal of Hubei Minzu University: Natural Science Edition, 2020, 38(2): 200–205. doi: 10.13501/j.cnki.42-1908/n.2020.06.017. [18] 张倩. 基于帕累托原理和节点地位的社交网络信息传播模型与控制方法[D]. [硕士论文], 西华大学, 2021. doi: 10.27411/d.cnki.gscgc.2021.000323.ZHANG Qian. Social network information dissemination models and control methods based on Pareto principle and node status[D]. [Master dissertation], Xihua University, 2021. doi: 10.27411/d.cnki.gscgc.2021.000323. [19] 崔雪莲, 那日萨. 基于消费者信任关系的在线口碑信息传播模型[J]. 系统管理学报, 2020, 29(3): 1090–1100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn1005-2542.2020.06.007.CUI Xuelian and Narisa. Modeling of online word-of-mouth information diffusion based on consumer trust relationship[J]. Journal of Systems & Management, 2020, 29(3): 1090–1100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn1005-2542.2020.06.007. [20] 沈庆磊, 邓月. 基于复杂网络的微商信息传播模型研究[J]. 模糊系统与数学, 2022, 36(2): 145–154.SHEN Qinglei and DENG Yue. Research on wechat information transmission model based on complex network[J]. Fuzzy Systems and Mathematics, 2022, 36(2): 145–154. [21] 王志双. 双层耦合网络上的传播行为与扩散动力学研究[D]. [博士论文], 天津理工大学, 2021. doi: 10.27360/d.cnki.gtlgy.2021.000825.WANG Zhishuang. Propagation behavior and diffusion dynamics in two-layered coupling networks[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Tianjin University of Technology, 2021. doi: 10.27360/d.cnki.gtlgy.2021.000825. [22] 王欢. 双层网络上的传播动力学建模及分析[D]. [硕士论文], 安徽大学, 2020. doi: 10.26917/d.cnki.ganhu.2020.001180.WANG Huan. Modeling and analysis of the spreading dynamics in two-layer multiplex networks[D]. [Master dissertation], Anhui University, 2020. doi: 10.26917/d.cnki.ganhu.2020.001180. [23] SCATÀ M, DI STEFANO A, LA CORTE A, et al. A multiplex social contagion dynamics model to shape and discriminate D2D content dissemination[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2021, 7(2): 581–593. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2020.3027697. [24] SCATÀ M, DI STEFANO A, LA CORTE A, et al. Quantifying the propagation of distress and mental disorders in social networks[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 5005. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-23260-2. [25] RAHMEDE C, IACOVACCI J, ARENAS A, et al. Centralities of nodes and influences of layers in large multiplex networks[J]. Journal of Complex Networks, 2018, 6(5): 733–752. doi: 10.1093/comnet/cnx050. [26] ZHANG Zufan, LIU Anqi, YI Yinxue, et al. Exploring the dynamical behavior of information diffusion in D2D communication environment[J]. Security and Communication Networks, 2020, 2020: 8848576. doi: 10.1155/2020/8848576. [27] SANG Chunyan and LIAO Shigen. Modeling and simulation of information dissemination model considering user’s awareness behavior in mobile social networks[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2020, 537: 122639. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2019.122639. [28] 杨云鹏, 樊重俊, 杨坚争, 等. 基于官方信息控制的多层网络谣言传播模型[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2018, 35(5): 1294–1297, 1314. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2018.05.003.YANG Yunpeng, FAN Chongjun, YANG Jianzheng, et al. Rumor propagation model on multilayered interconnected complex networks based on official information driven[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2018, 35(5): 1294–1297, 1314. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2018.05.003. [29] 罗章凯, 裴忠民, 熊伟, 等. 双层均质耦合网络信息传播动力学研究[J]. 计算机仿真, 2023, 40(1): 43–47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2023.01.009.LUO Zhangkai, PEI Zhongmin, XIONG Wei, et al. Research on dynamics of information spreading on double-layer coupled networks[J]. Computer Simulation, 2023, 40(1): 43–47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2023.01.009. [30] 朱恒民, 杨柳, 马静, 等. 基于耦合网络的线上线下互动舆情传播模型研究[J]. 情报杂志, 2016, 35(2): 139–144,150. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1965.2016.02.025.ZHU Hengmin, YANG Liu, MA Jing, et al. Study on public opinion propagation model based on coupled networks under onlineto offline interaction[J]. Journal of Intelligence, 2016, 35(2): 139–144,150. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1965.2016.02.025. [31] 魏静, 黄阳江豪, 朱恒民. 基于耦合网络的社交网络舆情传播模型研究[J]. 现代情报, 2019, 39(10): 110–118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0821.2019.10.013.WEI Jing, HUANG Yangjianghao, and ZHU Hengmin. Research on public opinion communication model of social network based on coupling network[J]. Journal of Modern Information, 2019, 39(10): 110–118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0821.2019.10.013. [32] 甘臣权, 刘安棋, 张祖凡, 等. D2D通信中用户意识与信息耦合传播建模分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(8): 2767–2776. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210535.GAN Chenquan, LIU Anqi, ZHANG Zufan, et al. Modeling and analysis of user awareness and information coupling propagation in D2D communications[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(8): 2767–2776. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210535. [33] 张欣欣, 许力, 徐振宇. 基于网络模体的移动社会网络信息可控传播方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(2): 635–643. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211429.ZHANG Xinxin, XU Li, and XU Zhenyu. Information propagation control method in mobile social networks based on network motifs[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(2): 635–643. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211429. [34] LI Wenyao, CAI Meng, ZHONG Xiaoni, et al. Coevolution of epidemic and infodemic on higher-order networks[J]. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 2023, 168: 113102. doi: 10.1016/J.CHAOS.2023.113102. [35] NIE Yanyi, LI Wenyao, PAN Liming, et al. Markovian approach to tackle competing pathogens in simplicial complex[J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2022, 417: 126773. doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2021.126773. -





 下载:
下载:







 下载:
下载:
