A Fusion Network for Infrared and Visible Images Based on Pre-trained Fixed Parameters and Deep Feature Modulation
-
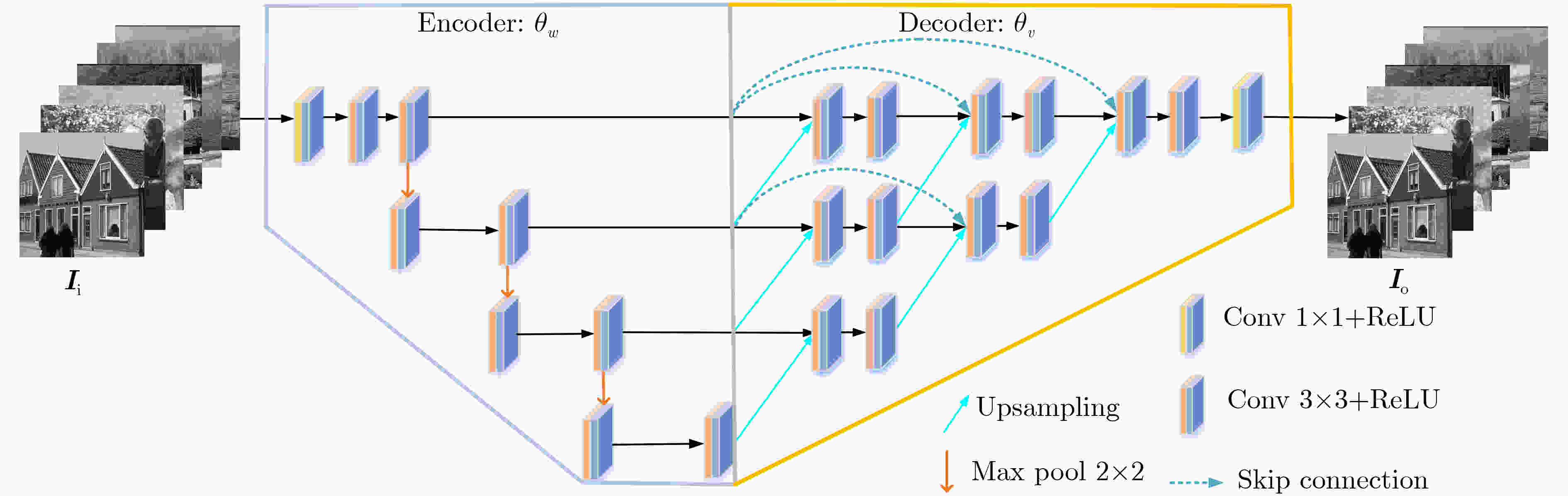
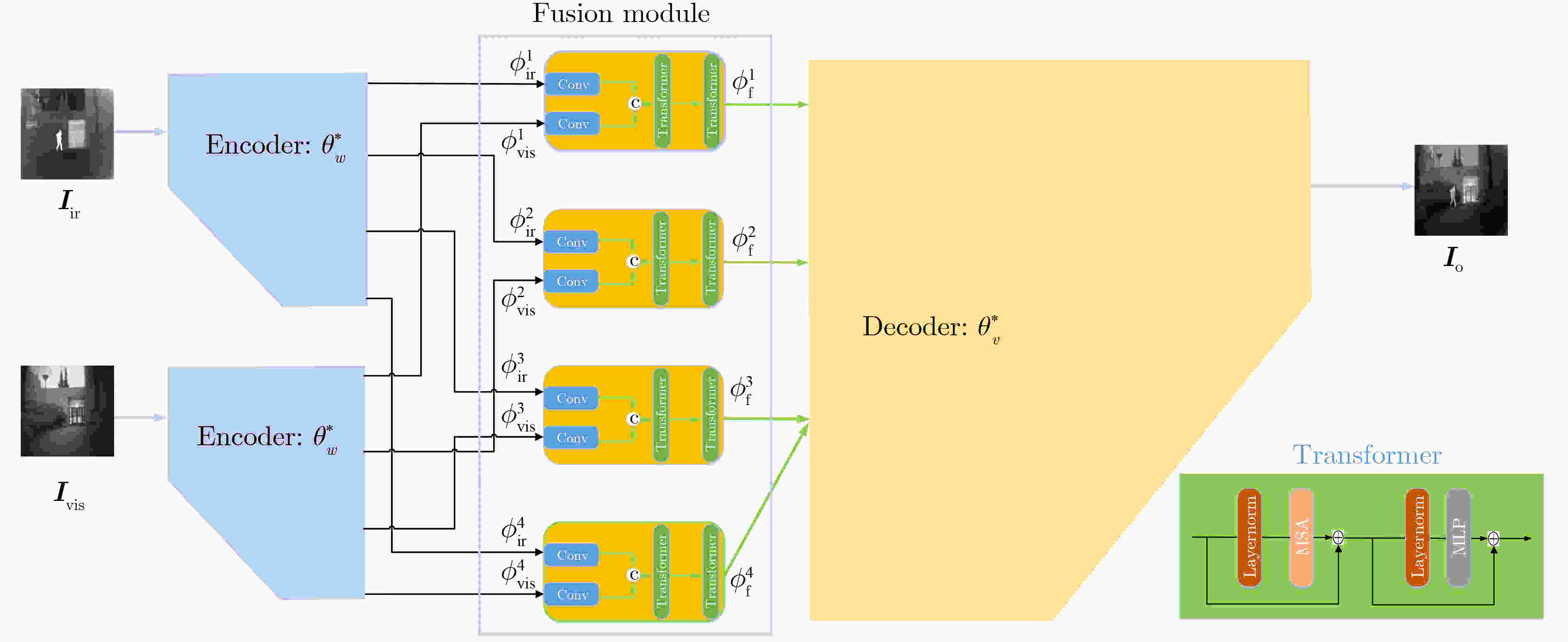
摘要: 为了更好地利用红外与可见光图像中互补的图像信息,得到符合人眼感知特性的融合图像,该文采用两阶段训练策略提出一种基于预训练固定参数和深度特征调制的红外与可见光图像融合网络(PDNet)。具体地,在自监督预训练阶段,以大量清晰的自然图像分别作为U型网络结构(UNet)的输入和输出,采用自编码器技术完成预训练。所获得编码器模块能有效提取输入图像的多尺度深度特征功能,而解码器模块则能将其重构为与输入图像差异极小的输出图像;在无监督融合训练阶段,将预训练编码器和解码器模块的网络参数保持固定不变,而在两者之间新增包含Transformer结构的融合模块。其中,Transformer结构中的多头自注意力机制能对编码器分别从红外和可见光图像提取到的深度特征权重进行合理分配,从而在多个尺度上将两者融合调制到自然图像深度特征的流型空间上来,进而保证融合特征经解码器重构后所获得融合图像的视觉感知效果。大量实验表明:与当前主流的融合模型(算法)相比,所提PDNet模型在多个客观评价指标方面具有显著优势,而在主观视觉评价上,也更符合人眼视觉感知特点。Abstract: To better leverage complementary image information from infrared and visible light images and generate fused images that align with human perception characteristics, a two-stage training strategy is proposed to obtain a novel infrared-visible image fusion Network based on pre-trained fixed Parameters and Deep feature modulation (PDNet). Specifically, in the self-supervised pre-training stage, a substantial dataset of clear natural images is employed as both inputs and outputs for the UNet backbone network, and pre-training is accomplished with autoencoder technology. As such, the resulting encoder module can proficiently extract multi-scale depth features from the input image, while the decoder module can faithfully reconstruct it into an output image with minimal deviation from the input. In the unsupervised fusion training stage, the pre-trained encoder and decoder module parameters remain fixed, and a fusion module featuring a Transformer structure is introduced between them. Within the Transformer structure, the multi-head self-attention mechanism allocates deep feature weights, extracted by the encoder from both infrared and visible light images, in a rational manner. This process fuses and modulates the deep image features at various scales into the manifold space of deep features of clear natural image, thereby ensuring the visual perception quality of the fused image after reconstruction by the decoder. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that, in comparison to current mainstream fusion models (algorithms), the proposed PDNet model exhibits substantial advantages across various objective evaluation metrics. Furthermore, in subjective visual evaluations, it aligns more closely with human visual perception characteristics.
-
表 1 损失函数${L_{{\text{un}}}}$中超参数$\lambda $取值对融合结果评价指标的影响
评价指标 $\lambda $ 0 25 50 75 100 125 150 175 200 En 6.766 9 6.949 8 6.932 3 6.937 4 6.953 3 7.085 1 7.155 7 7.127 6 7.144 1 SD 77.730 8 81.681 1 80.013 2 80.885 2 81.097 8 99.554 7 98.155 5 99.972 5 98.011 0 CC 0.454 8 0.509 2 0.509 6 0.509 3 0.510 4 0.416 6 0.450 4 0.426 3 0.451 5 VIF 0.901 0 0.848 8 0.837 0 0.844 2 0.841 4 0.985 1 0.936 1 0.841 4 0.947 1 SCD 1.595 4 1.766 9 1.746 6 1.745 8 1.767 7 1.572 6 1.698 7 1.626 3 1.690 6 PSNR 61.293 9 62.337 4 62.234 9 62.190 9 62.392 3 61.482 8 61.798 7 61.544 5 61.834 7 MS-SSIM 0.794 7 0.920 8 0.898 8 0.892 1 0.923 6 0.858 3 0.893 6 0.878 5 0.895 0 表 2 特征融合部分中Transformer模块对融合效果的影响
评价指标 Transformer个数 0 1 2 3 En 7.120 9 7.080 6 6.953 3 7.115 2 SD 112.593 5 100.349 8 81.097 8 113.844 2 CC 0.360 0 0.402 2 0.510 4 0.353 6 VIF 1.131 6 0.986 3 0.841 4 1.162 6 SCD 1.131 1 1.393 1 1.767 7 1.016 1 PSNR 60.665 8 61.393 5 62.392 3 60.745 7 MS-SSIM 0.805 0 0.830 1 0.923 6 0.799 4 表 3 采用1阶段和两阶段训练策略在VOT2020-RGBT测试集上的融合效果对比
训练策略 评价指标 En SD CC VIF SCD PSNR MS-SSIM 1阶段 7.182 8 109.516 7 0.379 1 1.039 5 1.252 5 60.989 0 0.832 6 2阶段 6.953 3 81.097 8 0.510 4 0.841 4 1.767 7 62.392 3 0.923 6 表 4 各方法在MSRS数据集上的指标值对比
评价指标 对比算法 GTF STDFusionNet ConvSR DCHWT DenseFuse U2Fusion TarDAL ReCoNet YDTR DATFuse PDNet En 5.483 5 5.244 1 6.030 8 6.346 6 5.936 8 5.372 2 6.349 5 4.233 7 5.645 1 6.420 3 6.360 5 SD 42.970 8 65.835 1 55.818 2 72.187 0 51.226 4 55.479 9 77.116 0 90.668 6 55.146 1 71.763 9 71.110 0 CC 0.525 4 0.541 0 0.647 5 0.604 2 0.659 8 0.6482 0.626 2 0.555 3 0.631 1 0.590 2 0.629 0 VIF 0.558 0 0.521 2 0.709 5 0.713 0 0.704 1 0.564 1 0.677 3 0.594 0 0.559 3 0.800 8 0.817 3 SCD 0.749 5 0.952 6 1.291 7 1.340 7 1.251 1 1.2439 1.484 6 1.262 0 1.138 1 1.285 1 1.506 4 PSNR 64.723 4 64.815 0 67.117 7 66.147 0 67.237 3 66.358 0 60.899 6 64.507 9 64.107 6 62.598 7 66.271 7 MS-SSIM 0.848 4 0.867 3 0.942 0 0.902 2 0.902 9 0.919 4 0.928 9 0.884 2 0.887 2 0.946 6 0.946 5 -
[1] CHANG Zhihao, FENG Zhixi, YANG Shuyuan, et al. AFT: Adaptive fusion transformer for visible and infrared images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2023, 32: 2077–2092. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2023.3263113. [2] WU Xin, HONG Danfeng, and CHANUSSOT J. UIU-Net: U-Net in U-Net for infrared small object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2023, 32: 364–376. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2022.3228497. [3] TANG Linfeng, YUAN Jiteng, ZHANG Hao, et al. PIAFusion: A progressive infrared and visible image fusion network based on illumination aware[J]. Information Fusion, 2022, 83/84: 79–92. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2022.03.007. [4] 冯鑫, 张建华, 胡开群, 等. 基于变分多尺度的红外与可见光图像融合[J]. 电子学报, 2018, 46(3): 680–687. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2018.03.025.FENG Xin, ZHANG Jianhua, HU Kaiqun, et al. The infrared and visible image fusion method based on variational multiscale[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2018, 46(3): 680–687. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2018.03.025. [5] RAM PRABHAKAR K, SAI SRIKAR V, and BABU R V. DeepFuse: A deep unsupervised approach for exposure fusion with extreme exposure image pairs[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 4714–4722. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.505. [6] LI Hui and WU Xiaojun. DenseFuse: A fusion approach to infrared and visible images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(5): 2614–2623. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2887342. [7] ZHANG Hao, XU Han, XIAO Yang, et al. Rethinking the image fusion: A fast unified image fusion network based on proportional maintenance of gradient and intensity[C]. The Thirty-Seventh AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, USA, 2020: 12797–12804. doi: 10.1609/AAAI.V34I07.6975. [8] MA Jiayi, YU Wei, LIANG Pengwei, et al. FusionGAN: A generative adversarial network for infrared and visible image fusion[J]. Information Fusion, 2019, 48: 11–26. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2018.09.004. [9] MA Jiayi, XU Han, JIANG Junjun, et al. DDcGAN: A dual-discriminator conditional generative adversarial network for multi-resolution image fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 4980–4995. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.2977573. [10] LI Jing, HUO Hongtao, LI Chang, et al. AttentionFGAN: Infrared and visible image fusion using attention-based generative adversarial networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2021, 23: 1383–1396. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2020.2997127. [11] XU Han, MA Jiayi, JIANG Junjun, et al. U2Fusion: A unified unsupervised image fusion network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(1): 502–518. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2020.3012548. [12] LIANG Jingyun, CAO Jiezhang, SUN Guolei, et al. SwinIR: Image restoration using swin transformer[C]. The 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 1833–1844. doi: 10.1109/ICCVW54120.2021.00210. [13] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, and BROX T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]. 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 2015: 234–241. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28. [14] WEI Yanyan, ZHANG Zhao, WANG Yang, et al. DerainCycleGAN: Rain attentive cycleGAN for single image deraining and rainmaking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 4788–4801. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3074804. [15] ZHANG Yuyang, XU Shibiao, WU Baoyuan, et al. Unsupervised multi-view constrained convolutional network for accurate depth estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 7019–7031. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.2997247. [16] KRISTAN M, LEONARDIS A, MATAS J, et al. The eighth visual object tracking VOT2020 challenge results[C]. European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 547–601. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-68238-5_39. [17] MA Jiayi, CHEN Chen, LI Chang, et al. Infrared and visible image fusion via gradient transfer and total variation minimization[J]. Information Fusion, 2016, 31: 100–109. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2016.02.001. [18] LIU Yu, CHEN Xun, WARD R K, et al. Image fusion with convolutional sparse representation[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2016, 23(12): 1882–1886. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2016.2618776. [19] KUMAR B K S. Multifocus and multispectral image fusion based on pixel significance using discrete cosine harmonic wavelet transform[J]. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2013, 7(6): 1125–1143. doi: 10.1007/s11760-012-0361-x. [20] MA Jiayi, TANG Linfeng, XU Meilong, et al. STDFusionNet: An infrared and visible image fusion network based on salient target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2021, 70: 1–13. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2021.3075747. [21] LIU Jinyuan, FAN Xin, HUANG Zhanbo, et al. Target-aware dual adversarial learning and a multi-scenario multi-modality benchmark to fuse infrared and visible for object detection[C]. 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 5792–5801. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00571. [22] HUANG Zhanbo, LIU Jinyuan, FAN Xin, et al. ReCoNet: Recurrent correction network for fast and efficient multi-modality image fusion[C]. 17th European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 2022: 539–555. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-19797-0_31. [23] TANG Wei, HE Fazhi, and LIU Yu. YDTR: Infrared and visible image fusion via Y-shape dynamic transformer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2023, 25: 5413–5428. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2022.3192661. [24] TANG Wei, HE Fazhi, LIU Yu, et al. DATFuse: Infrared and visible image fusion via dual attention transformer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2023, 33(7): 3159–3172. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2023.3234340. [25] 蔺素珍, 韩泽. 基于深度堆叠卷积神经网络的图像融合[J]. 计算机学报, 2017, 40(11): 2506–2518. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2017.02506.LIN Suzhen and HAN Ze. Images fusion based on deep stack convolutional neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2017, 40(11): 2506–2518. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2017.02506. [26] SHEIKH H R and BOVIK A C. Image information and visual quality[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2006, 15(2): 430–444. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2005.859378. [27] ASLANTAS V and BENDES E. A new image quality metric for image fusion: The sum of the correlations of differences[J]. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 2015, 69(12): 1890–1896. doi: 10.1016/j.aeue.2015.09.004. -






 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
