A Survey of Collaborative of Swarm Intelligence for Evolutionary Computation
-
摘要: 演化计算为代表的群体智能的迅速发展引发了人工智能领域新一轮技术变革。为满足多样化复杂系统应用需求,人工智能越来越趋向于跨级别的智能化、协同化研究。该文提出面向演化计算的群智协同的概念,根据群智协同层级将人工智能跨级别的智能化、协同化研究分为微观协同、中观协同与宏观协同,以群智协同视角对近年来上述分支领域相关研究做出了总结。首先,通过分析决策变量级协同、全局与局部级协同对微观协同进行了阐述。其次,从目标级协同和任务级协同两个维度对中观协同进行了总结。再次,以智能协同系统中存在的空天地海协同、车路云协同和端边云协同对宏观协同展开分析。最后,该文指出了面向演化计算的群智协同领域的研究挑战,并对相关领域发展方向进行了展望。Abstract: The rapid development of swarm intelligence, represented by evolutionary computation, has triggered a new wave of technological transformation in the field of artificial intelligence. To meet the diverse application needs of complex systems, artificial intelligence is increasingly moving towards cross-level intelligent and collaborative research. In this paper, the concept of swarm intelligence cooperation oriented towards evolutionary computation is proposed. Based on the hierarchical levels of swarm intelligence cooperation, artificial intelligence research across different levels is categorized into micro-level cooperation, meso-level cooperation, and macro-level cooperation. From the perspective of swarm intelligence cooperation, a summary is provided on recent research in the aforementioned branches. Firstly, the micro-level cooperation is discussed by analyzing decision variable level cooperation and global/local level cooperation. Secondly, the meso-level cooperation is summarized from the dimensions of objective-level cooperation and task-level cooperation. Furthermore, an analysis of macro-level cooperation is conducted through the examination of space-air-ground-sea cooperation, vehicle-road-cloud cooperation, and edge-cloud cooperation in intelligent collaborative systems. Finally, the research challenges in the field of swarm intelligence cooperation oriented towards evolutionary computation are identified, and future directions for related fields are proposed.
-
Key words:
- Collaborative optimization /
- Swarm intelligence /
- Evolutionary computation
-
表 1 决策变量级协同方法的研究总结
算法 策略 算法 策略 决策变量分组过程中 CPSO-SL[32] 固定部分决策变量为常数,
动态调整部分决策变量取值DECC-II[26] 预定义范围内动态调整
分组大小HCMPSO[39] 增益函数衡量解的贡献程度,
结合增益函数评估适应度MLCC[27] 自适应调整策略 DSMGA[36] 保留子组份中的优质解 CCFA[28], CCAS[29] 动态的子组份和子种群大小 FEA[31] ${R_i}$在完整解中计算适应度 FDA[33] 因子分布 DIMA[40] 信息交换机制 BMDA[34] 2元边际分布算法 演化算法完整解整合过程中 MIMIC[35] 简单链式分布 CPSO[38] 依据权重比例组合子组份 FEA[31] 重叠分组策略 DSMGA[36] 自动创建定制化重组算子 DSMGA[36] 依赖矩阵聚类 CPSO-SL[32] 优化后的子问题核心决策变量 演化算法优化评估过程中 FEA[31] 最佳适应度个体整合 CCGA[37], CPSO[38], DECC-II[26] 固定部分决策变量为最优值,
动态调整部分决策变量取值DIMA[40] 信息交流机制 表 2 全局与局部级协同方法的研究总结
算法 策略 算法 策略 以种群初始化的形式进行 Hybrid GA[48] 专门化交叉算子 DE+Opposition learning [42] 反向学习初始化 随机性形式的局部搜索策略 GA[43] 混合初始化和顺序变换 Tabu search+MA[49] 禁忌搜索 对问题进行预处理 AGLMA[50] 模拟退火 GTSP reduction algorithms [44] GTSP约简技术 HCS+MOEA[51] 局部帕累托集 MOGLS[46] 对模糊规则预筛选 自适应的局部搜索策略 确定性形式的局部搜索策略 SFMDE[52] 自适应选择 BS+MA[47] 分支界限法 SGMA[53] 模因和基因协同进化 表 3 目标级协同方法的研究总结
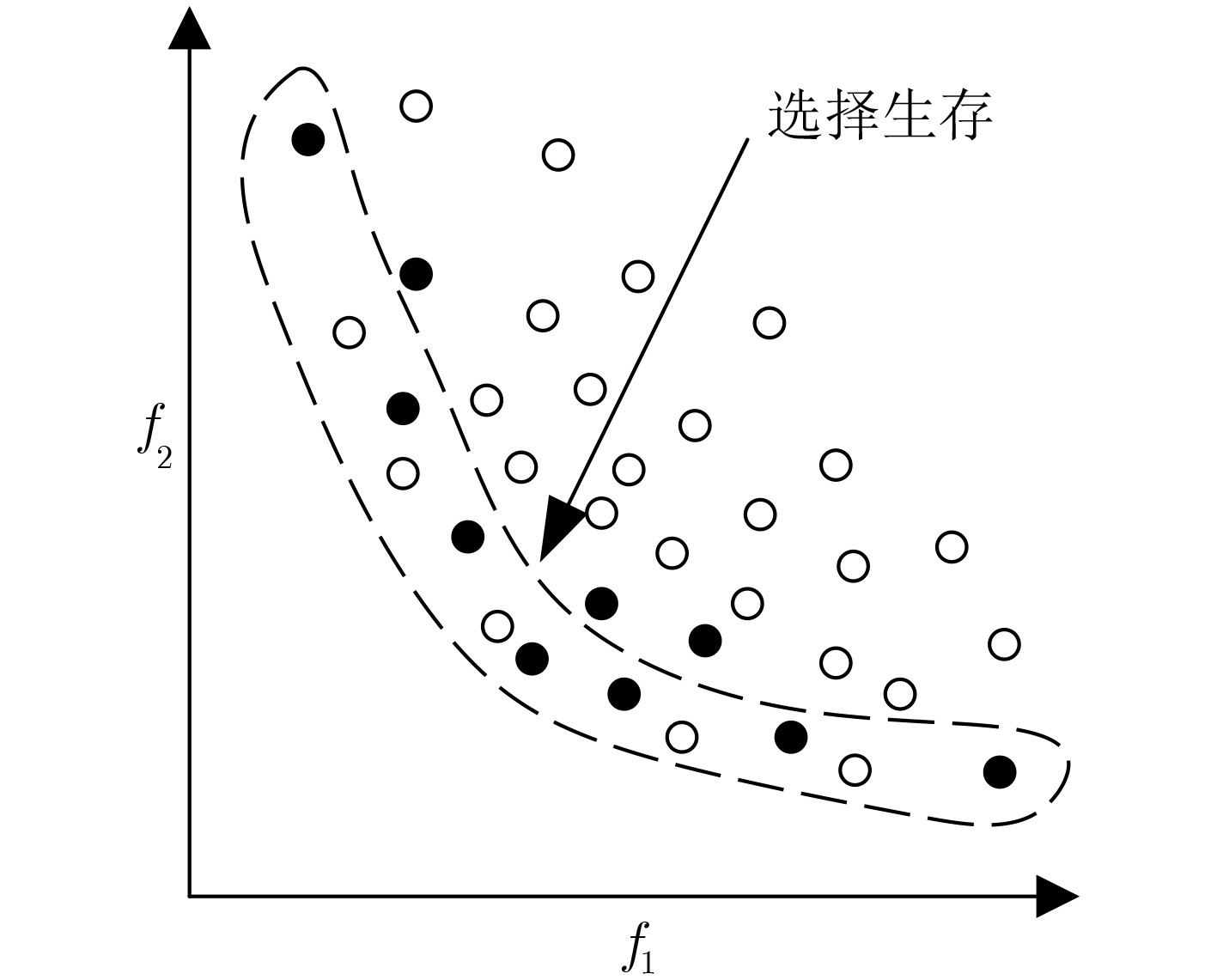
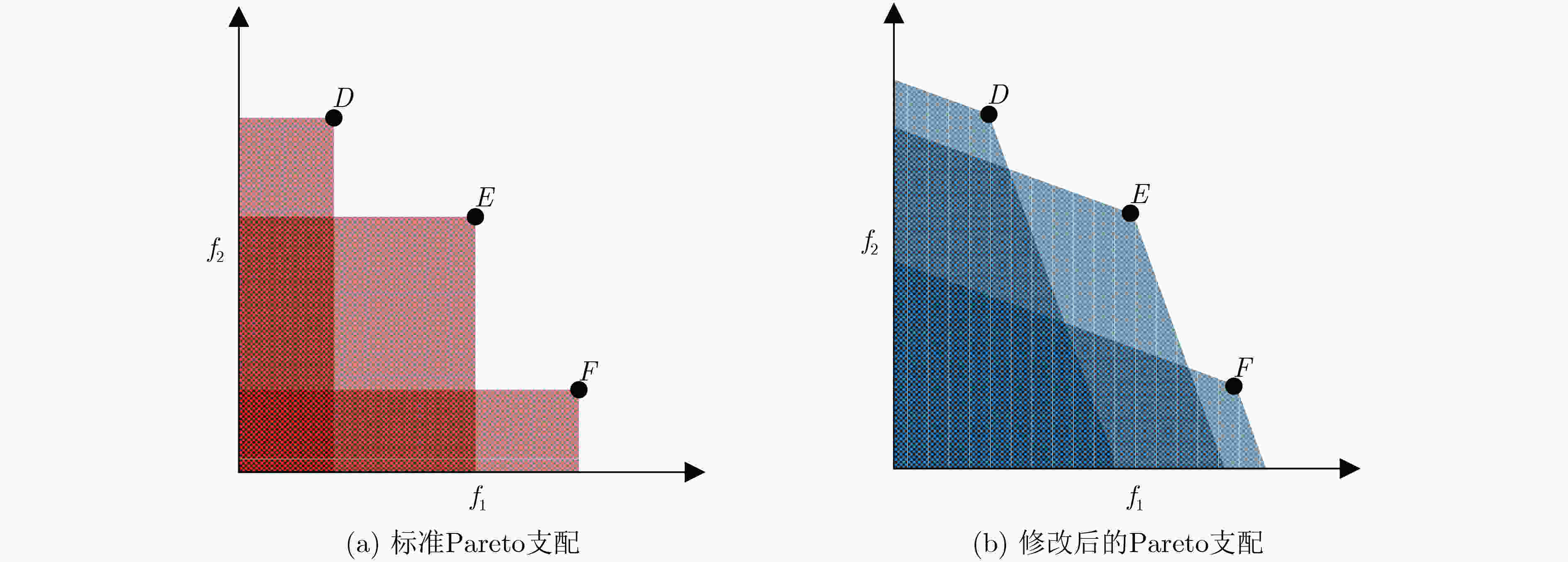
算法 策略 算法 策略 最优求解过程中 preferred +EA[73] 偏好(favour)关系 Goldberg[57] 基于Pareto的排序 $\varepsilon $-preferred+EA[74] 偏好关系(修改) 种群多样性维持过程中 基于偏好信息的协同 NPGA[65] 目标域适应度共享 DM+MOEA[77] MOP中引入偏好表达方法 Srinivas[66] 决策变量域适应度共享 NSGA-II[78] 参考点偏好信息(NSGA-II) 基于修改Pareto支配的协同 基于目标数量调节的协同 NSGA-II[71] 改良Pareto部分支配 PCA-NSGA-II[84] 基于PCA的目标简化 基于偏好关系的协同 SIBEA[85] 基于Pareto支配关系调节 表 4 任务级协同方法的研究总结
算法 策略 算法 策略 知识迁移时机 基于任务相似度衡量 MFEA[102] 历代跨任务知识迁移 CTFDC[125] 最佳解间距、适应度等级相关性、
适应度场景分析协同衡量EMT[103] 固定世代间隔知识迁移 MFEA[126] 协同度量($\xi $) MT-CPSO[104] 触发式知识迁移 任务选择 知识迁移内容 SaEF-AKT[128] KL散度衡量任务间进行选择 EMT[108] 非支配原则选择优质解 MSSTO[129] Wasserstein距离衡量相似性 知识迁移方式 group-based MFEA[130] 相似性信息与反馈信息结合 MFEA[102] 种群间模拟二进制交叉 AMTEA[131], TEMO-MPSs[132] 混合模型参数作任务选择概率 MFEA-Direction Vector[111] 搜索方向沿用 Symbiosis in Biocoenosis Optimization[133] 粗粒度方法自适应控制 EMT[103] 自编码器学习任务间线性映射 任务间知识迁移 MOMFEA-SADE[113] 子空间对齐策略 GMFEA[134] 个体均匀中心与样本均值之差 EMT-LTR[114] 学习任务关系 MFEA-Genetic transform strategy and Hyper-rectangle search strategy[135] 源域减后目标域加样本均值 ASCMFDE[115] 决策空间低维子空间的对齐矩阵 LDA-MFEA[136] 最小二乘法构建映射矩阵 AMTEA+${M_S}$[137] 神经网络对个体进行非线性匹配 -
[1] XU Qingzheng, WANG Na, WANG Lei, et al. Multi-task optimization and multi-task evolutionary computation in the past five years: A brief review[J]. Mathematics, 2021, 9(8): 864. doi: 10.3390/math9080864. [2] VERMA S, PANT M, and SNASEL V. A comprehensive review on NSGA-II for multi-objective combinatorial optimization problems[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 57757–57791. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3070634. [3] Osaba E, Del Ser J, Martinez A D, et al. Evolutionary multitask optimization: a methodological overview, challenges, and future research directions[J]. Cognitive Computation, 2022, 14(3): 927–954. doi: 10.1007/s12559-022-10012-8. [4] XU Qian, XU Zhanqi, and MA Tao. A survey of multiobjective evolutionary algorithms based on decomposition: Variants, challenges and future directions[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 41588–41614. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2973670. [5] LIU Xiaotong, SUN Chaoli, and WANG Hao. A new infill criterion based on sorting of approximation uncertainty for expensive evolutionary many-objective optimization[C]. IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Chicago, USA, 2023: 1–8. doi: 10.1109/CEC53210.2023.10405862. [6] NIMURA N and OYAMA A. Evolutionary topology optimization using quadtree genetic programming[C]. IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Padua, Italy, 2022: 1–8. doi: 10.1109/CEC55065.2022.9870331. [7] ZHAO Yizhe, LI Hao, WU Yue, et al. Endmember selection of hyperspectral images based on evolutionary multitask[C]. IEEE Congress on evolutionary computation (CEC), Glasgow, UK, 2020: 1–7. doi: 10.1109/CEC48606.2020.9185673. [8] 徐康宇, 刘元, 李密青, 等. 进化高维多目标优化研究综述[J]. 控制工程, 2023, 30(8): 1436–1449. doi: 10.14107/j.cnki.kzgc.20230186.XU Kangyu, LIU Yuan, LI Miqing, et al. Evolutionary many-objective optimization: A survey[J]. Control Engineering of China, 2023, 30(8): 1436–1449. doi: 10.14107/j.cnki.kzgc.20230186. [9] MA Xiaoliang, LI Xiaodong, ZHANG Qingfu, et al. A survey on cooperative co-evolutionary algorithms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2019, 23(3): 421–441. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2018.2868770. [10] 张峰, 陈新中. 连续昂贵多目标优化问题综述[J]. 软件导刊, 2023, 22(5): 248–252. doi: 10.11907/rjdk.221626.ZHANG Feng and CHEN Xinzhong. Survey of continuous expensive Multiobjective optimization problems[J]. Software Guide, 2023, 22(5): 248–252. doi: 10.11907/rjdk.221626. [11] 冯茜, 李擎, 全威, 等. 多目标粒子群优化算法研究综述[J]. 工程科学学报, 2021, 43(6): 745–753. doi: 10.13374/j.issn2095-9389.2020.10.31.001.FENG Qian, LI Qing, QUAN Wei, et al. Overview of multiobjective particle swarm optimization algorithm[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2021, 43(6): 745–753. doi: 10.13374/j.issn2095-9389.2020.10.31.001. [12] TIAN Ye, SI Langchun, ZHANG Xingyi, et al. Evolutionary large-scale multi-objective optimization: A survey[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2022, 54(8): 174. doi: 10.1145/3470971. [13] 高卫峰, 刘玲玲, 王振坤, 等. 基于分解的演化多目标优化算法综述[J]. 软件学报, 2023, 34(10): 4743–4771. doi: 10.13328/ j.cnki.jos.006672.GAO Weifeng, LIU Lingling, WANG Zhenkun, et al. Survey on multiobjective optimization evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition[J]. Journal of Software, 2023, 34(10): 4743–4771. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.006672. [14] 张维海, 彭称称, 蒋秀珊. 多目标动态优化中Pareto随机合作博弈研究综述[J]. 控制与决策, 2023, 38(7): 1789–1801. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2022.2097.ZHANG Weihai, PENG Chengcheng, and JIANG Xiushan. Pareto stochastic cooperative games in multiobjective dynamic optimization problems: A survey[J]. Control and Decision, 2023, 38(7): 1789–1801. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2022.2097. [15] LIANG Jing, BAN Xuanxuan, YU Kunjie, et al. A survey on evolutionary constrained multiobjective optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2023, 27(2): 201–221. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2022.3155533. [16] 李豪, 汪磊, 张元侨, 等. 演化多任务优化研究综述[J]. 软件学报, 2023, 34(2): 509–538. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.006704.LI Hao, WANG Lei, ZHANG Yuanqiao, et al. Survey of evolutionary multitasking optimization[J]. Journal of Software, 2023, 34(2): 509–538. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.006704. [17] TAN Ziying, LUO Linbo, and ZHONG Jinghui. Knowledge transfer in evolutionary multi-task optimization: A survey[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2023, 138: 110182. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2023.110182. [18] 程美英, 钱乾, 倪志伟. 多任务优化算法综述[J]. 控制与决策, 2023, 38(7): 1802–1815. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2021.1754.CHENG Meiying, QIAN Qian, and NI Zhiwei. Review of multi-task optimization algorithm[J]. Control and Decision, 2023, 38(7): 1802–1815. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2021.1754. [19] WEI Tingyang, WANG Shibin, ZHONG Jinghui, et al. A review on evolutionary multitask optimization: Trends and challenges[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2022, 26(5): 941–960. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2021.3139437. [20] 王丽萍, 林豪, 潘笑天, 等. 基于决策变量交互识别的多目标优化算法[J]. 浙江工业大学学报, 2021, 49(4): 355–367. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4303.2021.04.001.WANG Liping, LIN Hao, PAN Xiaotian, et al. Multi-objective optimization algorithm based on interactive identification of decision variables[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University of Technology, 2021, 49(4): 355–367. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4303.2021.04.001. [21] 白晓慧, 何小娟, 孙超利, 等. 基于决策变量分组的粒子群算法求解大规模优化问题[J]. 宁夏师范学院学报, 2020, 41(4): 50–56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1331.2020.04.008.BAI Xiaohui, HE Xiaojuan, SUN Chaoli, et al. Particle swarm optimization algorithm based on grouping of decision variables to solve large-scale optimization problems[J]. Journal of Ningxia Normal University, 2020, 41(4): 50–56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1331.2020.04.008. [22] 林涛, 霍丽娜. 基于变量分组的大规模多目标优化算法[J]. 郑州大学学报:理学版, 2018, 50(4): 8–13. doi: 10.13705/j.issn.1671-6841.2018037.LIN Tao and HUO Lina. Based on variable grouping for large-scale many-objective optimization algorithm[J]. Journal of Zhengzhou University:Natural Science Edition, 2018, 50(4): 8–13. doi: 10.13705/j.issn.1671-6841.2018037. [23] 邱飞岳, 胡烜, 王丽萍. 关联变量分组的分解多目标进化算法及其应用[J]. 小型微型计算机系统, 2018, 39(4): 644–650. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1220.2018.04.005.QIU Feiyue, HU Xuan, and WANG Liping. Multi-objective evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition using interacting variables grouping and its application[J]. Journal of Chinese Computer Systems, 2018, 39(4): 644–650. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1220.2018.04.005. [24] 邱飞岳, 胡烜, 王丽萍. 关联变量分组的分解多目标进化算法研究[J]. 计算机科学, 2017, 44(12): 202–210. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2017.12.037.QIU Feiyue, HU Xuan, and WANG Liping. Research on multi-objective evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition using interacting variables grouping[J]. Computer Science, 2017, 44(12): 202–210. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2017.12.037. [25] LI Xiaodong and YAO Xin. Cooperatively coevolving particle swarms for large scale optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2012, 16(2): 210–224. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2011.2112662. [26] YANG Zhenyu, TANG Ke, and YAO Xin. Differential evolution for high-dimensional function optimization[C]. IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Singapore, 2007: 3523–3530. doi: 10.1109/CEC.2007.4424929. [27] YANG Zhenyu, TANG Ke, and YAO Xin. Multilevel cooperative coevolution for large scale optimization[C]. IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Hong Kong, China, 2008: 1663–1670. doi: 10.1109/CEC.2008.4631014. [28] TRUNFIO G A. Enhancing the firefly algorithm through a cooperative coevolutionary approach: An empirical study on benchmark optimisation problems[J]. International Journal of Bio-Inspired Computation, 2014, 6(2): 108–125. doi: 10.1504/IJBIC.2014.060621. [29] TRUNFIO G A, TOPA P, and WAS J. A new algorithm for adapting the configuration of subcomponents in large-scale optimization with cooperative coevolution[J]. Information Sciences, 2016, 372: 773–795. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2016.08.080. [30] MEI Yi, OMIDVAR M N, LI Xiaodong, et al. A competitive divide-and-conquer algorithm for unconstrained large-scale black-box optimization[J]. ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software, 2016, 42(2): 1–24. doi: 10.1145/2791291. [31] STRASSER S, SHEPPARD J, FORTIER N, et al. Factored evolutionary algorithms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2017, 21(2): 281–293. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2016.2601922. [32] SUN Liang, YOSHIDA S, CHENG Xiaochun, et al. A cooperative particle swarm optimizer with statistical variable interdependence learning[J]. Information Sciences, 2012, 186(1): 20–39. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2011.09.033. [33] ZHANG Qingfu. On stability of fixed points of limit models of univariate marginal distribution algorithm and factorized distribution algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2004, 8(1): 80–93. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2003.819431. [34] PELIKAN M and MÜHLENBEIN H. The bivariate marginal distribution algorithm[C]. Engineering Design and Manufacturing on Advances in Soft Computing, London, UK, 1999: 521–535. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4471-0819-1_39. [35] DE BONET J S, ISBELL C L, and VIOLA P. MIMIC: Finding optima by estimating probability densities[C]. The 9th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Denver, USA, 1996: 424–430. doi: 10.5555/2998981.2999041. [36] YU Tianli, GOLDBERG D E, SASTRY K, et al. Dependency structure matrix, genetic algorithms, and effective recombination[J]. Evolutionary Computation, 2009, 17(4): 595–626. doi: 10.1162/evco.2009.17.4.17409. [37] POTTER M A and DE JONG K A. A cooperative coevolutionary approach to function optimization[C]. International Conference on Parallel Problem Solving from Nature, Jerusalem, Israel, 1994: 249–257. doi: 10.1007/3-540-58484-6_269. [38] VAN DEN BERGH F and ENGELBRECHT A P. A cooperative approach to particle swarm optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2004, 8(3): 225–239. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2004.826069. [39] ZHENG Yujun and CHEN Shengyong. Cooperative particle swarm optimization for multiobjective transportation planning[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2013, 39(1): 202–216. doi: 10.1007/s10489-012-0405-5. [40] SAYED E, ESSAM D, and SARKER R. Dependency identification technique for large scale optimization problems[C]. 2012 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Brisbane, Australia, 2012: 1–8. doi: 10.1109/CEC.2012.6256117. [41] 赵楷文, 王鹏, 童向荣. 基于双阶段搜索的约束进化多任务优化算法[J]. 计算机应用, 2024, 44(5): 1415–1422.ZHAO Kaiwen, WANG Peng, and TONG Xianggrong. Two-stage search-based constrained evolutionary multitasking optimization algorithm[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2024, 44(5): 1415–1422. [42] RAHNAMAYAN S, TIZHOOSH H R, and SALAMA M M A. A novel population initialization method for accelerating evolutionary algorithms[J]. Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 2007, 53(10): 1605–1614. doi: 10.1016/j.camwa.2006.07.013. [43] KANG R G and JUNG C Y. The optimal solution of TSP using the new mixture initialization and sequential transformation method in genetic algorithm[C]. 9th Pacific Rim International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Guilin, China, 2006: 1181–1185. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-36668-3_157. [44] GUTIN G and KARAPETYAN D. Generalized traveling salesman problem reduction algorithms[J]. arXiv: 0804.0735, 2008. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.0804.0735. [45] 杨磊, 张苏, 黄博, 等. 多任务协同优化学习高分辨SAR稀疏自聚焦成像算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(9): 2711–2719. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200300.YANG Lei, ZHANG Su, HUANG Bo, et al. Multi-task learning of sparse Autofocusing for high-resolution SAR imagery[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2021, 43(9): 2711–2719. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200300. [46] ISHIBUCHI H and YAMAMOTO T. Fuzzy rule selection by multi-objective genetic local search algorithms and rule evaluation measures in data mining[J]. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 2004, 141(1): 59–88. doi: 10.1016/S0165-0114(03)00114-3. [47] BLUM C, COTTA C, FERNÁNDEZ A J, et al. Hybridizations of metaheuristics with branch & bound derivates[M]. BLUM C, AGUILERA M J B, ROLI A, et al. Hybrid Metaheuristics: An Emerging Approach to Optimization. Berlin, Germany, 2008: 85–116. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-78295-7_4. [48] ALVARENGA G B, MATEUS G R, and DE TOMI G. Finding near optimal solutions for vehicle routing problems with time windows using hybrid genetic algorithm[C]. International Workshop Freight Transportation, Palermo, Italy, 2003: 113. [49] GALLARDO J E, COTTA C, and FERNÁNDEZ A J. Finding low autocorrelation binary sequences with memetic algorithms[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2009, 9(4): 1252–1262. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2009.03.005. [50] NERI F, KOTILAINEN N, and VAPA M. A memetic-neural approach to discover resources in P2P networks[M]. COTTA C and HEMERT J. Recent Advances in Evolutionary Computation for Combinatorial Optimization. Berlin, Germany, 2008: 113–129. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-70807-0_8. [51] LARA A, SANCHEZ G, COELLO C A C, et al. HCS: A new local search strategy for memetic multiobjective evolutionary algorithms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2010, 14(1): 112–132. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2009.2024143. [52] CAPONIO A, NERI F, and TIRRONEN V. Super-fit control adaptation in memetic differential evolution frameworks[J]. Soft Computing, 2009, 13(8): 811–831. doi: 10.1007/s00500-008-0357-1. [53] KRASNOGOR N and GUSTAFSON S. A study on the use of self-generation in memetic algorithms[J]. Natural Computing, 2004, 3(1): 53–76. doi: 10.1023/B:NACO.0000023419.83147.67. [54] 王志鸿, 王高才, 赵启飞. 基于改进NSGA-III的D2D协同MEC多目标优化研究[J]. 计算机科学, 2024, 51(3): 280–288. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.221100250.WANG Zhihong, WANG Gaocai, and ZHAO Qifei. Multi-objective optimization of D2D collaborative MEC based on improved NSGA-III[J]. Computer Science, 2024, 51(3): 280–288. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.221100250. [55] 李雪莹, 刘青青, 范勤勤. 基于算法自动选择的自适应约束多目标进化算法[J]. 控制工程, 2023: 1–9. doi: 10.14107/j.cnki.kzgc.20220224.LI Xueying, LIU Qingqing, and FAN Qinqin. Self-adaptive constrained multi-objective evolutionary algorithm based on algorithm automation selection[J]. Control Engineering of China, 2023: 1–9. doi: 10.14107/j.cnki.kzgc.20220224. [56] 程雪峰, 董明刚. 基于RNN信息累积的动态多目标优化算法[J]. 计算机科学, 2023, 45(10): 1–12.CHENG Xuefeng and DONG Minggang. Dynamic multi-objective optimization algorithm based on RNN information accumulation[J]. Computer Science, 2023, 45(10): 1–12. [57] GOLBERG D E. Genetic Algorithms in Search, Optimization and Machine Learning[M]. Boston, USA: Addison-Wesley, 1989: 36. [58] ZHANG Qingfu and LI Hui. MOEA/D: A multiobjective evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2007, 11(6): 712–731. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2007.892759. [59] 白富生, 陈姣伶. 基于聚类的昂贵多目标优化代理辅助进化算法[J]. 运筹学学报, 2022, 26(4): 31–42. doi: 10.15960/j.cnki.issn.1007-6093.2022.04.003.BAI Fusheng and CHEN Jiaoling. A clustering-based surrogate-assisted evolutionary algorithm for expensive multi-objective optimization[J]. Operations Research Transactions, 2022, 26(4): 31–42. doi: 10.15960/j.cnki.issn.1007-6093.2022.04.003. [60] HAN Honggui, FU Shijia, SUN Haoyuan, et al. Hierarchical nonlinear model predictive control with multi-time-scale for wastewater treatment process[J]. Journal of Process Control, 2021, 108: 125–135. doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2021.11.002. [61] FAN Qinqin, ZHANG Yilian, and LI Ning. An autoselection strategy of multiobjective evolutionary algorithms based on performance indicator and its application[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2022, 19(3): 2422–2436. doi: 10.1109/TASE.2021.3084741. [62] DONG Zhiming, WANG Xianpeng, and TANG Lixin. Color-coating scheduling with a multiobjective evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition and dynamic local search[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2021, 18(4): 1590–1601. doi: 10.1109/TASE.2020.3011428. [63] ALHARBI M, HONG Peiying, and LALEG-KIRATI T M. Sliding window neural network based sensing of bacteria in wastewater treatment plants[J]. Journal of Process Control, 2022, 110: 35–44. doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2021.12.006. [64] 焦大利, 姚亦飞, 王成章, 等. 基于双分类器辅助进化的多目标优化算法[J]. 北华大学学报:自然科学版, 2023, 24(5): 664–670. doi: 10.11713/j.issn.1009-4822.2023.05.020.JIAO Dali, YAO Yifei, WANG Chengzhang, et al. Multi-objective optimization evolutionary algorithm based on double classifier-assisted evolution[J]. Journal of Beihua University:Natural Science, 2023, 24(5): 664–670. doi: 10.11713/j.issn.1009-4822.2023.05.020. [65] HORN J, NAFPLIOTIS N, and GOLDBERG D E. A niched Pareto genetic algorithm for multiobjective optimization[C]. The 1st IEEE Conference on Evolutionary Computation, Orlando, USA, 1994: 82–87. doi: 10.1109/ICEC.1994.350037. [66] SRINIVAS N and DEB K. Muiltiobjective optimization using nondominated sorting in genetic algorithms[J]. Evolutionary Computation, 1994, 2(3): 221–248. doi: 10.1162/evco.1994.2.3.221. [67] 王旭健, 张峰干, 姚敏立. 基于聚类引导和目标值和的高维多目标进化算法[J]. 控制与决策, 2023, 38(10): 1–9. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2023.0596.WANG Xujian, ZHANG Fenggan, and YAO Minli. A many-objective evolutionary algorithm based on clustering and the sum of objectives[J]. Control and Decision, 2023, 38(10): 1–9. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2023.0596. [68] 曹嘉乐, 杨磊, 田井林, 等. 面向高维多目标优化的双阶段双种群进化算法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2024, 60(9): 159–171.CAO Jiale, YANG Lei, TIAN Jinglin, et al. Dual-stage dual-population evolutionary algorithm for many-objective optimization[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2024, 60(9): 159–171. [69] 高梦琦, 冯翔, 虞慧群, 等. 基于在线学习稀疏特征的大规模多目标进化算法[J]. 计算机科学, 2024, 51(3): 56–62. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.230100004.GAO Mengqi, FENG Xiang, YU Huiqun, et al. Large-scale multi-objective evolutionary algorithm based on online learning of sparse features[J]. Computer Science, 2024, 51(3): 56–62. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.230100004. [70] 谢承旺, 潘嘉敏, 郭华, 等. 一种采用混合策略的大规模多目标进化算法[J]. 计算机学报, 2024, 47(1): 69–89. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2024.00069.XIE Chengwang, PAN Jiamin, GUO Hua, et al. A large scale multi-objective evolutionary algorithm adopting hybrid strategies[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2024, 47(1): 69–89. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2024.00069. [71] SATO H, AGUIRRE H E, and TANAKA K. Controlling dominance area of solutions and its impact on the performance of MOEAs[C]. 4th International Conference on Evolutionary Multi-criterion Optimization, Matsushima, Japan, 2007: 5–20. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-70928-2_5. [72] DEB K, PRATAP A, AGARWAL S, et al. A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2002, 6(2): 182–197. doi: 10.1109/4235.996017. [73] DRECHSLER N, DRECHSLER R, and BECKER B. Multi-objective optimisation based on relation favour[C]. Proceedings of the First International Conference on Evolutionary Multi-criterion Optimization, Zurich, Switzerland, 2001: 154–166. doi: 10.1007/3-540-44719-9_11. [74] SÜLFLOW A, DRECHSLER N, and DRECHSLER R. Robust multi-objective optimization in high dimensional spaces[C]. 4th International Conference on Evolutionary Multi-criterion Optimization, Matsushima, Japan, 2007: 715–726. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-70928-2_54. [75] 王松波. 考虑帕累托最优解的多目标优化进化算法[J]. 数学的实践与认识, 2022, 52(9): 132–146.WANG Songbo. Multi-objective optimization evolutionary algorithm considering Pareto optimal solution[J]. Mathematics in Practice and Theory, 2022, 52(9): 132–146. [76] 梁正平, 林万鹏, 胡凯峰, 等. 基于帕累托前沿面曲率预估的超多目标进化算法[J]. 软件学报, 2023, 34(9): 4096–4113. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.006648.LIANG Zhengping, LIN Wanpeng, HU Kaifeng, et al. Many-objective evolutionary algorithm based on curvature estimation of Pareto front[J]. Journal of Software, 2023, 34(9): 4096–4113. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.006648. [77] FLEMING P J, PURSHOUSE R C, and LYGOE R J. Many-objective optimization: An engineering design perspective[C]. 3rd International Conference on Evolutionary Multi-Criterion Optimization, Guanajuato, Mexico, 2005: 14–32. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-31880-4_2. [78] DEB K and SUNDAR J. Reference point based multi-objective optimization using evolutionary algorithms[C]. The 8th Annual Conference on Genetic and Evolutionary Computation, Seattle, USA, 2006: 635–642. doi: 10.1145/1143997.1144112. [79] 谢根琳, 程国振, 梁浩, 等. 基于多目标优化算法NSGA-II的软件多样化组合方法[J]. 计算机科学, 2023, 45(10): 1–15.XIE Genlin, CHENG Guozhen, LAING Hao, et al. Software diversity composition based on multi-objective optimization algorithm NSGA-II[J]. Computer Science, 2023, 45(10): 1–15. [80] ORTIZ-MARTÍNEZ V M, MARTÍNEZ-FRUTOS J, HONTORIA E, et al. Multiplicity of solutions in model-based multiobjective optimization of wastewater treatment plants[J]. Optimization and Engineering, 2021, 22(2): 1–16. doi: 10.1007/s11081-020-09500-3. [81] HAN Honggui, LIU Zheng, LU Wei, et al. Dynamic MOPSO-based optimal control for wastewater treatment process[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021, 51(5): 2518–2528. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2019.2925534. [82] 张继旺, 刘锁, 龚庶, 等. 基于改进多目标粒子群的大型设备群检测策略优化方法[J]. 机电工程, 2024, 41(3): 504–511.ZHANG Jiwang, LIU Suo, GONG Shu, et al. Detection strategy optimization of large equipment group based on improved MOPSO algorithm[J]. Journal of Mechanical & Electrical Engineering, 2024, 41(3): 504–511. [83] 刘海林, 肖俊荣. 基于分解和超平面拟合的进化超多目标优化降维算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(9): 3289–3298. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210605.LIU Hailin and XIAO Junrong. Objective reduction algorithm based on decomposition and hyperplane approximation for evolutionary many-objective optimization[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(9): 3289–3298. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210605. [84] DEB K and SAXENA D. Searching for Pareto-optimal solutions through dimensionality reduction for certain large-dimensional multi-objective optimization problems[C]. IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Los Alamitos, USA, 2006: 3352–3360. [85] BROCKHOFF D and ZITZLER E. Improving hypervolume-based multiobjective evolutionary algorithms by using objective reduction methods[C]. IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Singapore, 2007: 2086–2093. doi: 10.1109/CEC.2007.4424730. [86] TAN K C, FENG Liang, and JIANG Min. Evolutionary transfer optimization—A new frontier in evolutionary computation research[J]. IEEE Computational Intelligence Magazine, 2021, 16(1): 22–33. doi: 10.1109/MCI.2020.3039066. [87] ZHAN Zhihui, SHI Lin, TAN K C, et al. A survey on evolutionary computation for complex continuous optimization[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2022, 55(1): 59–110. doi: 10.1007/s10462-021-10042-y. [88] ZHAN Zhihui, ZHANG Jun, LIN Ying, et al. Matrix-based evolutionary computation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computational Intelligence, 2022, 6(2): 315–328. doi: 10.1109/TETCI.2020.3047410. [89] LI Jianyu, ZHAN Zhihui, TAN K C, et al. A meta-knowledge transfer-based differential evolution for multitask optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2022, 26(4): 719–734. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2021.3131236. [90] LI Jianyu, ZHAN Zhihui, XU Jin, et al. Surrogate-assisted hybrid-model estimation of distribution algorithm for mixed-variable hyperparameters optimization in convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(5): 2338–2352. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3106399. [91] BALI K K, GUPTA A, ONG Y S, et al. Cognizant multitasking in multiobjective multifactorial evolution: MO-MFEA-II[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021, 51(4): 1784–1796. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.2981733. [92] LI Jianyu, ZHAN Zhihui, WANG Hua, et al. Data-driven evolutionary algorithm with perturbation-based ensemble surrogates[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021, 51(8): 3925–3937. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.3008280. [93] LI Jianyu, ZHAN Zhihui, LIU Rundong, et al. Generation-level parallelism for evolutionary computation: A pipeline-based parallel particle swarm optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021, 51(10): 4848–4859. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.3028070. [94] SUN Jianyong, LIU Xin, BÄCK T, et al. Learning adaptive differential evolution algorithm from optimization experiences by policy gradient[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2021, 25(4): 666–680. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2021.3060811. [95] 葛媛媛, 陈得宝, 邹锋. 多群多策略差分大规模多目标优化算法[J]. 控制与决策, 2024, 39(2): 429–439. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2022.1154.GE Yuanyuan, CHEN Debao, and ZOU Feng. A large-scale multi-objective optimization based on multi-population and multi-strategy differential algorithm[J]. Control and Decision, 2024, 39(2): 429–439. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2022.1154. [96] LIU Xiaofang, ZHAN Zhihui, and ZHANG Jun. Resource-aware distributed differential evolution for training expensive neural-network-based controller in power electronic circuit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(11): 6286–6296. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3075205. [97] YANG Ming, ZHOU Aimin, LI Changhe, et al. An efficient recursive differential grouping for large-scale continuous problems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2021, 25(1): 159–171. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2020.3009390. [98] CHEN Zonggan, LIN Ying, GONG Yuejiao, et al. Maximizing lifetime of range-adjustable wireless sensor networks: A neighborhood-based estimation of distribution algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021, 51(11): 5433–5444. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.2977858. [99] ZHANG Xin, ZHAN Zhihui, FANG Wei, et al. Multipopulation ant colony system with knowledge-based local searches for multiobjective supply chain configuration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2022, 26(3): 512–526. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2021.3097339. [100] FENG Liang, ZHOU Wei, LIU Weichen, et al. Solving dynamic multiobjective problem via autoencoding evolutionary search[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(5): 2649–2662. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.3017017.71. [101] 程美英, 钱乾, 熊伟清. 信息迁移多任务优化共生生物搜索算法[J]. 计算机应用, 2023, 43(7): 2237–2247. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2022060896.CHENG Meiying, QIAN Qian, and XIONG Weiqing. Symbiotic organisms search algorithm for information transfer multi-task optimization[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2023, 43(7): 2237–2247. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2022060896. [102] GUPTA A, ONG Y S, and FENG Liang. Multifactorial evolution: Toward evolutionary multitasking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2016, 20(3): 343–357. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2015.2458037. [103] FENG Liang, ZHOU Lei, ZHONG Jinghui, et al. Evolutionary multitasking via explicit autoencoding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2019, 49(9): 3457–3470. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2845361. [104] YUAN Yuan, ONG Y S, GUPTA A, et al. Evolutionary multitasking in permutation-based combinatorial optimization problems: Realization with TSP, QAP, LOP, and JSP[C]. 2016 IEEE Region 10 Conference (TENCON), Singapore, 2016: 3157–3164. doi: 10.1109/TENCON.2016.7848632. [105] 程美英, 钱乾, 倪志伟, 等. 信息筛选多任务优化自组织迁移算法[J]. 计算机应用, 2021, 41(6): 1748–1755. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2020091390.CHENG Meiying, QIAN Qian, NI Zhiwei, et al. Self-organized migrating algorithm for multi-task optimization with information filtering[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2021, 41(6): 1748–1755. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2020091390. [106] 程美英, 钱乾, 倪志伟. 基于种群多样性控制的多级信息迁移多任务优化粒子群算法[J]. 控制与决策, 2024, 39(3): 728–738. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2022.1195.CHENG Meiying, QIAN Qian, and NI Zhiwei. Multi-level information transfer multi-task PSO based on population diversity control[J]. Control and Decision, 2024, 39(3): 728–738. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2022.1195. [107] BALI K K, ONG Y S, GUPTA A, et al. Multifactorial evolutionary algorithm with online transfer parameter estimation: MFEA-II[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2020, 24(1): 69–83. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2019.2906927. [108] LIN Jiabin, LIU Hailin, TAN K C, et al. An effective knowledge transfer approach for multiobjective multitasking optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 51(6): 3238–3248. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.2969025. [109] 马慧, 冯翔, 虞慧群. 基于两层知识迁移的多代理多任务优化方法[J]. 计算机科学, 2023, 50(10): 203–213. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.220900242.MA Hui, FENG Xiang, and YU Huiqun. Multi-surrogate multi-task optimization approach based on two-layer knowledge transfer[J]. Computer Science, 2023, 50(10): 203–213. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.220900242. [110] SONG Hui, QIN A K, TSAI P W, et al. Multitasking multi-swarm optimization[C]. IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Wellington, New Zealand, 2019: 1937–1944. doi: 10.1109/CEC.2019.8790009. [111] YIN Jian, ZHU Anmin, ZHU Zexuan, et al. Multifactorial evolutionary algorithm enhanced with cross-task search direction[C]. The IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Wellington, New Zealand, 2019: 2244–2251. doi: 10.1109/CEC.2019.8789959. [112] FENG Yinglan, FENG Liang, HOU Yaqing, et al. Large-scale optimization via evolutionary multitasking assisted random embedding[C]. The IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 1–8. doi: 10.1109/CEC48606.2020.9185660. [113] LIANG Zhengping, DONG Hao, LIU Cheng, et al. Evolutionary multitasking for multiobjective optimization with subspace alignment and adaptive differential evolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(4): 2096–2109. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.2980888. [114] CHEN Zefeng, ZHOU Yuren, and HE Xiaoyu. Learning task relationships in evolutionary multitasking for multiobjective continuous optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 52(6): 5278–5289. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.3029176. [115] TANG Zedong, GONG Maoguo, WU Yue, et al. Regularized evolutionary multitask optimization: Learning to intertask transfer in aligned subspace[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2021, 25(2): 262–276. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2020.3023480. [116] SEENIVASAN L, MITHERAN S, ISLAM M, et al. Global-reasoned multi-task learning model for surgical scene understanding[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2022, 7(2): 3858–3865. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2022.3146544. [117] LIU Yiqi, YUAN Jingyi, CAI Baoping, et al. Multi-step and multi-task learning to predict quality-related variables in wastewater treatment processes[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2023, 180: 404–416. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2023.10.015. [118] BA-ALAWI A H, AL-MASNI M A, and YOO C. Simultaneous sensor fault diagnosis and reconstruction for intelligent monitoring in wastewater treatment plants: An explainable deep multi-task learning model[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2023, 55: 104119. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2023.104119. [119] HAN Honggui, BAI Xing, YANG Hongyan, et al. Multitask particle swarm optimization with dynamic transformation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computing, 2023, 11(3): 749–763. doi: 10.1109/TETC.2023.3268182. [120] HAN Honggui, BAI Xing, HOU Ying, et al. Adaptive multi-task optimization strategy for wastewater treatment process[J]. Journal of Process Control, 2022, 119: 44–54. doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2022.09.007. [121] 唐枫, 冯翔, 虞慧群. 基于自适应知识迁移与资源分配的多任务协同优化算法[J]. 计算机科学, 2022, 49(7): 254–262. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.210600184.TANG Feng, FENG Xiang, and YU Huiqun. Multi-task cooperative optimization algorithm based on adaptive knowledge transfer and resource allocation[J]. Computer Science, 2022, 49(7): 254–262. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.210600184. [122] GU A, LU Songtao, RAM P, et al. Min-max bilevel multi-objective optimization with applications in machine learning[J]. arXiv: 2203.01924, 2022. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2203.01924. [123] HU Quanqi, ZHONG Yongjian, and YANG Tianbao. Multi-block min-max bilevel optimization with applications in multi-task deep AUC maximization[C]. Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 29552–29565. [124] 邱鸿辉, 刘海林, 陈磊. 基于协方差矩阵调整的多目标多任务优化算法[J]. 计算机工程, 2022, 48(8): 306–312. doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0062365.QIU Honghui, LIU Hailin, and CHEN Lei. Multi-objective multi-tasking optimization algorithm based on adjustment of covariance matrix[J]. Computer Engineering, 2022, 48(8): 306–312. doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0062365. [125] ZHOU Lei, FENG Liang, ZHONG Jinghui, et al. A study of similarity measure between tasks for multifactorial evolutionary algorithm[C]. The Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference Companion, Kyoto, Japan, 2018: 229–230. doi: 10.1145/3205651.3205736. [126] GUPTA A, ONG Y S, DA B, et al. Landscape synergy in evolutionary multitasking[C]. The IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Vancouver, Canada, 2016: 3076–3083. doi: 10.1109/CEC.2016.7744178. [127] SHANG Qingxia, ZHANG Liangjie, FENG Liang, et al. A preliminary study of adaptive task selection in explicit evolutionary many-tasking[C]. IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Wellington, New Zealand, 2019: 2153–2159. doi: 10.1109/CEC.2019.8789909. [128] HUANG Shijia, ZHONG Jinghui, and YU Weijie. Surrogate-assisted evolutionary framework with adaptive knowledge transfer for multi-task optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computing, 2021, 9(4): 1930–1944. doi: 10.1109/TETC.2019.2945775. [129] ZHANG Jun, ZHOU Weien, CHEN Xianqi, et al. Multisource selective transfer framework in multiobjective optimization problems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2020, 24(3): 424–438. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2019.2926107. [130] TANG Jing, CHEN Yingke, DENG Zixuan, et al. A group-based approach to improve multifactorial evolutionary algorithm[C]. The 27th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 3870–3876. doi: 10.5555/3304222.3304307. [131] DA Bingshui, GUPTA A, and ONG Y S. Curbing negative influences online for seamless transfer evolutionary optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2019, 49(12): 4365–4378. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2864345. [132] MIN A T W, ONG Y S, GUPTA A, et al. Multiproblem surrogates: Transfer evolutionary multiobjective optimization of computationally expensive problems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2019, 23(1): 15–28. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2017.2783441. [133] LIAW R T and TING C K. Evolutionary manytasking optimization based on symbiosis in biocoenosis[C]. The AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, USA, 2019: 4295–4303. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v33i01.33014295. [134] DING Jinliang, YANG Cuie, JIN Yaochu, et al. Generalized multitasking for evolutionary optimization of expensive problems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2019, 23(1): 44–58. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2017.2785351. [135] LIANG Zhengping, ZHANG Jian, FENG Liang, et al. A hybrid of genetic transform and hyper-rectangle search strategies for evolutionary multi-tasking[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2019, 138: 112798. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2019.07.015. [136] BALI K K, GUPTA A, FENG Liang, et al. Linearized domain adaptation in evolutionary multitasking[C]. The IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Donostia, Spain, 2017: 1295–1302. doi: 10.1109/CEC.2017.7969454. [137] LIM R, GUPTA A, ONG Y S, et al. Non-linear domain adaptation in transfer evolutionary optimization[J]. Cognitive Computation, 2021, 13(2): 290–307. doi: 10.1007/s12559-020-09777-7. [138] XUE Xiaoming, ZHANG Kai, TAN K C, et al. Affine transformation-enhanced multifactorial optimization for heterogeneous problems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(7): 6217–6231. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.3036393. [139] HUBENKO V P, RAINES R A, MILLS R F, et al. Improving the global information grid’s performance through satellite communications layer enhancements[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2006, 44(11): 66–72. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2006.248167. [140] 刘明骞, 高晓腾, 李明, 等. 空地协同场景下通信干扰智能识别方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(3): 825–834. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211260.LIU Mingqian, GAO Xiaoteng, LI Ming, et al. Communication interference intelligent recognition in the air-to-ground collaboration scenario[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(3): 825–834. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211260. [141] LYU Feng, YANG Ping, WU Huaqing, et al. Service-oriented dynamic resource slicing and optimization for space-air-ground integrated vehicular networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(7): 7469–7483. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2021.3070542. [142] WANG Guangchao, ZHOU Sheng, NIU Zhisheng, et al. Service function chain planning with resource balancing in space-air-ground integrated networks[C]. 2019 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Waikoloa, USA, 2019: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/GLOBECOM38437.2019.9013557. [143] KREUTZ D, RAMOS F M V, VERÍSSIMO P E, et al. Software-defined networking: A comprehensive survey[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2015, 103(1): 14–76. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2014.2371999. [144] DE JESUS GIL HERRERA J and VEGA J F B. Network functions virtualization: A survey[J]. IEEE Latin America Transactions, 2016, 14(2): 983–997. doi: 10.1109/TLA.2016.7437249. [145] PROMWONGSA N, EBRAHIMZADEH A, GLITHO R H, et al. Joint VNF placement and scheduling for latency-sensitive services[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2022, 9(4): 2432–2449. doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2022.3163927. [146] OLADEJO S O and FALOWO O E. 5G network slicing: A multi-tenancy scenario[C]. 2017 Global Wireless Summit (GWS), Cape Town, South Africa, 2017: 88–92. doi: 10.1109/GWS.2017.8300476. [147] 付书航, 周笛, 盛敏, 等. 空天地海一体化网络体系架构与网络切片技术[J]. 移动通信, 2021, 45(5): 8–14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.2021.05.002.FU Shuhang, ZHOU Di, SHENG Min, et al. An architecture and network slicing technology in space-air-ground-sea integrated network[J]. Mobile Communications, 2021, 45(5): 8–14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.2021.05.002. [148] DAI Hongning, WU Yulei, IMRAN M, et al. Integration of blockchain and network softwarization for space-air-ground-sea integrated networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Magazine, 2022, 5(1): 166–172. doi: 10.1109/IOTM.004.2100098. [149] 李克强, 李家文, 常雪阳, 等. 智能网联汽车云控系统原理及其典型应用[J]. 汽车安全与节能学报, 2020, 11(3): 261–275. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8484.2020.03.001.LI Keqiang, LI Jiawen, CHANG Xueyang, et al. Principles and typical applications of cloud control system for intelligent and connected vehicles[J]. Journal of Automotive Safety and Energy, 2020, 11(3): 261–275. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8484.2020.03.001. [150] CAI Kunhai, TIAN Yanling, LIU Xianping, et al. Modeling and controller design of a 6-DOF precision positioning system[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2018, 104: 536–555. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2017.11.002. [151] 何欣枫, 田俊峰, 娄健. 面向边缘计算的可信协同框架[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(12): 4256–4264. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211045.HE Xinfeng, TIAN Junfeng, and LOU Jian. Collaborative trustworthy framework for edge computing[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(12): 4256–4264. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211045. [152] 张红霞, 吕智豪, 席诗语, 等. 面向绿色计算的车辆协同任务卸载方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(1): 175–183. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230051.ZHANG Hongxia, LÜ Zhihao, XI Shiyu, et al. A method for offloading vehicle collaborative tasks for green computing[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(1): 175–183. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230051. [153] 王练, 闫润搏, 徐静. 车载边缘计算中多任务部分卸载方案研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(3): 1094–1101. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211620.WANG Lian, YAN Runbo, and XU Jing. Research on multi-task partial offloading scheme in vehicular edge computing[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(3): 1094–1101. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211620. [154] 邵苏杰, 柴睿均, 郭少勇, 等. 基于位置预测的智慧公路边缘任务协同机制[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(4): 1154–1162. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220279.SHAO Sujie, CHAI Ruijun, GUO Shaoyong, et al. A collaborative mechanism for smart highway edge tasks based on location prediction[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(4): 1154–1162. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220279. [155] TONG Liang, LI Yong, and GAO Wei. A hierarchical edge cloud architecture for mobile computing[C]. IEEE INFOCOM 2016 - The 35th Annual IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications, San Francisco, USA, 2016: 1–9. doi: 10.1109/INFOCOM.2016.7524340. [156] 董裕民, 张静, 谢昌佐, 等. 云边端架构下边缘智能计算关键问题综述: 计算优化与计算卸载[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(3): 765–776. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230390.DONG Yumin, ZHANG Jing, XIE Changzuo, et al. A survey of key issues in edge intelligent computing under cloud-edge-terminal architecture: Computing optimization and computing offloading[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(3): 765–776. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230390. [157] 周天清, 曾新亮, 胡海琴. 基于混合粒子群算法的计算卸载成本优化[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(9): 3065–3074. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211390.ZHOU Tianqing, ZENG Xinliang, and HU Haiqin. Computation offloading cost optimization based on hybrid particle swarm optimization algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(9): 3065–3074. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211390. [158] TULI S, MAHMUD R, TULI S, et al. Fogbus: A blockchain-based lightweight framework for edge and fog computing[J]. Journal of Systems and Software, 2019, 154: 22–36. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2019.04.050. [159] LI Meng, ZHU Liehuang, and LIN Xiaodong. Efficient and privacy-preserving carpooling using blockchain-assisted vehicular fog computing[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(3): 4573–4584. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2868076. [160] 麦伟杰, 刘伟莉, 钟竞辉. 基于机器学习的演化多任务优化框架[J]. 计算机学报, 2024, 47(1): 29–51. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2024.00029.MAI Weijie, LIU Weili, and ZHONG Jinghui. Evolutionary many-task optimization framework based on machine learning[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2024, 47(1): 29–51. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2024.00029. [161] 胡智勇, 于千城, 王之赐, 等. 基于多目标优化的联邦学习进化算法[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2024, 41(2): 415–420,437. doi: 10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2023.05.0235.HU Zhiyong, YU Qiancheng, WANG Zhici, et al. Federated learning evolutionary algorithm based on multi-objective optimization[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2024, 41(2): 415–420,437. doi: 10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2023.05.0235. -





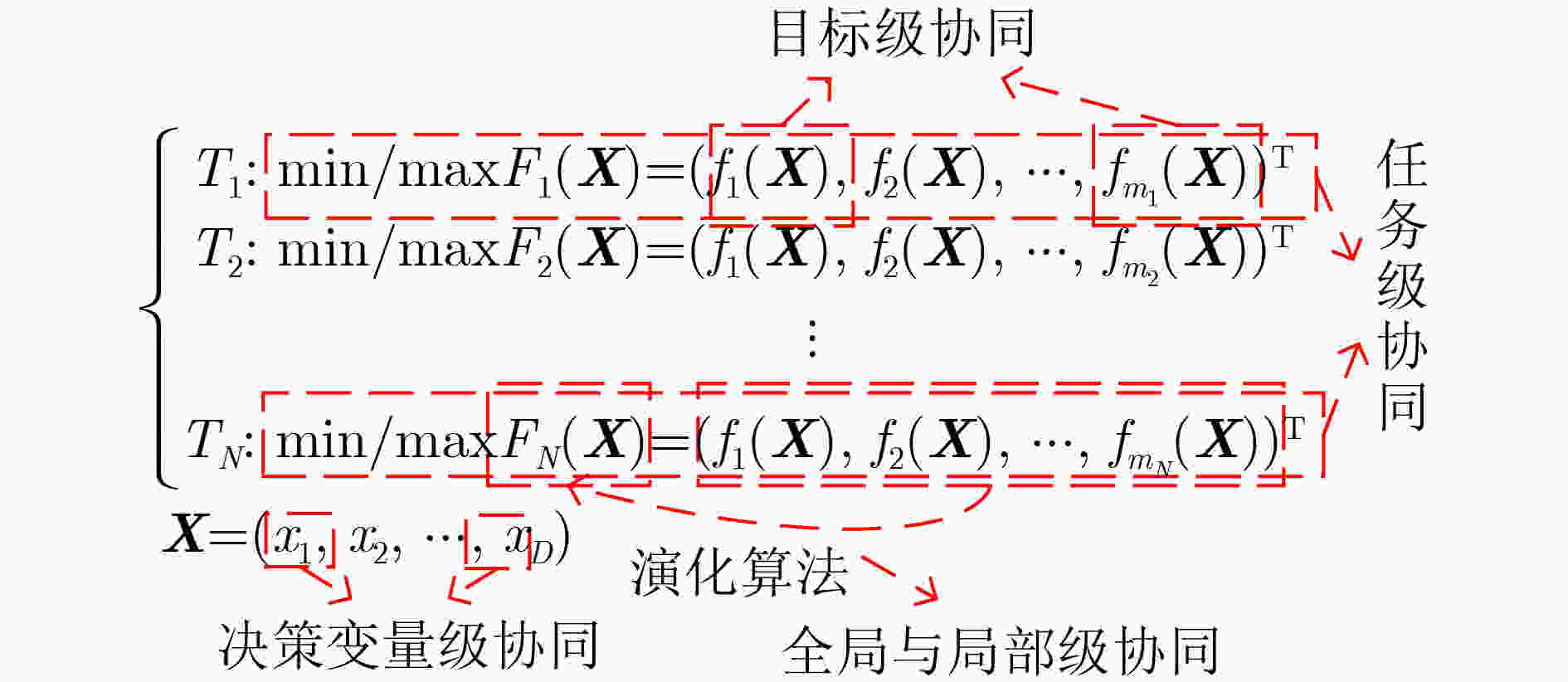
 下载:
下载:
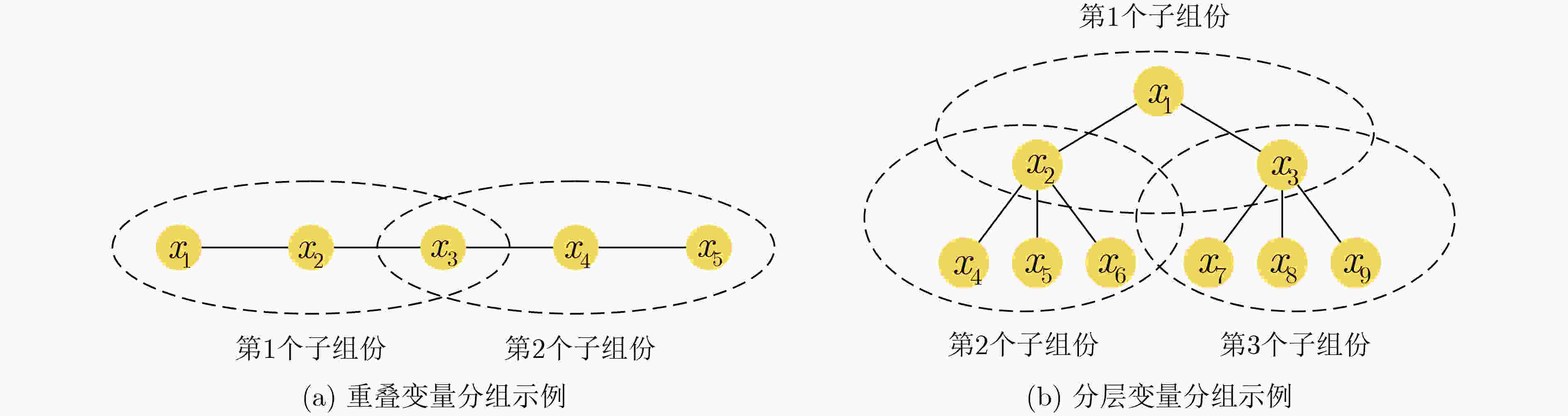

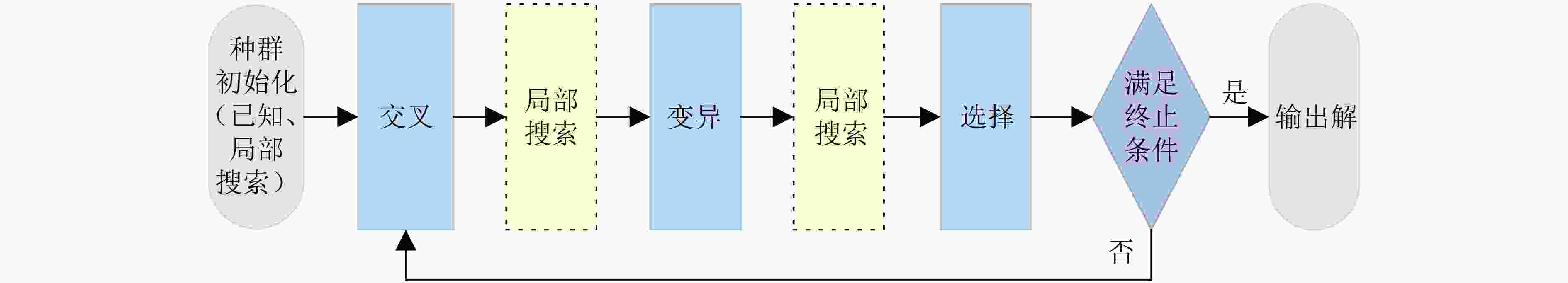
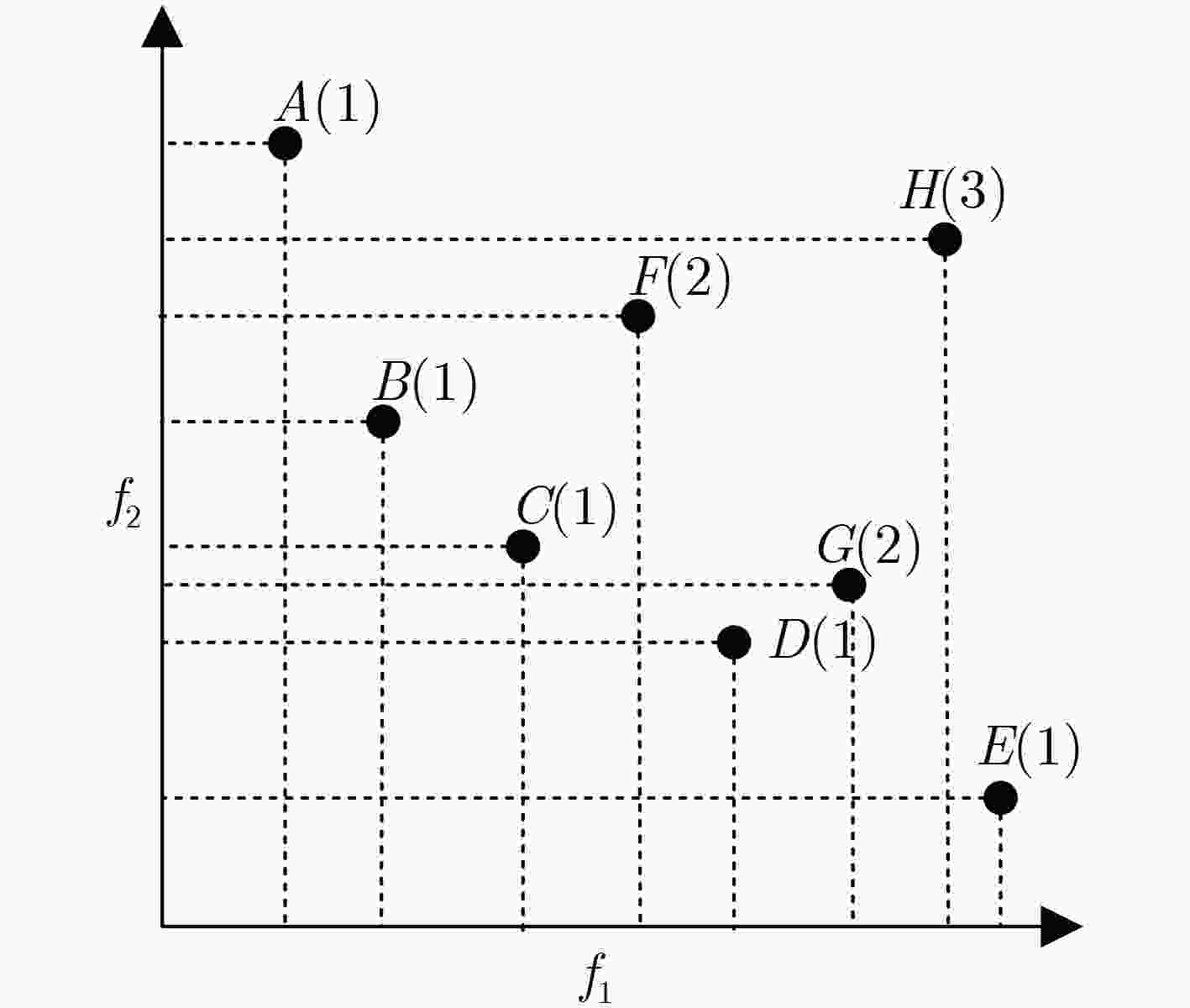


 下载:
下载:
