Design of High Throughput True Random Number Generator Based on Metastability Superposition Cells
-
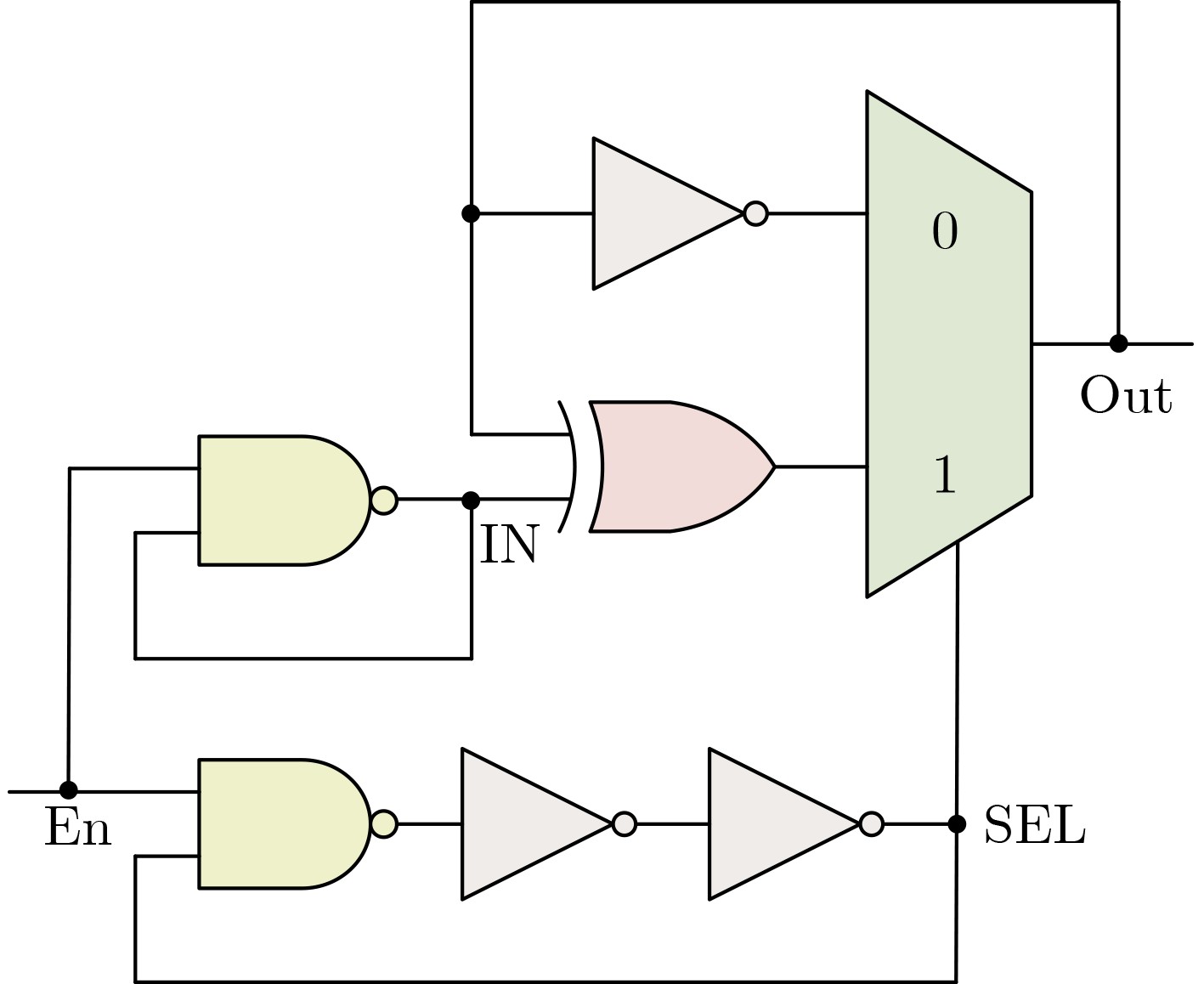
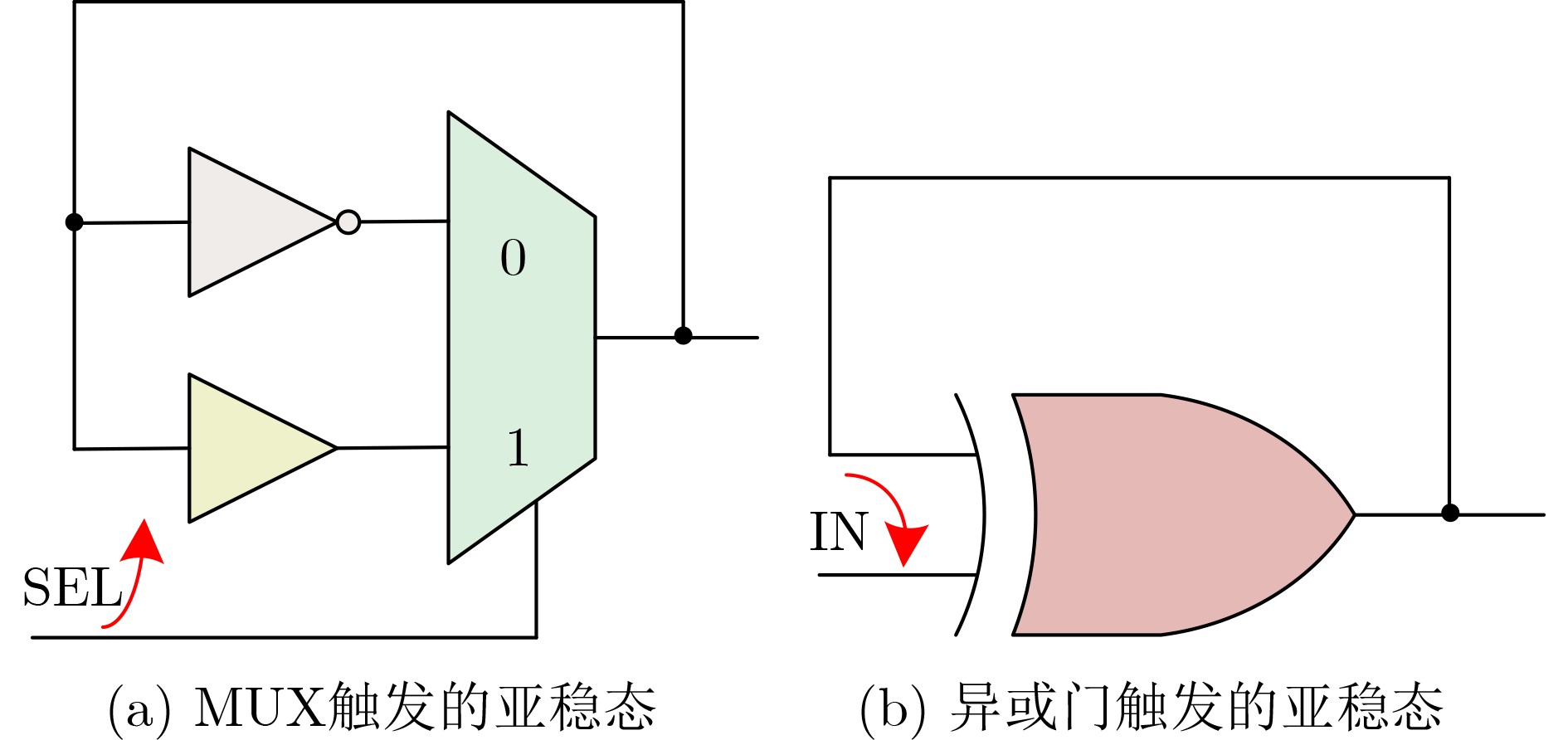
摘要: 真随机数发生器(TRNG)作为一类重要的硬件安全原语,在密钥生成、初始化向量和协议中的身份认证等加密领域得到应用。为设计出高吞吐量的轻量级TRNG,该文研究了利用多路选择器(MUX)和异或门(XOR gate)的开关特性来产生亚稳态的方法,提出一种基于亚稳态叠加单元(MS-cell)的TRNG(MS-TRNG)设计。它将MUX和异或门触发的亚稳态进行叠加,从而提高TRNG的熵。所提TRNG分别在Xilinx Virtex-7和Xilinx Artix-7 FPGA开发板中实现,无需后处理电路。与其他先进的TRNG相比,所提TRNG具有最高的吞吐量和极低的硬件开销,并且它所生成的随机序列通过了NIST测试和一系列性能测试。Abstract: True Random Number Generator (TRNG), as an important hardware security primitive, is used in key generation, initialization vector and identity authentication in protocols. In order to design a lightweight TRNG with high throughput, the method of generating metastability is studied by using the switching characteristics of MUltipleXer (MUX) and XOR gate, and a TRNG design based on Metastability Superposition (MS-TRNG) cell (MS-cell) is proposed. It superimposes MUX and XOR gate guided metastases, thereby increasing the entropy of TRNG. The proposed TRNG is implemented in Xilinx Virtex-7 and Xilinx Artix-7 FPGA development boards, respectively, without the need for post-processing circuits. Compared to other advanced TRNGS, the proposed TRNG has the highest throughput and extremely low hardware overhead, and the random sequences it generates pass NIST testing and a series of performance tests.
-
表 1 MS-cell的工作模式
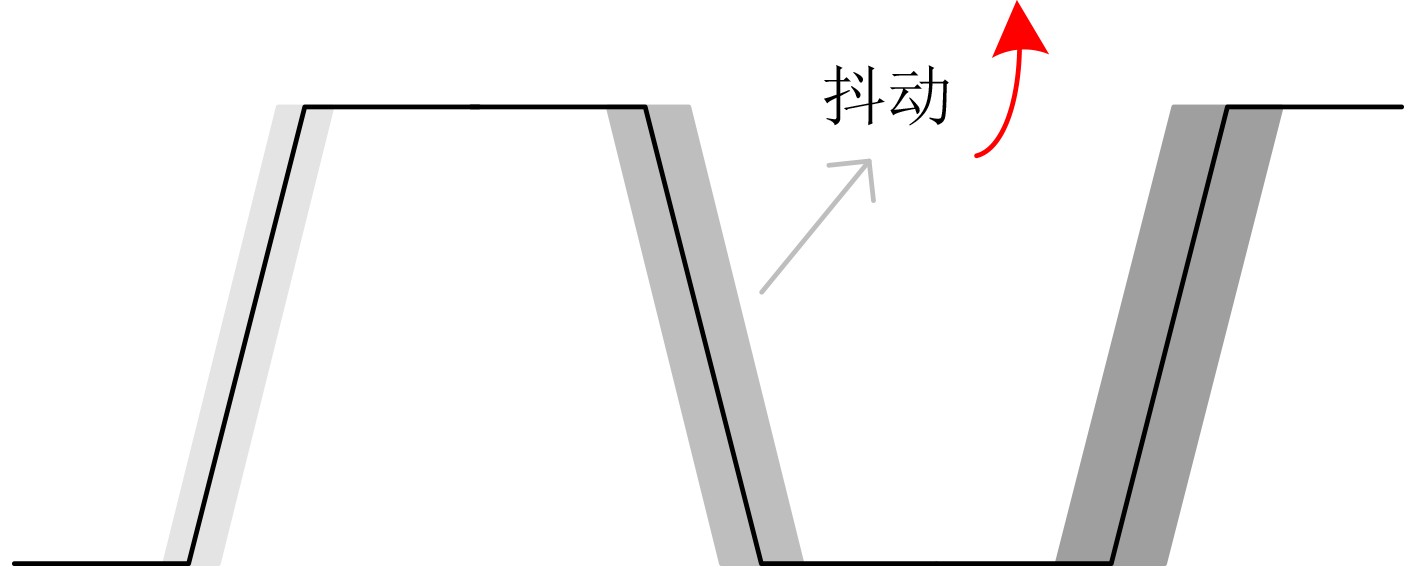
SEL脉冲 IN脉冲 熵源 ↘ × 反相器触发的抖动 0 × 反相器触发的抖动 ↗ ↘ MUX与异或门触发的亚稳态叠加 ↗ 0 MUX触发的亚稳态 ↗ ↗ 异或门触发的抖动 ↗ 1 异或门触发的抖动 1 ↘ 异或门触发的亚稳态 1 0 无熵源(保持) 1 ↗ 异或门触发的抖动 1 1 异或门触发的抖动 表 2 NIST SP 800-22测试结果
测试项目 Artix-7 Virtex-7 P值 通过率 总体 P值 通过率 总体 近似熵检测 0.503917 99 通过 0.509126 98 通过 块内频数检测 0.510257 100 通过 0.480771 98 通过 累加和检测 0.537681 100 通过 0.466125 98 通过 离散傅里叶变换检测 0.454209 99 通过 0.522061 100 通过 频率检测 0.546769 99 通过 0.460289 98 通过 线性复杂度检测 0.461250 99 通过 0.474038 98 通过 块内最长运行检测 0.510434 100 通过 0.522953 99 通过 非重叠模板匹配检测 0.495718 99 通过 0.500575 99 通过 重叠模板匹配检测 0.465718 99 通过 0.507311 99 通过 随机偏移检测 0.271823 98 通过 0.310572 99 通过 随机偏移变化检测 0.270109 99 通过 0.315353 98 通过 2元矩阵秩检测 0.526488 98 通过 0.495522 100 通过 运行检测 0.550720 97 通过 0.554121 98 通过 序列检测 0.496321 97 通过 0.515058 100 通过 通用统计检测 0.478454 100 通过 0.476515 99 通过 表 3 NIST SP 800-90B Non-IID测试结果
测试项目 Artix-7 Virtex-7 P (max) h-min P (max) h-min 最频值 0.501712 0.995069 0.501694 0.995120 碰撞 0.537109 0.896712 0.539062 0.891476 马尔可夫 4.0306e–39 0.996439 4.4813e–39 0.995244 压缩 0.5 1 0.506836 0.980409 元组 0.526629 0.925141 0.519390 0.945111 最长重复字串长度 0.502963 0.991475 0.501607 0.995369 多个MCW 0.501673 0.995182 0.500678 0.998046 滞后 0.500954 0.997251 0.500901 0.997404 多个MMC 0.500685 0.998025 0.501520 0.995621 LZ78Y算法 0.501425 0.995896 0.500968 0.997211 表 4 NIST SP 800-90B IID测试结果
测试项目 Artix-7 Result Virtex-7 Result IID 置换检验 通过 通过 卡方独立检验 通过 通过 卡方拟合优度检验 通过 通过 最长重复字串长度测试 通过 通过 重启动测试 通过 通过 最小熵测试 0.995069 0.995120 表 5 与其他先进TRNG的对比
方法 熵源 硬件资源 吞吐量(Mbit/s) 功耗(mW) 后处理电路 [9] 抖动 50LUTs/79FFs 280.0 – 有 [12] 抖动 56LUTs/19FFs 100.0 1.150 有 [14] 抖动 24LUTs/2FFs 290.0 3703.000 无 [16] 抖动 32LUTs/55FFs/33Slices 12.5 9.514 无 [19] 亚稳态 38LUTs/121FFs/38Slices 300.0 119.000 有 [24] 抖动+亚稳态 271LUTs/199Cells 1.0 90.000 有 [25] 抖动+亚稳态 36LUTs/0FFs 12.5 – 无 [26] 抖动 37LUTs/25FFs 160.0 – 无 本文 抖动+亚稳态 29LUTs/4FFs 500.0 123.000 无 -
[1] CORRIGAN-GIBBS H, MU W, BONEH D, et al. Ensuring high-quality randomness in cryptographic key generation[C]. 2013 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer & Communications Security, Berlin, Germany, 2013: 685–696. doi: 10.1145/2508859.2516680. [2] CHAKRABORTY S, GARG A, and SURI M. True random number generation from commodity NVM chips[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2020, 67(3): 888–894. doi: 10.1109/TED.2019.2963203. [3] YANG Bohan, ROŽIC V, GRUJIC M, et al. ES-TRNG: A high-throughput, low-area true random number generator based on edge sampling[J]. IACR Transactions on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems, 2018, 2018(3): 267–292. doi: 10.13154/tches.v2018.i3.267-292. [4] TANG Qianying, KIM B, LAO Yingjie, et al. True random number generator circuits based on single- and multi-phase beat frequency detection[C]. IEEE 2014 Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, San Jose, USA, 2014: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/CICC.2014.6946136. [5] ROBOSON S, LEUNG B, and GONG G. Truly random number generator based on a ring oscillator utilizing last passage time[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II:Express Briefs, 2014, 61(12): 937–941. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2014.2362715. [6] KWOK S H M and LAM E Y. FPGA-based high-speed true random number generator for cryptographic applications[C]. 2006 IEEE Region 10 Conference, Hong Kong, China, 2006: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/TENCON.2006.344013. [7] FISCHER V, DRUTAROVSKÝ M, ŠIMKA M, et al. High performance true random number generator in Altera stratix FPLDs[C]. 14th International Conference and Field Programmable Logic and Application, Leuven, Belgium, 2004: 555–564. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-30117-2_57. [8] MEITEI H B and KUMAR M. FPGA implantations of TRNG architecture using ADPLL based on FIR filter as a loop filter[J]. SN Applied Sciences, 2022, 4(4): 96. doi: 10.1007/s42452-022-04981-6. [9] LIN Jianming, WANG Yonggang, ZHAO Zelong, et al. A new method of true random number generation based on Galois ring oscillator with event sampling architecture in FPGA[C]. 2020 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference, Dubrovnik, Croatia, 2020: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/I2MTC43012.2020.9129357. [10] GOLIC J D J. New methods for digital generation and postprocessing of random data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2006, 55(10): 1217–1229. doi: 10.1109/TC.2006.164. [11] DICHTL M. Fibonacci ring oscillators as true random number generators—a security risk[J]. IACR Cryptology ePrint Archive, 2015, 2015: 270. [12] WANG Xinyu, LIANG Huaguo, WANG Yanjie, et al. High-throughput portable true random number generator based on jitter-latch structure[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2021, 68(2): 741–750. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2020.3037173. [13] GU Haoang, DENG Fangyu, WANG Qin, et al. A four-phase self-timed ring based true random number generator on FPGA[C]. 2022 IEEE 16th International Conference on Solid-State & Integrated Circuit Technology (ICSICT), Nangjing, China, 2022: 1–3. doi: 10.1109/ICSICT55466.2022.9963322. [14] CUI Jianguo, YI Maoxiang, CAO Di, et al. Design of true random number generator based on multi-stage feedback ring oscillator[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II:Express Briefs, 2022, 69(3): 1752–1756. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2021.3111049. [15] PARK J, KIM B, and SIM J Y. A PVT-tolerant oscillation-collapse-based true random number generator with an odd number of inverter stages[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II:Express Briefs, 2022, 69(10): 4058–4062. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2022.3184950. [16] GRUJIĆ M and VERBAUWHEDE I. TROT: A three-edge ring oscillator based true random number generator with time-to-digital conversion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2022, 69(6): 2435–2448. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2022.3158022. [17] DI PATRIZIO STANCHIERI G, DE MARCELLIS A, PALANGE E, et al. A true random number generator architecture based on a reduced number of FPGA primitives[J]. AEU - International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 2019, 105: 15–23. doi: 10.1016/j.aeue.2019.03.006. [18] MAJZOOBI M, KOUSHANFAR F, and DEVADAS S. FPGA-based true random number generation using circuit metastability with adaptive feedback control[C]. 13th International Workshop on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems, Nara, Japan, 2011: 17–32. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-23951-9_2. [19] FRUSTACI F, SPAGNOLO F, PERRI S, et al. A high-speed FPGA-based true random number generator using metastability with clock managers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II:Express Briefs, 2023, 70(2): 756–760. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2022.3211278. [20] WIECZOREK P Z. Dual-metastability FPGA-based true random number generator[J]. Electronics Letters, 2013, 49(12): 744–745. doi: 10.1049/el.2012.4126. [21] VON NEUMANN J. Various techniques used in connection with random digits[J]. National Bureau of Standards Applied Mathematics Series, 1951, 12: 36–38. [22] WIECZOREK P Z. An FPGA implementation of the resolve time-based true random number generator with quality control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2014, 61(12): 3450–3459. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2014.2338615. [23] JIN Liyu, YI Maoxiang, XIAO Yuan, et al. A dynamically reconfigurable entropy source circuit for high-throughput true random number generator[J]. Microelectronics Journal, 2023, 133: 105690. doi: 10.1016/j.mejo.2023.105690. [24] WIECZOREK P Z. Lightweight TRNG based on multiphase timing of bistables[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2016, 63(7): 1043–1054. doi: 10.1109/tcsi.2016.2555248. [25] DELLA SALA R, BELLIZIA D, and SCOTTI G. High-throughput FPGA-compatible TRNG architecture exploiting multistimuli metastable cells[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2022, 69(12): 4886–4897. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2022.3199218. [26] MEI Faqiang, ZHANG Lei, GU Chongyan, et al. A highly flexible lightweight and high speed true random number generator on FPGA[C]. 2018 IEEE Computer Society Annual Symposium on VLSI (ISVLSI), Hong Kong, China, 2018: 399–404. doi: 10.1109/ISVLSI.2018.00079. -





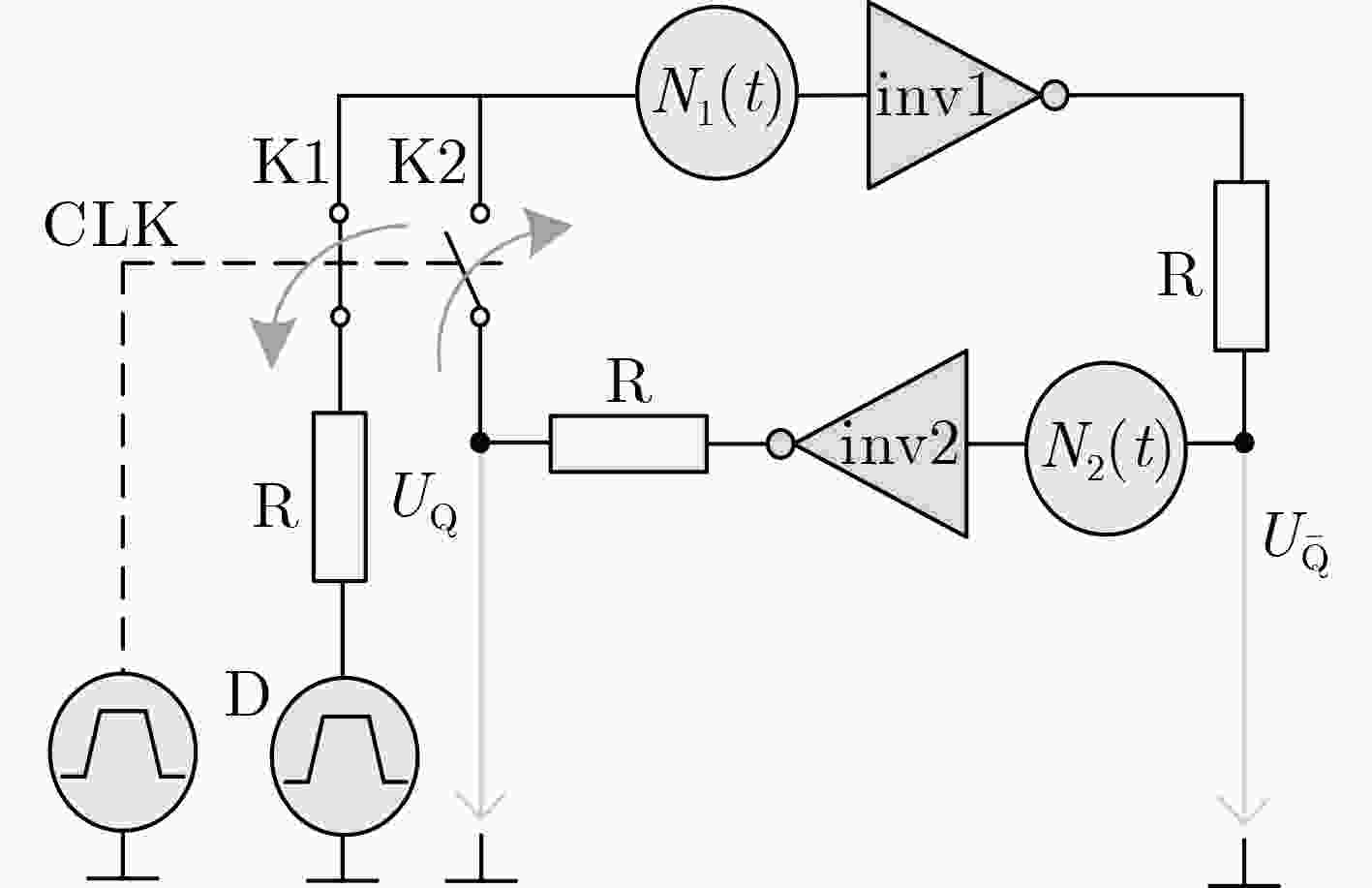
 下载:
下载:
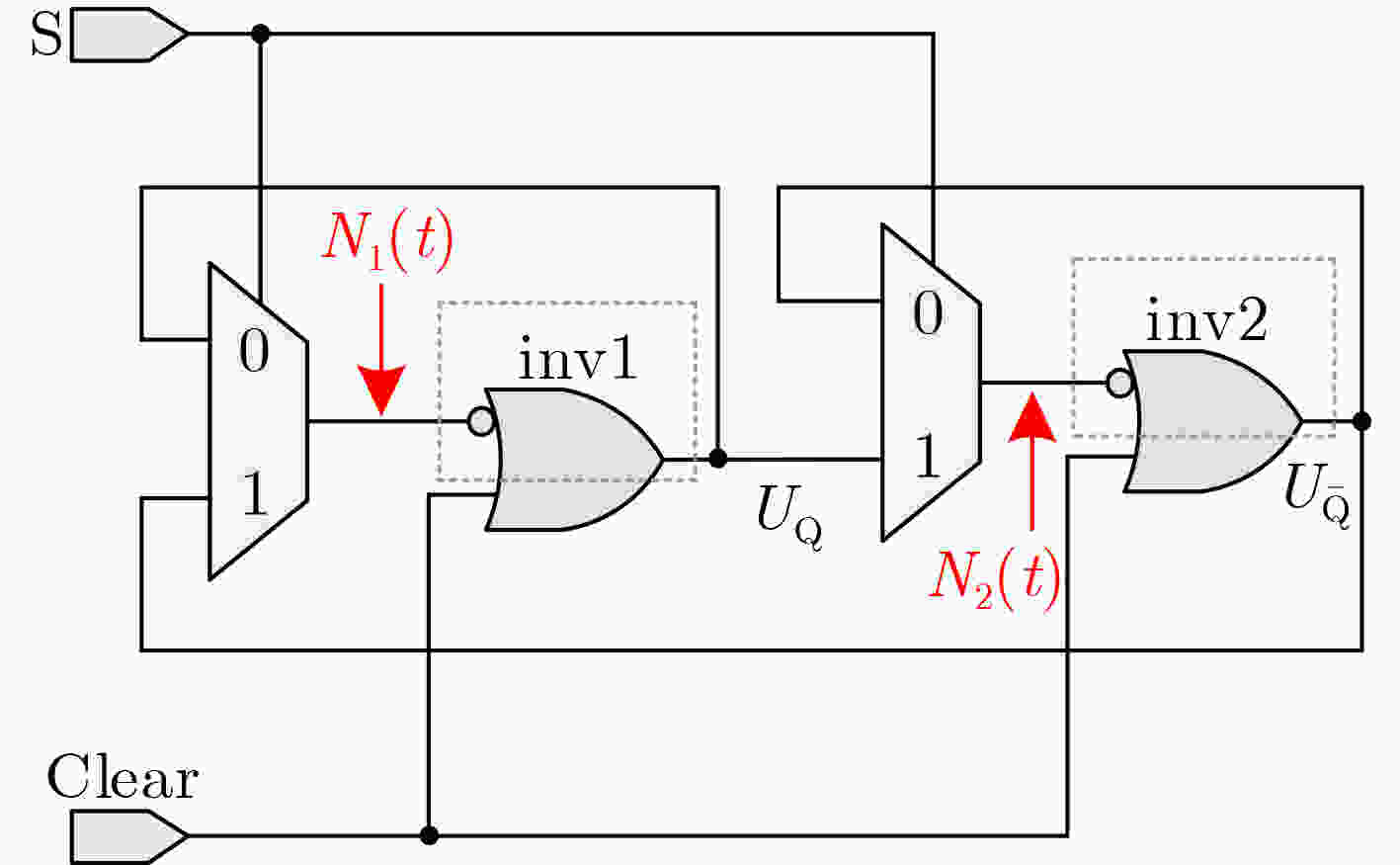
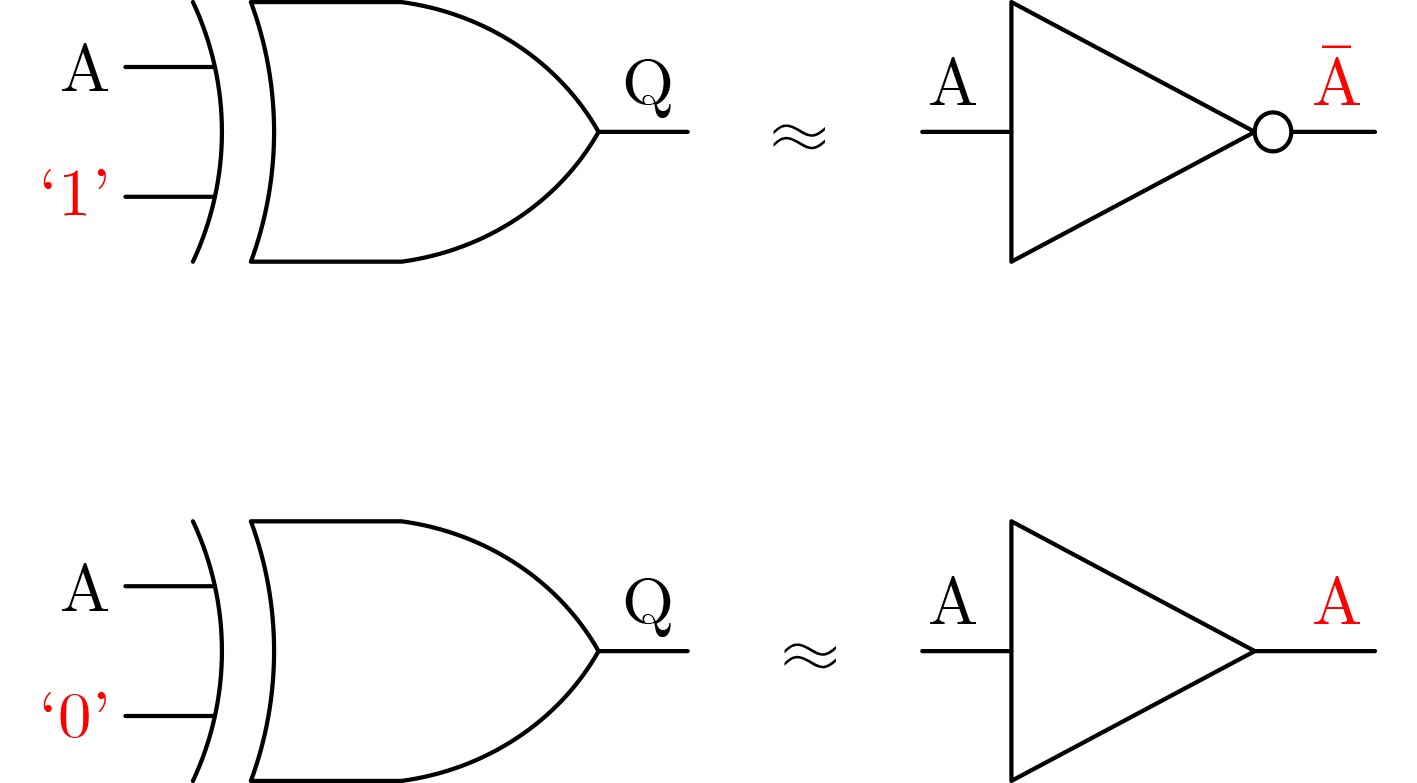
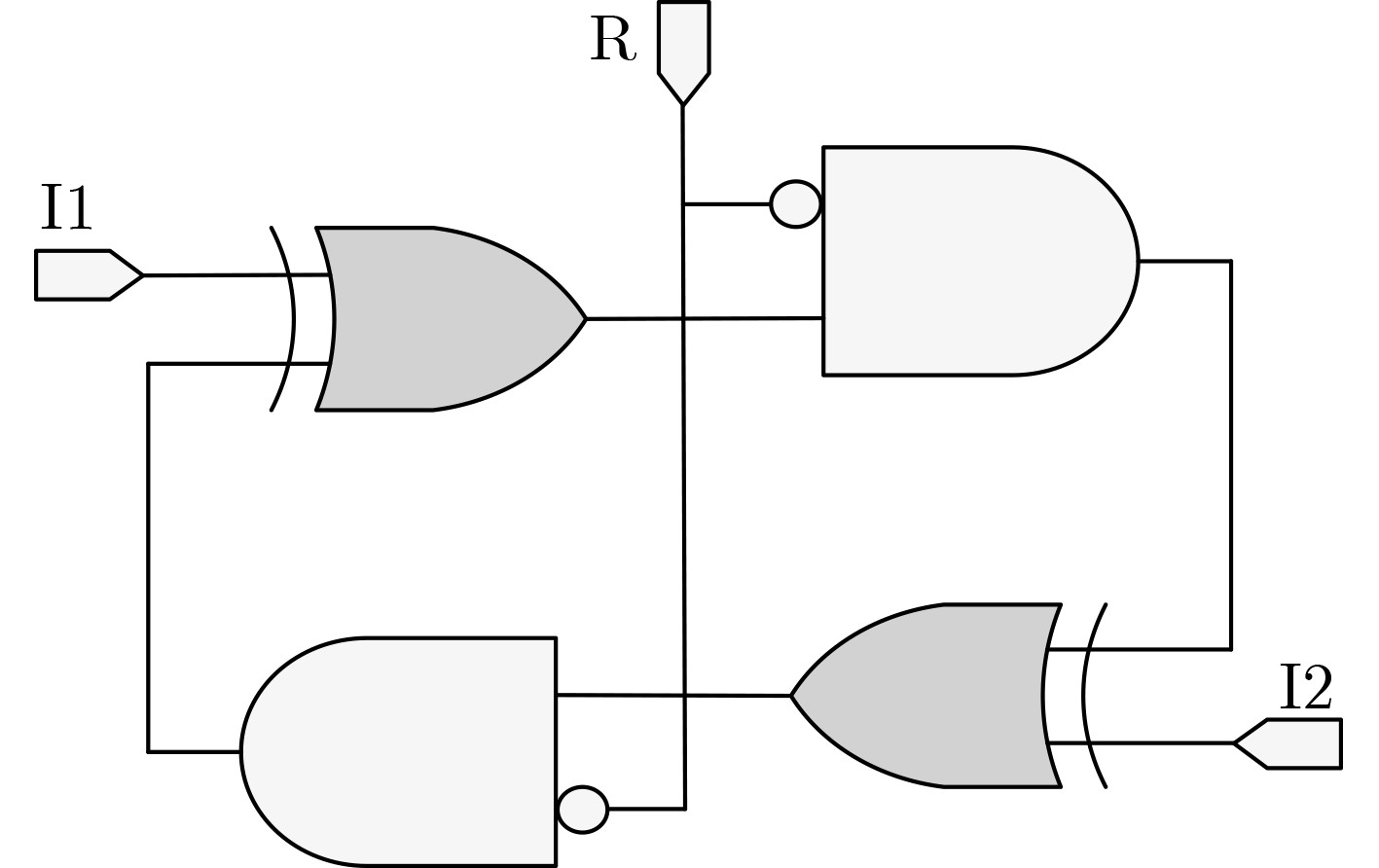
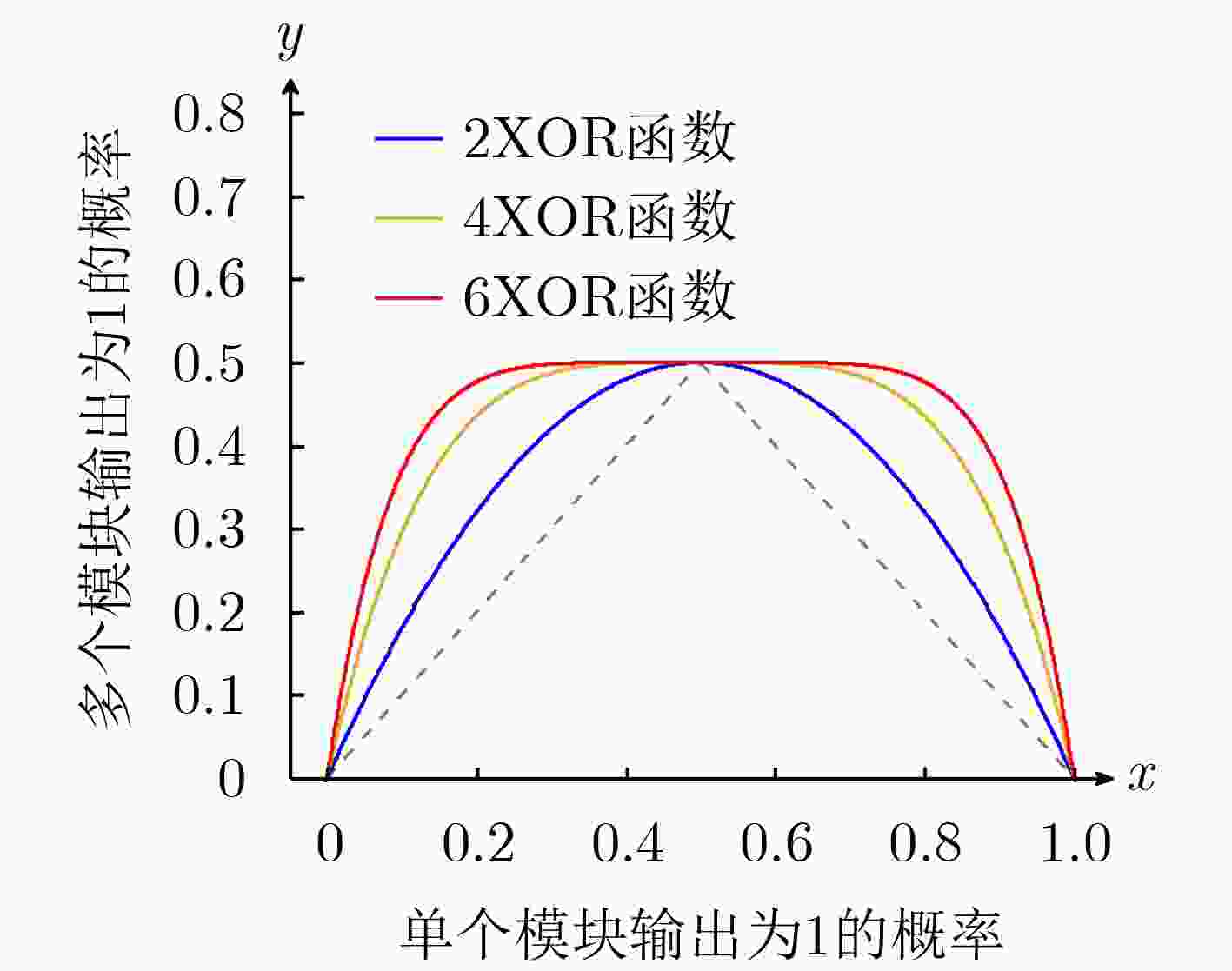
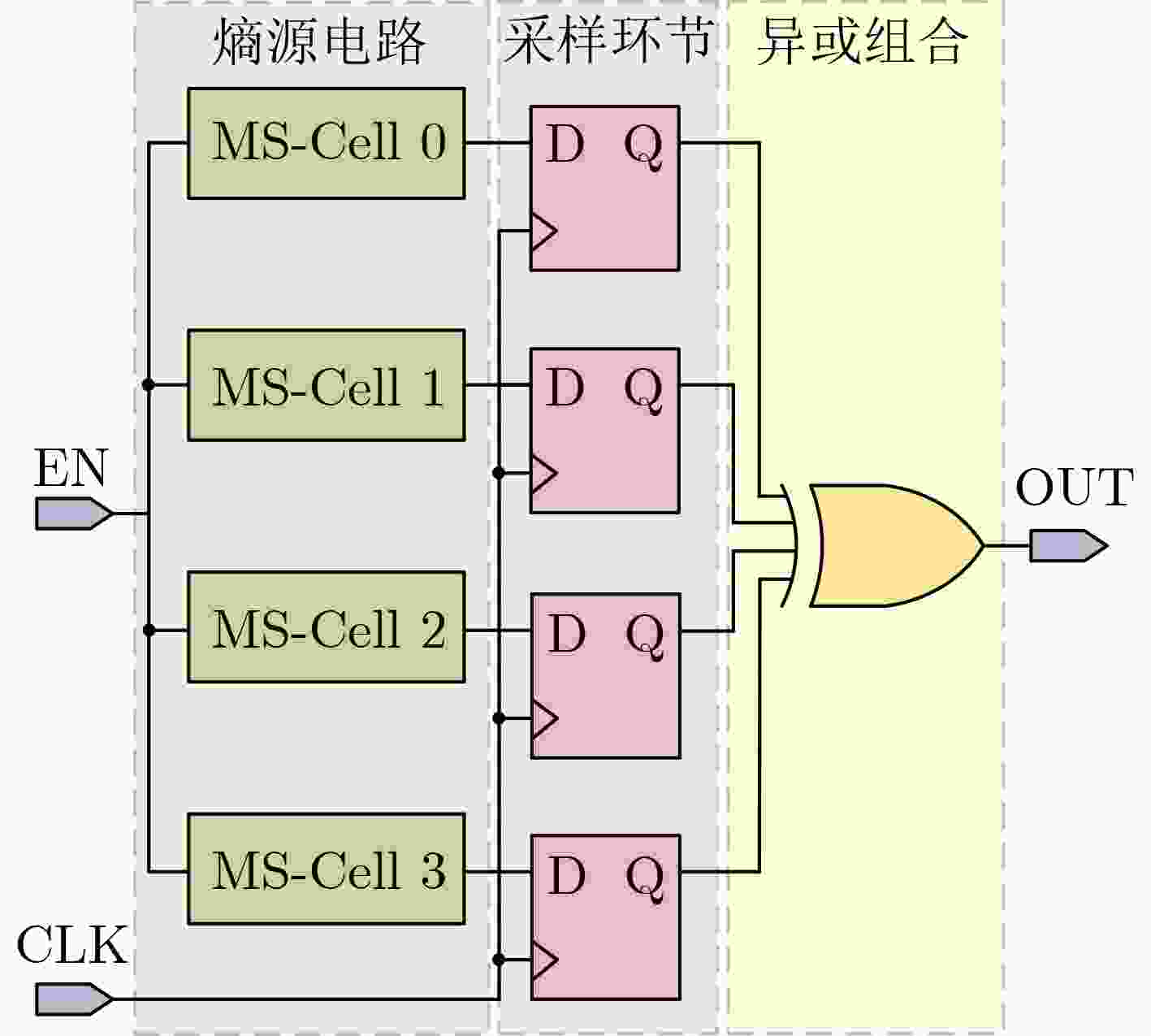

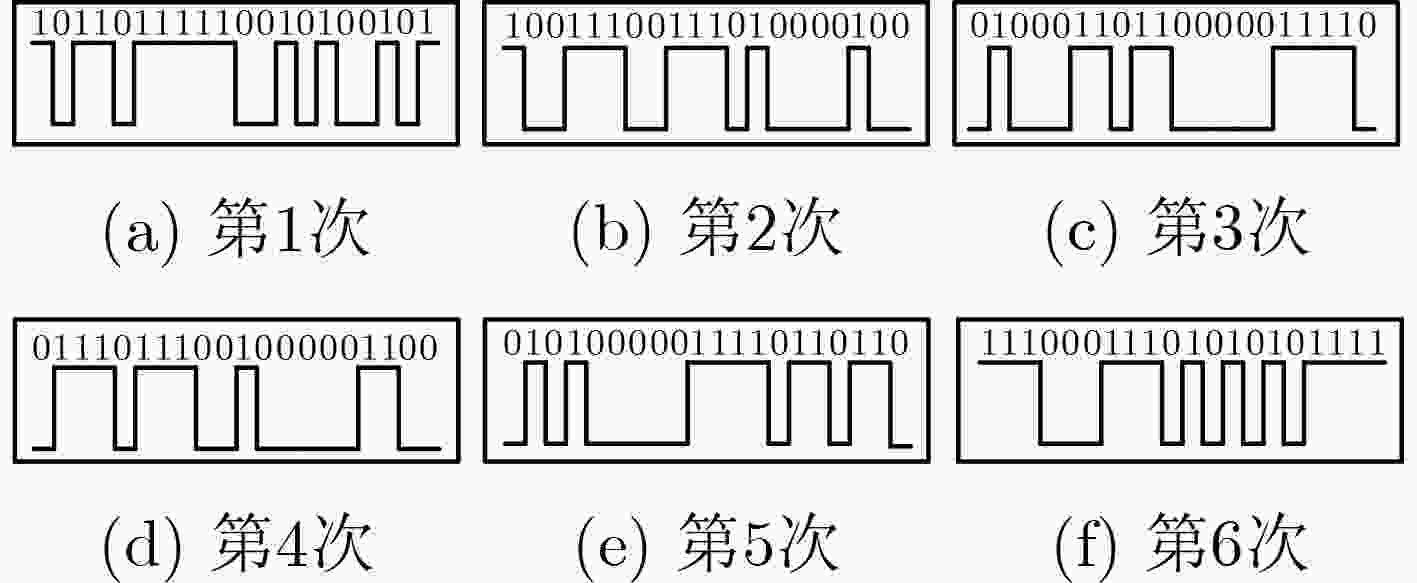
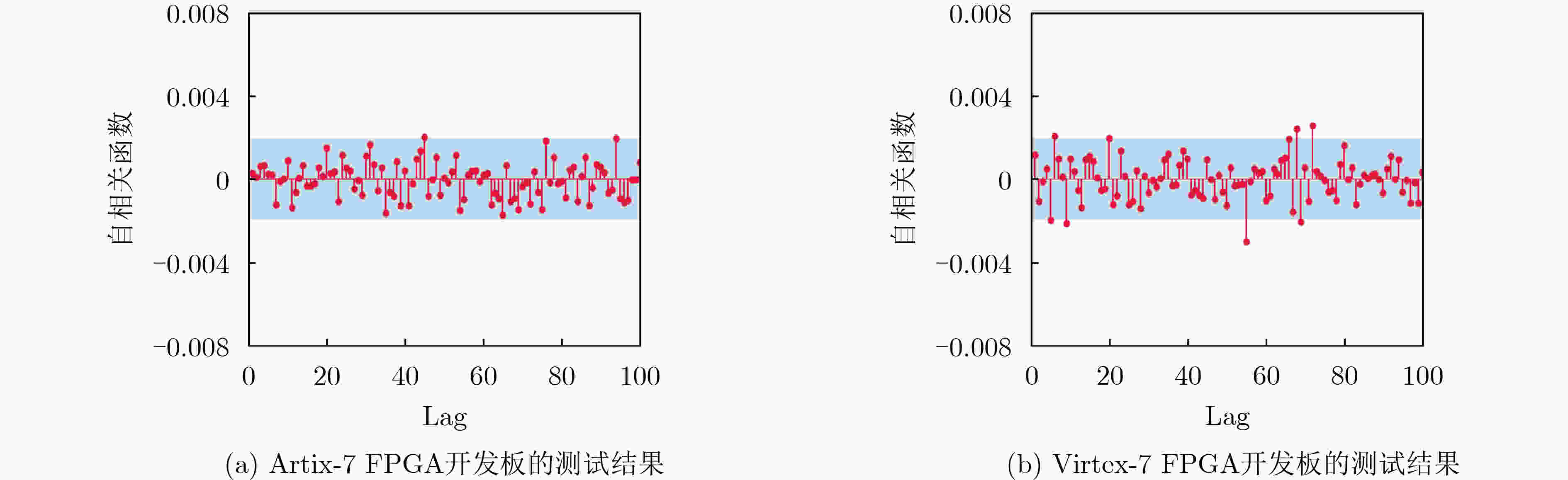
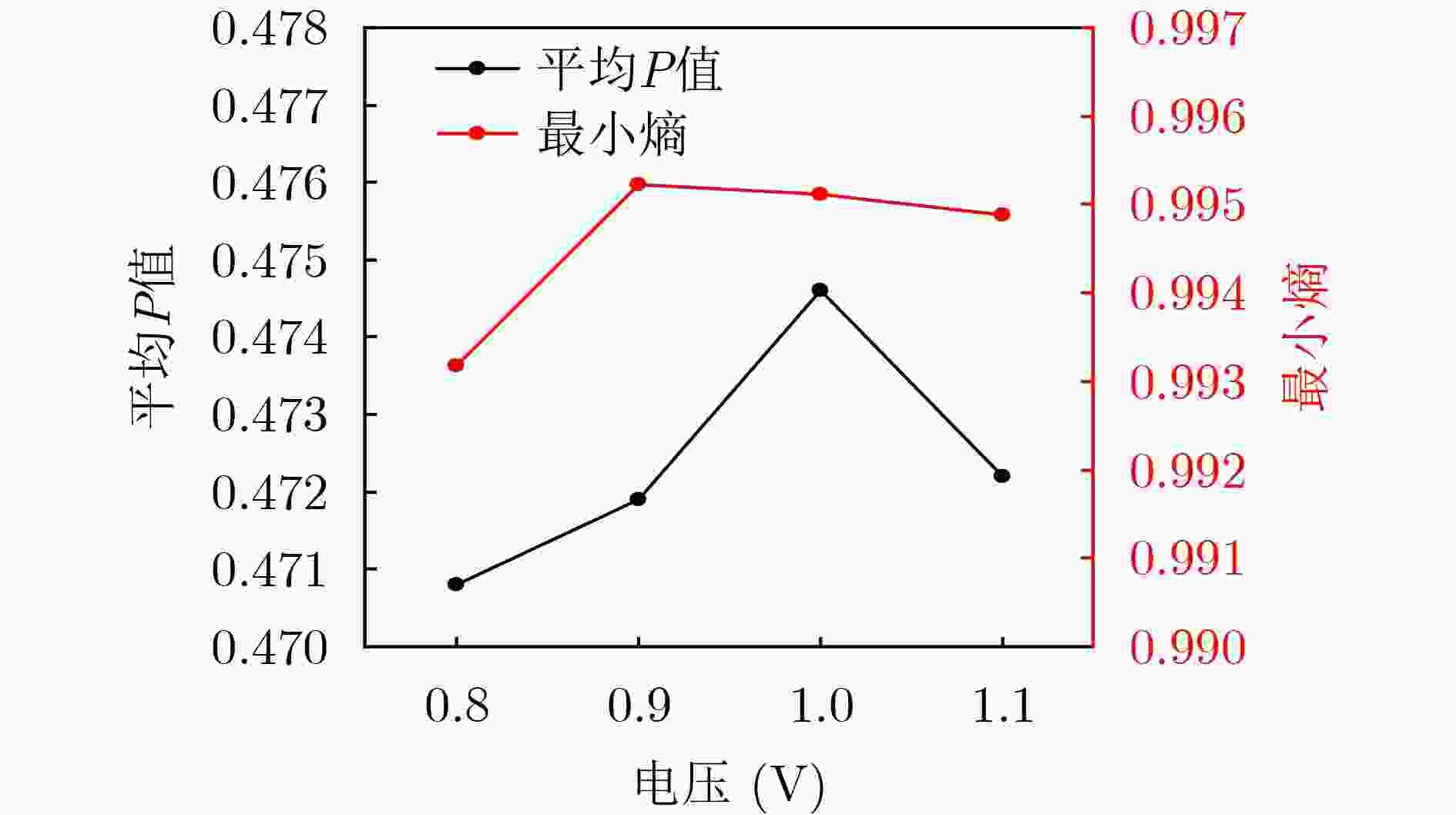
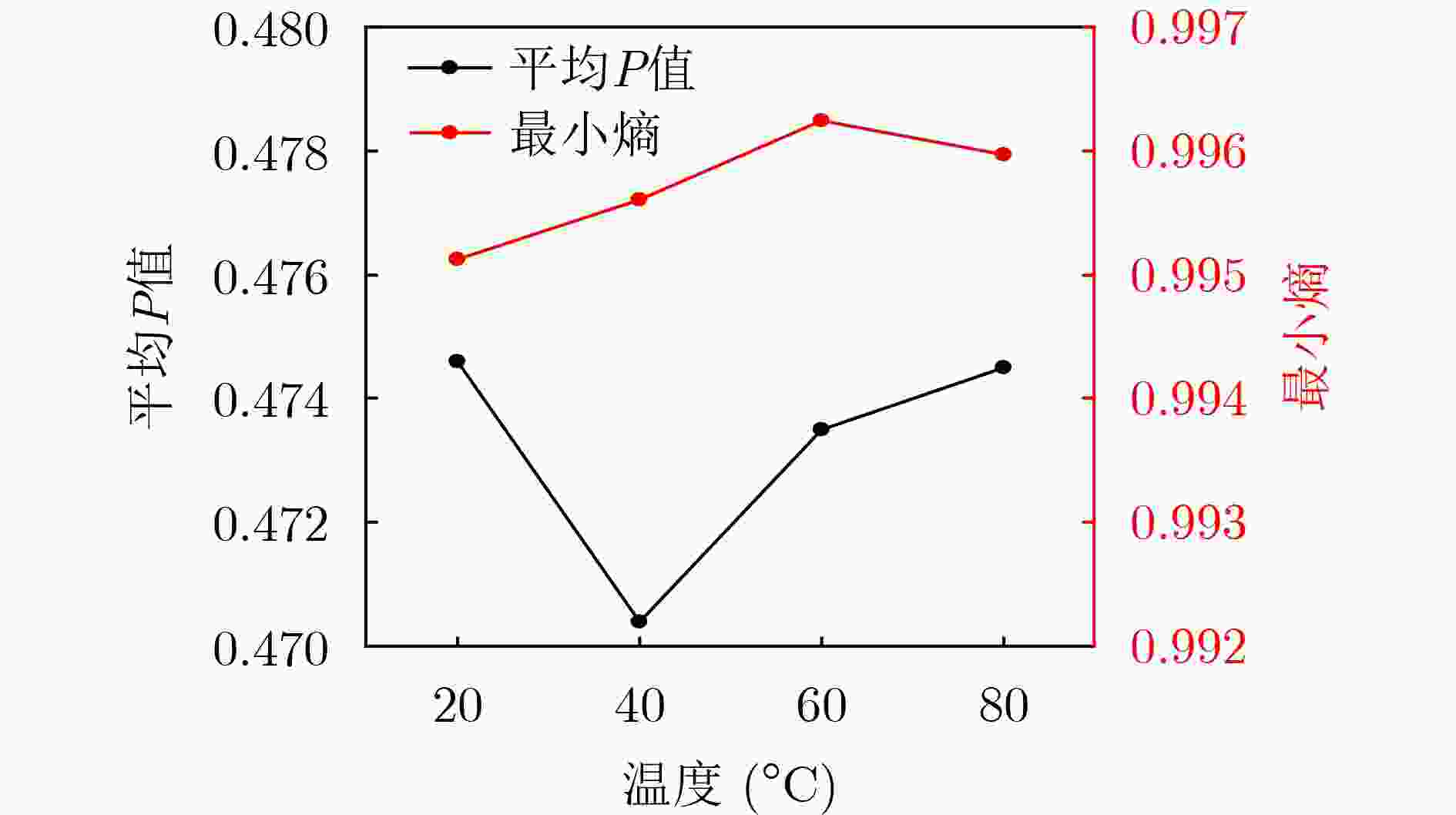


 下载:
下载:
