Overview of Holographic Multiple-Input Multiple-Output Technology for 6G Wireless Networks
-
摘要: 未来的第6代(6G)无线通信系统需要支持超大规模的用户需求,且对频谱效率和能源效率的要求越来越高。在此背景下,全息多输入多输出(MIMO)技术由于其具有智能可重构、电磁可调控、高方向性增益、成本低廉和部署灵活等潜力而愈发受到关注。在全息MIMO系统中,大量微小而廉价的天线单元被紧密集成,使其在低硬件成本的情况下能够实现高方向性增益,同时其可以对电磁波进行灵活的调控,从而有效提升了无线通信性能。该文从全息MIMO技术出发,首先简要介绍了全息MIMO的发展过程、技术现状、分类和特点,然后对全息MIMO在视距场景和空间平稳散射的非视距场景的信道模型进行了介绍,最后阐述了全息MIMO面对的挑战和未来趋势,并进行了总结。Abstract: The future Sixth-Generation (6G) wireless communication systems are required to support ultra-large-scale user demands, with increasing demands for spectrum efficiency and energy efficiency. In this context, Holographic Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (HMIMO) technology has gained increasing attention due to its potential for intelligent reconfigurability, electromagnetic tunability, high directional gain, cost-effectiveness, and flexible deployment. In holographic MIMO system, large amount small and cheap antenna units are integrated tightly, thus realize high directional gain at a low hardware cost and flexible adjustment of electromagnetic wave at the same time, thereby effectively enhancing the performance of wireless communication. A brief introduction to holographic MIMO technology is provided at the start of this paper, covering its current status, development process, classification, and key characteristics. Subsequently, the channel model for holographic MIMO in line-of-sight scenarios and non-line-of-sight scenarios with spatially smooth scattering is presented. Finally, the challenges and future trends faced by holographic MIMO technology are described, and the article is concluded.
-
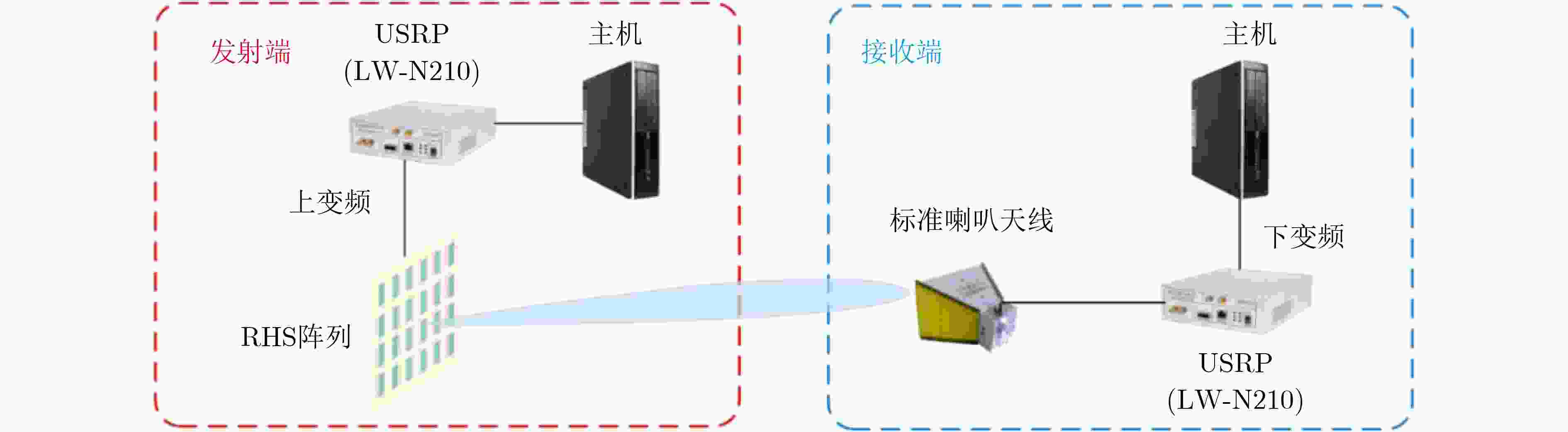
图 1 全息MIMO通信平台硬件模块示意图[23]
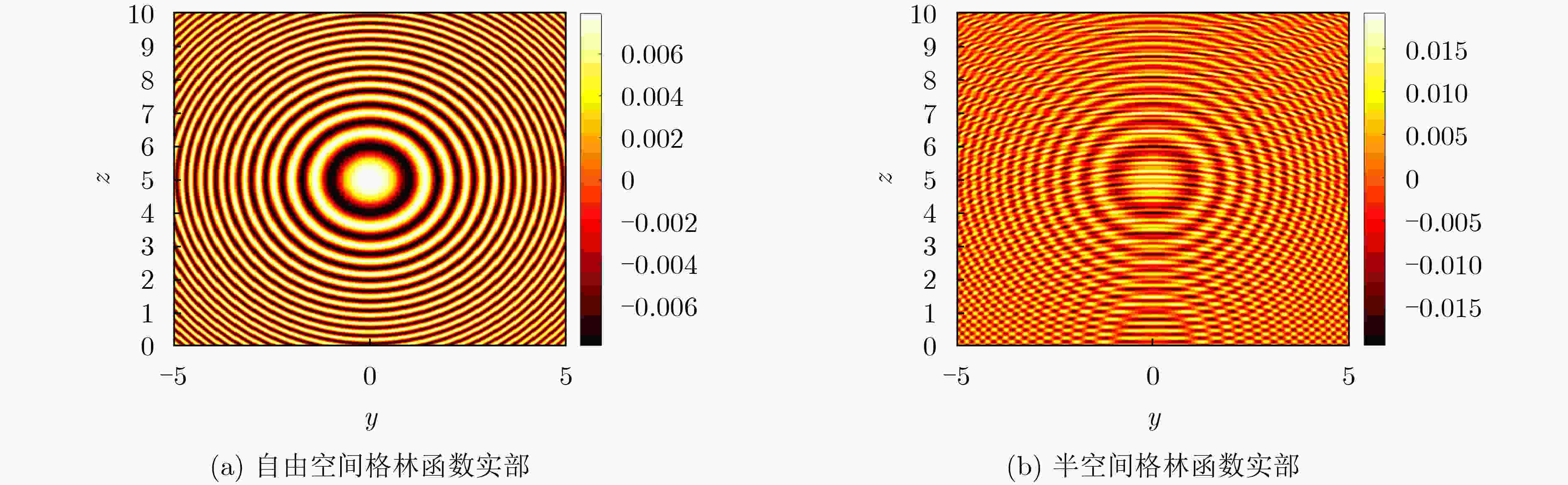
图 2 自由空间和半空间的格林函数实部对比图[29]
-
[1] 张海君, 陈安琪, 李亚博, 等. 6G移动网络关键技术[J]. 通信学报, 2022, 43(7): 189–202. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2022140.ZHANG Haijun, CHEN Anqi, LI Yabo, et al. Key technologies of 6G mobile network[J]. Journal on Communications, 2022, 43(7): 189–202. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2022140. [2] 张平, 陈岩, 吴超楠. 6G: 新一代移动通信技术发展态势及展望[J]. 中国工程科学, 2023, 25(6): 1–8. doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2023.06.001.ZHANG Ping, CHEN Yan, and WU Chaonan. Six-generation mobile communication: Development trend and outlook[J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2023, 25(6): 1–8. doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2023.06.001. [3] ANON. More than 50 billion connected devices[R]. Stockholm, Sweden: Ericsson, 2011. [4] HE Ruisi, SCHNEIDER C, AI Bo, et al. Propagation channels of 5G millimeter-wave vehicle-to-vehicle communications: Recent advances and future challenges[J]. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 2020, 15(1): 16–26. doi: 10.1109/MVT.2019.2928898. [5] BENECK R J, DAS A, MACKERTICH-SENGERDY G, et al. Reconfigurable antennas: A review of recent progress and future prospects for next generation[J]. Progress in Electromagnetics Research, 2021, 171: 89–121. doi: 10.2528/PIER21081109. [6] WANG Yipeng, CHEN Xiaoming, PEI Huiling, et al. MIMO performance enhancement of MIMO arrays using PCS-based near-field optimization technique[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2023, 66(6): 162302. doi: 10.1007/s11432-022-3595-y. [7] WANG Yipeng, CHEN Xiaoming, LIU Xiaobo, et al. Improvement of diversity and capacity of MIMO system using Scatterer array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2022, 70(1): 789–794. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2021.3098568IF. [8] CHEN Xiaoming, ZHAO Mengran, HUANG Huilin, et al. Simultaneous decoupling and decorrelation scheme of MIMO arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71(2): 2164–2169. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3134180. [9] HE Ruisi, AI Bo, ZHONG Zhangdui, et al. 5G for railways: Next generation railway dedicated communications[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2022, 60(12): 130–136. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.005.2200328. [10] DI RENZO M, HAAS H, GHRAYEB A, et al. Spatial modulation for generalized MIMO: Challenges, opportunities, and implementation[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2014, 102(1): 56–103. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2013.2287851. [11] WANG Dongming, ZHANG Yu, WEI Hao, et al. An overview of transmission theory and techniques of large-scale antenna systems for 5G wireless communications[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2016, 59(8): 081301. doi: 10.1007/s11432-016-0278-5. [12] AKYILDIZ I F, HAN Chong, and NIE Shuai. Combating the distance problem in the millimeter wave and terahertz frequency bands[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2018, 56(6): 102–108. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2018.1700928. [13] PIZZO A, SANGUINETTI L, and MARZETTA T L. Fourier plane-wave series expansion for Holographic MIMO communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(9): 6890–6905. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2022.3152965. [14] DENG Ruoqi, DI Boya, ZHANG Hongliang, et al. Holographic MIMO for LEO satellite communications aided by reconfigurable holographic surfaces[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2022, 40(10): 3071–3085. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2022.3196110. [15] WAN Ziwei, GAO Zhen, GAO Feifei, et al. Terahertz massive MIMO with holographic reconfigurable intelligent surfaces[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(7): 4732–4750. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3064949. [16] ADHIKARY A, MUNIR M S, RAHA A D, et al. Artificial intelligence framework for target oriented integrated sensing and communication in holographic MIMO[C]. NOMS 2023–2023 IEEE/IFIP Network Operations and Management Symposium, Miami, USA, 2023: 1–7. doi: 10.1109/NOMS56928.2023.10154354. [17] 高子路, 孙韶辉, 李丽. 面向新一代移动通信的智能超表面技术综述[J]. 电信科学, 2022, 38(10): 20–35. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-0801.2022278.GAO Zilu, SUN Shaohui, and LI Li. Overview of reconfigurable intelligent surface for new-generation mobile communication[J]. Telecommunications Science, 2022, 38(10): 20–35. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-0801.2022278. [18] 潘时龙, 宗柏青, 唐震宙, 等. 面向6G的智能全息无线电[J]. 无线电通信技术, 2022, 48(1): 1–15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3114.2022.01.001.PAN Shilong, ZONG Baiqing, TANG Zhenzhou, et al. Intelligent Holographic Radio for 6G[J]. Radio Communications Technology, 2022, 48(1): 1–15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3114.2022.01.001. [19] 袁晓志, 彭莉, 张琳峰. 全息通信对未来网络的需求与挑战[J]. 电信科学, 2020, 36(12): 59–64. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-0801.2020307.YUAN Xiaozhi, PENG Li, and ZHANG Linfeng. Requirement and challenge of holographic-type communication to the future network[J]. Telecommunications Science, 2020, 36(12): 59–64. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-0801.2020307. [20] DESCHAMPS G A. Some remarks on radio-frequency holography[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1967, 55(4): 570–571. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1967.5596. [21] CHECCACCI P, RUSSO V, and SCHEGGI A. Holographic antennas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1970, 18(6): 811–813. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1970.1139788. [22] LIZUKA K, MIZUSAWA M, URASAKI S, et al. Volume-type holographic antenna[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1975, 23(6): 807–810. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1975.1141175. [23] SLEASMAN T, IMANI M F, XU Wangren, et al. Waveguide-fed tunable metamaterial element for dynamic apertures[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2016, 15: 606–609. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2015.2462818. [24] 邓若琪, 张雨童, 张浩波, 等. 全息无线电: 全息超表面赋能的超大规模MIMO新范式[J]. 电子学报, 2022, 50(12): 2984–2995. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20221136.DENG Ruoqi, ZHANG Yutong, ZHANG Haobo, et al. Holographic radio: A new paradigm for ultra-massive MIMO enabled by reconfigurable holographic surfaces[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2022, 50(12): 2984–2995. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20221136. [25] PIZZO A, MARZETTA T L, and SANGUINETTI L. Spatial characterization of holographic MIMO channels[J]. arXiv: 1911.04853, 2019. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1911.04853. [26] PIZZO A, MARZETTA T L, and SANGUINETTI L. Holographic MIMO communications under spatially-stationary scattering[C]. The 54th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers, Pacific Grove, USA, 2020: 702–706. doi: 10.1109/IEEECONF51394.2020.9443506. [27] PIZZO A, MARZETTA T L, and SANGUINETTI L. Spatially-stationary model for holographic MIMO small-scale fading[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2020, 38(9): 1964–1979. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2020.3000877. [28] PIZZO A, SANGUINETTI L, and MARZETTA T L. Spatial characterization of electromagnetic random channels[J]. IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society, 2022, 3: 847–866. doi: 10.1109/OJCOMS.2022.3171409. [29] JIANG Yuhua and GAO Feifei. Electromagnetic channel model for near field MIMO systems in the half space[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2023, 27(2): 706–710. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2022.3229445. [30] WEI Li, HUANG Chongwen, ALEXANDROPOULOS G C, et al. Multi-user wireless communications with holographic MIMO surfaces: A convenient channel model and spectral efficiency analysis[C]. 2022 Joint European Conference on Networks and Communications & 6G Summit (EuCNC/6G Summit), Grenoble, France, 2022: 488–493. doi: 10.1109/EuCNC/6GSummit54941.2022.9815574. [31] WEI Li, HUANG Chongwen, ALEXANDROPOULOS G C, et al. Multi-user holographic MIMO surfaces: Channel modeling and spectral efficiency analysis[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2022, 16(5): 1112–1124. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2022.3176140. [32] JI Ran, CHEN Shuo, HUANG Chongwen, et al. Extra DoF of near-field holographic MIMO communications leveraging evanescent waves[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2023, 12(4): 580–584. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2023.3234003. [33] ZHANG Yuan, ZHANG Jianhua, ZHANG Yuxiang, et al. Capacity analysis of holographic MIMO channels with practical constraints[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2023, 12(6): 1101–1105. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2023.3262691. [34] SANGUINETTI L, D’AMICO A A, and DEBBAH M. Wavenumber-division multiplexing in line-of-sight holographic MIMO communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2023, 22(4): 2186–2201. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2022.3208961. [35] ZHANG Zijian and DAI Linglong. Pattern-division multiplexing for multi-user continuous-aperture MIMO[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2023, 41(8): 2350–2366. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2023.3288244. [36] YURDUSEVEN O, MARKS D L, FROMENTEZE T, et al. Dynamically reconfigurable holographic metasurface aperture for a mills-cross monochromatic microwave camera[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(5): 5281–5291. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.005281. [37] HU Shu, RUSEK F, and EDFORS O. Beyond massive MIMO: The potential of data transmission with large intelligent surfaces[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(10): 2746–2758. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2816577. [38] DI RENZO M, DEBBAH M, PHAN-HUY D T, et al. Smart radio environments empowered by reconfigurable AI meta-surfaces: An idea whose time has come[J]. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2019, 2019(1): 129. doi: 10.1186/s13638-019-1438-9. [39] HUANG Chongwen, ZAPPONE A, ALEXANDROPOULOS G C, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for energy efficiency in wireless communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(8): 4157–4170. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2922609. [40] ZENG Shuhao, ZHANG Hongliang, DI Boya, et al. Multi-user holographic MIMO systems: Reconfigurable refractive surface or phased array?[C]. GLOBECOM 2022–2022 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2022: 645–650. doi: 10.1109/GLOBECOM48099.2022.10000596. [41] SHEEMAR C K, TOMASIN S, SLOCK D, et al. Intelligent reflecting surfaces assisted millimeter wave MIMO full duplex systems[J]. arXiv: 2211.10700, 2022. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2211.10700. [42] ADHIKARY A, MUNIR M S, RAHA A D, et al. Integrated sensing, localization, and communication in holographic mimo-enabled wireless network: A deep learning approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2023, 21(1): 789–809. doi: 10.1109/TNSM.2023.3292269. [43] HUANG Chongwen, HU Shu, ALEXANDROPOULOS G C, et al. Holographic MIMO surfaces for 6G wireless networks: Opportunities, challenges, and trends[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2020, 27(5): 118–125. doi: 10.1109/MWC.001.1900534. [44] HU Xinyuan, DENG Ruoqi, DI Boya, et al. Holographic beamforming for Ultra Massive MIMO with limited radiation amplitudes: How many quantized bits do we need?[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2022, 26(6): 1403–1407. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2022.3151801. [45] LIASKOS C, NIE S, TSIOLIARIDOU A, et al. A new wireless communication paradigm through software-controlled metasurfaces[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2018, 56(9): 162–169. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2018.1700659. [46] DAVIDE D and DECARLI N. Holographic communication using intelligent surfaces[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2021, 59(6): 35–41. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.2001156. [47] CHEW W C. Waves and Fields in Inhomogenous Media[M]. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 1999: 375–381. [48] CHEW W C. Waves and Fields in Inhomogenous Media[M]. New York: Wiley-IEEE Press, 1995: 384–387. [49] FRANCESCHETTI M. Wave Theory of Information[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2017: 244–261. doi: 10.1017/9781139136334. [50] TAHA A, ALRABEIAH M, and ALKHATEEB A. Enabling large intelligent surfaces with compressive sensing and deep learning[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 44304–44321. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3064073. [51] WU Qingqing and ZHANG Rui. Intelligent reflecting surface enhanced wireless network via joint active and passive beamforming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(11): 5394–5409. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2936025. [52] CHEN Xiaoming, ZHANG Shuai, and LI Qinlong. A review of mutual coupling in MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 24706–24719. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2830653. [53] LI Ang and MASOUROS C. Exploiting constructive mutual coupling in P2P MIMO by analog-digital phase alignment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2017, 16(3): 1948–1962. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2017.2657631. [54] HAN Zixiang, SHEN Shanpu, ZHANG Yujie, et al. A pattern correlation decomposition method for analysis of ESPAR in single-RF MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(7): 4654–4668. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3131612. -





 下载:
下载:
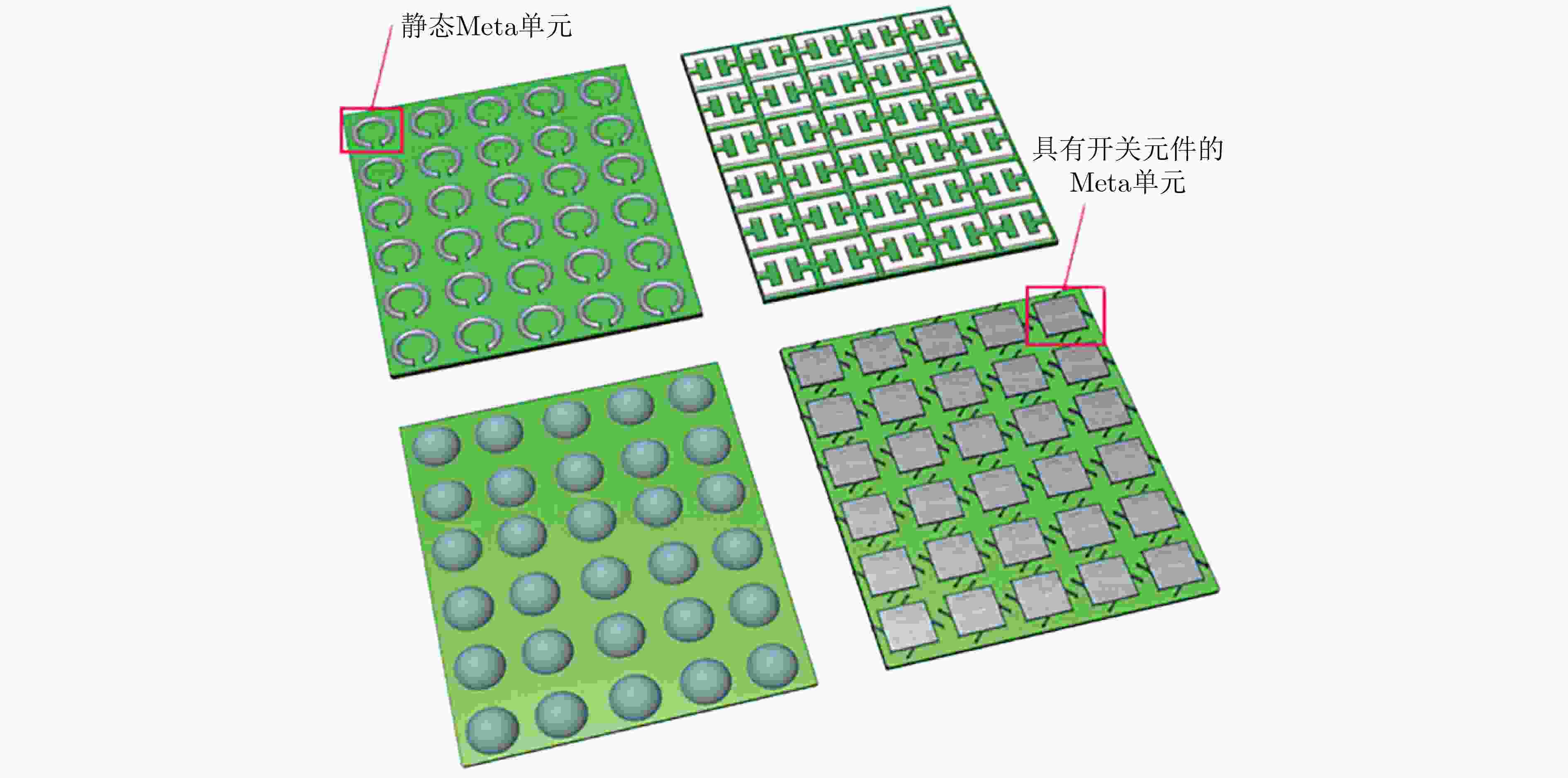
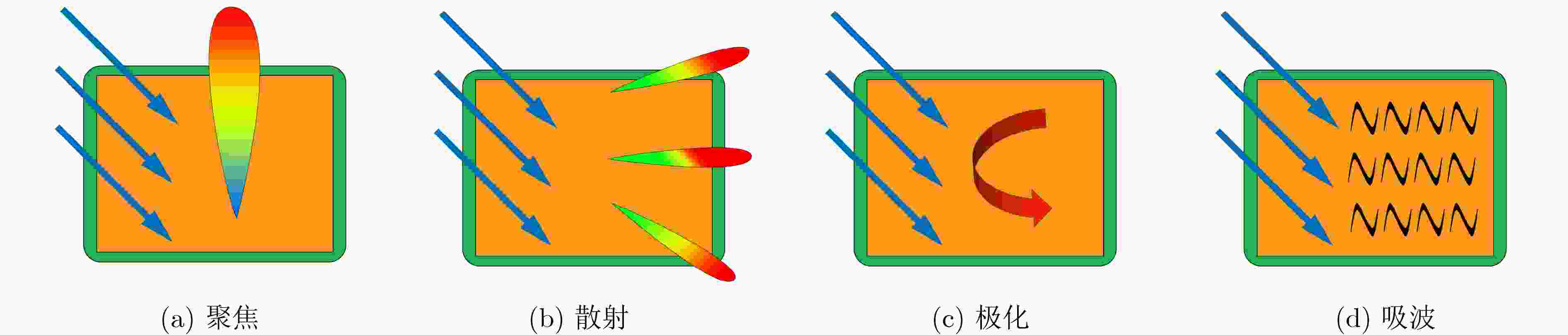
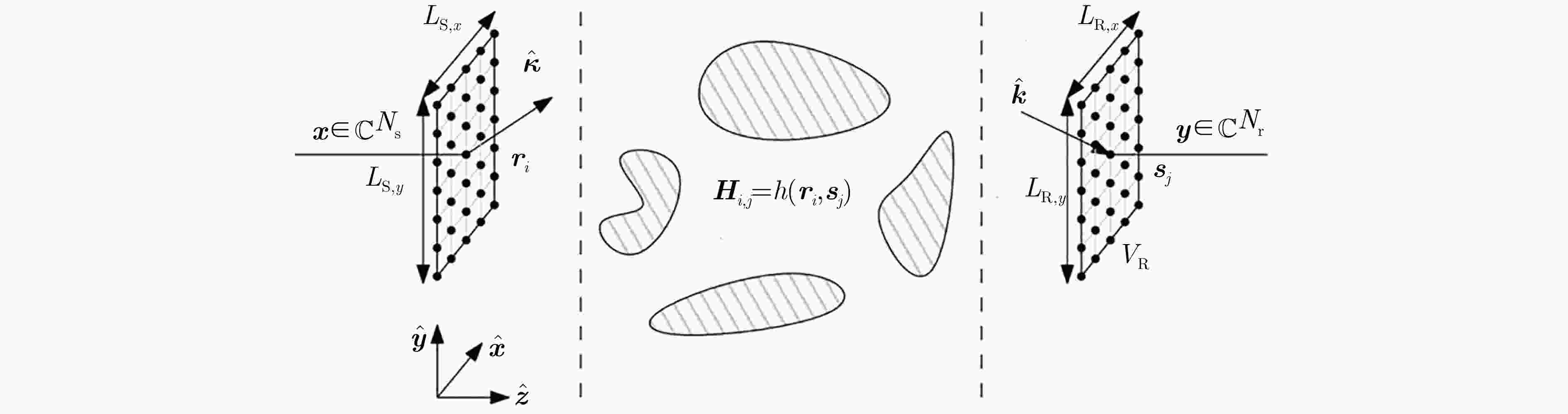
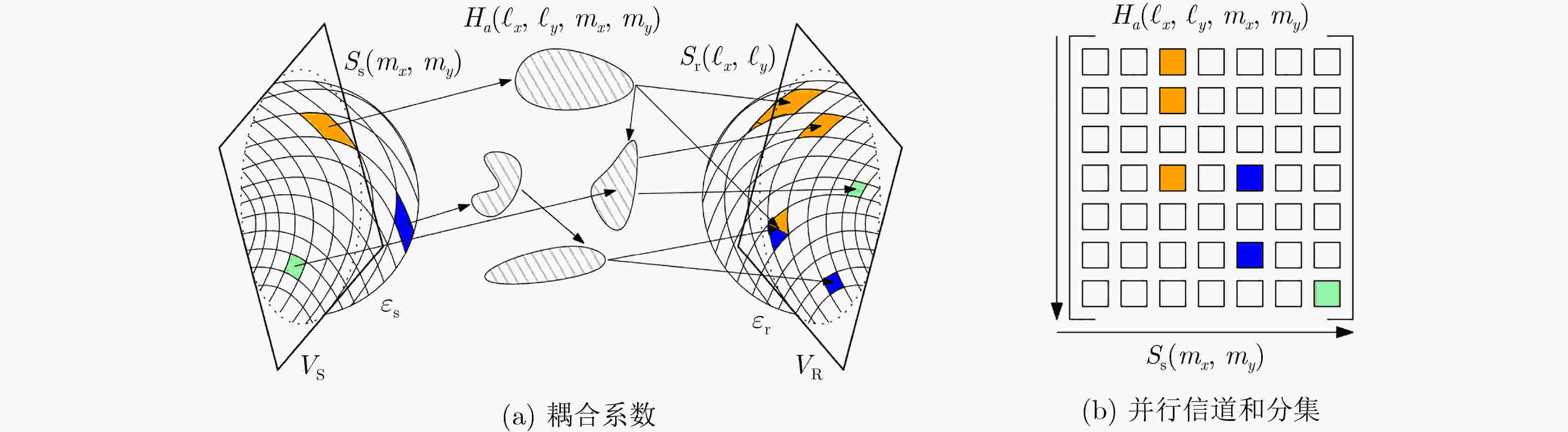


 下载:
下载:
