High-precision Direction Finding Based on Time Modulation Array with Single Radio Frequency Channel and Composite Baselines
-
摘要: 随着定位系统的快速发展,人们对高精度、低成本测向技术的需求日益增大。传统测向方法复杂的硬件结构和高昂的经济成本阻碍了其广泛应用。近年来,基于时间调制阵列(TMA)的测向技术克服了传统测向方法的缺陷,但为了确保测量精度,阵列中仍必须保持足够的单元数量。因此出现了一个问题,即是否能在确保高测向精度的前提下减少时间调制阵列中的单元数量,从而尽可能降低系统的硬件复杂度。所以,该文提出一种基于时间调制阵列的单通道复合基线测向方法并进行了实验验证。该方法将4根天线按特定的间隔排列,形成复合基线系统,利用现场可编程门阵列(FPGA)和单接收通道,实现了高精度、低成本的测向。为了验证所提方法的有效性,该文设计、制作并测量了工作在S波段的原型系统,并与现有测向方法进行了详细比较。该工作对高精度、低成本测向系统的开发和应用具有重要意义。Abstract: With the rapid developments of positioning systems, high-precision and low-cost direction-finding technologies are urgently needed. The hardware complexity and economic cost of traditional direction-finding methods have hindered their wide applications. Recently, direction finding based on Time-Modulated Arrays (TMAs) has overcome the shortcomings of traditional direction-finding methods. Nevertheless, to ensure measurement accuracy, one has to keep an adequate number of array elements in common TMAs. Consequently, a question arises, i.e., is it possible to reduce the number of array elements in TMAs, thus making the hardware complexity as low as possible? A novel direction-finding method based on the TMA with a single radio frequency channel and composite baselines is proposed in this paper. In the method, four antennas are meticulously arranged at specific intervals to form double-long baselines, and accurate and low-cost direction finding is realized with the ingenious usage of Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) and single receiving channel. To verify the effectiveness of the method, a prototype system in the S band is designed, fabricated, and measured. Detailed comparisons with the existing methods are provided. The work will benefit the development and application of high-precision and low-cost direction-finding systems.
-
Key words:
- Direction finding /
- Spectrum harmonic analysis /
- Time-modulated array /
- Antenna array
-
表 1 实验1结果(º)
入射角度 测量角度 绝对误差 0 2.17 2.17 10 10.68 0.68 20 22.07 2.07 30 32.26 2.26 40 42.65 2.65 50 53.420 3.42 60 263.19 3.19 70 72.20 2.20 表 2 实验2结果(º)
入射角度 测量角度 绝对误差 0 1.37 1.37 10 10.03 0.03 20 21.06 1.06 30 31.15 1.15 40 41.26 1.26 50 51.34 1.34 60 61.65 1.65 70 72.60 2.60 -
[1] PAN Cunhua, REN Hong, WANG Kezhi, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for 6G systems: Principles, applications, and research directions[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2021, 59(6): 14–20. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.2001076. [2] YUAN Jie, LIANG Yingchang, JOUNG Jingon, et al. Intelligent reflecting surface-assisted cognitive radio system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(1): 675–687. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2020.3033006. [3] LI Sixian, DUO Bin, YUAN Xiaojun, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surface assisted UAV communication: Joint trajectory design and passive beamforming[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(5): 716–720. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.2966705. [4] AI Yun, DEFIGUEIREDO F A P, KONG Long, et al. Secure vehicular communications through reconfigurable intelligent surfaces[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(7): 7272–7276. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3088441. [5] AL-HILO A, SAMIR M, ELHATTAB M, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surface enabled vehicular communication: Joint user scheduling and passive beamforming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71(3): 2333–2345. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3141935. [6] BASAR E, DI RENZO M, DE ROSNY J, et al. Wireless communications through reconfigurable intelligent surfaces[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 116753–116773. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2935192. [7] BURTNYK N, MCLEISH C W, and WOLFE J. Interferometer direction finder for the H. F. band[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Electrical Engineers, 1963, 110(7): 1165–1170. doi: 10.1049/piee.1963.0162. [8] WATT R A W and HERD J F. An instantaneous direct-reading radiogoniometer[J]. Journal of the Institution of Electrical Engineers, 1926, 64(353): 611–617. doi: 10.1049/jiee-1.1926.0051. [9] KRIM H and VIBERG M. Two decades of array signal processing research: The parametric approach[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 1996, 13(4): 67–94. doi: 10.1109/79.526899. [10] SCHMIDT R. Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1986, 34(3): 276–280. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1986.1143830. [11] RAO B D and HARI K V S. Performance analysis of root-music[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1989, 37(12): 1939–1949. doi: 10.1109/29.45540. [12] ROY R and KAILATH T. ESPRIT-estimation of signal parameters via rotational invariance techniques[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1989, 37(7): 984–995. doi: 10.1109/29.32276. [13] SHANKS H E and BICKMORE R W. Four-dimensional electromagnetic radiators[J]. Canadian Journal of Physics, 1959, 37(3): 263–275. doi: 10.1139/p59-031. [14] FONDEVILA J, BRÉGAINS J C, ARES F, et al. Application of time modulation in the synthesis of sum and difference patterns by using linear arrays[J]. Microwave and Optical Technology Letters, 2006, 48(5): 829–832. doi: 10.1002/mop.21489. [15] XIA Dexiao, WANG Xin, HAN Jiaqi, et al. Accurate 2-D DOA estimation based on active metasurface with nonuniformly periodic time modulation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2023, 71(8): 3424–3435. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2022.3222322. [16] ZHOU Qunyan, WU Junwei, WANG Siran, et al. Two-dimensional direction-of-arrival estimation based on time-domain-coding digital metasurface[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2022, 121(18): 181702. doi: 10.1063/5.0124291. [17] HE Chong, CAO Anjie, CHEN Jingfeng, et al. Direction finding by time-modulated linear array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2018, 66(7): 3642–3652. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2018.2835164. [18] HE Chong, CHEN Jingfeng, LIANG Xianling, et al. High-accuracy DOA estimation based on time-modulated array with long and short baselines[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2018, 17(8): 1391–1395. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2018.2846805. [19] JACOBS E and RALSTON E W. Ambiguity resolution in interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1981, AES-17(6): 766–780. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1981.309127. [20] TANG Wankai, CHEN Mingzheng, CHEN Xiangyu, et al. Wireless communications with reconfigurable intelligent surface: Path loss modeling and experimental measurement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(1): 421–439. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3024887. -





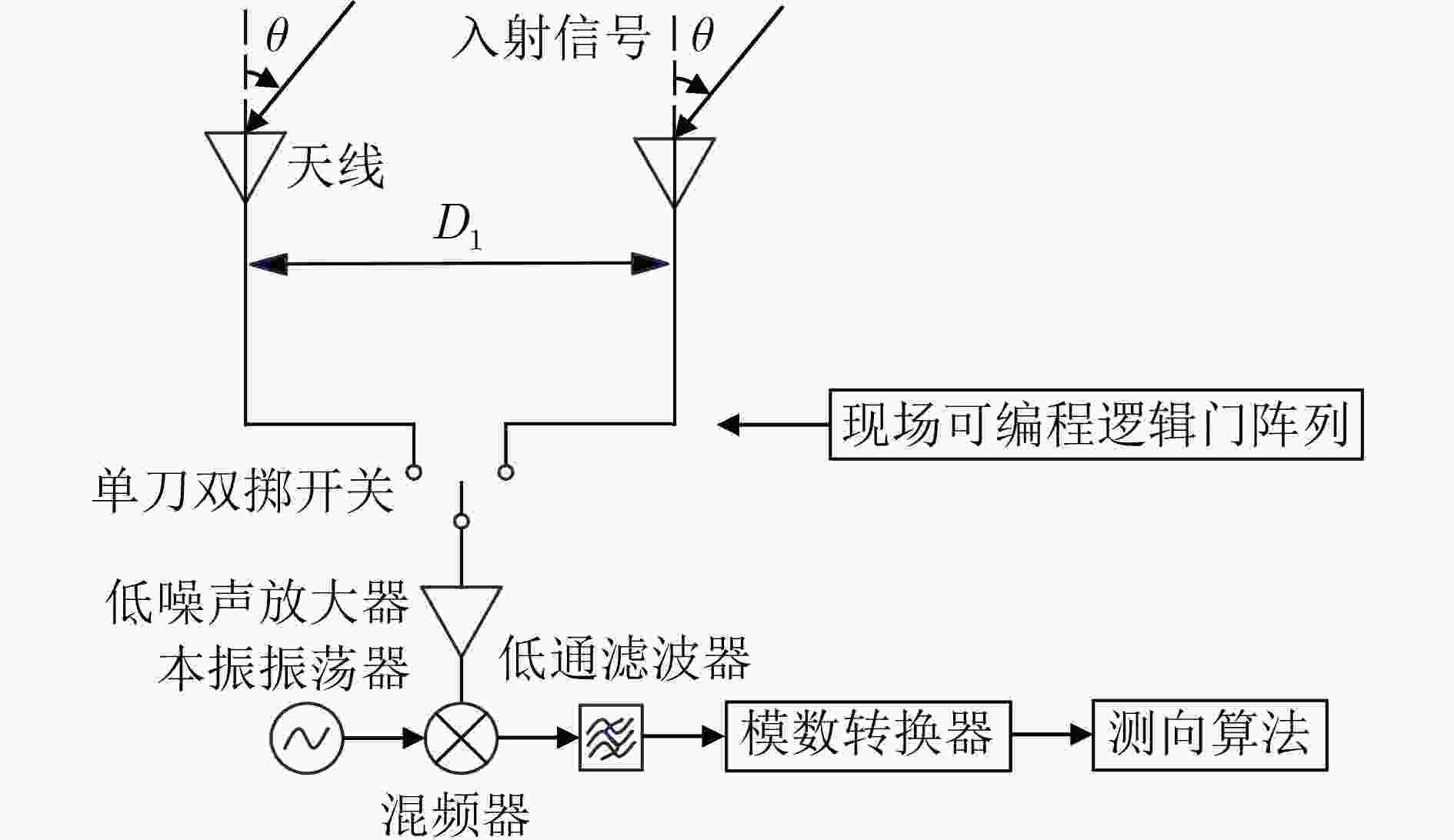
 下载:
下载:
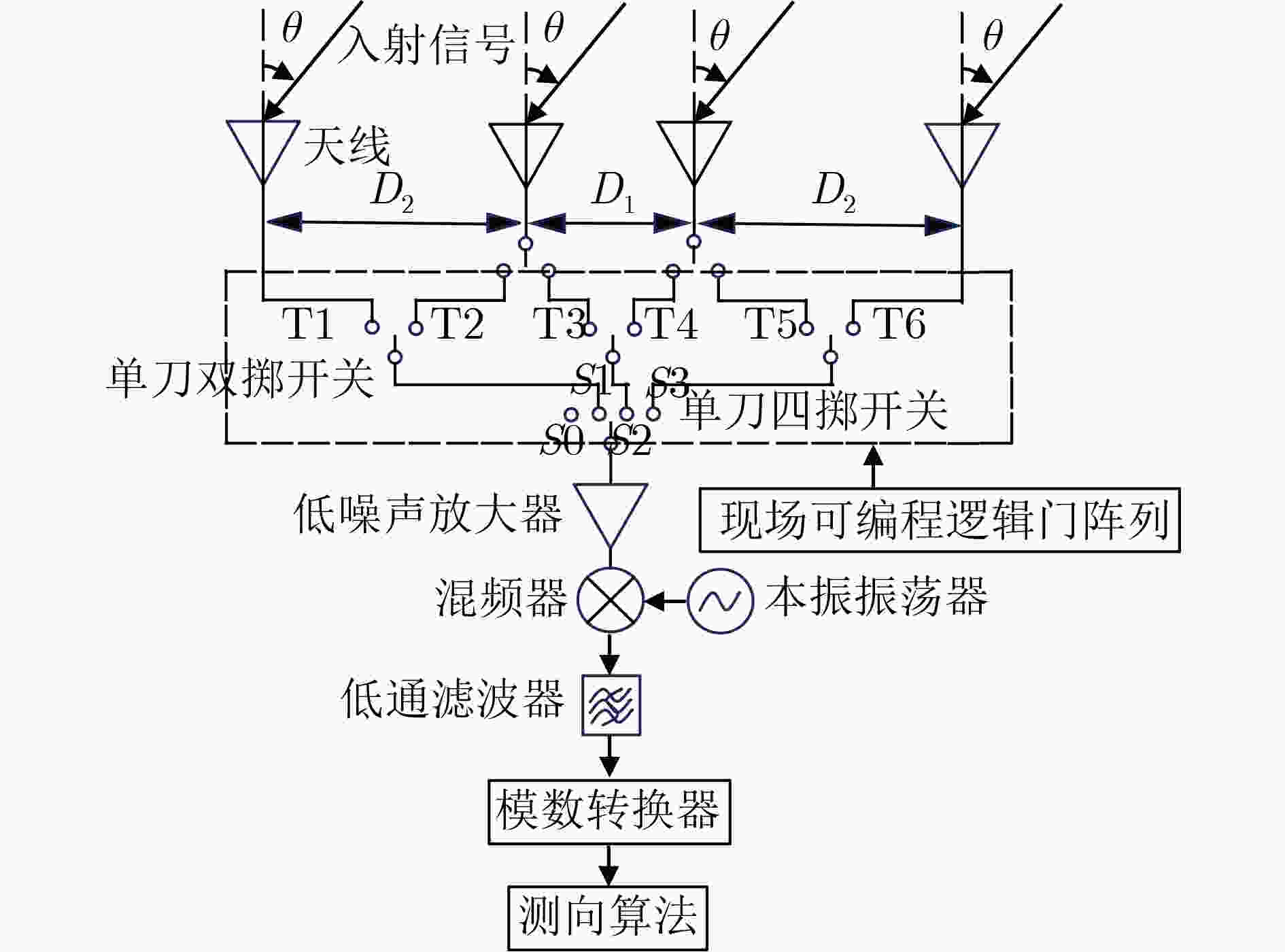
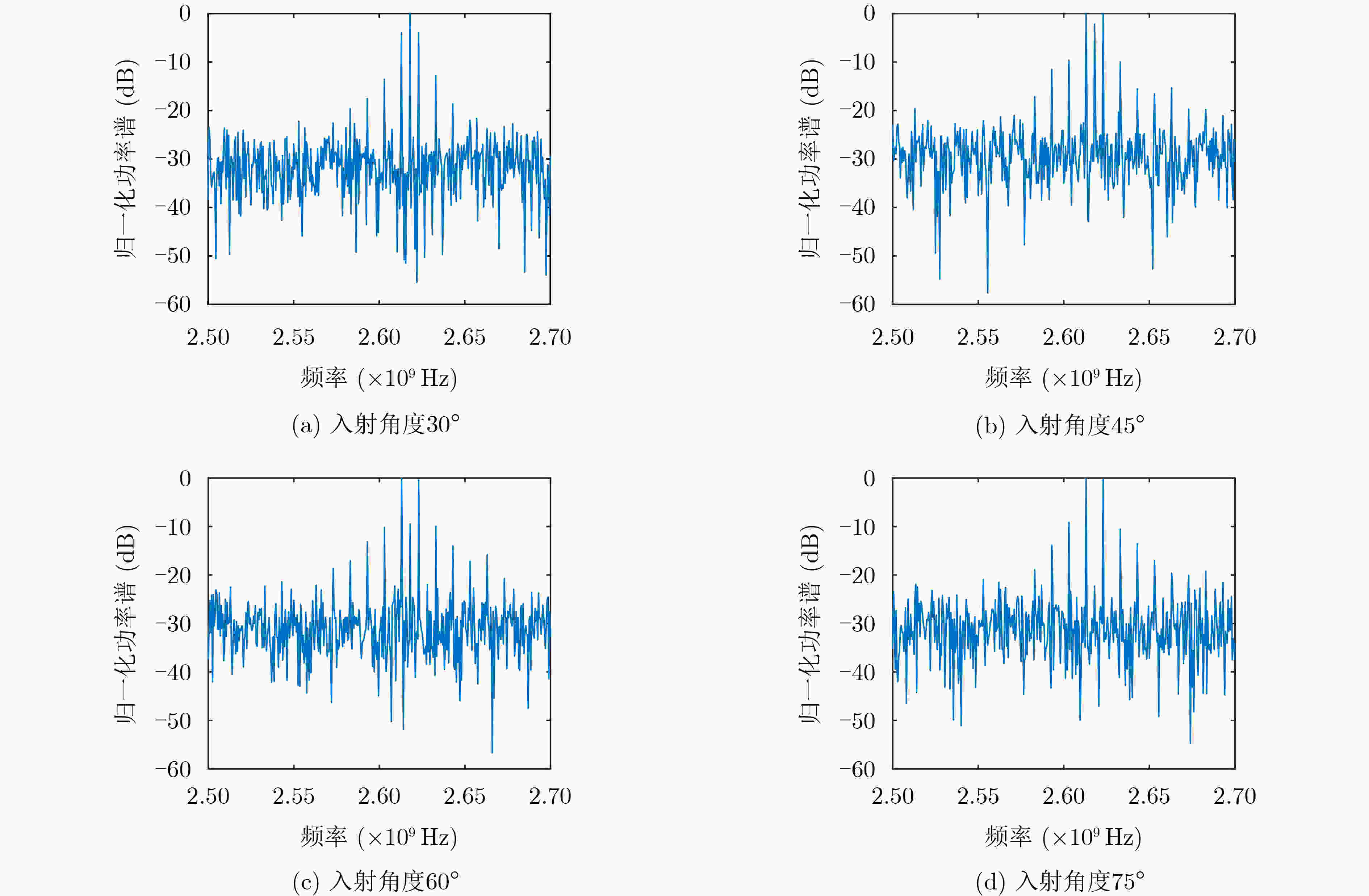
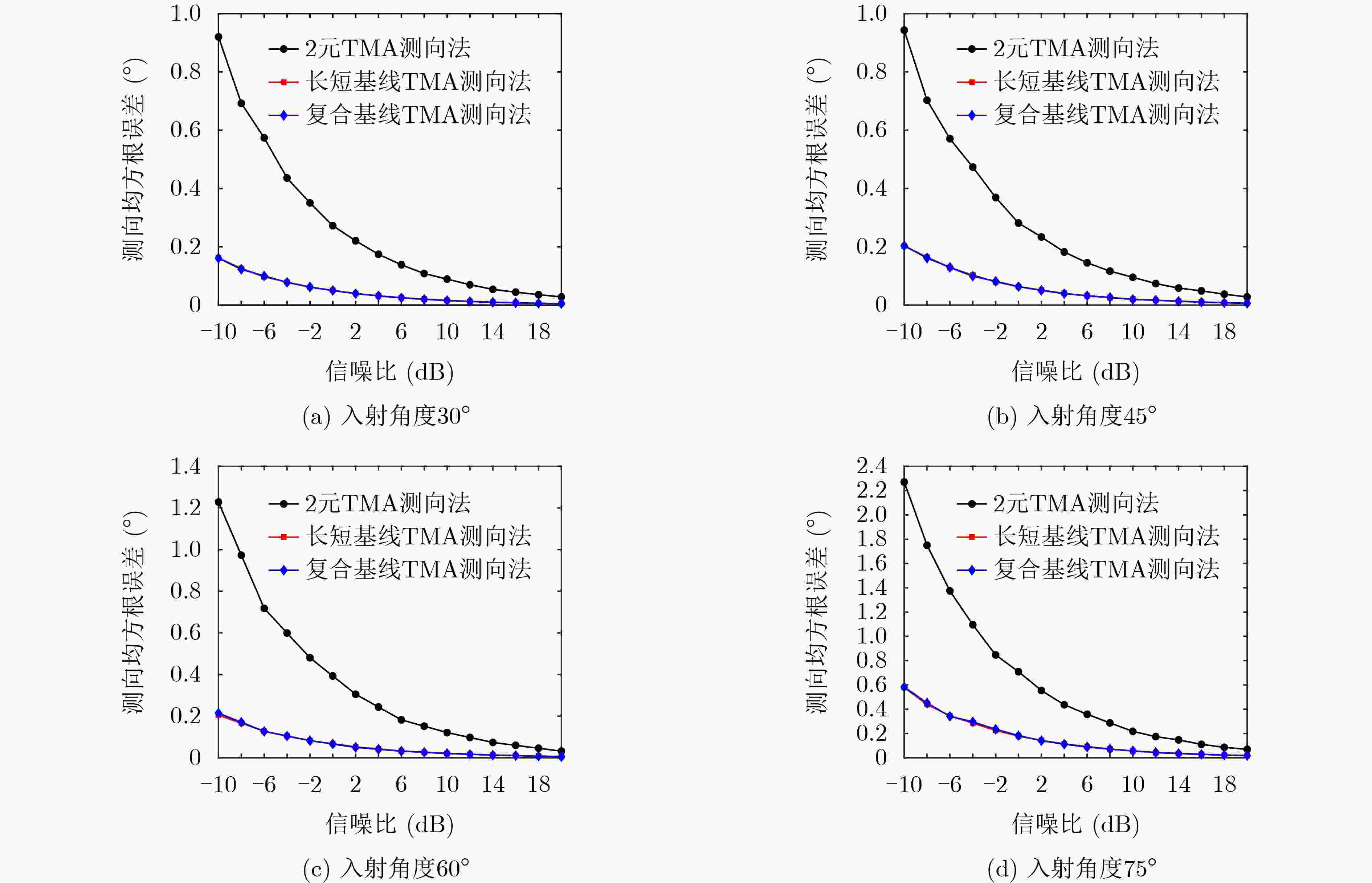
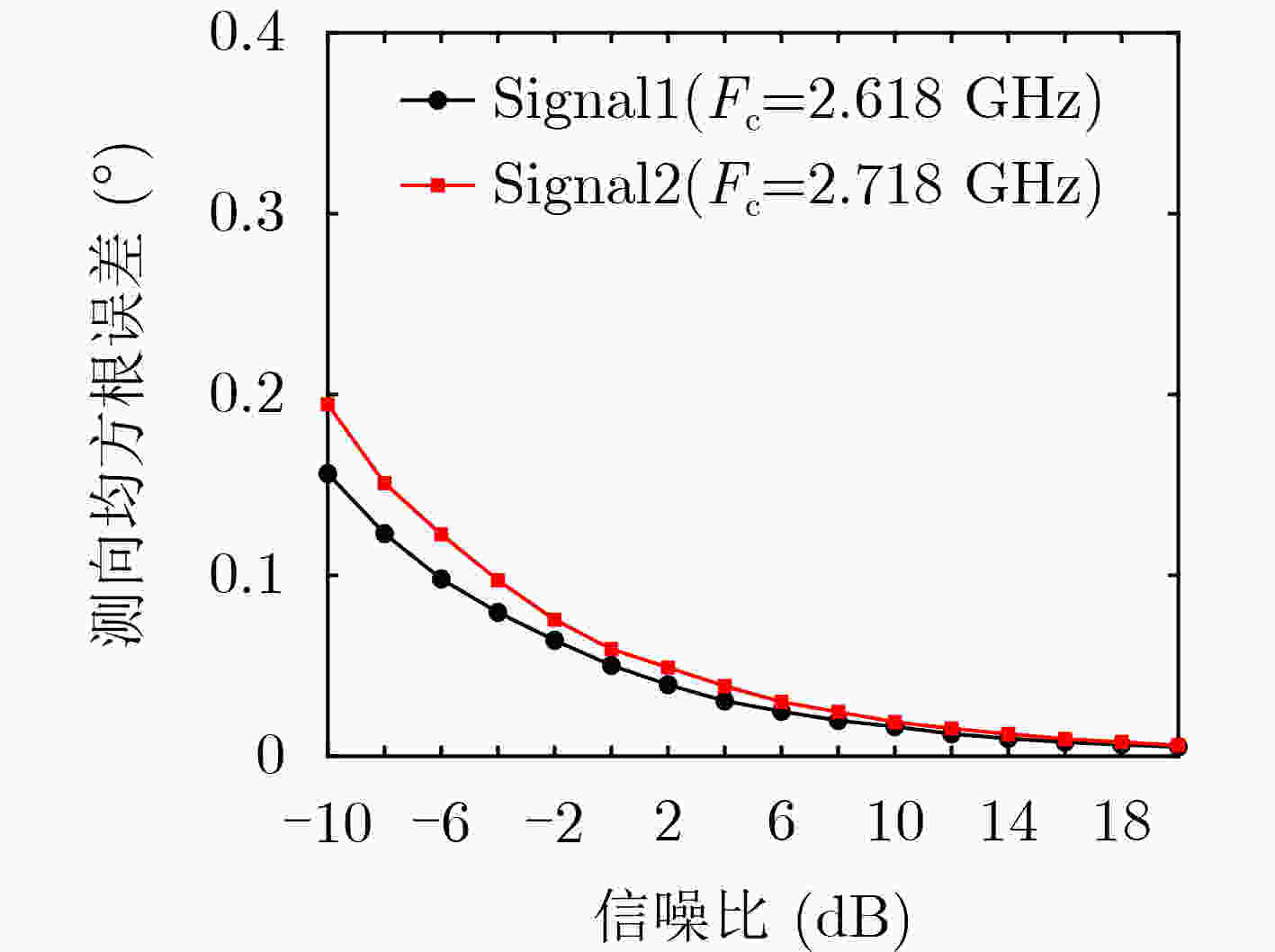

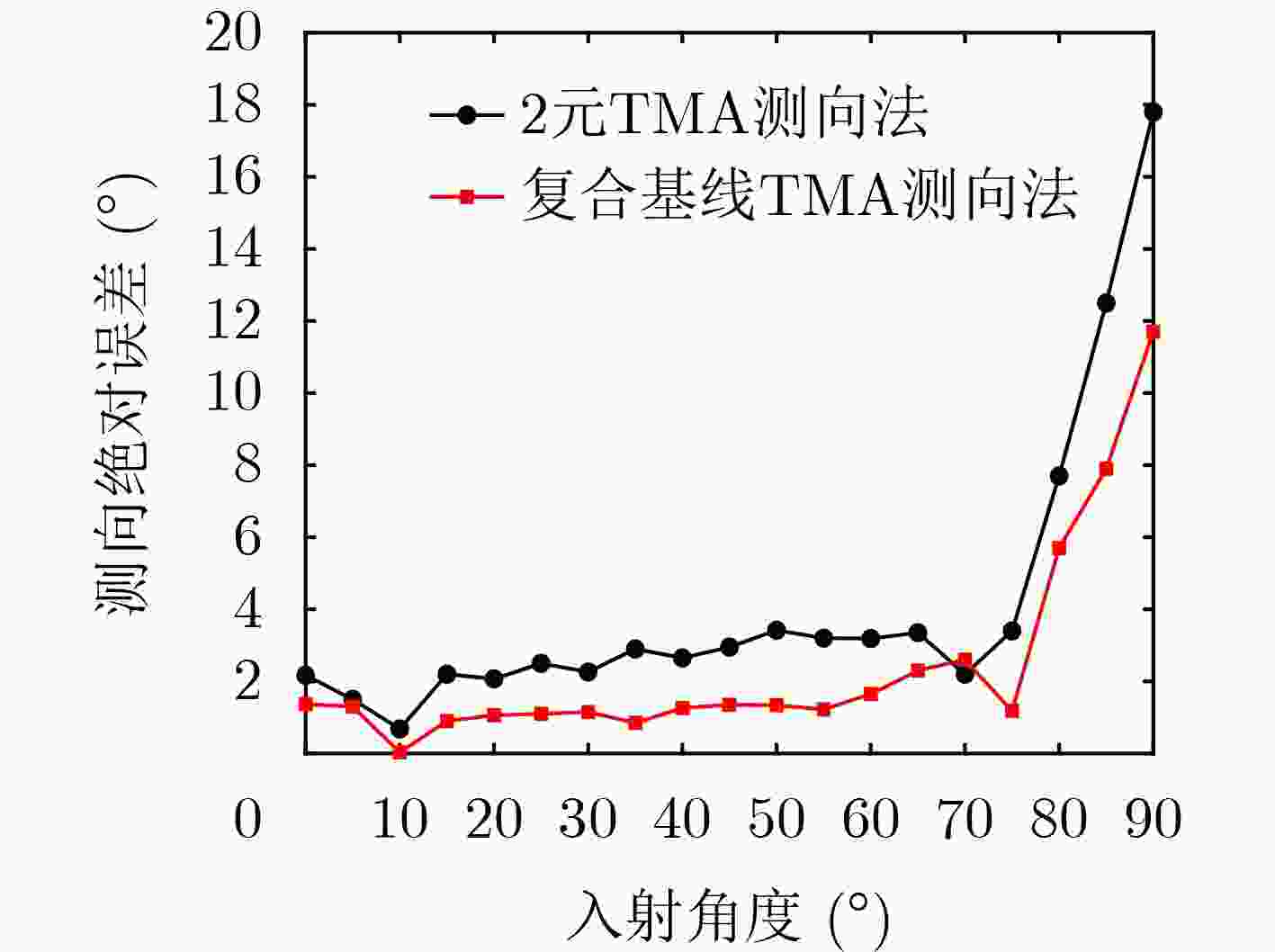


 下载:
下载:
