Design of Strong Physical Unclonable Function Circuit Against Machine Learning Attacks Based on Chaos Mapping
-
摘要: 物理不可克隆函数(PUF)在硬件安全领域具有广阔的应用前景,然而易受到基于机器学习等建模攻击。通过对强PUF电路结构和混沌映射机理的研究,该文提出一种可有效抵御机器学习建模攻击的PUF电路。该电路将原始激励作为混沌映射初始值,利用PUF激励响应映射时间与混沌算法迭代深度之间的内在联系产生不可预测的混沌值,并采用PUF中间响应反馈加密激励,进一步提升激励与响应映射的复杂度,增强PUF的抗机器学习攻击能力。该PUF采用Artix-7 FPGA实现,测试结果表明,即使选用的激励响应对数量高达106组,基于逻辑回归、支持向量机和人工神经网络的攻击预测率仍接近50%的理想值,并具有良好的随机性、唯一性和稳定性。Abstract: Physical Unclonable Function (PUF) has broad application prospects in the field of hardware security, but it is susceptible to modeling attacks based on machine learning. By studying the strong PUF circuit structure and chaotic mapping mechanism, a PUF circuit that can effectively resist machine learning modeling attacks is proposed. This circuit takes the original excitation as the initial value of the chaotic mapping, utilizes the internal relationship between the PUF excitation response mapping time and the iteration depth of the chaotic algorithm to generate unpredictable chaotic values, and uses PUF intermediate response feedback to encrypt the excitation. It can further improve the complexity of excitation and response mapping, thereby enhancing the resistance of PUF to machine learning attacks. The PUF is implemented using Artix-7 FPGA. The test results show that even with up to 1 million sets of excitation response pairs selected, the attack prediction rate based on logistic regression, support vector machine, and artificial neural network is still close to the ideal value of 50%. And the PUF has good randomness, uniqueness, and stability.
-
表 1 CM-PUF 的随机性NIST 测试结果
NIST检测项 APUF 5XOR-PUF CM-PUF P-value Proportion P-value Proportion P-value Proportion 频率检验 0* 4/50 0* 0/50 0* 39/50 场内频数检验 0* 0/50 0* 1/50 0.026 948 50/50 游程检验 0* 0/50 0* 0/50 0* 28/50 块内最长游程检验 0* 0/50 0* 0/50 0* 36/50 2元矩阵秩检验 0.574 903 47/50 0.425 305 50/50 0.236 810 50/50 离散傅里叶变换检验 0* 0/50 0* 0/50 0.108 791 50/50 非重叠模块匹配检验 0* 37/50 0.322 346 50/50 0.991 468 50/50 重叠模块匹配检验 0* 11/50 0* 19/50 0.383 827 49/50 线性复杂度检验 0.236 810 49/50 0.419 021 49/50 0.779 188 48/50 累积和检验 0* 0/50 0* 0/50 0* 40/50 通用统计检验 0* 0/50 0* 0/50 0* 50/50 近似熵检验 0* 0/50 0* 0/50 0.013 569 46/50 序列检验 0* 0/50 0* 0/50 0* 26/50 *表示P-value 的值非常小,接近于0 表 2 各类PUF电路统计特性、抗攻击能力与硬件开销对比
PUF类型 随机性(%) 唯一性(%) 稳定性(%) 机器学习攻击预测率(%) 硬件开销 LR ANN SVM LUTs FFs SLICEs APUF[1] 50.73 49.56 99.02 99.30 99.12 98.98 266 278 109 2XOR-PUF[1] 50.13 49.35 98.36 96.91 96.63 96.74 469 279 177 5XOR-PUF[1] 50.07 50.59 92.54 53.89 85.47 54.31 786 282 440 CT PUF[4] 49.00~50.00 49.00~50.00 92.00 57.00 – 55.00 731 486 244 CaPUF[6] 46.38 47.03 88.47 50.00~56.00 – 50.00~56.00 5723 – – CM-PUF 50.53 50.08 98.74 50.33 50.33 50.24 491 546 240 -
[1] ZHOU Ziyu, LI Gang, and WANG Pengjun. A challenge-screening strategy for enhancing the stability of strong PUF based on machine learning[J]. Microelectronics Journal, 2023, 131: 105667. doi: 10.1016/j.mejo.2022.105667. [2] 汪鹏君, 连佳娜, 陈博. 基于序列密码的强PUF抗机器学习攻击方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(9): 2474–2481. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210726.WANG Pengjun, LIAN Jiana, and CHEN Bo. Sequence cipher based machine learning-attack resistance method for strong-PUF[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2021, 43(9): 2474–2481. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210726. [3] LI Hui, LI Gang, WANG Pengjun, et al. A novel machine learning attack resistant APUF with dual-edge acquisition[C]. Asian Hardware Oriented Security and Trust Symposium (AsianHOST), Singapore, 2022: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/AsianHOST56390.2022.10022247. [4] XIE Yuanfeng, LI Gang, WANG Pengjun, et al. A compact weak PUF circuit based on MOSFET subthreshold leakage current[J]. IEICE Electronics Express, 2022, 19(21): 20220415. doi: 10.1587/elex.19.20220415. [5] ALI R, MA Haoyuan, HOU Zhengyi, et al. A reconfigurable arbiter MPUF with high resistance against machine learning attack[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2021, 57(10): 1–7. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2021.3102838. [6] ZHANG Jiliang, SHEN Chaoqun, GUO Zhiyang, et al. CT PUF: Configurable tristate PUF against machine learning attacks for IoT Security[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(16): 14452–14462. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3090475. [7] WU Linjun, HU Yupeng, ZHANG Kehuan, et al. FLAM-PUF: A response–feedback-based lightweight anti-machine-learning-attack PUF[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2022, 41(11): 4433–4444. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2022.3197696. [8] NASSAR H, BAUER L, and HENKEL J. CaPUF: Cascaded PUF structure for machine learning resiliency[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2022, 41(11): 4349–4360. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2022.3197539. [9] ZHANG Jieyun, XU Chongyao, LAW M K, et al. A 4T/cell amplifier-chain-based XOR PUF with strong machine learning attack resilience[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2022, 69(1): 366–377. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2021.3114084. [10] OUN A and NIAMAT M. Design of a delay-based FPGA PUF resistant to machine learning attacks[C]. IEEE International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), Lansing, USA, 2021: 865–868. doi: 10.1109/MWSCAS47672.2021.9531815. [11] AVVARU S V S, ZENG Ziqing, and PARHI K K. Homogeneous and heterogeneous feed-forward XOR physical Unclonable functions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2020, 15: 2485–2498. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2020.2968113. [12] SHAH N, CHATTERJEE D, SAPUI B, et al. Introducing recurrence in strong PUFs for enhanced machine learning attack resistance[J]. IEEE Journal on Emerging and Selected Topics in Circuits and Systems, 2021, 11(2): 319–332. doi: 10.1109/JETCAS.2021.3075767. [13] WANG Yale, WANG Chenghua, GU Chongyan, et al. A dynamically configurable PUF and dynamic matching authentication protocol[J]. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computing, 2022, 10(2): 1091–1104. doi: 10.1109/TETC.2021.3072421. [14] WANG Yale, WANG Chenghua, GU Chongyan, et al. A generic dynamic responding mechanism and secure authentication protocol for strong PUFs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2022, 30(9): 1256–1268. doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2022.3189953. [15] 张笑天, 汪鹏君, 张跃军, 等. 基于动态亚阈值的延迟型PUF电路设计[J]. 华东理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2022, 48(2): 237–243. doi: 10.14135/j.cnki.1006-3080.20210203001.ZHANG Xiaotian, WANG Pengjun, ZHANG Yuejun, et al. Design of delayed PUF circuit based on dynamic subthreshold[J]. Journal of East China University of Science and Technology, 2022, 48(2): 237–243. doi: 10.14135/j.cnki.1006-3080.20210203001. [16] PAN Peng, WANG Haiquan, SHEN Lei, et al. Equivalence of joint ML-decoding and separate MMSE-ML decoding for training-based MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 178862–178869. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2958700. [17] 杨剑锋, 乔佩蕊, 李永梅, 等. 机器学习分类问题及算法研究综述[J]. 统计与决策, 2019, 35(6): 36–40. doi: 10.13546/j.cnki.tjyjc.2019.06.008.YANG Jianfeng, QIAO Peirui, LI Yongmei, et al. A review of machine-learning classification and algorithms[J]. Statistics & Decision, 2019, 35(6): 36–40. doi: 10.13546/j.cnki.tjyjc.2019.06.008. [18] 魏旭晖, 王辉. 异构网络下TCP拥塞控制的混沌特性分析[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2015, 27(7): 1541–1547. doi: 10.16182/j.cnki.joss.2015.07.018.WEI Xuhui and WANG Hui. Chaos analysis for TCP congestion control in heterogeneous networks[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2015, 27(7): 1541–1547. doi: 10.16182/j.cnki.joss.2015.07.018. [19] WANNABOON C and KETTHONG P. A simple random-bit generator implemented on FPGA based on Signum chaotic map[C]. 2022 International Conference on Digital Government Technology and Innovation (DGTi-CON), Bangkok, Thailand, 2022: 101–104. doi: 10.1109/DGTi-CON53875.2022.9849189. [20] LEE C Y, BHARATHI K, LANSFORD J, et al. NIST-lite: Randomness testing of RNGs on an energy-constrained platform[C]. IEEE 39th International Conference on Computer Design (ICCD), Storrs, USA, 2021: 41–48. doi: 10.1109/ICCD53106.2021.00019. -





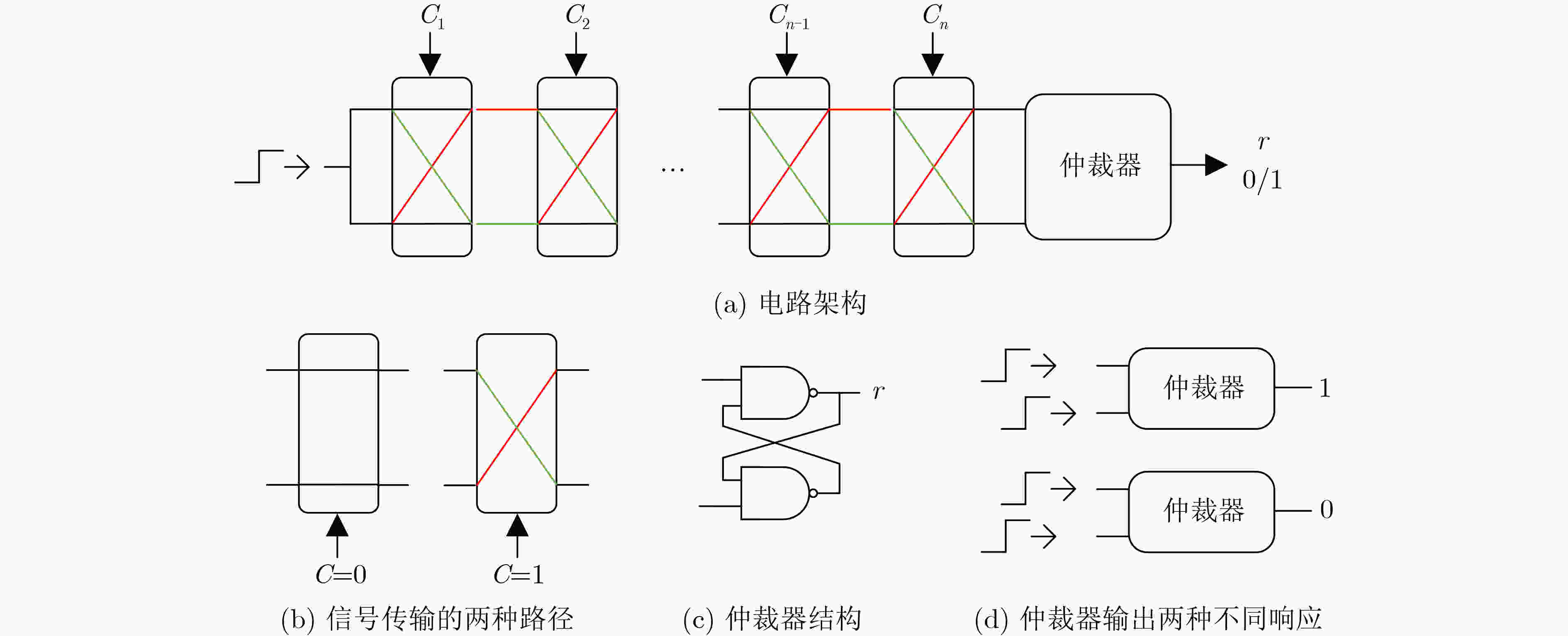
 下载:
下载:
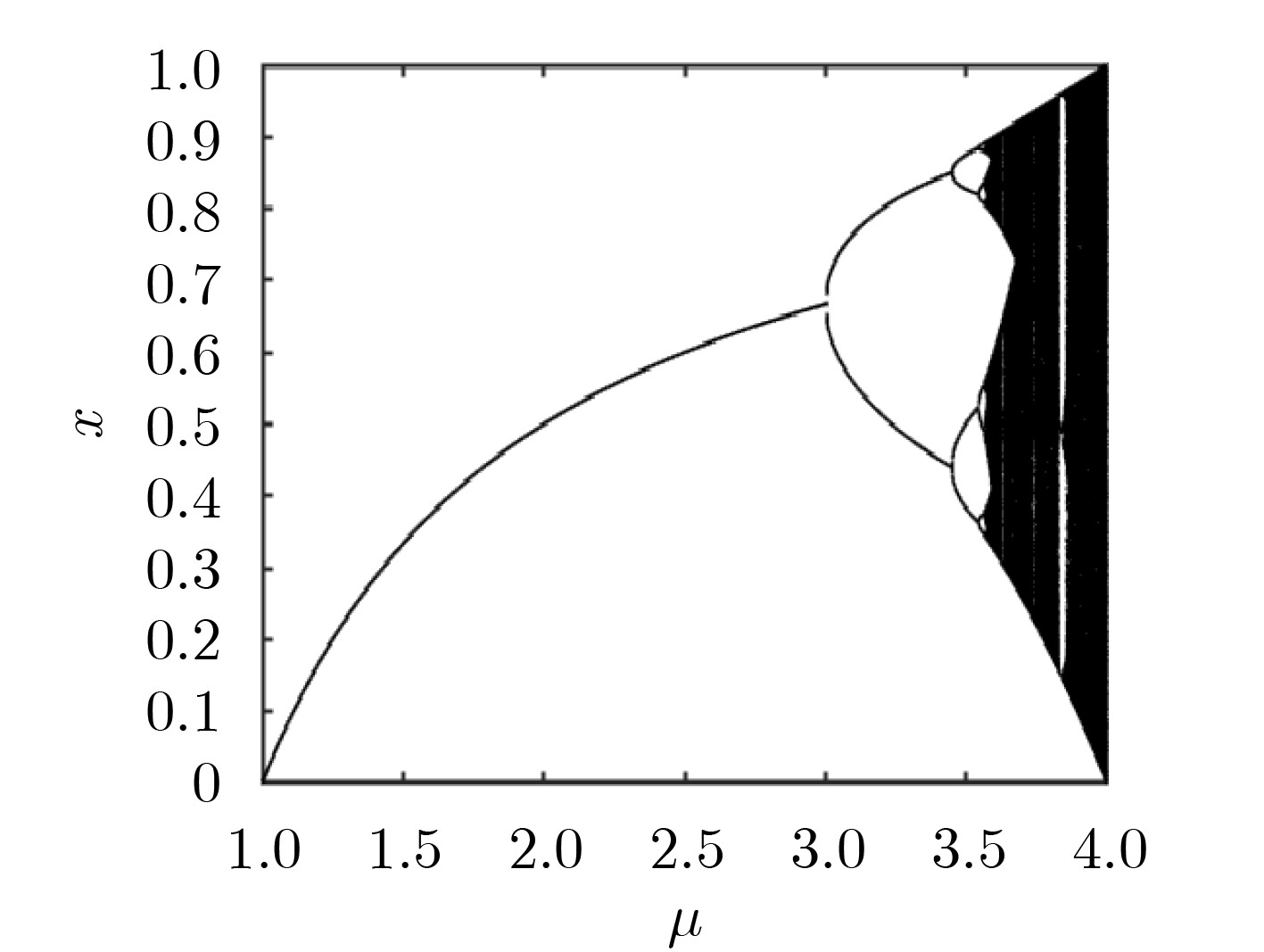
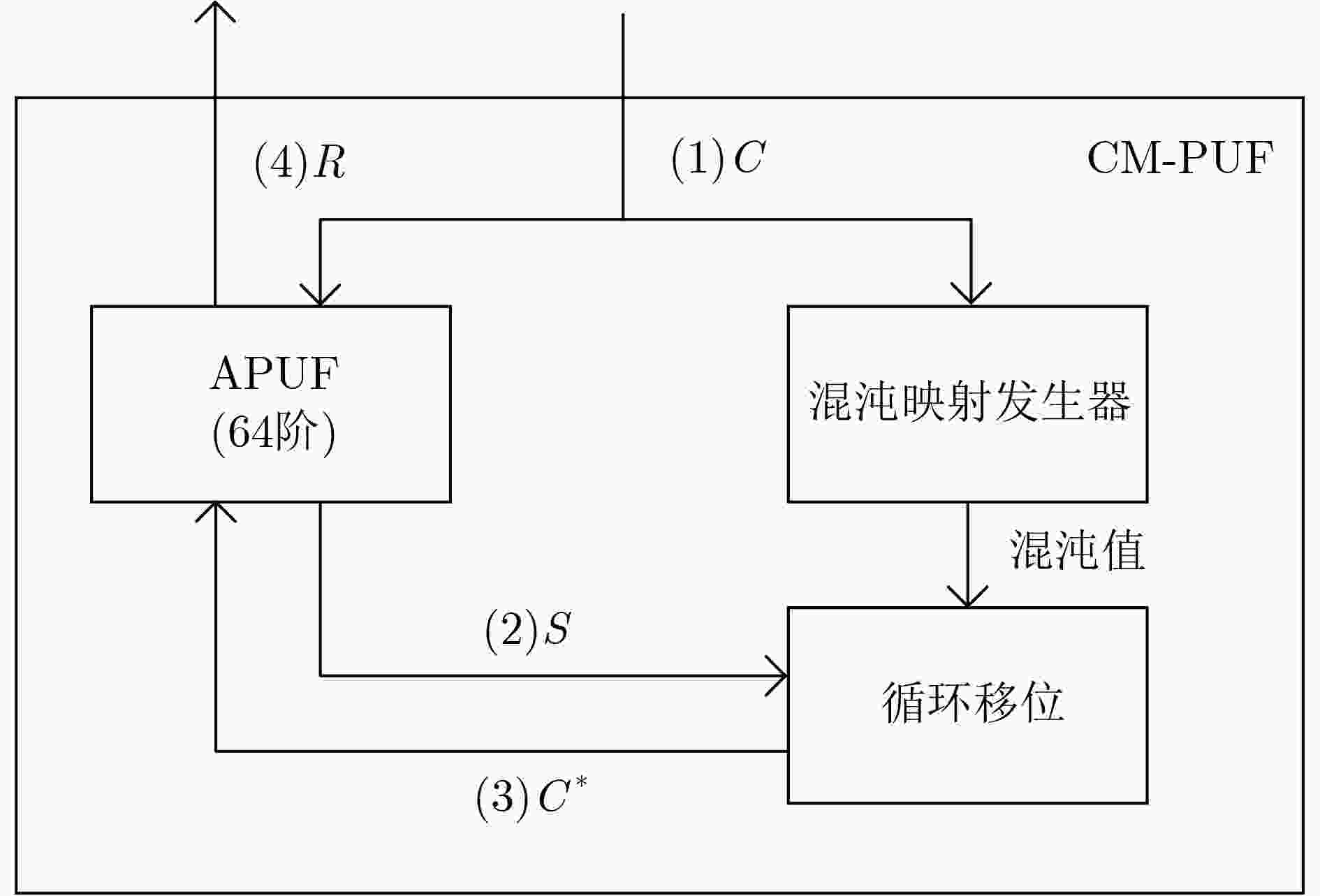
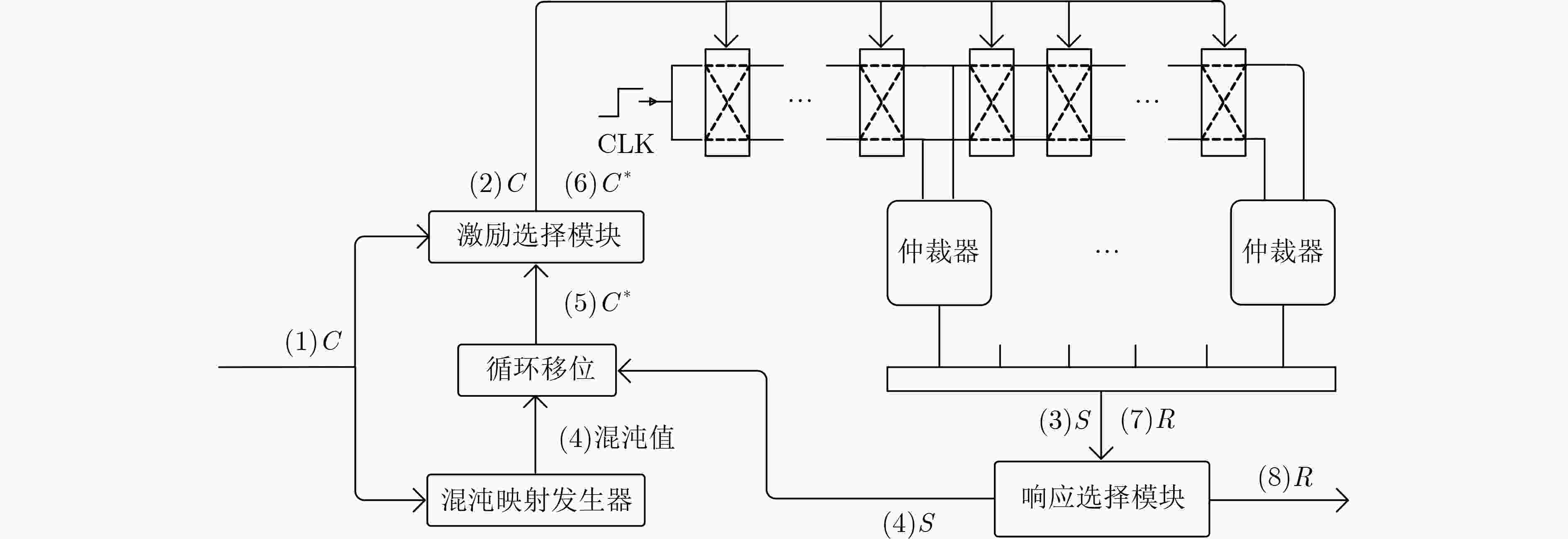
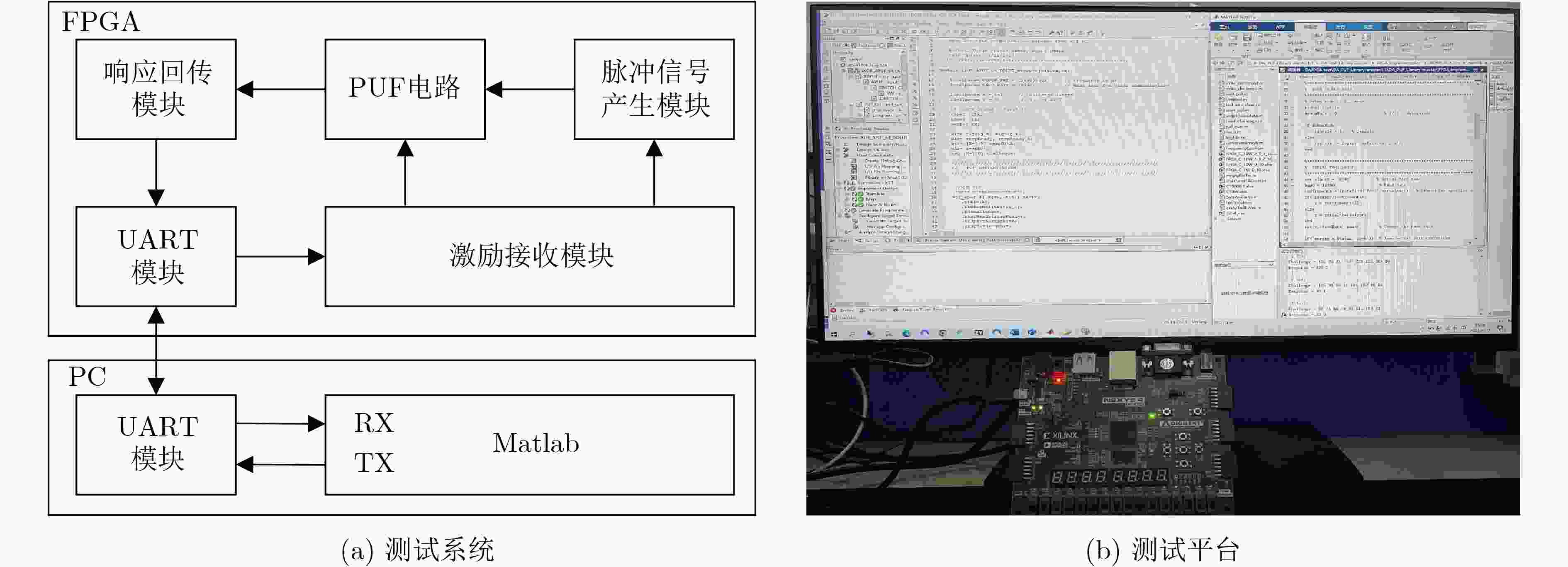
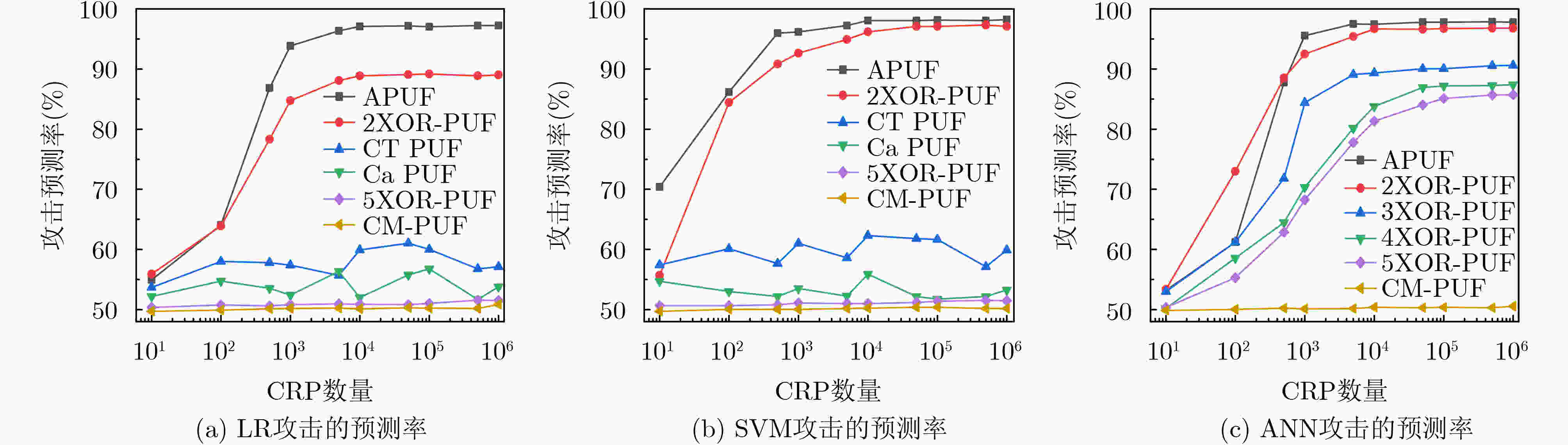
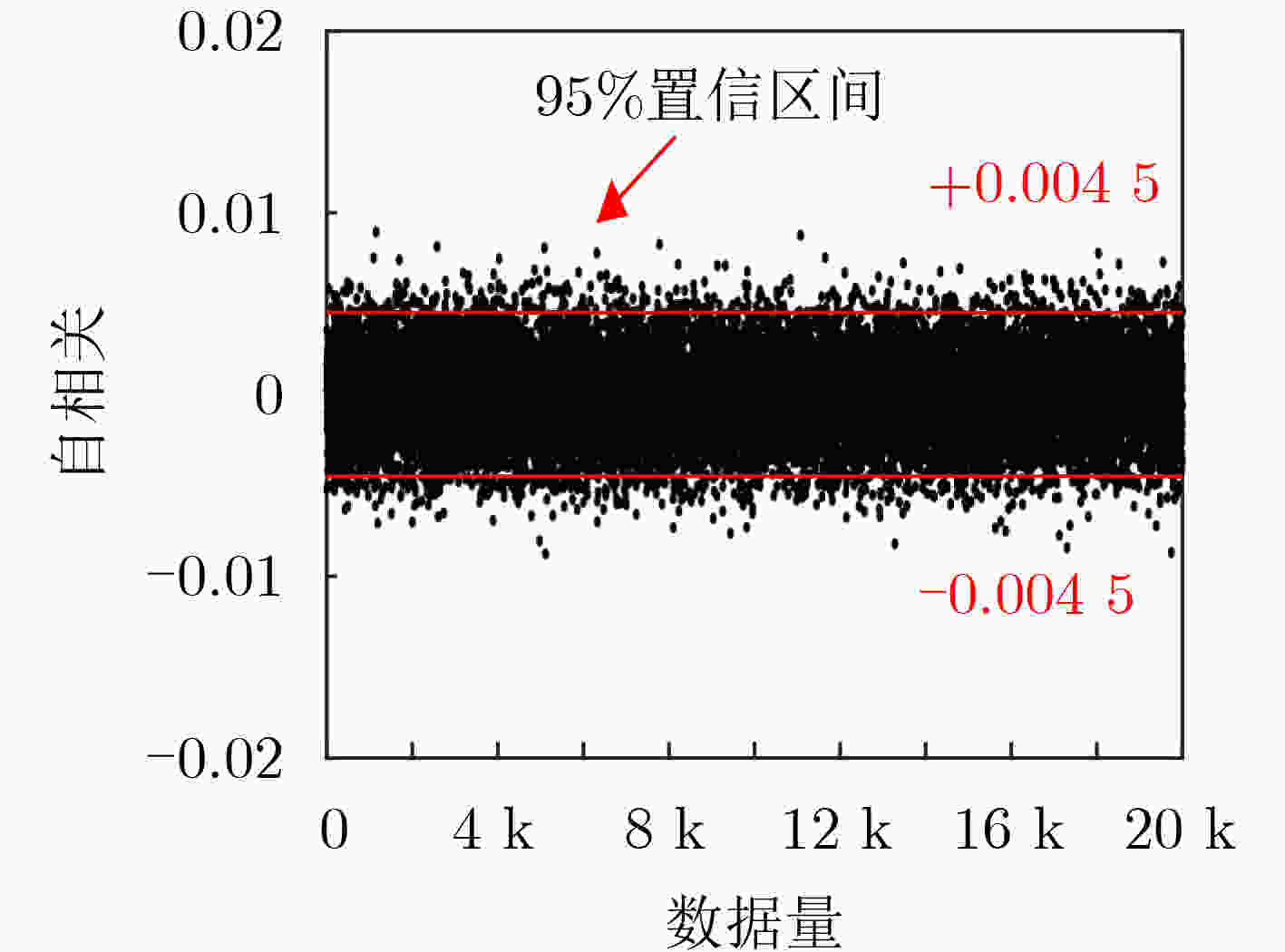
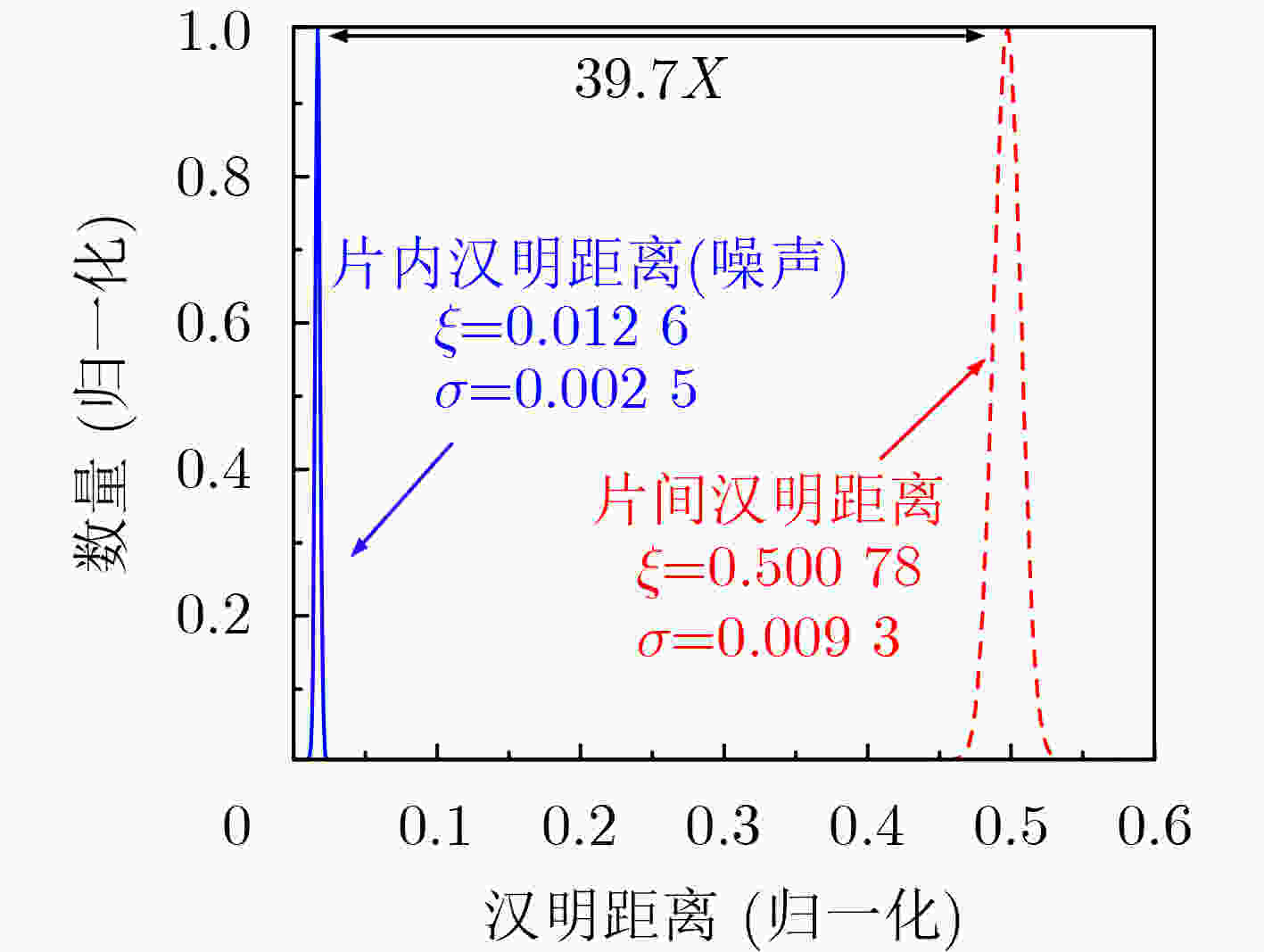


 下载:
下载:
