An Overview on Multi-dimensional Expanded Integrated Sensing and Communication for 6G
-
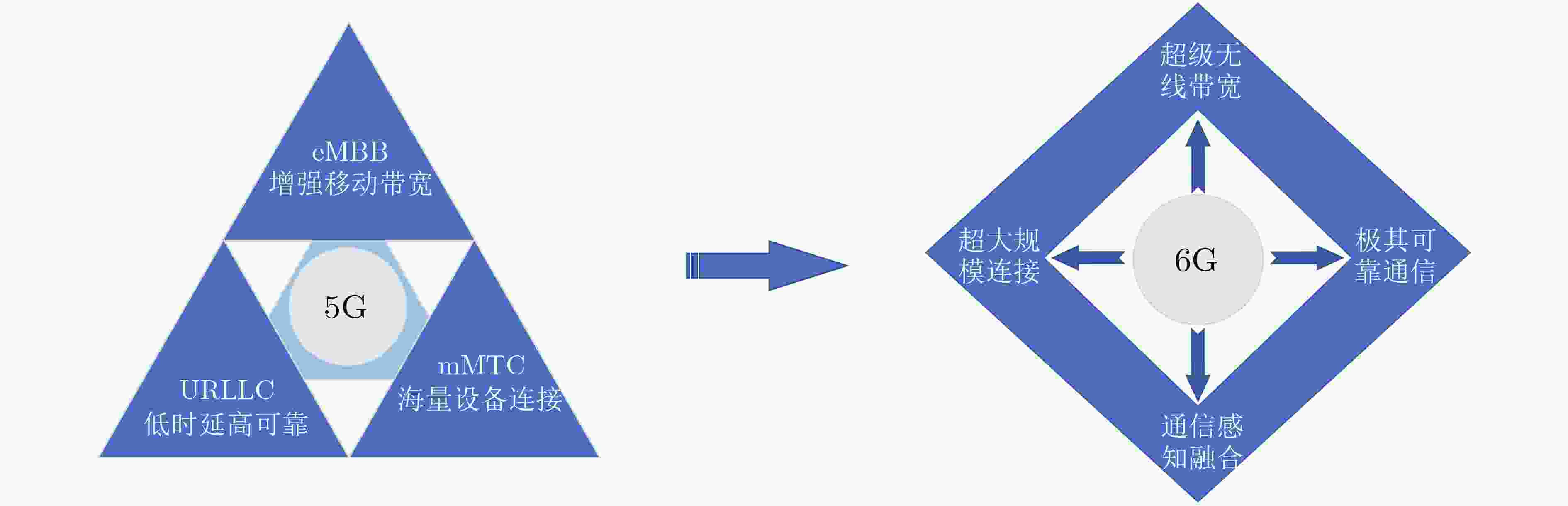
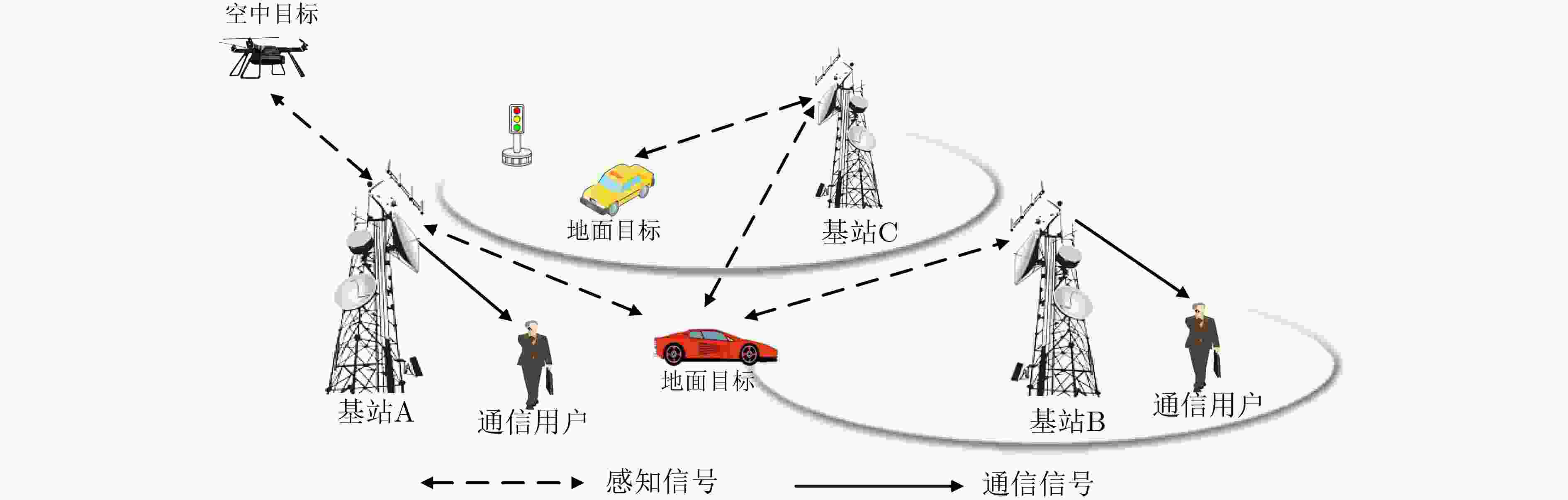
摘要: 面对第6代移动通信(6G)网络立体覆盖的互联感知需求和无线设备广泛接入造成的频谱稀缺问题,基于无人机(UAV)的机动性和智能反射面(IRS)重构无线传播环境特性的多维扩展通感一体化可实现立体网络空间中通信和感知功能的相互协同,有效提升频谱效率和硬件资源的利用率,满足6G万物智联的无线网络愿景。该文针对6G多维扩展通感一体化网络架构展开综述。首先,概述了 6G网络愿景和通感一体化的理论基础,并讨论基于UAV和IRS多维扩展通感一体化的应用场景、发展趋势和性能指标。然后,探讨了超大规模多输入多输出天线、太赫兹、无线携能通信、人工智能、隐蔽通信和有源反射面等6G关键前沿技术在基于无人机和智能反射面多维扩展通感一体化网络中的潜在应用。最后,展望了未来6G多维扩展通感一体化的发展方向及关键技术挑战。Abstract: Facing the demand for interconnectivity sensing of three-dimensional coverage for the sixth-Generation mobile communication (6G) networks and the spectrum scarcity issue caused by the widespread access of wireless devices, the multi-dimensional expanded Integrated Sensing and Communication (ISAC), based on Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV) and Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces (IRS), is capable of achieving synergistic communication and sensing functions in the three-dimensional network space. This can effectively enhance spectrum efficiency, hardware resource utilization, and align with the wireless network vision of 6G Internet of Everything. This paper provides an overview of the architecture for the 6G multi-dimensional expanded ISAC. Firstly, it summarizes the theoretical foundations of the 6G network vision and ISAC networks, and the application scenarios, development trends, and performance indicators of multi-dimensional expanded ISAC based on UAV and IRS are discussed. Then, it investigates the potential applications of 6G key technologies, such as ultra-massive multiple-input and multiple-output antenna, terahertz, simultaneous wireless information and power transfer, artificial intelligence, covert communication, and active IRS, in multi-dimensional expanded ISAC networks based on UAV and IRS. Finally, the future development direction and key technical challenges of 6G multi-dimensional expanded ISAC sre prospected.
-
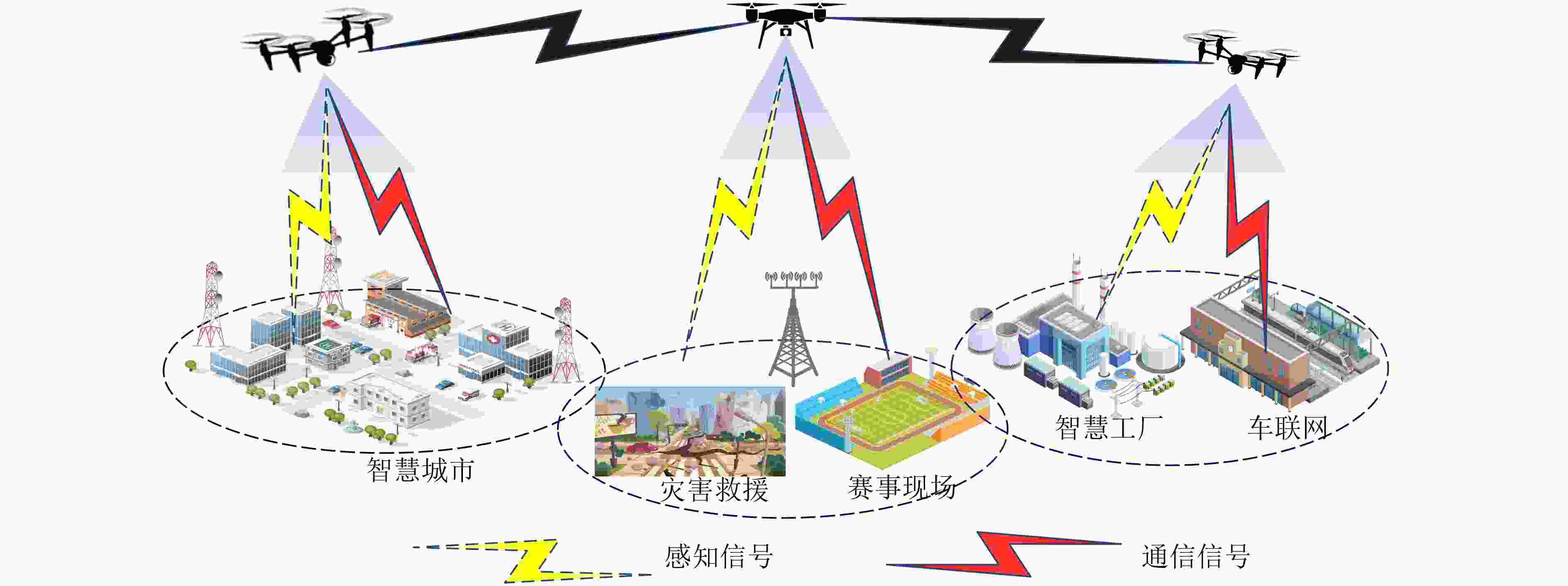
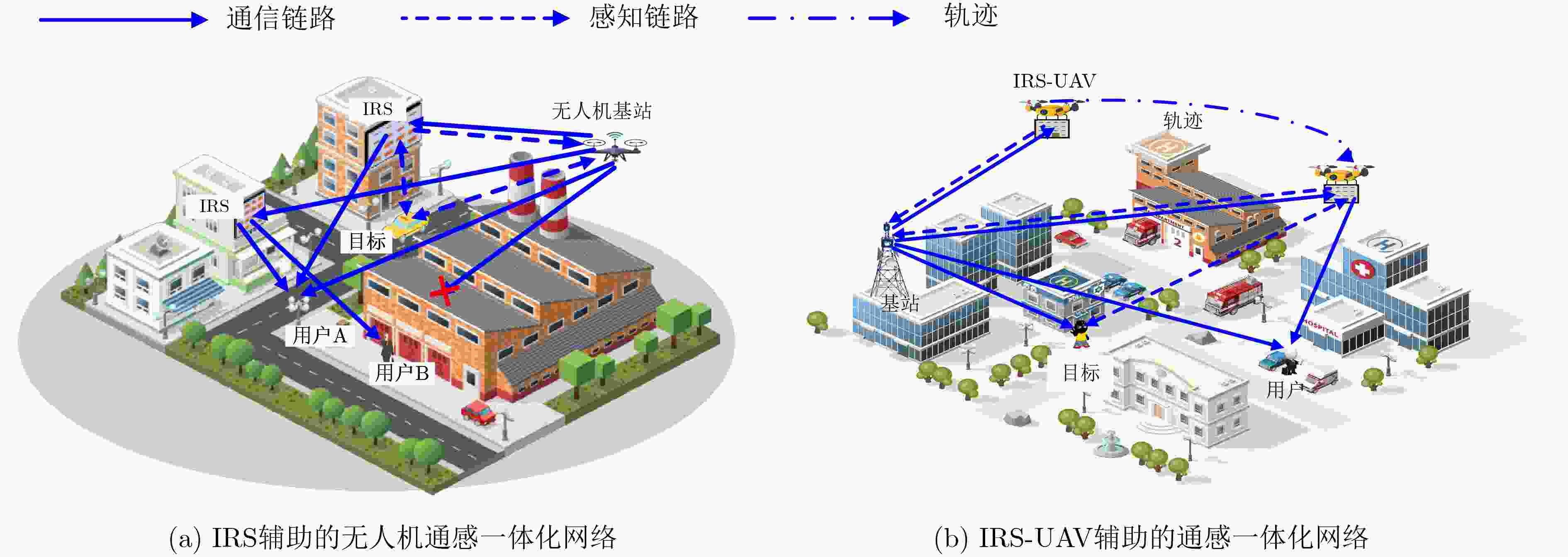
表 1 基于UAV和IRS多维扩展的通感一体化网络应用场景
场景/应用分类 同步成像与环境重构 高精度定位与跟踪 增强人类感官 动作和表情识别 智慧工厂 区域检测和环境感知 设备定位和安装 自动化测量和控制 产品质量检测 垂直行业 智慧农业 作物生理监测和生产 自动化收取和存储 种植环境检测 作物质量监管 智慧交通 3D道路成像 无人驾驶与辅助驾驶 雨雾天气路况监测 安全驾驶 环境监测 无人机集群管理 水利水文监测 污染与空气质量检测 残障保障服务 公共服务 公共安全 灾害应急管理和疏散 交通运输安全 无接触安全检测 突发事件预测 城市管理 城市环境监督 城市文明监察 建筑安全风险检测 全时段监控 灾难救援 灾情评估与灾后重建 人员定位与物资投送 灾区环境检测 人员搜救 极端场景 战场支援 实时情报获取 精确打击支持 敌对目标监视和侦测 敌情侦测与分析 应用 太空探测 地球和大气监测 太空垃圾探测 星际空间探测 航天员健康检测 海洋勘探 海洋资源勘探 海上巡逻与航行安全 海洋气象和气候监测 海洋生态监测 表 2 现有ISAC和波形设计简要总结
表 3 基于UAV和IRS的多维扩展通感一体化网络性能指标
性能分类 性能指标 具体要求 通信性能 带宽和速率
稳定性传输数据的速度和容量,较大的带宽能够支持高分辨率图像、视频等大数据传输
保障UAV在高速运动和复杂环境中通信连接的可靠性,防止干扰和信号丢失感知性能 感知范围
感知精度感知功能的有效覆盖区域,UAV和IRS可提供更广泛的环境信息
感知系统识别目标和获取环境信息的准确度和可靠性,影响系统的决策能力多源数据
融合性能数据融合精度
传输时延不同传感器数据融合后的信息准确性,能够提供更全面、准确的环境认知
确保感知数据的快速获取和信息交互效率,提高系统的实时决策能力数据质量
和准确性鲁棒性
隐私和安全性在干扰和突发情况下,UAV的移动性和IRS环境重构能力保障系统功能的弹性设计
提供安全的数据传输和存储机制,保障敏感信息的安全传输网络协
同性能自适应性
能耗和计算资源基于IRS-UAV的无线网络需实现空地网络的相互协同,适应环境和任务需求的变化
保持低能耗,确保感知和数据处理和计算不过度消耗电力,提高UAV的续航能力 -
[1] 易芝玲, 王森, 韩双锋, 等. 从5G到6G的思考: 需求、挑战与技术发展趋势[J]. 北京邮电大学学报, 2020, 43(2): 1–9. doi: 10.13190/j.jbupt.2020-024.YI Zhiling, WANG Sen, HAN Shuangfeng, et al. From 5G to 6G: Requirements, challenges and technical trends[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2020, 43(2): 1–9. doi: 10.13190/j.jbupt.2020-024. [2] LIU Guangyi, HUANG Yuhong, LI Na, et al. Vision, requirements and network architecture of 6G mobile network beyond 2030[J]. China Communications, 2020, 17(9): 92–104. doi: 10.23919/JCC.2020.09.008. [3] ZHANG Shunqing, XIANG Chenlu, and XU Shugong. 6G: Connecting everything by 1000 times price reduction[J]. IEEE Open Journal of Vehicular Technology, 2020, 1: 107–115. doi: 10.1109/OJVT.2020.2980003. [4] HAN Chong, WANG Yiqin, LI Yuanbo, et al. Terahertz wireless channels: A holistic survey on measurement, modeling, and analysis[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2022, 24(3): 1670–1707. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2022.3182539. [5] 赵亚军, 郁光辉, 徐汉青. 6G移动通信网络: 愿景、挑战与关键技术[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2019, 49(8): 963–987. doi: 10.1360/N112019-00033.ZHAO Yajun, YU Guanghui, and XU Hanqing. 6G mobile communication networks: Vision, challenges, and key technologies[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Informationis, 2019, 49(8): 963–987. doi: 10.1360/N112019-00033. [6] AKAN O B and ARIK M. Internet of radars: Sensing versus sending with joint radar-communications[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2020, 58(9): 13–19. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.1900550. [7] LIU Rang, LI Ming, LUO Honghao, et al. Integrated sensing and communication with reconfigurable intelligent surfaces: Opportunities, applications, and future directions[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2023, 30(1): 50–57. doi: 10.1109/MWC.002.2200206. [8] 张嘉慧, 王新奕, 费泽松, 等. 6G通感融合网络中的物理层安全: 机遇与挑战[J]. 移动通信, 2023, 47(3): 55–61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.20230204-0002.ZHANG Jiahui, WANG Xinyi, FEI Zesong, et al. Physical layer security in 6G integrated sensing and communication systems: Opportunities and challenges[J]. Mobile Communications, 2023, 47(3): 55–61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.20230204-0002. [9] 陈新颖, 盛敏, 李博, 等. 面向6G的无人机通信综述[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(3): 781–789. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210789.CHEN Xinying, SHENG Min, LI Bo, et al. Survey on unmanned aerial vehicle communications for 6G[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(3): 781–789. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210789. [10] 朱政宇, 王梓晅, 徐金雷, 等. 智能反射面辅助的未来无线通信: 现状与展望[J]. 航空学报, 2022, 43(2): 025014. doi: 10.7527/s1000-6893.2021.25014.ZHU Zhengyu, WANG Zixuan, XU Jinlei, et al. Future wireless communication assisted by intelligent reflecting surface: State of art and prospects[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2022, 43(2): 025014. doi: 10.7527/s1000-6893.2021.25014. [11] 朱政宇, 徐金雷, 孙钢灿, 等. 基于IRS辅助的SWIPT物联网系统安全波束成形设计[J]. 通信学报, 2021, 42(4): 185–193. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000−436x.2021060.ZHU Zhengyu, XU Jinlei, SUN Gangcan, et al. Secure beamforming design for IRS-assisted SWIPT internet of things system[J]. Journal on Communications, 2021, 42(4): 185–193. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000−436x.2021060. [12] PANG Xiaowei, SHENG Min, ZHAO Nan, et al. When UAV meets IRS: Expanding air-ground networks via passive reflection[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2021, 28(5): 164–170. doi: 10.1109/MWC.010.2000528. [13] HE Yinghui, CAI Yunlong, MAO Hao, et al. RIS-assisted communication radar coexistence: Joint beamforming design and analysis[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2022, 40(7): 2131–2145. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2022.3155507. [14] SU Yuhua, PANG Xiaowei, CHEN Shanzhi, et al. Spectrum and energy efficiency optimization in IRS-assisted UAV networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2022, 70(10): 6489–6502. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2022.3201122. [15] LIU Fan, CUI Yuanhao, MASOUROS C, et al. Integrated sensing and communications: Toward dual-functional wireless networks for 6G and beyond[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2022, 40(6): 1728–1767. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2022.3156632. [16] 伍光新, 姚元, 祁琳琳. 雷达通信波形一体化发展综述[J]. 现代雷达, 2021, 43(9): 37–45. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2021.09.007.WU Guangxin, YAO Yuan, and QI Linlin. An overview on radar-communication integration of waveform[J]. Modern Radar, 2021, 43(9): 37–45. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2021.09.007. [17] IMT-2030(6G)推进组. 6G网络架构愿景与关键技术展望白皮书[R]. 2021.IMT-2030 (6G) Promotion Group. 6G Network Architecture Vision and Key Technology Outlook White Paper[R]. 2021. [18] CUI Yanpeng, FENG Zhiyong, ZHANG Qixun, et al. Toward trusted and swift UAV communication: ISAC-enabled dual identity mapping[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2023, 30(1): 58–66. doi: 10.1109/MWC.003.2200207. [19] MENG Kaitao, WU Qingqing, MA Shaodan, et al. Throughput maximization for UAV-enabled integrated periodic sensing and communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2023, 22(1): 671–687. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2022.3197623. [20] SHAO Xiaodan, YOU Changsheng, MA Wenyan, et al. Target sensing with intelligent reflecting surface: Architecture and performance[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2022, 40(7): 2070–2084. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2022.3155546. [21] YOU Changsheng, KANG Zhenyu, ZENG Yong, et al. Enabling smart reflection in integrated air-ground wireless network: IRS meets UAV[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2021, 28(6): 138–144. doi: 10.1109/MWC.001.2100148. [22] PANG Xiaowei, ZHAO Nan, TANG Jie, et al. IRS-assisted secure UAV transmission via joint trajectory and beamforming design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2022, 70(2): 1140–1152. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3136563. [23] 李国琳, 郭文彬. 雷达通信一体化波形设计综述[J]. 移动通信, 2022, 46(5): 38–44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.2022.05.006.LI Guolin and GUO Wenbin. Waveform design for integrated radar and communication: A survey[J]. Mobile Communications, 2022, 46(5): 38–44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.2022.05.006. [24] BAYESTEH A, 何佳, 陈雁, 等. 通信感知一体化——从概念到实践[EB/OL].https://www.huawei.com/cn/huaweitech/future-technologies/integrated-sensing-communication-concept-practice, 2022.BAYESTEH A, HE Jia, CHEN Yan, et al. Integration of communication and perception-from concept to practice[EB/OL].https://www.huawei.com/cn/huaweitech/future-technologies/integrated-sensing-communication-concept-practice, 2022. [25] XIAO Zhiqiang and ZENG Yong, Waveform design and performance analysis for full-duplex integrated sensing and communication [J] IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2022, 40(6):1823–1837. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2022.3155509. [26] HUANG Tianyao, SHLEZINGER N, XU Xingyu, et al. MAJoRCom: A dual-function radar communication system using index modulation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 3423–3438. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.2994394. [27] NOWAK M, WICKS M, ZHANG Zhiping, et al. Co-designed radar-communication using linear frequency modulation waveform[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2016, 31(10): 28–35. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2016.150236. [28] KUMARI P, MYERS N J, and HEATH R W. Adaptive and fast combined waveform-beamforming design for mmWave automotive joint communication-radar[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2021, 15(4): 996–1012. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2021.3071592. [29] LIU Yongjun, LIAO Guisheng, and YANG Zhiwei. Robust OFDM integrated radar and communications waveform design based on information theory[J]. Signal Processing, 2019, 162: 317–329. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2019.05.001. [30] LIU Fan, ZHOU Longfei, MASOUROS C, et al. Toward dual-functional radar-communication systems: Optimal waveform design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(16): 4264–4279. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2847648. [31] XIAO Zhiqiang and ZENG Yong. Waveform design and performance analysis for full-duplex integrated sensing and communication[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2022, 40(6): 1823–1837. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2022.3155509. [32] BAXTER W, ABOUTANIOS E, and HASSANIEN A. Joint radar and communications for frequency-hopped MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2022, 70: 729–742. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2022.3142909. [33] CUI Yuanhao, LIU Fan, JING Xiaojun, et al,Integrating sensing and communications for ubiquitous IoT: Applications, trends,and challenges[J]. IEEE Network, 2021, 35(5):158–167. doi: 10.1109/MNET.010.2100152. [34] XU Yu, ZHANG Tiankui, LIU Yuanwei, et al. UAV-enabled integrated sensing, computing, and communication: A fundamental trade-off[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2023, 12(5): 843–847. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2023.3245728. [35] 中国通信学会. 通感算一体化网络前沿报告(2021年)[R]. 中国通信学会, 2021.China Communications Society. Frontier Report on the Integrated Sensing, Communication and Computing Network[R]. China Communications Society, 2021. [36] ZHANG Zhengquan, XIAO Yue, MA Zheng, et al. 6G wireless networks: Vision, requirements, architecture, and key technologies[J]. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 2019, 14(3): 28–41. doi: 10.1109/MVT.2019.2921208. [37] CHEN Zhi, MA Xinying, ZHANG Bo, et al. A survey on terahertz communications[J]. China Communications, 2019, 16(2): 1–35. doi: 10.12676/j.cc.2019.02.001. [38] IMT-2030(6G)推进组. 太赫兹通信技术研究报告[R]. 2022.IMT-2030 (6G) Promotion Group. Terahertz Communication Technology Research Report[R]. 2022. [39] CLERCKX B, ZHANG Rui, SCHOBER R, et al. Fundamentals of wireless information and power transfer: From RF energy harvester models to signal and system designs[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2019, 37(1): 4–33. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2018.2872615. [40] WANG Jiadai, LIU Jiajia, LI Jingyi, et al. Artificial intelligence-assisted network slicing: Network assurance and service provisioning in 6G[J]. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 2023, 18(1): 49–58. doi: 10.1109/MVT.2022.3228399. [41] LIU Peng, FEI Zesong, WANG Xinyi, et al. Outage constrained robust secure beamforming in integrated sensing and communication systems[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2022, 11(11): 2260–2264. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2022.3198683. [42] 王超, 安建平, 邢成文, 等. 面向空间信息网络的隐蔽通信技术综述[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2023. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2023-0101.WANG Chao, AN Jianping, XING Chengwen, et al. A review of covert communication technologies for space information networks[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Informationis, 2023. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2023-0101. [43] ZHANG Zijian, DAI Linglong, CHEN Xibi, et al. Active RIS vs. passive RIS: Which will prevail in 6G?[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2023, 71(3): 1707–1725. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2022.3231893. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
