Direct Acyclic Graph Blockchain-based Personalized Federated Mutual Distillation Learning in Internet of Vehicles
-
摘要: 联邦学习(FL)作为一种分布式训练方法,在车联网(IoV)中得到了广泛应用。区别于传统机器学习,FL允许智能网联车辆(CAVs)通过共享模型而非原始数据来协同训练全局模型,从而保护CAV隐私和数据安全。为了提升联邦学习模型精度,降低通信开销,该文首先提出一种基于有向无环图(DAG)区块链和CAVs的IoV架构,分别负责全局模型共享和本地模型训练。其次,设计了一种基于DAG区块链的异步联邦互蒸馏学习(DAFML)算法在本地同时训练教师和学生模型,教师模型的专业级网络结构可取得更高精度,学生模型的轻量级网络结构可降低通信开销,并采用互蒸馏学习使教师模型和学生模型从互相转移的软标签中学习知识以更新模型。此外,为了进一步提高模型精度,基于全局训练轮次和模型精度设定个性化权值来调节互蒸馏占比。仿真结果表明,DAFML算法在模型精度和蒸馏比率方面优于其他比较算法。Abstract: Federated Learning (FL) emerges as a distributed training method in the Internet of Vehicle (IoV), allowing Connected and Automated Vehicles (CAVs) to train a global model by exchanging models instead of raw data, protecting data privacy. Due to the limitation of model accuracy and communication overhead in FL, in this paper, a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) blockchain-based IoV is proposed that comprises a DAG layer and a CAV layer for model sharing and training, respectively. Furthermore, a DAG blockchain-based Asynchronous Federated Mutual distillation Learning (DAFML) algorithm is introduced to improve the model performance, which utilizes a teacher model and a student model to mutual distillation in the local training. Specifically, the teacher model with a professional network could achieve higher model accuracy, while the student model with a lightweight network could reduce the communication overhead in contrast. Moreover, to further improve the model accuracy, the personalized weight based on global epoch and model accuracy is designed to adjust the mutual distillation in the model updating. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed DAFML algorithm outperforms other benchmarks in terms of the model accuracy and distillation ratio.
-
表 1 缩略词表
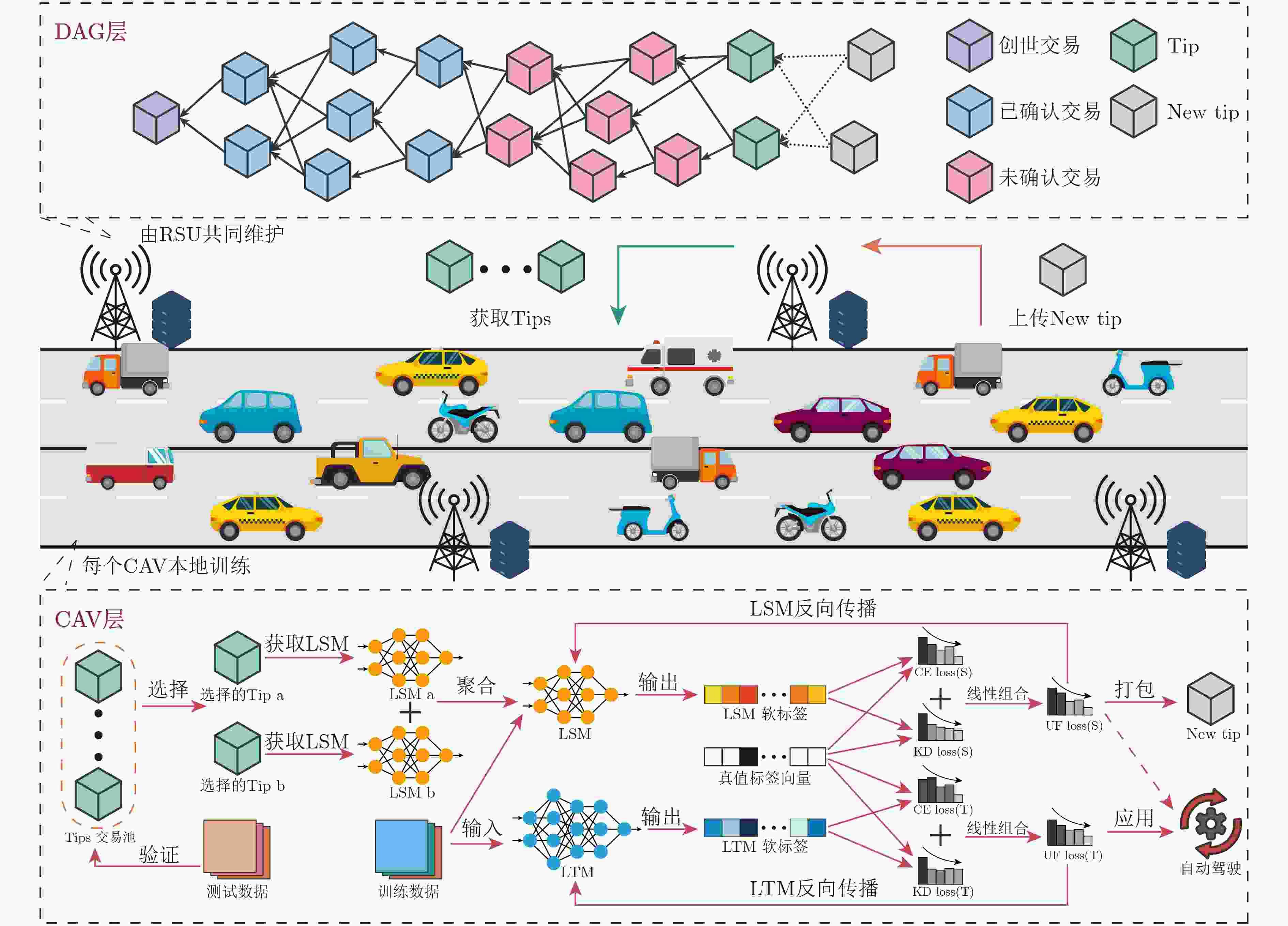
英文缩写 英文全称 中文全称 FL Federated Learning 联邦学习 IoV Internet of Vehicle 车联网 DAG Directed Acyclic Graph 有向无环图 CAV Connected and Automated Vehicle 智能网联汽车 RSU Road Side Unit 路侧单元 LSM Local Student Model 本地学生模型 LTM Local Teacher Model 本地教师模型 TSP Traffic Signs Preprocessed 交通标志预处理 CNN Convolutional Neural Network 卷积神经网络 1 基于DAG区块链的异步联邦互蒸馏学习算法(DAFML)
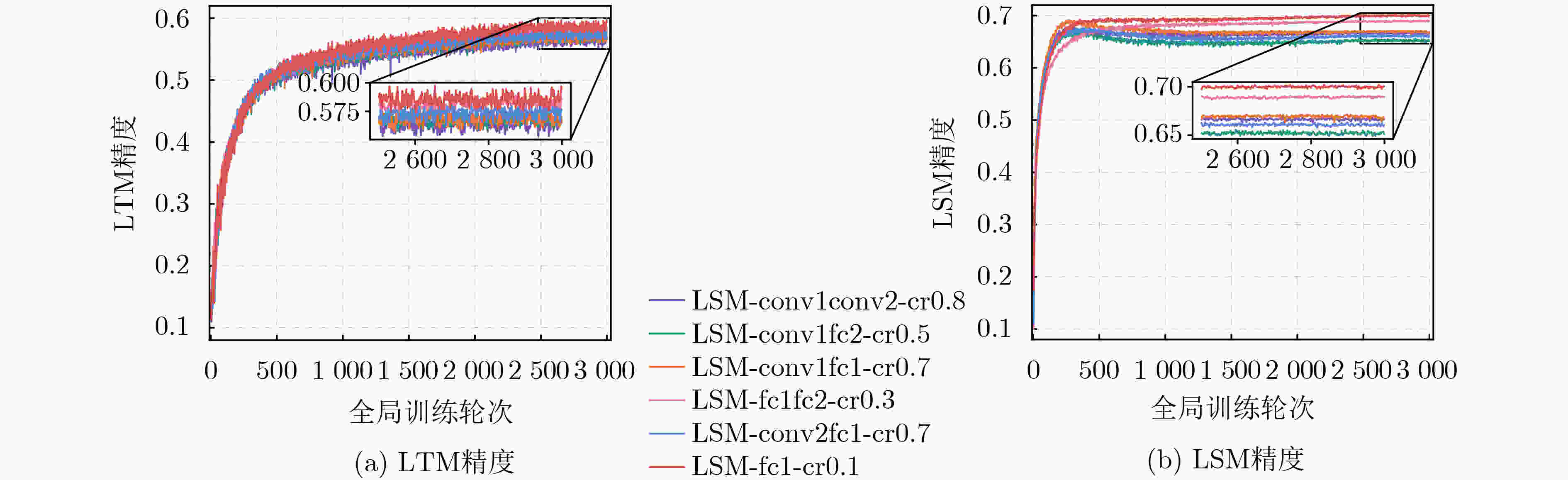
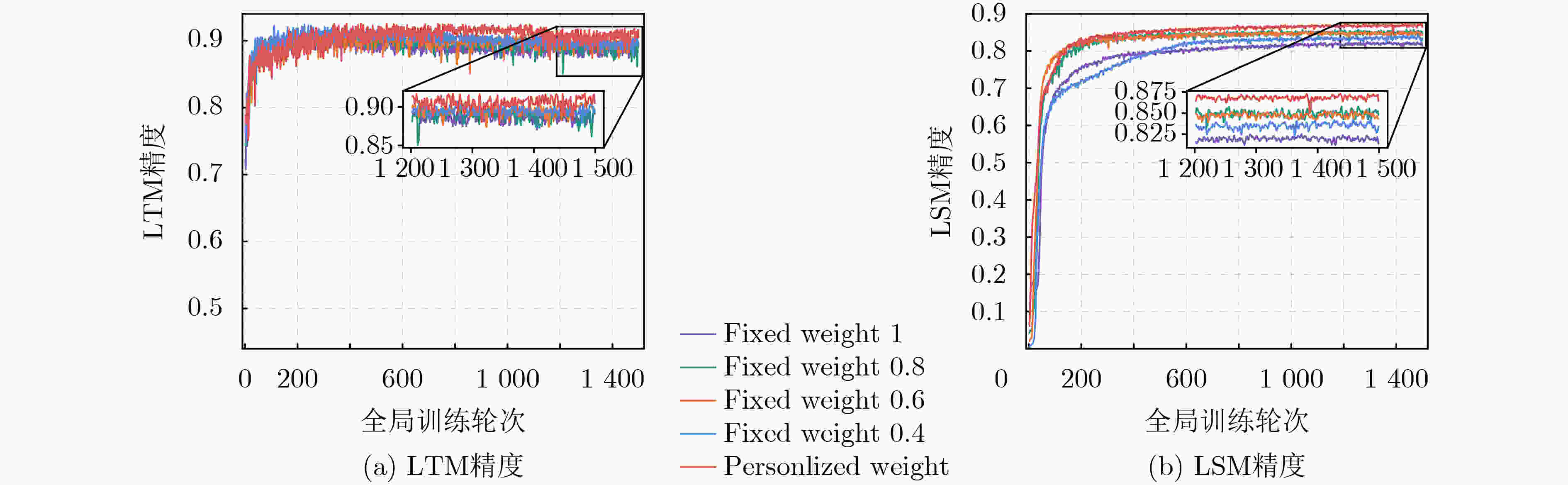
输入:最大全局训练轮次 $K$,初始模型$w_{\rm s}^{(0)}$, 衰减阈值$\delta $,本地迭代轮次$R$,学习率$\eta $ 输出:最优全局学生模型$w_{\rm s}^*$和LTM $ w_{n,{{\mathrm{t}}}}^*,\forall n \in {{\mathcal{N}}} $ (1)随机初始化LTM $w_{n,{t}}^{(0)},\forall n \in {{\mathcal{N}}}$ (2)for $k = 1:K$ (3) if 网络中CAV处于空闲 then (4) 等概抽取一个空闲CAV作为本轮训练的CAV $n$ (5) end if (6) 从Tips中随机抽取5个Tips测试其模型精度 (7) 选取精度最高的两个模型$w_{{{\mathrm{a}}},{{\mathrm{s}}}}^{(k)}$和$w_{{{\mathrm{b}}},{{\mathrm{s}}}}^{(k)}$ (8) 聚合LSM$w_{n,{{\mathrm{s}}}}^{(k)} = (w_{{{\mathrm{a}}},{{\mathrm{s}}}}^{(k)} + w_{{{\mathrm{b}}},{{\mathrm{s}}}}^{(k)})/2$ (9) 测试LTM和LSM的精度$ {{\mathrm{acc}}}_{n,{{\mathrm{t}}}}^{(k)} $和$ {{\mathrm{acc}}}_{n,{{\mathrm{s}}}}^{(k)} $ (10) 计算个性化权值$\lambda _{n,{{\mathrm{t}}}}^{(k)}$和$\lambda _{n,{{\mathrm{s}}}}^{(k)}$ (11) for $r = 1:R$ (12) 根据(7)和(8)计算$\ell _{n,{{\mathrm{t}}}}^{\rm{CE}}$和$\ell _{n,{{\mathrm{s}}}}^{\rm{CE}}$ (13) 根据(11)和(12)计算$ \ell _{n,{{\mathrm{t}}}}^{\rm{KD}} $和$ \ell _{n,{{\mathrm{s}}}}^{\rm{KD}} $ (14) 根据(5)和(6)计算$\ell _{n,{{\mathrm{t}}}}^{\rm{UF}}$和$\ell _{n,{\mathrm{s}}}^{\rm{UF}}$ (15) 根据(13)更新LTM $w_{n,{{\mathrm{t}}}}^{(k,r + 1)}$ (16) 根据(14)更新LSM $w_{n,{{\mathrm{s}}}}^{(k,r + 1)}$ (17) end for (18) 将$w_{n,{{\mathrm{s}}}}^{k,R}$打包成New Tip并上传至相邻的RSU (19)end for 表 2 IID和NonIID场景下的模型精度
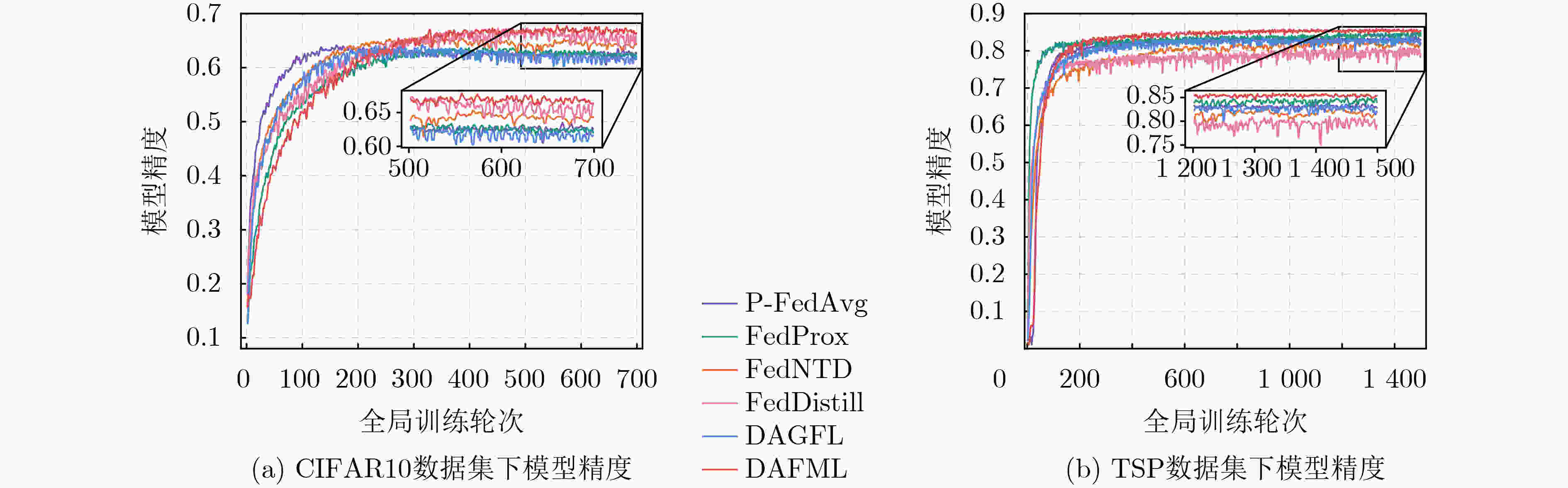
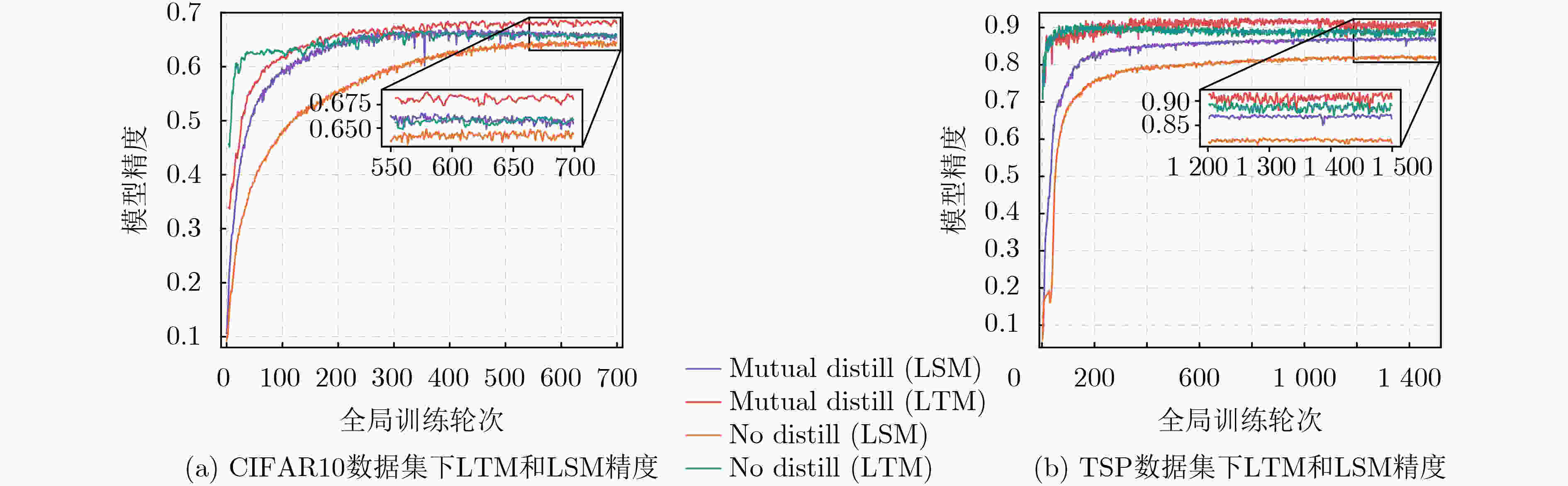
算法 IID NonIID($\alpha = 10$) CIFAR10 TSP CIFAR10 TSP DADFL $ 64.1 \pm 0.1 $ $ 82.3 \pm 0.1 $ $61.8 \pm 0.3$ $ 82.8 \pm 0.3 $ FedDistil $65.6 \pm 0.2$ $77.7 \pm 0.6$ $64.8 \pm 0.5$ $79.9 \pm 0.7$ FedNTD $64.8 \pm 0.3$ $84.0 \pm 0.2$ $63.3 \pm 0.3$ $82.1 \pm 0.3$ P-FedAvg $62.5 \pm 0.1$ $82.3 \pm 0.1$ $62.0 \pm 0.2$ $83.4 \pm 0.1$ FedProx $63.4 \pm 0.2$ $85.0 \pm 0.3$ $62.1 \pm 0.2$ $84.2 \pm 0.2$ DAFML $65.8 \pm 0.2$ $86.9 \pm 0.3$ $65.7 \pm 0.5$ $85.5 \pm 0.1$ -
[1] HUANG Xiaoge, YIN Hongbo, CHEN Qianbin, et al. DAG-based swarm learning: A secure asynchronous learning framework for internet of vehicles[J]. Digital Communications and Networks, 2023. doi: 10.1016/j.dcan.2023.10.004. [2] YIN Hongbo, HUANG Xiaoge, WU Yuhang, et al. Multi-region asynchronous swarm learning for data sharing in large-scale internet of vehicles[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2023, 27(11): 2978–2982. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2023.3314662. [3] MCMAHAN B, MOORE E, RAMAGE D, et al. Communication-efficient learning of deep networks from decentralized data[C]. The 20th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Fort Lauderdale, USA, 2017: 1273–1282. [4] HUANG Xiaoge, WU Yuhang, LIANG Chengchao, et al. Distance-aware hierarchical federated learning in blockchain-enabled edge computing network[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(21): 19163–19176. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3279983. [5] FENG Lei, ZHAO Yiqi, GUO Shaoyong, et al. BAFL: A blockchain-based asynchronous federated learning framework[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2022, 71(5): 1092–1103. doi: 10.1109/TC.2021.3072033. [6] XIAO Huizi, ZHAO Jun, PEI Qingqi, et al. Vehicle selection and resource optimization for federated learning in vehicular edge computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(8): 11073–11087. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2021.3099597. [7] CAO Mingrui, ZHANG Long, and CAO Bin. Toward on-device federated learning: A direct acyclic graph-based blockchain approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(4): 2028–2042. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3105810. [8] ZHENG Haifeng, GAO Min, CHEN Zhizhang, et al. A distributed hierarchical deep computation model for federated learning in edge computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 17(12): 7946–7956. doi: 10.1109/TII.2021.3065719. [9] WU Chuhan, WU Fangzhao, LYU Lingjuan, et al. Communication-efficient federated learning via knowledge distillation[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 2023. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29763-x. [10] JEONG E, OH S, KIM H, et al. Communication-efficient on-device machine learning: Federated distillation and augmentation under non-IID private data[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1811.11479v1, 2018. [11] LEE G, JEONG M, SHIN Y, et al. Preservation of the global knowledge by not-true distillation in federated learning[C]. The 36th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 2787. [12] FALLAH A, MOKHTARI A, and OZDAGLAR A. Personalized federated learning: A meta-learning approach[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2002.07948, 2020. [13] LI Tian, SAHU A K, ZAHEER M, et al. Federated optimization in heterogeneous networks[C]. Machine Learning and Systems, Austin, USA, 2020: 429–450. [14] JIANG Yuang, WANG Shiqiang, VALLS V, et al. Model pruning enables efficient federated learning on edge devices[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(12): 10374–10386. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3166101. [15] WEN Dingzhu, JEON K J, and HUANG Kaibin. Federated dropout—a simple approach for enabling federated learning on resource constrained devices[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2022, 11(5): 923–927. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2022.3149783. [16] NORI M K, YUN S, and KIM I M. Fast federated learning by balancing communication trade-offs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(8): 5168–5182. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3083316. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
