Research on Resource Allocation and Trajectory Optimization of a Multitask Unmanned Aerial Vehicles Assisted Communication Network
-
摘要: 装载各种有效荷载的无人机(UAV)能够实现传感、通信和计算等多任务,因而常被部署到数据采集(DA)和辅助计算等领域。但是到目前为止,绝大多数研究仅专注于单一功能的无人机辅助的通信网络资源分配与轨迹优化,对于面向多任务的资源分配和轨迹优化问题还未解决。为此,该文提出一种综合考虑无人机数据采集、数据广播以及计算任务卸载的无人机辅助的通信网络资源优化的分配策略,旨在通过联合优化传输占空比、用户发射功率与无人机轨迹,在满足目标位置采集数据实时广播的前提下,最大化用户卸载量。为了解决多变量耦合优化问题,提出了基于块坐标下降(BCD)和连续凸逼近(SCA)的高效迭代优化算法,将耦合优化问题分解为3个子问题进行迭代优化。最后,大量仿真结果表明,该算法在公平性和总卸载计算量方面都优于其他测试方案。Abstract: Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV) loaded with various payloads can achieve multiple tasks such as sensing, communication, and computing, and are often deployed in fields such as Data Acquisition (DA) and auxiliary computing. However, so far, the vast majority of research has only focused on single function drone resource allocation and trajectory optimization, and the problem of multi task oriented drone resource allocation and trajectory optimization has not been solved yet. Therefore, an allocation strategy for optimizing drone communication network resources is proposed that comprehensively considers drone data acquisition, data broadcasting, and computing task offloading. The aim is to maximize user offloading by jointly optimizing transmission duty cycle, user transmission power, and drone trajectory, while meeting the real-time broadcast of target location data collection. In order to solve the problem of multivariable coupled optimization, an efficient iterative optimization algorithm based on Block Coordinate Descent (BCD) and Successive Convex Approximate (SCA) is proposed. The coupled optimization problem is decomposed into three sub problems for iterative optimization. Finally, a large number of simulation results show that the algorithm outperforms other testing schemes in terms of fairness and total offloading computation.
-
1 面向多任务的无人机轨迹和资源迭代优化算法
(1) 初始化最大误差 $ \varepsilon $ 、总量吐量迭代值obj、最大迭代次数 $ \alpha $ 与
$ {{{D}}^i}\left( n \right) = \left\{ {{\boldsymbol{A}}_n^i,{\boldsymbol{Q}}_n^i,{\boldsymbol{P}}_{m,n}^i} \right\} $(2) $ {\bf{while}} $ $ i \lt \alpha $ $ {\bf{do}} $ (3) $ i = i + 1, $ (4) 给定 $ \left\{ {{\boldsymbol{Q}}_n^i,{\boldsymbol{P}}_{m,n}^i} \right\} $ ,求解占空比子问题P1,得到最优情况
$ \left\{ {{\boldsymbol{A}}_n^{i + 1},{\boldsymbol{Q}}_n^i,{\boldsymbol{P}}_{m,n}^i} \right\} $ ;(5) 给定 $ \left\{ {{\boldsymbol{A}}_n^{i + 1},{\boldsymbol{Q}}_n^i} \right\} $ ,求解功率子问题P2,得到最优情况
$ \left\{ {{\boldsymbol{A}}_n^{i + 1},{\boldsymbol{Q}}_n^i,{\boldsymbol{P}}_{m,n}^{i + 1}} \right\} $ ;(6) 给定 $ \left\{ {{\boldsymbol{A}}_n^{i + 1},{\boldsymbol{P}}_{m,n}^{i + 1}} \right\} $ ,求解轨迹子问题P3.1,得到最优情
况 $ \left\{ {{\boldsymbol{A}}_n^{i + 1},{\boldsymbol{Q}}_n^{i + 1},{\boldsymbol{P}}_{m,n}^{i + 1}} \right\} $ ;(7) 将 $ \left\{ {{\boldsymbol{A}}_n^{i + 1},{\boldsymbol{Q}}_n^{i + 1},{\boldsymbol{P}}_{m,n}^{i + 1}} \right\} $ 带入目标函数中计算当前总吞吐
量迭代值objnew;(8) $ {\bf{if }}{\text{ abs}}\left( {{\text{objnew}} - {\text{obj}}} \right) \le \varepsilon {\text{ }}{\bf{then}} $ break (9) else $ {\text{obj}} = {\text{objnew}} $ ; (10) end while (11) 输出最优参数值 $ \left\{ {{\boldsymbol{A}}_n^*,{\boldsymbol{Q}}_n^*,{\boldsymbol{P}}_{m,n}^*} \right\} = \left\{ {{\boldsymbol{A}}_n^i,{\boldsymbol{Q}}_n^i,{\boldsymbol{P}}_{m,n}^i} \right\} $ ,
计算获得当前最大的总吞吐量为 $ {\text{ob}}{{\text{j}}^*} = {\text{objnew}} $ ;表 1 关键的仿真参数
参数 取值 参数 取值 飞行高度$ H $ 100 m 最大传输能量$ {E_{\max }} $ 0.4 J 飞行时隙$ N $ 60 最小传输速率$ {R_{\min }} $ 4×104 bit/s 飞行周期$ T $ 60 s 最大平均功率$ {P_{\max }} $ 500 mW 信道带宽$ B $ 1 MHz 目标区域半径$ {d_{{\text{set}}}} $ 10 m 最大速度$ {V_{\max }} $ 20 m/s 功率谱密度$ {N_0} $ –90 dBm/Hz 信道功率增益$ {\beta _0} $ –60 dB 目标位置数据量$ {D_k} $ 7×106 bit -
[1] VAN HUYNH D, DO-DUY T, NGUYEN L D, et al. Real-time optimized path planning and energy consumption for data collection in unmanned Ariel vehicles-aided intelligent wireless sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022, 18(4): 2753–2761. doi: 10.1109/TII.2021.3114358. [2] YU Zhe, GONG Yanmin, GONG Shimin, et al. Joint task offloading and resource allocation in UAV-enabled mobile edge computing[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(4): 3147–3159. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.2965898. [3] OLLERO A, TOGNON M, SUAREZ A, et al. Past, present, and future of aerial robotic manipulators[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2022, 38(1): 626–645. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2021.3084395. [4] LIU Yi, NIE Jiangtian, LI Xuandi, et al. Federated learning in the sky: Aerial-ground air quality sensing framework with UAV swarms[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(12): 9827–9837. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3021006. [5] ZENG Yao and TANG Jianhua. MEC-assisted real-time data acquisition and processing for UAV with general missions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(1): 1058–1072. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3203704. [6] YANG Zheyuan, BI Suzhi, and ZHANG Y J A. Online trajectory and resource optimization for stochastic UAV-enabled MEC systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(7): 5629–5643. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2022.3142365. [7] ZHANG Shuhang, ZHANG Hongliang, HAN Zhu, et al. Age of information in a cellular internet of UAVs: Sensing and communication trade-off design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(10): 6578–6592. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3004162. [8] LI Tianyang, LENG Supeng, WANG Zhihong, et al. Intelligent resource allocation schemes for UAV-swarm-based cooperative sensing[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(21): 21570–21582. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3183099. [9] MENG Kaitao, HE Xiaofan, WU Qingqing, et al. Multi-UAV collaborative sensing and communication: Joint task allocation and power optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2023, 22(6): 4232–4246. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2022.3224143. [10] LYU Liang, ZENG Fanzi, XIAO Zhu, et al. Computation bits maximization in UAV-enabled mobile-edge computing system[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(13): 10640–10651. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3123429. [11] NIE Yiwen, ZHAO Junhui, GAO Feifei, et al. Semi-distributed resource management in UAV-aided MEC systems: A multi-agent federated reinforcement learning approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(12): 13162–13173. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3118446. [12] LIANG Tianhao, LIU Wentao, YANG Jiayan, et al. Age of information based scheduling for UAV aided emergency communication networks[C]. ICC 2022-IEEE International Conference on Communications, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2022: 5128–5133. doi: 10.1109/ICC45855.2022.9838496. [13] ZHANG Liang and ANSARI N. Latency-aware IoT service provisioning in UAV-aided mobile-edge computing networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(10): 10573–10580. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3005117. [14] HU Zhenzhen, ZENG Fanzi, XIAO Zhu, et al. Computation efficiency maximization and QoE-provisioning in UAV-enabled MEC communication systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2021, 8(2): 1630–1645. doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2021.3068123. [15] SUN Mengying, XU Xiaodong, QIN Xiaoqi, et al. AoI-energy-aware UAV-assisted data collection for IoT networks: A deep reinforcement learning method[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(24): 17275–17289. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3078701. [16] LU Weidang, DING Yu, GAO Yuan, et al. Secure NOMA-based UAV-MEC network towards a flying eavesdropper[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2022, 70(5): 3364–3376. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2022.3159703. [17] LU Weidang, DING Yu, GAO Yuan, et al. Resource and trajectory optimization for secure communications in dual unmanned aerial vehicle mobile edge computing systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022, 18(4): 2704–2713. doi: 10.1109/TII.2021.3087726. [18] 裴二荣, 陈新虎, 陈琪美, 等. 基于全频谱共享的三维轨迹和功率优化方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 3(46): 835–847. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230261.PEI Errong, CHEN Xinhu, CHEN Qimei, et al. 3D trajectory and power optimization method based on full spectrum sharing[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 3(46): 835–847. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230261. -






 下载:
下载:

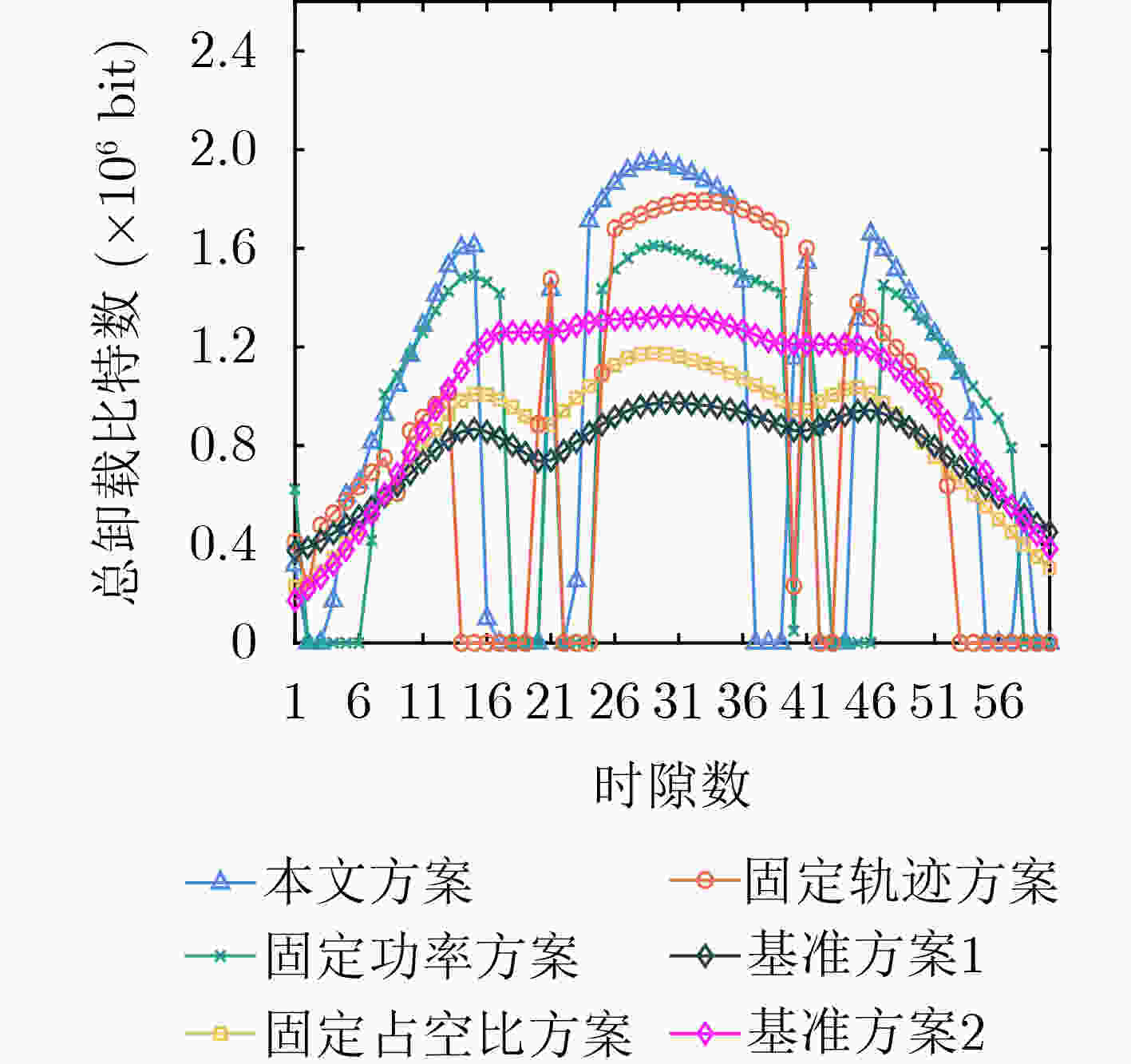
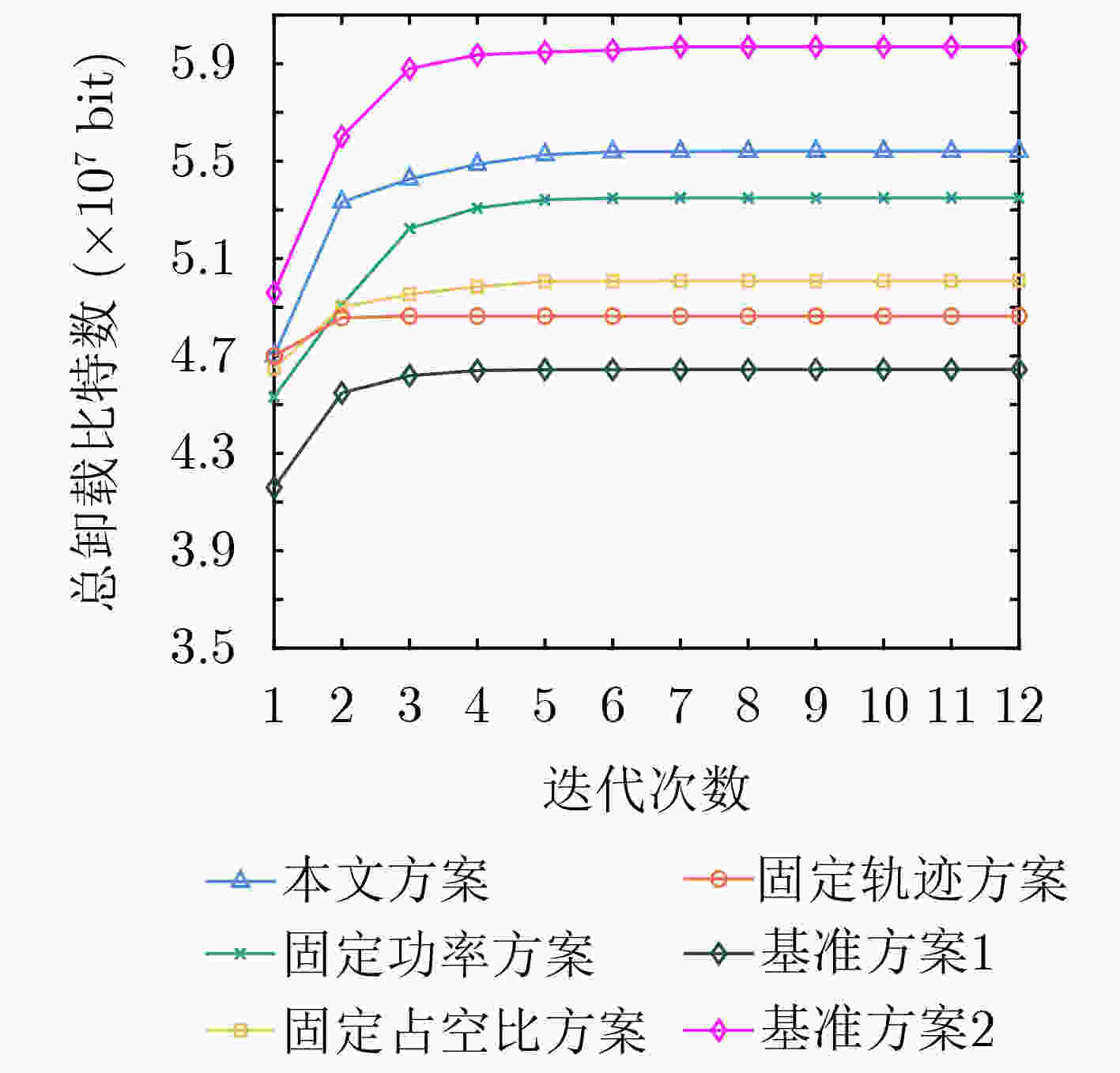


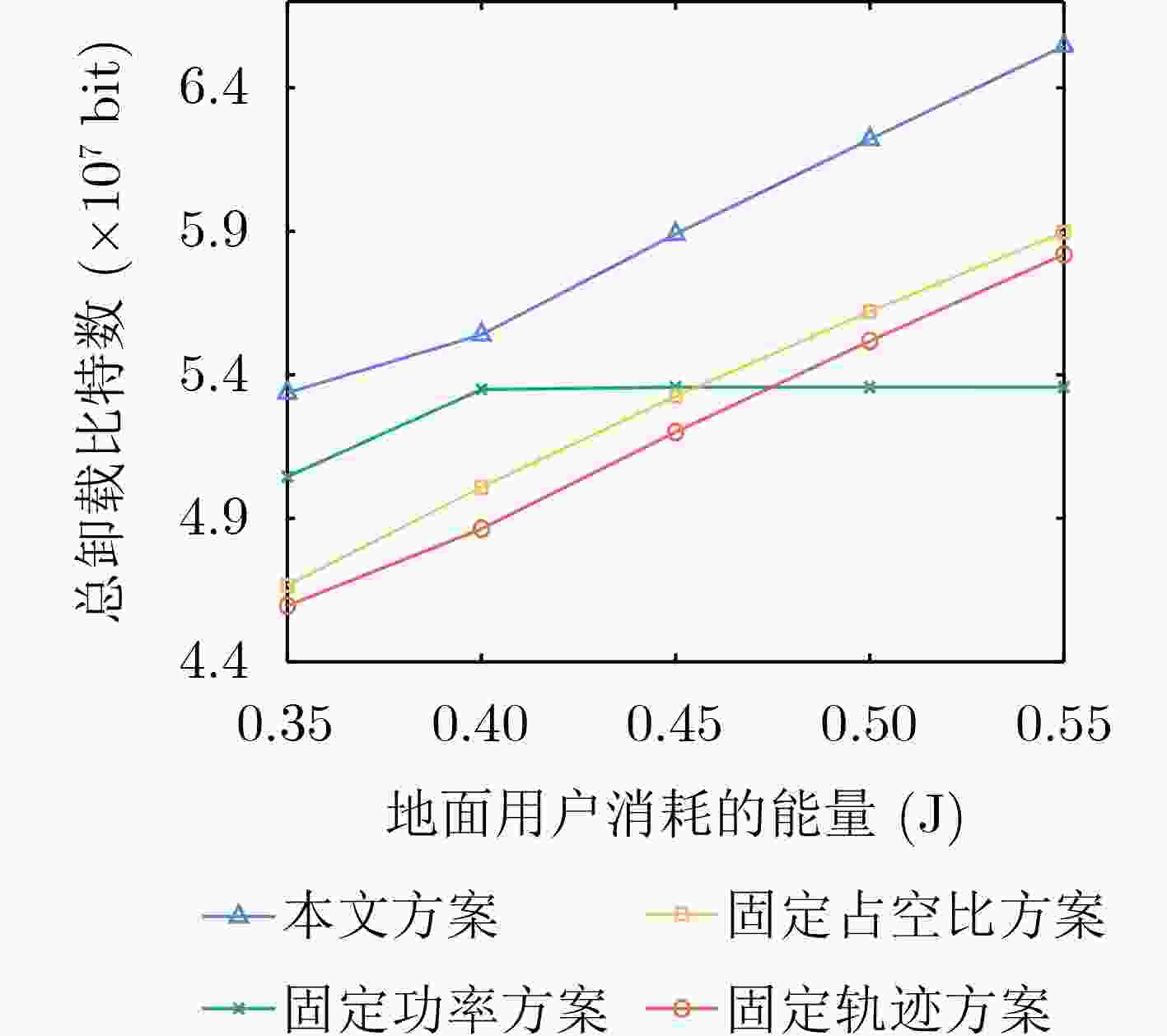
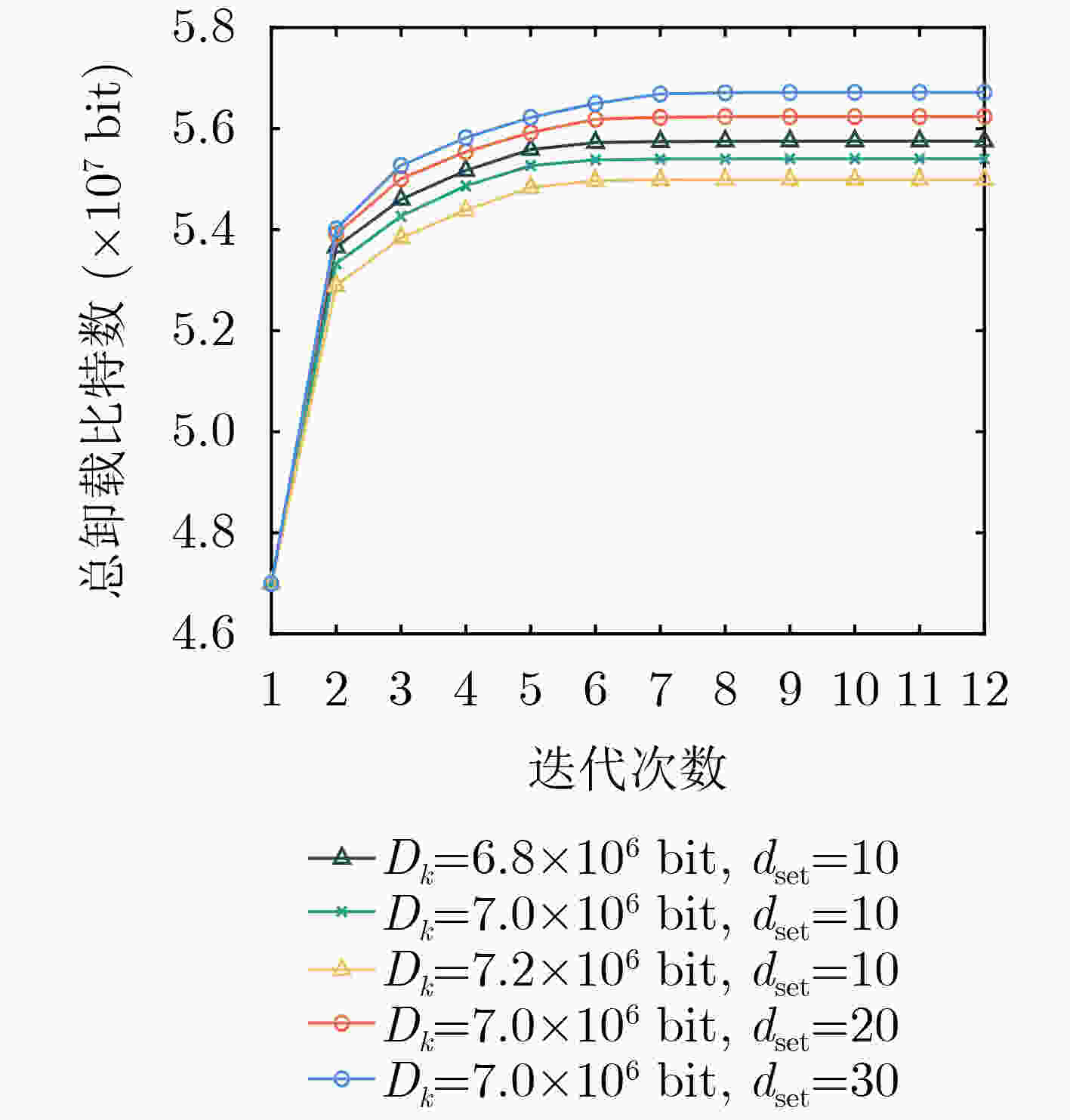


 下载:
下载:
