Research on the Integrated Absolute Calibration of BeiDou Time and Frequency Transfer Chain
-
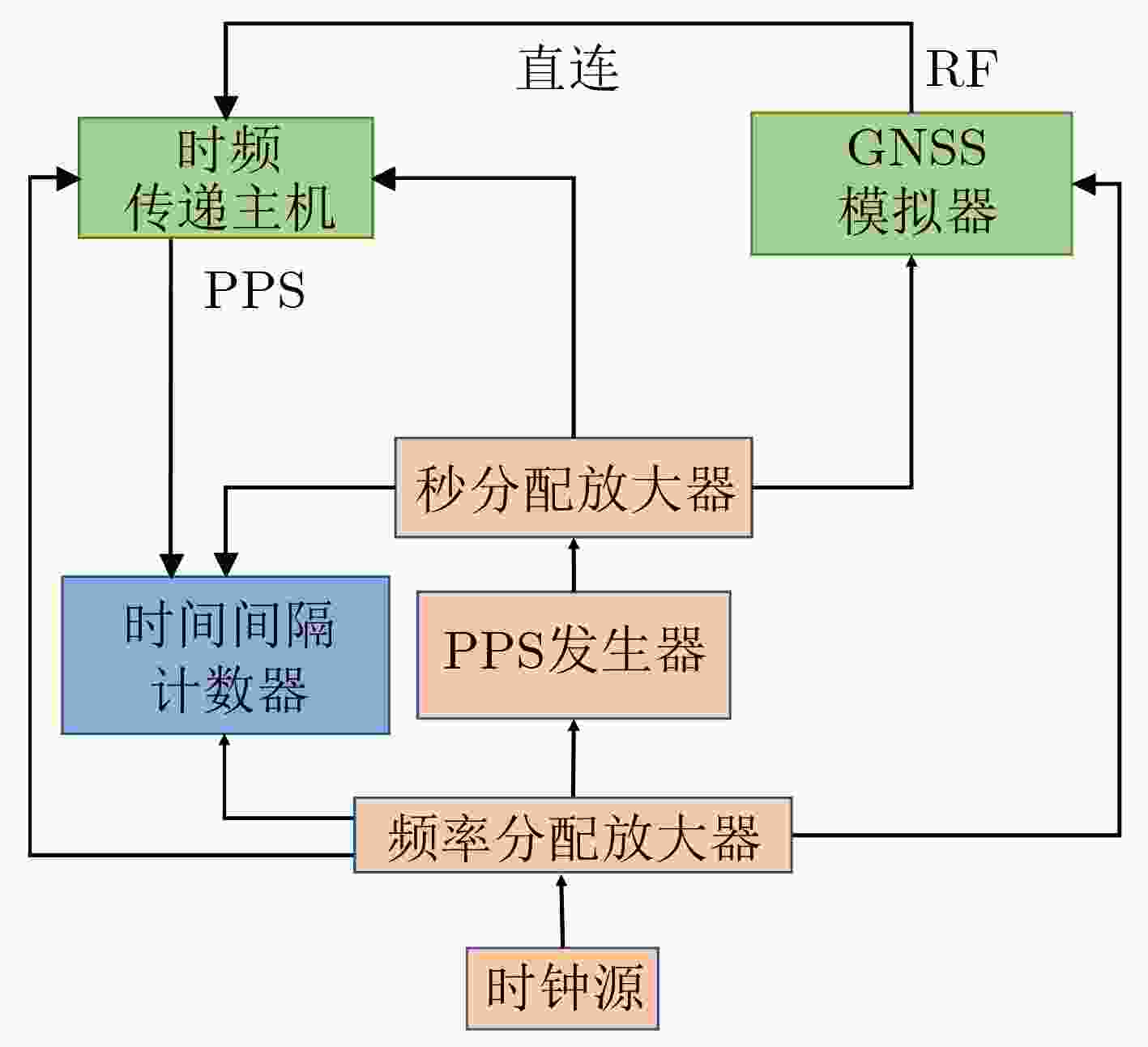
摘要: 全球导航卫星系统(GNSS)时频传递因其较好的不确定度水平及使用方便等特点,已成为当前应用最广泛的时频传递技术。时频传递链校准是时间和频率量值精准传递的关键与必要前提,传统的分步绝对校准技术存在校准步骤复杂、不确定度来源多的问题。针对上述问题,该文提出一种整体绝对校准技术,对北斗卫星导航系统(BDS)时频传递链进行整体一次性校准,测量不确定度更低。通过对时频传递链整体绝对校准方法的研究,搭建了时频传递链整体绝对校准系统及实验平台,实现了北斗时频传递链的整体与分步绝对校准实验,评估其不确定度。结果表明两种方法校准结果一致性优于1.76 ns,合成标准不确定度分别评定为0.80 ns与1.00 ns。Abstract: Global Navigation Satellite System(GNSS) time and frequency transfer has become the most widely used time and frequency transfer technique due to its fine uncertainty level and ease of use. Time and frequency transfer calibration is the key and necessary prerequisite for the accurate transfer of time and frequency values. The seperated absolute calibration technique suffers from complex calibration steps and multiple sources of uncertainty. To address these problems, an integrated absolute calibration technique with fewer implementation steps and fewer sources of uncertainty is proposed in this paper, i.e., an integrated one-time calibration of the BeiDou navigation Satellite system (BDS) time and frequency transfer chain, with lower measurement uncertainty. In this paper, through the research on the integrated absolute calibration method of time and frequency transfer chain, the integrated absolute calibration system and experimental platform of the time and frequency transfer chain are constructed, and the seperated absolute calibration and integrated absolute calibration experiments based on one actual BDS time and frequency transfer chain are realized and their uncertainties are evaluated. The results showed that the consistency of the calibration results under the two methods is better than 1.76 ns, and the synthetic standard uncertainties are 0.80 ns and 1.00 ns respectively.
-
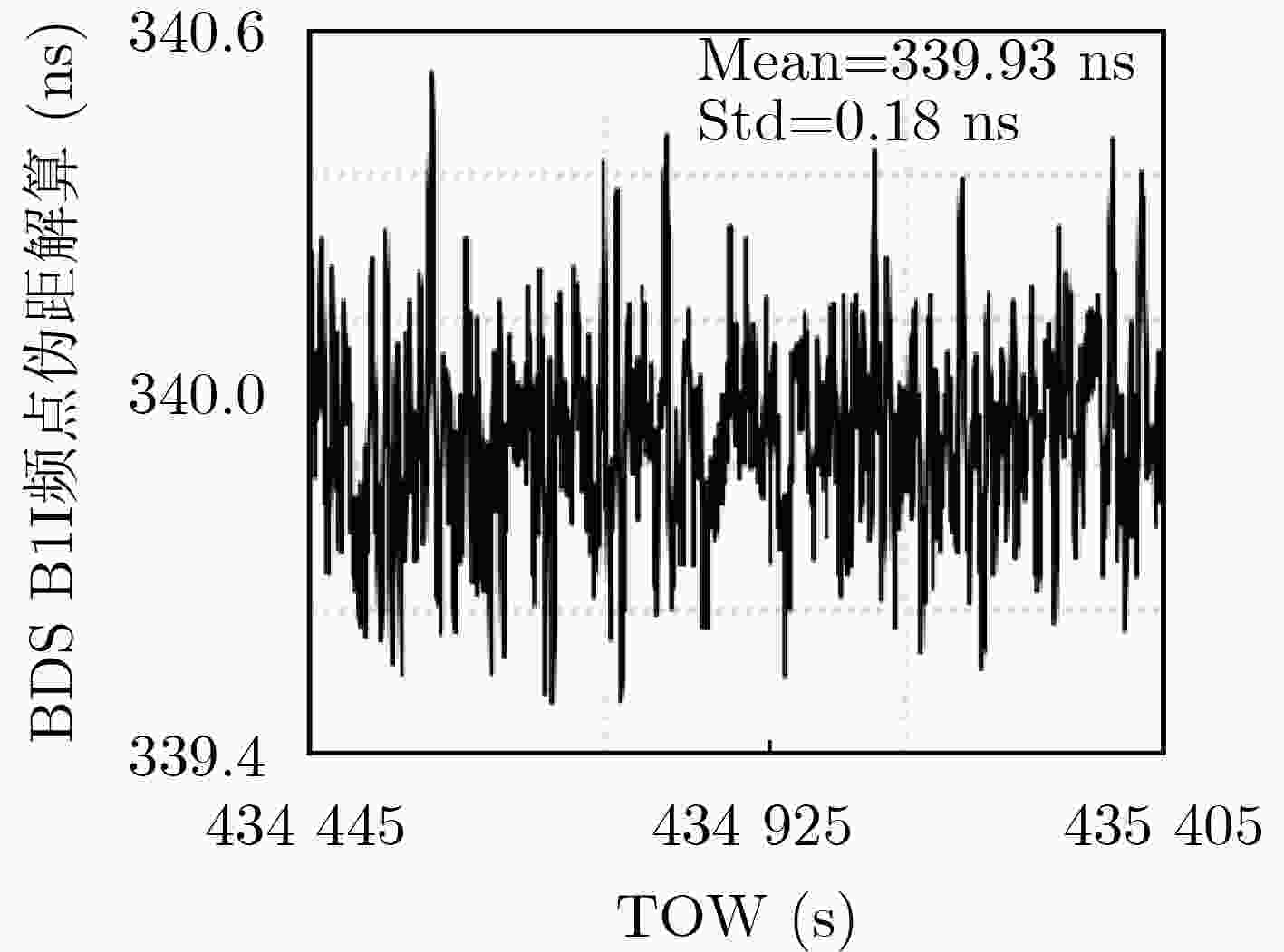
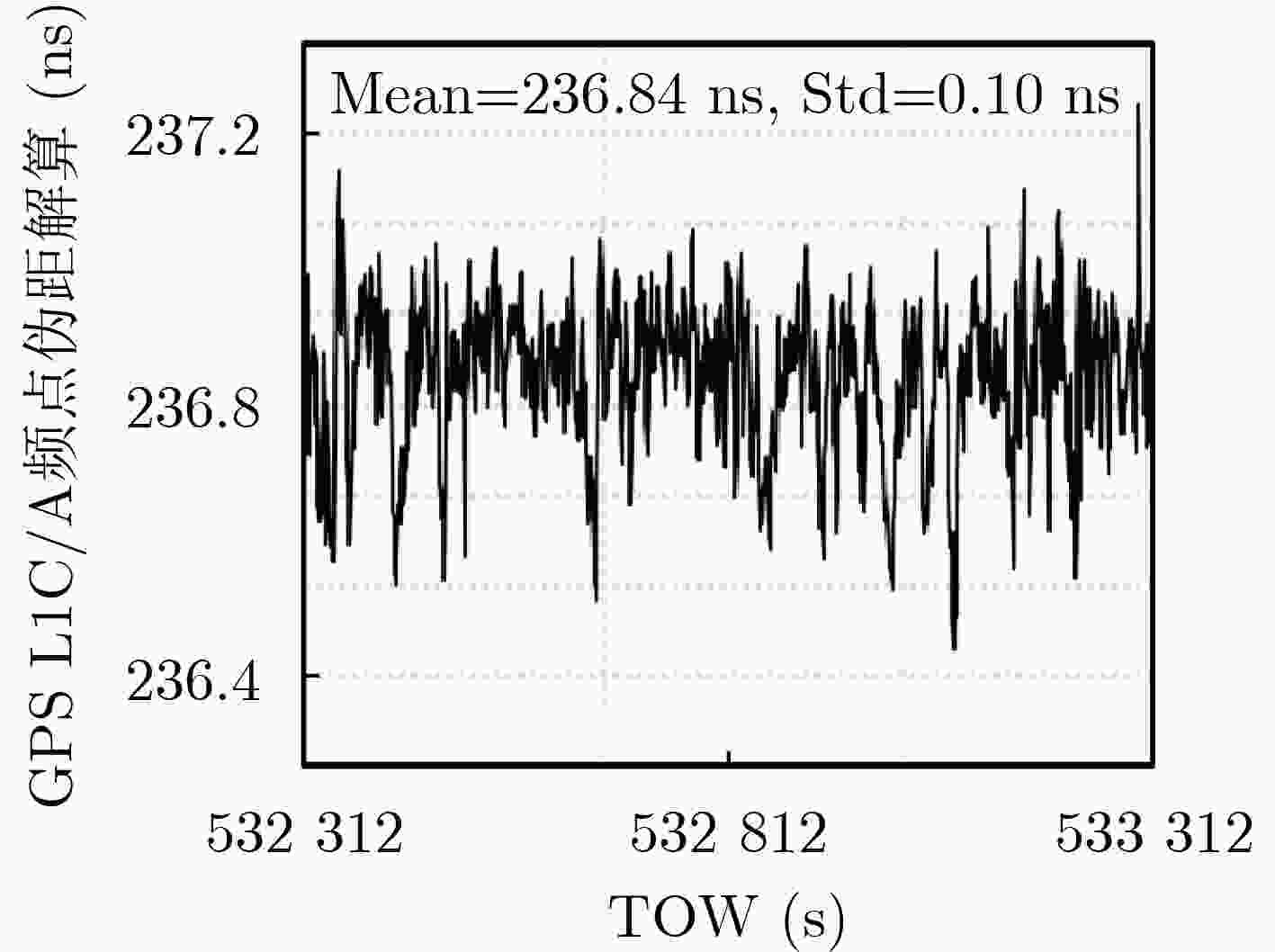
表 1 时频传递链TL07整体绝对校准结果(ns)
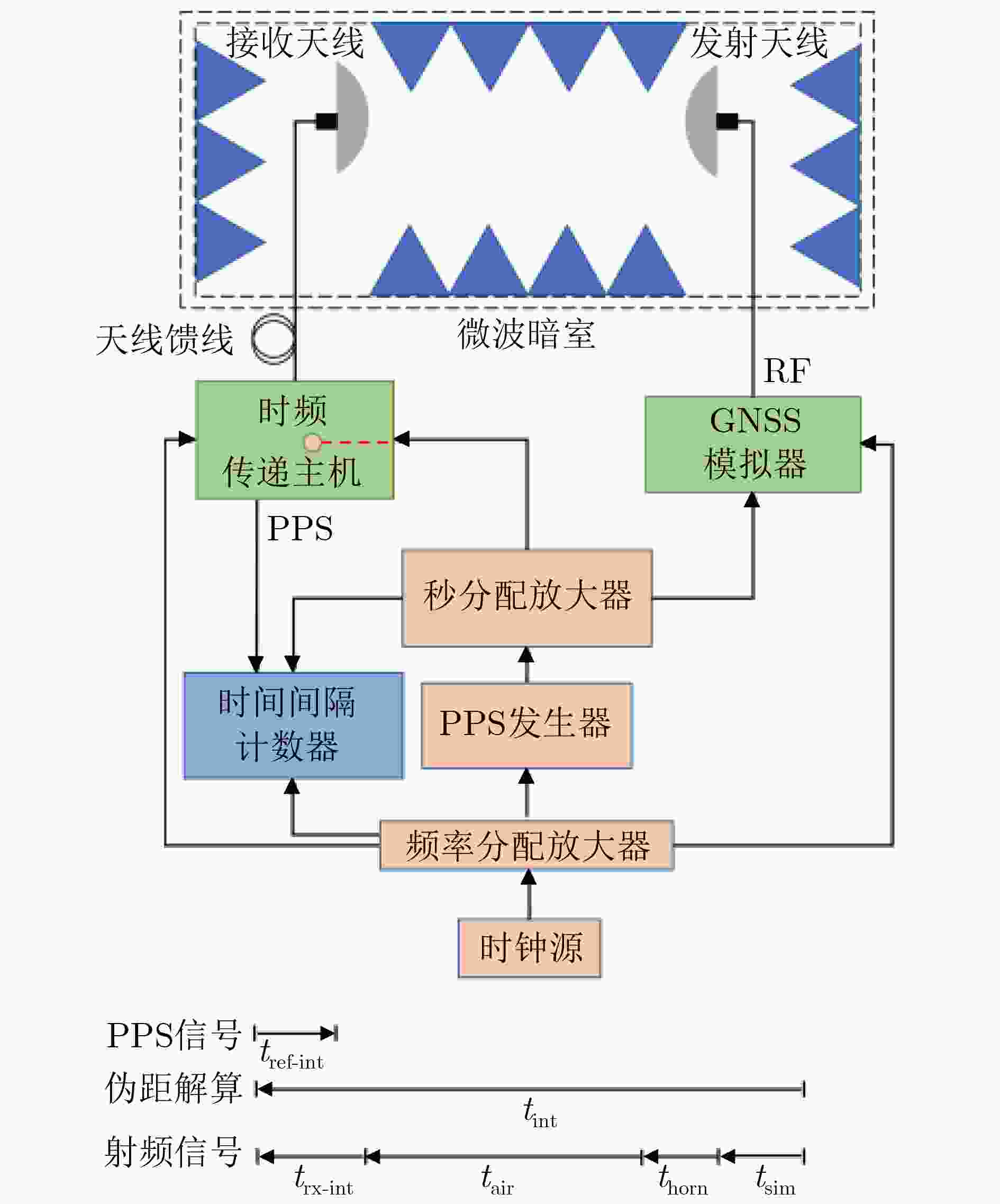
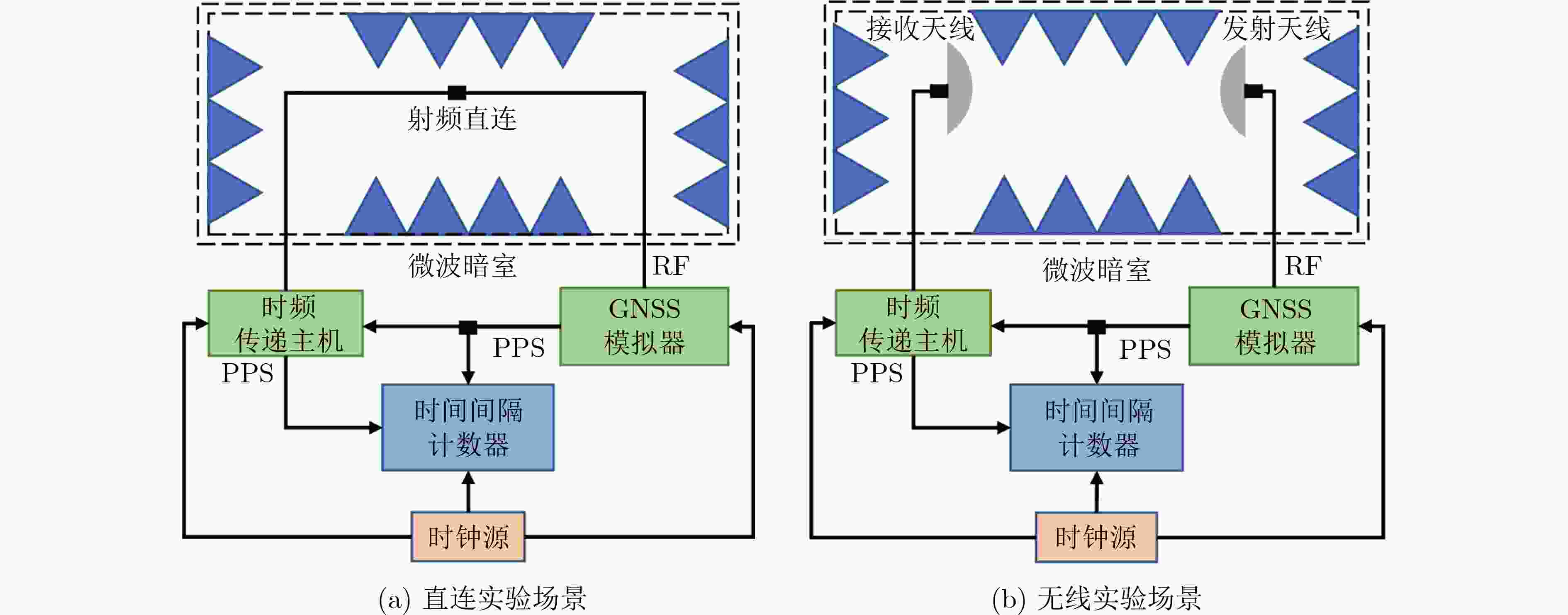
tint tsim tair thorn tref-int trx-int BDS B1I 339.93 151.10 2.00 1.75 57.25 242.33 GPS L1C/A 471.04 256.90 2.00 0.85 36.11 247.40 表 2 时频传递链TL07分步绝对校准结果(ns)
tsep tsim tgnss tref-sep tcab trx-sep BDS B1I 97.58 151.10 14.43 57.24 222.42 240.57 GPS L1C/A 227.07 256.90 17.48 36.06 222.42 246.13 表 3 发射天线校准不确定度评估(ns)
校准不确定度来源 类型 值 天线相位中心路径测量 B 0.01 天线相位中心稳定性 B 0.02 开关机特性 B 0.13 GNSS射频信号输入功率电平 B 0.10 GNSS模拟器通道间偏差 B 0.01 热灵敏度 B 0.20 重复性 A 0.16 合成标准不确定度 / 0.31 表 4 GNSS模拟器校准不确定度评估(ns)
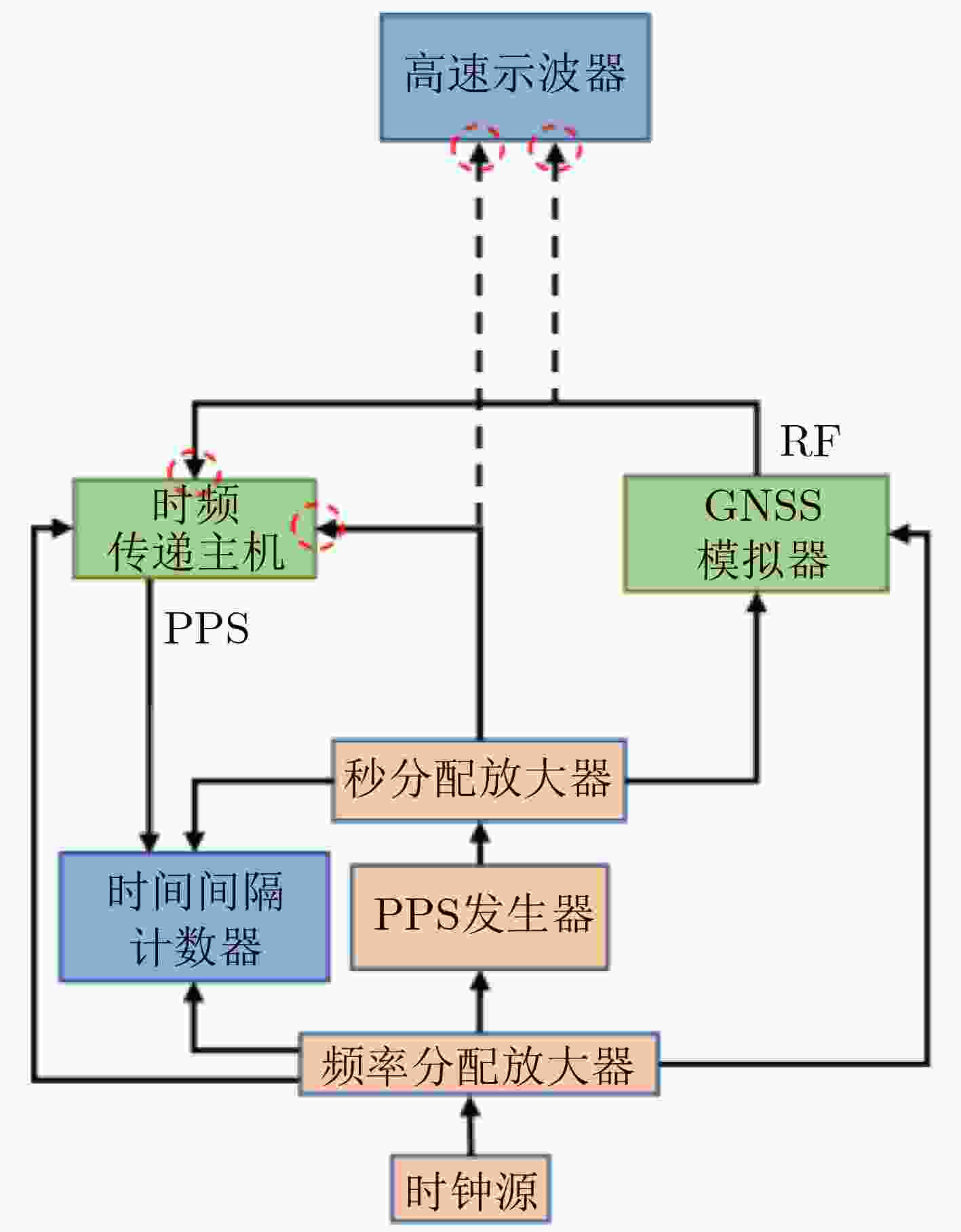
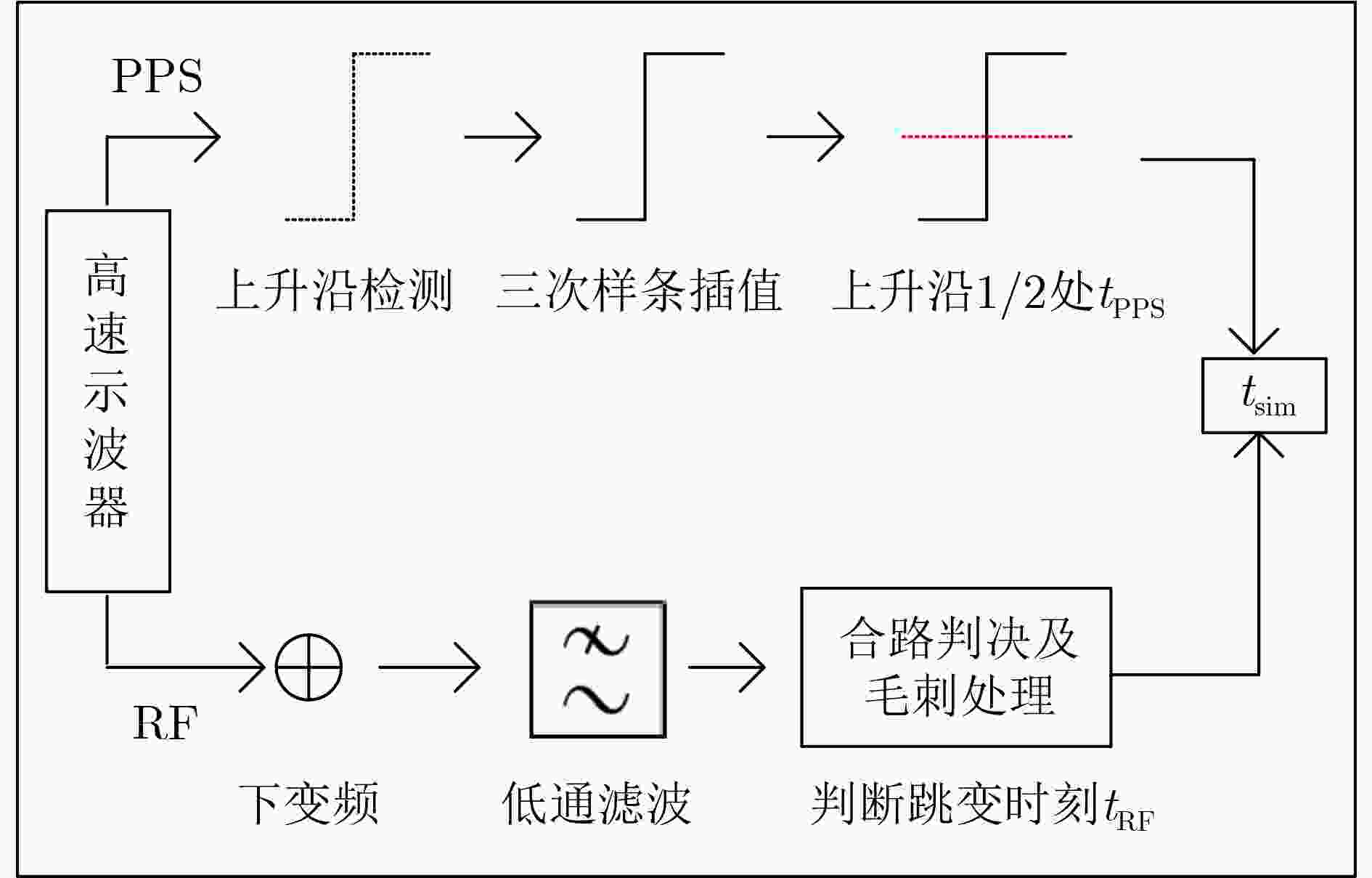
校准不确定度来源 类型 值 高速实时示波器分辨率 B 0.05 高速实时示波器触发误差 B 0.20 相干数据处理 B 0.20 开关机特性 B 0.50 配置RF功率 B 0.10 合成标准不确定度 / 0.59 表 5 参考时延测量不确定度评估(ns)
校准不确定度来源 类型 值 时间间隔计数器分辨率误差 B 0.10 时间间隔计数器相对误差 B 0.05 重复性 A 0.06 合成标准不确定度 / 0.13 表 6 伪距解算不确定度评估(ns)
校准不确定度来源 类型 值 GNSS模拟器通道间偏差 B 0.01 热灵敏度 B 0.20 开关机特性 B 0.13 GNSS射频信号输入功率电平 B 0.10 重复性 A 0.18 合成标准不确定度 / 0.32 表 7 整体绝对校准不确定度评估(ns)
校准不确定度来源 值 发射天线校准 0.31 GNSS模拟器校准 0.59 参考时延测量 0.13 伪距解算 0.32 合成标准不确定度 0.80 表 8 GNSS天线校准不确定度评估(ns)
校准不确定度来源 类型 值 天线相位中心路径测量 B 0.01 天线相位中心稳定性 B 0.02 开关机特性 B 0.13 RF输入功率电平 B 0.10 模拟器通道间偏差 B 0.01 热灵敏度 B 0.20 发射天线校准 B 0.31 重复性 A 0.18 合成标准不确定度 / 0.44 表 9 天线馈线校准不确定度评估(ns)
校准不确定度来源 类型 值 矢量网络分析仪两接口初始校准 B 0.20 线缆形变 B 0.15 温度效应 B 0.12 转接头 B 0.40 重复性 A 0.20 合成标准不确定度 / 0.53 表 10 时频传递主机校准不确定度评估(ns)
校准不确定度来源 类型 值 GNSS模拟器校准 矢量网络分析仪两接口初始校准 B 0.20 线缆形变 B 0.15 温度效应 B 0.12 转接头 B 0.40 重复性 A 0.20 参考时延测量 时间间隔计数器分辨率误差 B 0.10 时间间隔计数器相对误差 B 0.05 重复性 A 0.06 伪距解算 模拟器通道间偏差 B 0.01 热灵敏度 B 0.20 开关机特性 B 0.13 RF输入功率电平 B 0.10 重复性 A 0.18 合成标准不确定度 / 0.63 表 11 分步绝对校准不确定度评估(ns)
校准不确定度来源 值 GNSS天线校准 0.44 天线馈线校准 0.53 时频传递主机校准 0.63 合成标准不确定度 1.00 表 12 绝对校准步骤比对
校准步骤 整体 分步 发射天线校准 √ √ GNSS天线校准 × √ 天线馈线校准 × √ GNSS模拟器校准 √ √ 参考时延测量 √ √ 伪距解算 √ √ 表 13 绝对校准结果比对(ns)
序号 整体 分步 偏差 BDS B1I 校准结果 242.33 240.57 1.76 不确定度评定 0.80 1.00 / GPS L1C/A 校准结果 247.4 246.13 1.27 不确定度评定 0.80 1.00 / -
[1] PETIT G and DEFRAIGNE P. Calibration of GNSS stations for UTC[J]. Metrologia, 2023, 60(2): 025009. doi: 10.1088/1681-7575/acbd52 [2] DELPORTE J and VALAT D. CNES Accurate monitoring of GNSS time scales based on absolute calibration[C]. 2022 Joint Conference of the European Frequency and Time Forum and IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium, Paris, France, 2022: 1–5. [3] 梁坤, 张爱敏. GLONASS时间频率传递研究[J]. 计量学报, 2011, 32(2): 172–177. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1158.2011.02.17LIANG Kun and ZHANG Aimin. Study on time and frequency dissemination by GLONASS[J]. Acta Metrologica Sinica, 2011, 32(2): 172–177. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1158.2011.02.17 [4] REN Zhiling, GONG Hang, PENG Jing, et al. Common-view time transfer with BeiDou new navigation signals[C]. The 15th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, BioMedical Engineering and Informatics (CISP-BMEI), Beijing, China, 2022: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/CISP-BMEI56279.2022.9980287. [5] LI Guojun, WANG Cunjun, and YE Huchun. Performance analysis of BeiDou-3 common-view time transferring[J]. Chinese Astronomy and Astrophysics, 2022, 46(4): 471–485. doi: 10.1016/j.chinastron.2022.11.006 [6] PETIT G, JIANG Z, UHRICH P, et al. Differential calibration of Ashtech Z12-T receivers for accurate time comparisons[C]. The 14th European Frequency and Time Forum, Turin, Italy, 2000: 40–4. [7] PETIT G, JIANG Zhiheng, WHITE J, et al. Absolute calibration of an Ashtech Z12-T GPS receiver[J]. GPS Solutions, 2001, 4(4): 41–46. doi: 10.1007/pl00012865 [8] VALAT D and DELPORTE J. Absolute calibration of timing receiver chains at the nanosecond uncertainty level for GNSS time scales monitoring[J]. Metrologia, 2020, 57(2): 025019. doi: 10.1088/1681-7575/ab57f5 [9] GARBIN E, DEFRAIGNE P, KRYSTEK P, et al. Absolute calibration of GNSS timing stations and its applicability to real signals[J]. Metrologia, 2019, 56(1): 015010. doi: 10.1088/1681-7575/aaf2bc [10] KASAT N, NEELAPPA S A, SINGH F B, et al. Absolute calibration of NavIC reference receiver[C]. 2022 URSI Regional Conference on Radio Science, Indore, India, 2022: 1–4. [11] LIANG Kun, FELICITAS A, GERARD P, et al. Evaluation of BeiDou time transfer over multiple inter-continental baselines towards UTC contribution[J]. Metrologia, 2018, 55(4): 513–525. doi: 10.1088/1681-7575/aac586 [12] LIANG Kun, ZHANG Aimin, YANG Zhiqiang, et al. Experimental research on BeiDou time transfer using the NIM made GNSS time and frequency receivers at the BIPM in Euro-Asia link[C]. 2017 Joint Conference of the European Frequency and Time Forum and IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium, Besancon, France, 2017: 788–797. doi: 10.1109/FCS.2017.8089036. [13] 陶香琴. 标准钢卷尺测量结果不确定度评估[J]. 中国计量, 2005(2): 66–69. doi: 10.16569/j.cnki.cn11-3720/t.2005.02.045TAO Xiangqin. Uncertainty assessment of measurement results of standard steel tape measure[J]. China Metrology, 2005(2): 66–69. doi: 10.16569/j.cnki.cn11-3720/t.2005.02.045 [14] 国家质量监督检验检疫总局. JJF 1403-2013 全球导航卫星系统(GNSS)接收机(时间测量型)校准规范[S]. 北京: 中国质检出版社, 2013.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine. JJF 1403-2013 Calibration specification for GNSS receivers used in time measurement[S]. Beijing: China Quality Inspection Press, 2013. [15] ROVERA D, ABGRALL M, UHRICH P, et al. Techniques of antenna cable delay measurement for GPS time transfer[C]. 2015 Joint Conference of the IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium & the European Frequency and Time Forum, Denver, USA, 2015: 239–244. doi: 10.1109/FCS.2015.7138832. [16] LIANG Kun, FELDMANN T, BAUCH A, et al. Performance evaluation of NIM GPS receivers in use for time transfer with PTB[C]. The EFTF-2010 24th European Frequency and Time Forum, Noordwijk, Netherlands, 2010: 1–8. doi: 10.1109/EFTF.2010.6533694. -





 下载:
下载:

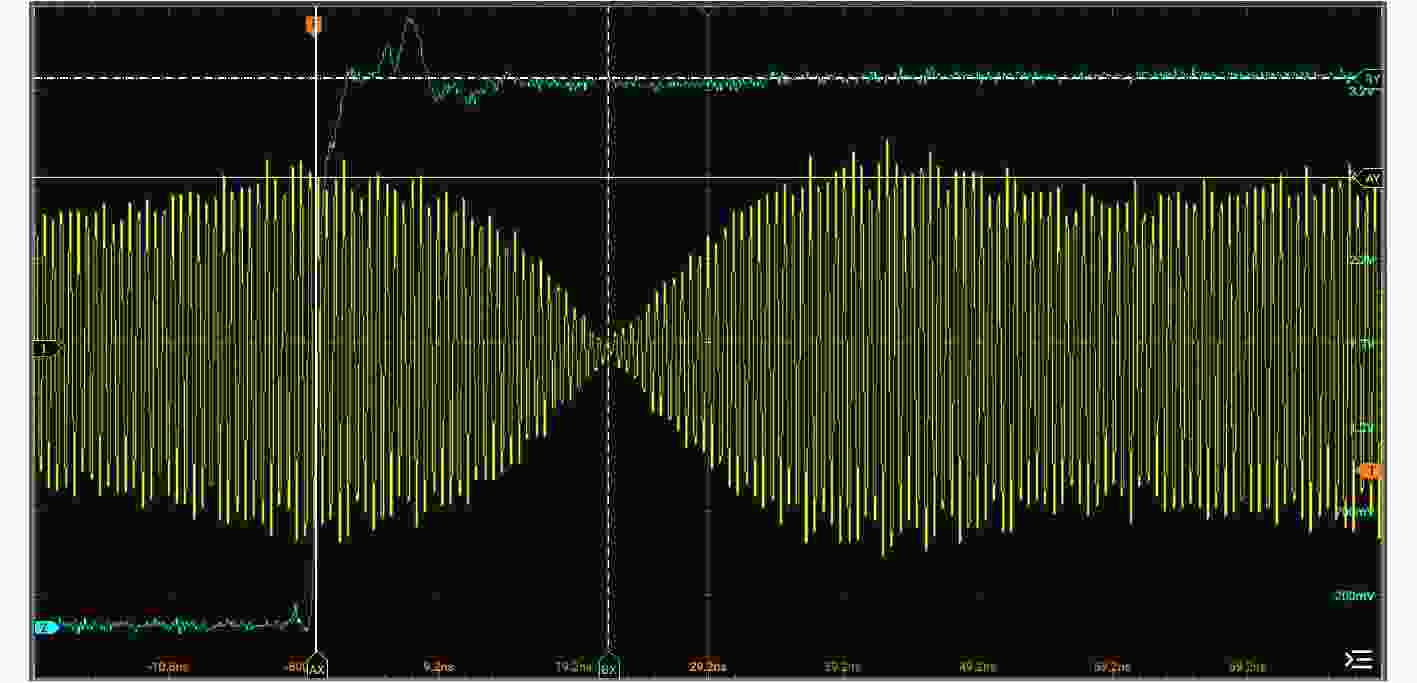
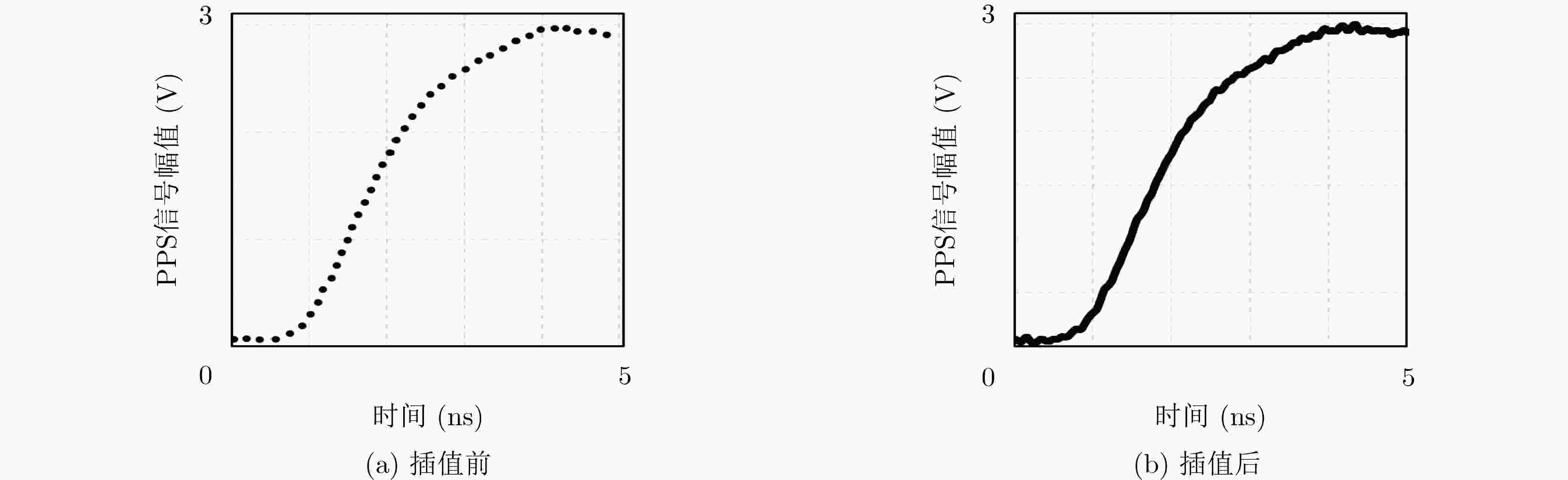



 下载:
下载:
