Trajectory Optimization Research of Wireless Power Communication Networks Assisted by Aerial Intelligent Reflecting Surface
-
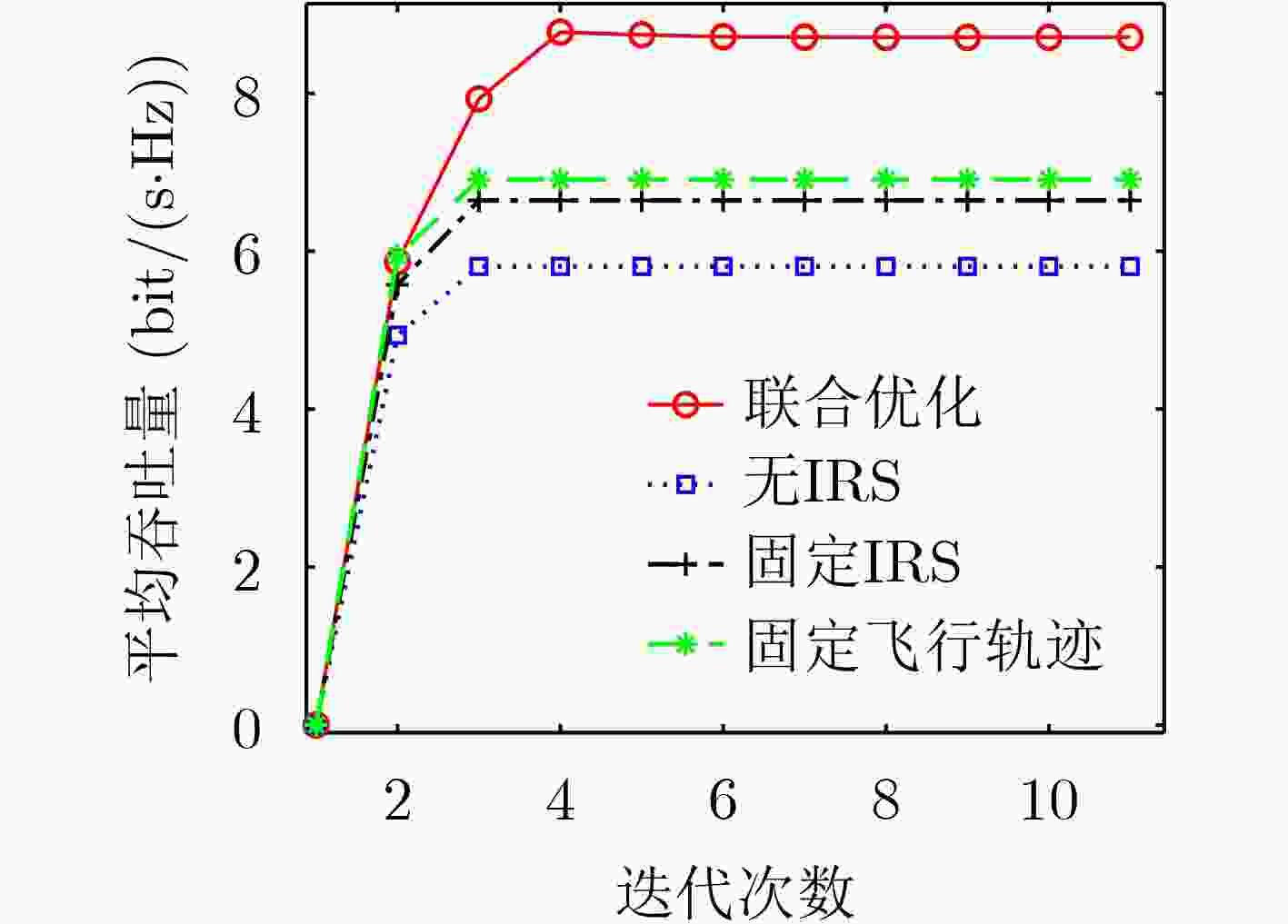
摘要: 由于无人机(UAV)良好的机动性、可靠性和快速部署等特性,无人机搭载智能反射面(IRS)可以有效解决复杂无线场景中混合接入点和节点之间由于障碍物遮挡导致信息传输和能量传输效率低的问题。该文提出一种基于时间划分的空中智能反射面辅助无线供能通信网络架构,充分利用空中智能反射面的灵活性提高网络性能。该架构针对每一个时隙,采用先收集能量后传输信息方案实现能量和数据的分时传输。在满足节点能量收集阈值的前提下,建立一个联合空中智能反射面飞行轨迹、节点选择关联变量、时隙分配比率和智能反射面相位的多变量耦合优化问题。采用块坐标下降算法把原始优化问题分解为4个子问题分别进行求解。首先根据波束对齐原理求解出智能反射面最优相位的闭式解,然后通过引入辅助变量并采用连续凸近似方法使非凸问题转变为凸问题,最后利用交替优化算法迭代求解。仿真结果表明,该文提出的联合优化方案具有很好的收敛性能并可以显著提高系统平均吞吐量。Abstract: Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) equipped with Intelligent Reflecting Surface (IRS) can effectively solve the problem of inefficient information and energy transmission between the hybrid access point and nodes in complex wireless scenarios due to obstacle occlusion. A novel framework for aerial IRS-assisted wireless powered communication networks is proposed that exploits the flexibility of aerial IRS to improve the performance of the network. The architecture achieves the transmission of energy and data for each time slot employing the harvest-then-transmit scheme. A multi-variable coupled optimization problem that combines the flight trajectory, node selection association variable, time slot allocation ratio, and the phase is established while satisfying the node energy harvesting threshold. Thus, the block coordinate descent algorithm is utilized to decompose the optimization problem into four sub-problems to be solved separately. Firstly, the closed-form solution for the optimal phase of the intelligent reflecting surface is derived based on the beam alignment theory. Secondly, the non-convex problem is transformed into a convex problem by introducing auxiliary variables and employing a successive convex approximation algorithm. Finally, the solution is iteratively solved utilizing the block coordinate descent algorithm. Simulation results show that the proposed scheme has excellent convergence performance and significantly improve the average throughput.
-
1 联合优化算法
初始化$ {{\boldsymbol{U}}_0} $, $ {{\boldsymbol{\varTheta}} _0} $, $ {{{\alpha}} _0} $和$ {{{\tau}} _0} $;设置最大迭代回合$ {L_{{\mathrm{MAX}}}} $和精度$ \vartheta $; 根据初始化的$ {{\boldsymbol{U}}_0} $计算$ {{\boldsymbol{\varTheta}} _0} $; While: (1)设置迭代回合$ l = l + 1 $; (2)给定$ {{\boldsymbol{U}}_{l - 1}} $, $ {{\boldsymbol{\varTheta}} _{l - 1}} $和$ {{{\tau}} _{l - 1}} $,通过求解问题P2更新$ {\alpha _l} $; (3)给定$ {{{\alpha}} _{l - 1}} $, $ {{\boldsymbol{\varTheta}} _{l - 1}} $和$ {{{\tau }}_{l - 1}} $,通过求解问题P4更新$ {{\boldsymbol{U}}_l} $; (4)根据求解的$ {{\boldsymbol{U}}_l} $更新$ {{\boldsymbol{\varTheta}} _l} $; (5)给定$ {\alpha _l} $, $ {{\boldsymbol{U}}_l} $和$ {{\boldsymbol{\varTheta}} _l} $,通过求解P5优化$ {{{\tau}} _l} $; (6)给定$ {\alpha _l} $, $ {{\boldsymbol{U}}_l} $和$ {{\boldsymbol{\varTheta}} _l} $,计算 $ {F_l} = \dfrac{1}{N}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{n = 1}^N {\displaystyle\sum\limits_{k = 1}^K {{\alpha _k}[n]{R_k}[n]} } $; Until: $ ({F_l} - {F_{l - 1}})/{F_l} < \vartheta $或$ l \ge {L_{{\mathrm{MAX}}}} $;
结束并输出最优的$ {\boldsymbol{U}} $, ${\boldsymbol{ \varTheta}} $, $ \alpha $和$ {{\tau}} $;表 1 仿真参数
仿真参数 数值 仿真参数 数值 UAV飞行高度($ {H_{\mathrm{U}}} $) 10 m HAP高度($ {H_{\mathrm{B}}} $) 5 m 环境参数(a, b) 0.6, 0.11 参考信道增益($ {\beta _0} $) –0.054 6 高斯白噪声($ {\sigma ^2} $) –80 dBm UAV最大飞行速度($ {V_{\max }} $) 10 m/s 每一个时隙长度($ {\delta _t} $) 1 s 节点获取能量阈值($ {E_{{\mathrm{thr}}}} $) 5×10–3 J -
[1] WANG Chengxiang, YOU Xiaohu, GAO Xiqi, et al. On the road to 6G: Visions, requirements, key technologies, and testbeds[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2023, 25(2): 905–974. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2023.3249835. [2] 朱政宇, 徐金雷, 孙钢灿, 等. 基于IRS辅助的SWIPT物联网系统安全波束成形设计[J]. 通信学报, 2021, 42(4): 185–193. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2021060.ZHU Zhengyu, XU Jinlei, SUN Gangcan, et al. Secure beamforming design for IRS-assisted SWIPT internet of things system[J]. Journal on Communications, 2021, 42(4): 185–193. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2021060. [3] LIU Heng, ZHANG Yan, GONG Shiqi, et al. Optimal transmission strategy and time allocation for RIS-enhanced partially WPSNs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(9): 7207–7221. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2022.3156732. [4] 张晓茜, 徐勇军. 面向零功耗物联网的反向散射通信综述[J]. 通信学报, 2022, 43(11): 199–212. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2022199.ZHANG Xiaoqian and XU Yongjun. Survey on backscatter communication for zero-power IoT[J]. Journal on Communications, 2022, 43(11): 199–212. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2022199. [5] HUA Meng, WU Qingqing, and POOR H V. Power-efficient passive beamforming and resource allocation for IRS-aided WPCNs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2022, 70(5): 3250–3265. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2022.3161688. [6] 王兆瑞, 刘亮, 李航, 等. 面向6G物联网的智能反射表面设计[J]. 物联网学报, 2020, 4(2): 84–95. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-3750.2020.00160.WANG Zhaorui, LIU Liang, LI Hang, et al. Intelligent reflecting surface design for 6G-assited internet of things[J]. Chinese Journal on Internet of Things, 2020, 4(2): 84–95. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-3750.2020.00160. [7] WU Qingqing, ZHANG Shuowen, ZHENG Beixiong, et al. Intelligent reflecting surface-aided wireless communications: A tutorial[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(5): 3313–3351. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3051897. [8] PAN Qianqian, WU Jun, ZHANG Xi, et al. Differential privacy and IRS empowered intelligent energy harvesting for 6G internet of things[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(22): 22109–22122. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3104833. [9] WU Qingqing, GUAN Xinrong, and ZHANG Rui. Intelligent reflecting surface-aided wireless energy and information transmission: An overview[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2022, 110(1): 150–170. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2021.3121790. [10] WU Qingqing, ZHOU Xiaobo, CHEN Wen, et al. IRS-aided WPCNs: A new optimization framework for dynamic IRS beamforming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(7): 4725–4739. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3132666. [11] ZHU Lipeng, ZHANG Jun, XIAO Zhenyu, et al. Millimeter-wave full-duplex UAV relay: Joint positioning, beamforming, and power control[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2020, 38(9): 2057–2073. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2020.3000879. [12] 李斌, 刘文帅, 谢万城, 等. 智能反射面赋能无人机边缘网络计算卸载方案[J]. 通信学报, 2022, 43(10): 223–233. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2022196.LI Bin, LIU Wenshuai, XIE Wancheng, et al. Computation offloading scheme for RIS-empowered UAV edge network[J]. Journal on Communications, 2022, 43(10): 223–233. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2022196. [13] 刘志新, 赵松晗, 杨毅, 等. 智能反射面辅助的无人机无线携能通信网络吞吐量最大化算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(7): 2325–2331. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220195.LIU Zhixin, ZHAO Songhan, YANG Yi, et al. Throughput maximization algorithm for intelligent reflecting surface-aided unmanned aerial vehicle communication networks with wireless energy transfer[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(7): 2325–2331. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220195. [14] LI Sixian, DUO Bin, YUAN Xiaojun, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surface assisted UAV communication: Joint trajectory design and passive beamforming[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(5): 716–720. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.2966705. [15] MEI Haibo, YANG Kun, LIU Qiang, et al. 3D-trajectory and phase-shift design for RIS-assisted UAV systems using deep reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71(3): 3020–3029. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3143839. [16] GUROBI. GUROBI mathematical optimization solver[EB/OL]. https://www.gurobi.com/, 2019. [17] GRANT M C and BOYD S P. Graph implementations for nonsmooth convex programs[C]. Recent Advances in Learning and Control, London, UK, 2008: 95–110. doi: 10.1007/978-1-84800-155-8_7. [18] LIU Yuan, HAN Pengxia, and ZHAO Shengjie. Flexible and reliable multiuser SWIPT IoT network enhanced by UAV-mounted intelligent reflecting surface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2022, 71(2): 1092–1103. doi: 10.1109/TR.2022.3161336. [19] ZHOU Yi, JIN Zhanqi, SHI Huaguang, et al. Flying IRS: QoE-driven trajectory optimization and resource allocation based on adaptive deployment for WPCNs in 6G IoT[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3322266. -






 下载:
下载:








 下载:
下载:
