Abnormal Traffic Detection Method Based on Traffic Spatial-temporal Features and Adaptive Weighting Coefficients
-
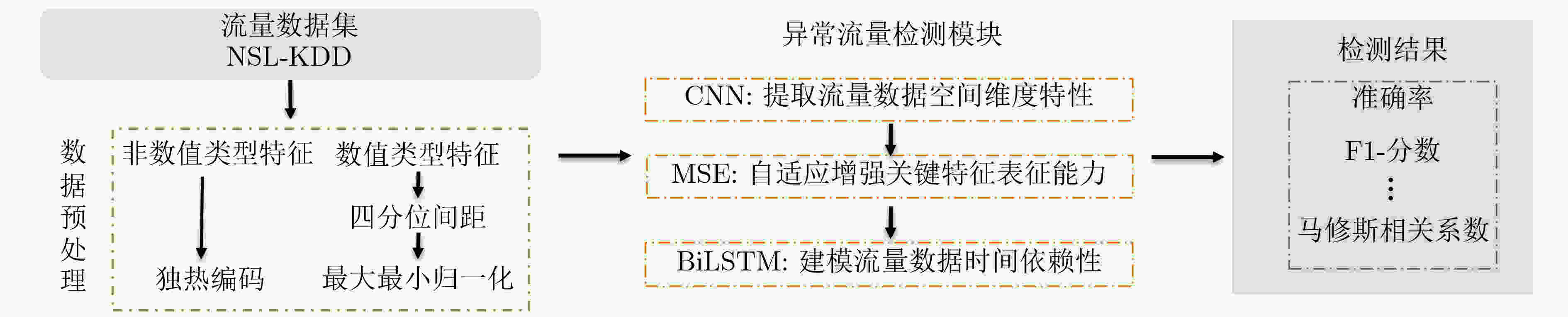
摘要: 针对传统异常流量检测模型对流量数据时空特性利用率较低从而导致检测模型性能较差的问题,该文提出一种基于融合卷积神经网络(CNN)、多头挤压激励机制(MSE)和双向长短期记忆(BiLSTM)网络的异常流量检测方法MSECNN-BiLSTM。利用1维CNN挖掘空间尺度下的异常流量特征,并引入MSE,多角度自适应特征加权,强化模型全局特征的关联能力。将网络流量的特征输入BiLSTM,捕捉流量数据的时序依赖性,进一步建立网络流量在时间尺度上的关系模型。利用softmax分类器进行预测分类,实验结果验证了所提模型在异常流量检测领域的有效性。Abstract: Considering the problem that the performance of the traditional abnormal traffic detection models is limited by the low utilization of spatiotemporal features of traffic data, an abnormal traffic detection method MSECNN-BiLSTM based on the combination of Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), Multi head Squeeze Excitation mechanism (MSE), and Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (BiLSTM) network is proposed. The one-dimensional CNN is used to capture abnormal traffic features at spatial scales. The MSE mechanism is introduced to adaptively calibrate the feature weights and strengthen the model’s ability to correlate global features from multiple perspectives. The traffic features are input into BiLSTM to capture the temporal dependencies of the traffic data and further model the relationship of network traffic on the time scale. The softmax classifier is employed for traffic detection. The experimental results verify that the proposed model is effective in the field of abnormal traffic detection.
-
表 1 超参数设置
超参数 参数值 Optimizer Adam Batch size 128 Training epoch 100 Learning rate 0.001 表 2 采用 MSECNN-BiLSTM 及其单一组成部分在 NSL-KDD 上的实验结果(%)
方法 Accuracy Precision Recall F1-score MCC MSECNN 85.31 86.63 87.73 87.18 69.99 BiLSTM 80.95 90.58 74.25 81.61 63.57 MSECNN-BiLSTM 88.74 89.90 90.36 90.13 77.02 表 3 MSE 模块对实验结果的影响(%)
方法 Accuracy Precision Recall F1-score MCC CNN 80.42 97.07 67.65 79.73 65.75 SECNN 83.59 96.00 74.27 83.75 70.04 MSECNN 85.31 86.63 87.73 87.18 69.99 SECNN-BiLSTM 85.90 88.52 86.43 87.47 71.39 MSECNN-BiLSTM 88.74 89.90 90.36 90.13 77.02 表 4 MSECNN-BiLSTM 与现有网络结构的实验对比(%)
方法 Accuracy Precision Recall F1-score MCC KNN 76.96 92.37 64.89 76.23 58.43 DT 78.98 91.94 69.13 78.92 61.17 SVM 75.38 91.63 62.46 74.28 55.81 ResNet 81.78 96.86 70.27 81.45 67.65 MSECNN-BiLSTM 88.74 89.90 90.36 90.13 77.02 表 5 与现有异常流量检测模型进行对比(%)
方法 Accuracy Precision Recall F1-score TSODE 77.38 83.64 77.38 77.08 CNN-CapSA 77.21 83.59 77.21 76.89 LCVAE 85.51 97.61 68.90 80.78 MSECNN-BiLSTM 88.74 89.90 90.36 90.13 -
[1] IMRANA Y, XIANG YANPING, ALI L, et al. A bidirectional lstm deep learning approach for intrusion detection[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2021, 185: 115524. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115524. [2] Kasperky. 安全报告[EB/OL]. https://www.kaspersky.com.cn/about/press-releases/2023_phishing, 2023. [3] IKRAM S T and CHERUKURI A K. Improving accuracy of intrusion detection model using PCA and optimized SVM[J]. Journal of Computing and Information Technology, 2016, 24(2): 133–148. doi: 10.20532/cit.2016.1002701. [4] WANG Huiwen, GU Jie, WANG Shanshan, et al. An effective intrusion detection framework based on SVM with feature augmentation[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2017, 136: 130–139. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2017.09.014. [5] 潘成胜, 李志祥, 杨雯升, 等. 基于二次特征提取和BiLSTM-Attention的网络流量异常检测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(12): 4539–4547. doi: 10.11999/JEIT221296.PAN Chengsheng, LI Zhixiang, YANG Wensheng, et al. Anomaly detection method of network traffic based on secondary feature extraction and BiLSTM-attention[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(12): 4539–4547. doi: 10.11999/JEIT221296. [6] LECUN Y, BENGIO Y, and HINTON G. Deep learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 521(7553): 436–444. doi: 10.1038/nature14539. [7] LI Yanmiao, XU Yingying, LIU Zhi, et al. Robust detection for network intrusion of industrial IoT based on multi-CNN fusion[J]. Measurement, 2020, 154: 107450. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2019.107450. [8] 陈思佳, 罗志增. 基于长短时记忆和卷积神经网络的手势肌电识别研究[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2021, 42(2): 162–170.CHEN Sijia and LUO Zhizeng. Research on gesture EMG recognition based on long short-term memory and convolutional neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2021, 42(2): 162–170. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.J2007103. [9] KANNA P R and SANTHI P. Unified deep learning approach for efficient intrusion detection system using integrated spatial–temporal features[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2021, 226: 107132. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2021.107132. [10] JIANG Feng, FU Yunsheng, GUPTA B B, et al. Deep learning based multi-channel intelligent attack detection for data security[J]. IEEE transactions on Sustainable Computing, 2020, 5(2): 204–212. doi: 10.1109/TSUSC.2018.2793284. [11] SIVAMOHAN S, SRIDHAR S S, and KRISHNAVENI S. An effective recurrent neural network (RNN) based intrusion detection via bi-directional long short-term memory[C]. 2021 International Conference on Intelligent Technologies (CONIT), Hubli, India, 2021: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/CONIT51480.2021.9498552. [12] HUANG Buliao, ZHU Yunhui, USMAN M, et al. Graph neural networks for missing value classification in a task-driven metric space[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2023, 35(8): 8073–8084. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2022.3198689. [13] HAO Yi, LI Jie, WANG Nanan, et al. Spatiotemporal consistency-enhanced network for video anomaly detection[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2022, 121: 108232. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2021.108232. [14] XU Lixiang, ZHOU Biao, LI Xinlu, et al. Gaussian process image classification based on multi-layer convolution kernel function[J]. Neurocomputing, 2022, 480: 99–109. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2022.01.048. [15] HU Jie, SHEN Li, and SUN Gang. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7132–7141. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00745. [16] HOCHREITER S and SCHMIDHUBER J. Long short-term memory[J]. Neural Computation, 1997, 9(8): 1735–1780. doi: 10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735. [17] GEETHA T V and DEEPA A J. A FKPCA-GWO WDBiLSTM classifier for intrusion detection system in cloud environments[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2022, 253: 109557. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2022.109557. [18] TAVALLAEE M, BAGHERI E, LU Wei, et al. A detailed analysis of the KDD CUP 99 data set[C]. 2009 IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence for Security and Defense Applications, Ottawa, Canada, 2009: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/CISDA.2009.5356528. [19] FATANI A, ABD ELAZIZ M, DAHOU A, et al. IoT intrusion detection system using deep learning and enhanced transient search optimization[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 123448–123464. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3109081. [20] ABD ELAZIZ M, AL-QANESS M A A, DAHOU A, et al. Intrusion detection approach for cloud and IoT environments using deep learning and Capuchin Search Algorithm[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2023, 176: 103402. doi: 10.1016/j.advengsoft.2022.103402. [21] XU Xing, LI Jie, YANG Yang, et al. Toward effective intrusion detection using log-cosh conditional variational autoencoder[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(8): 6187–6196. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3034621. -






 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
