Closely Spaced Objects Super-resolution Method Using Array Camera Images
-
摘要: 空天威胁目标通常距离成像系统较远,导致其在图像中信噪比低、尺寸小,即呈现为弱小目标。由于系统分辨率限制,当目标以密集目标群出现时,往往在图像中形成未分辨目标簇,对目标发现、跟踪、识别等带来挑战。阵列相机可以提供多个视角的互补观测信息,采用融合阵列相机图像的超分辨技术,可有效提升弱小目标分辨能力,为分辨密集多目标提供技术途径。该文分析了空间邻近目标与阵列相机之间的几何关系,并提出一种基于阵列相机图像稀疏重建的邻近目标超分辨率方法。利用空间邻近目标在像平面上稀疏性先验假设和阵列相机多视图之间关于目标的投影约束,仿真实验结果表明所提方法能够有效分辨空间邻近目标,实现对空间邻近目标位置和数量的准确估计。Abstract: The aerial targets are usually far from the imaging system, making the imaged results have weak radiation intensity and limited imaging area. Especially when aerial target groups are distributed in a dense form, make further the imaged results have overlapping projection of such dense targets, and limit the performance of subsequent detection, track, and identification tasks. The array camera imaging system can provide complementary information about the target from multiple views and make effectively up for the deficiency of a single camera in detecting the resolution of nearby aerial targets. In this paper, the geometric relationship between nearby aerial targets and array cameras is studied and a super-resolution method for nearby targets based on sparse reconstruction of array camera images is proposed. Thanks to the prior assumption of sparsity of nearby aerial targets on the image plane and the transfer constraints between multiple views of array cameras regarding the target, relevant simulation experiments show that the proposed method can well super-resolve the obtained images of nearby targets and estimate effectively the position and number of nearby aerial targets.
-
Key words:
- Array camera /
- Closely spaced objects /
- Super-resolution /
- Sparse reconstruction
-
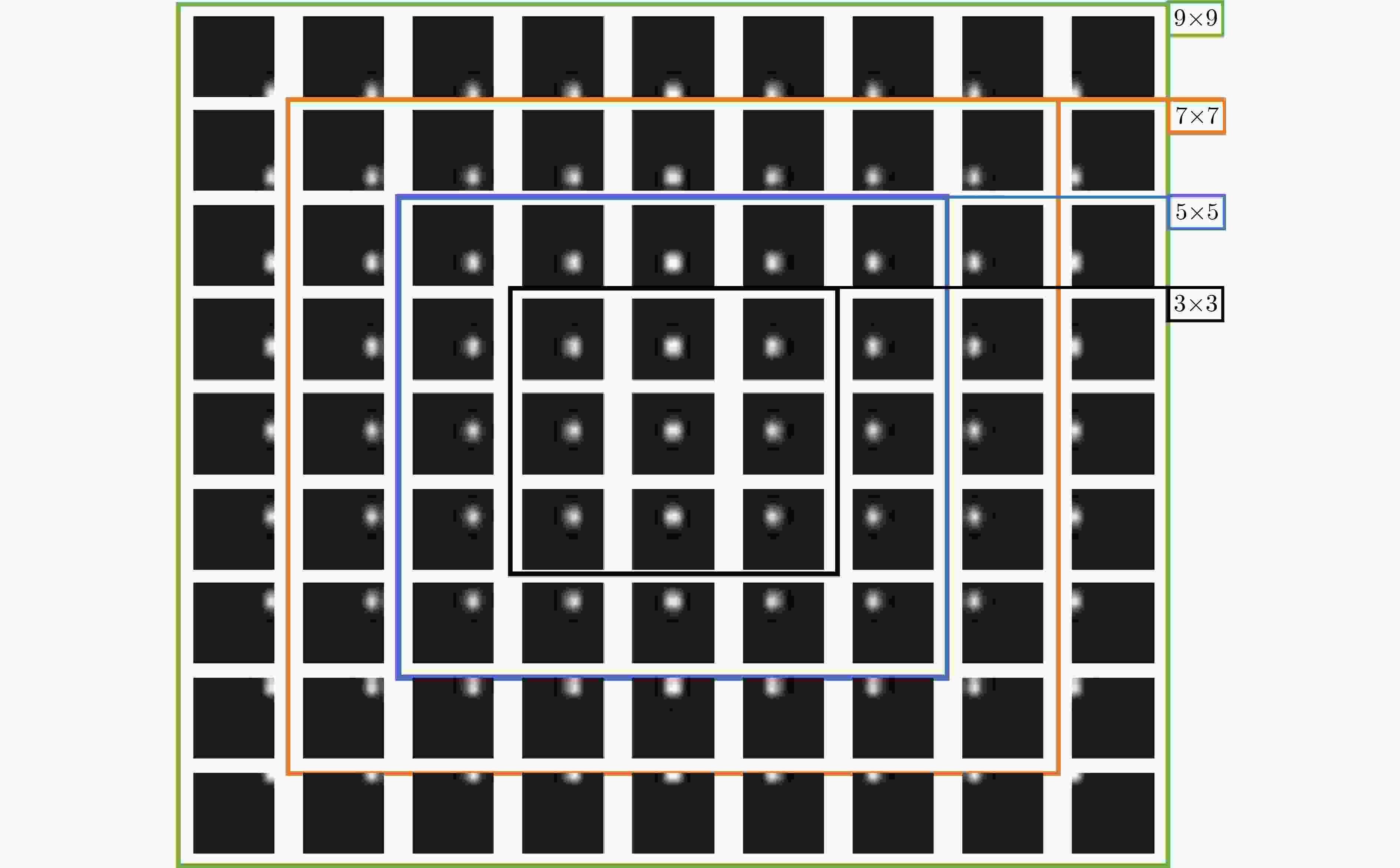
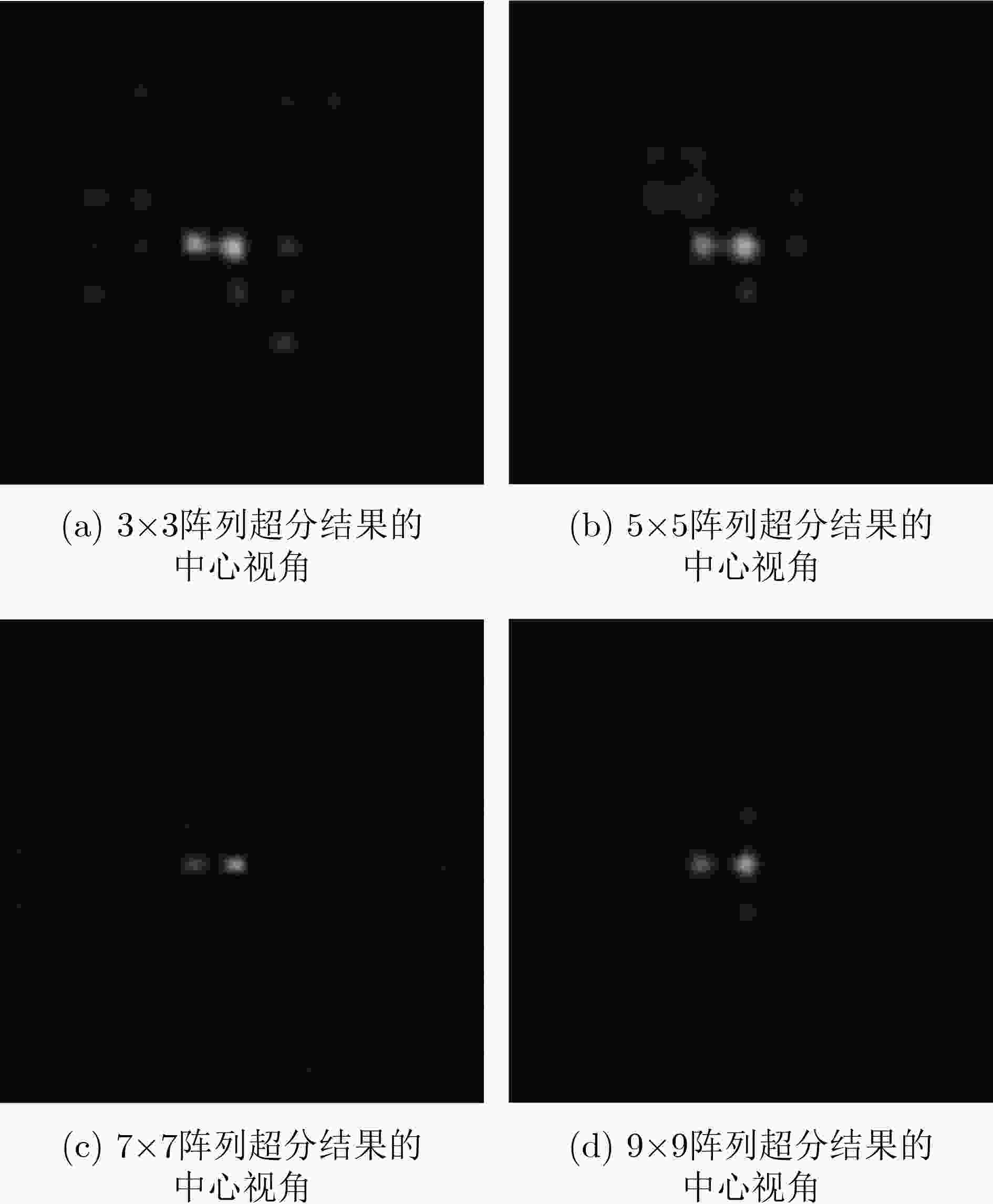
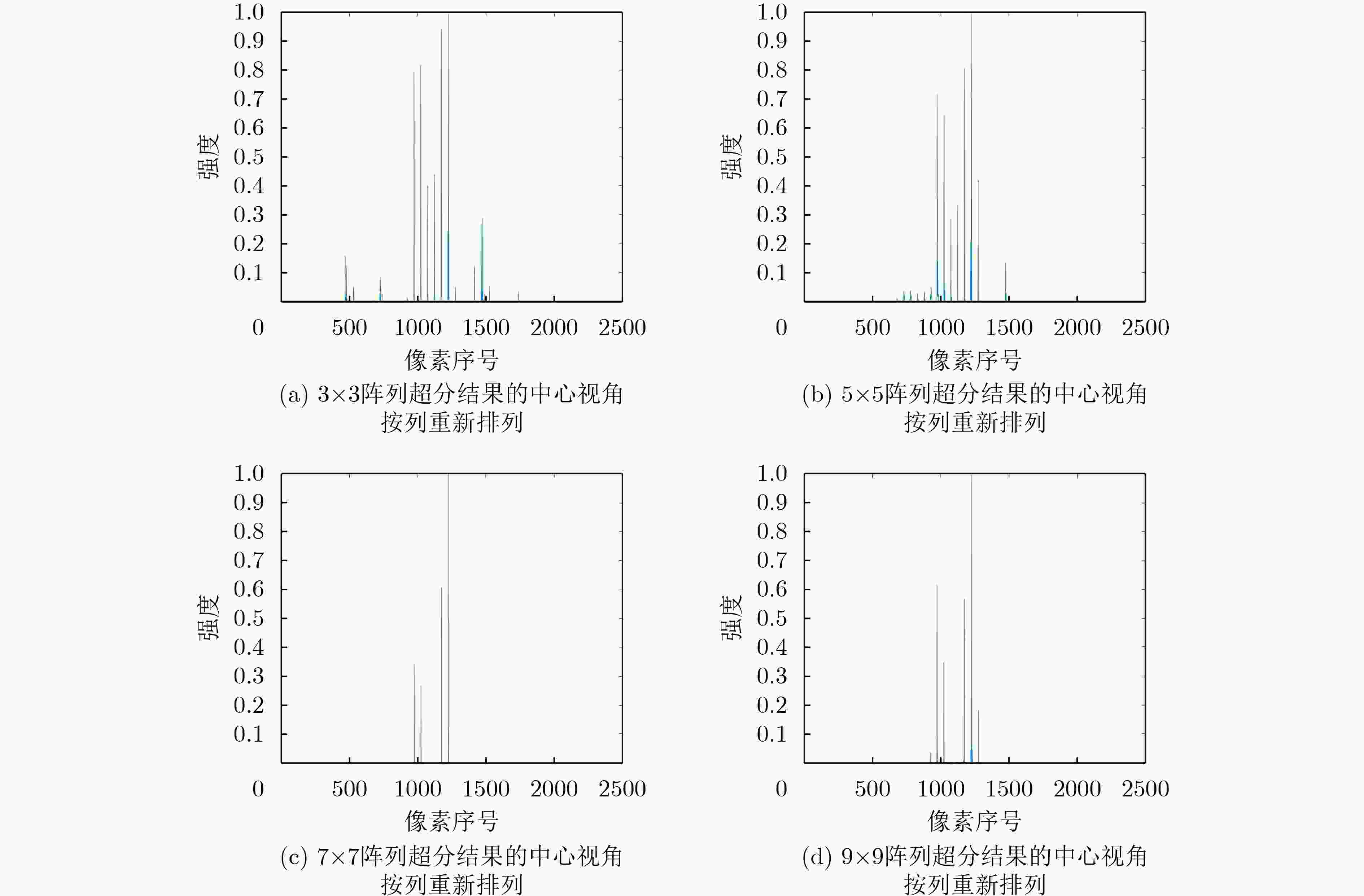
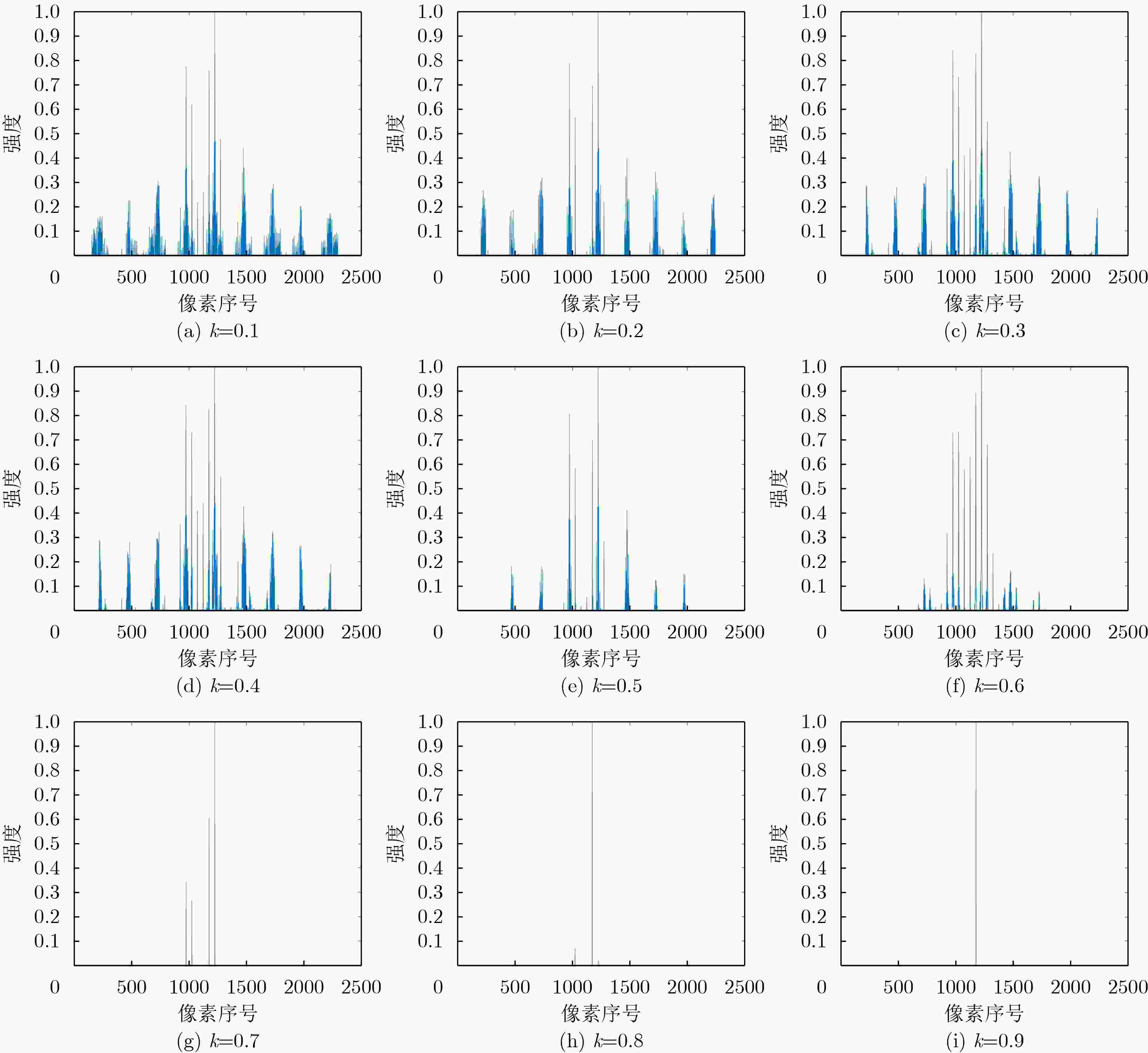
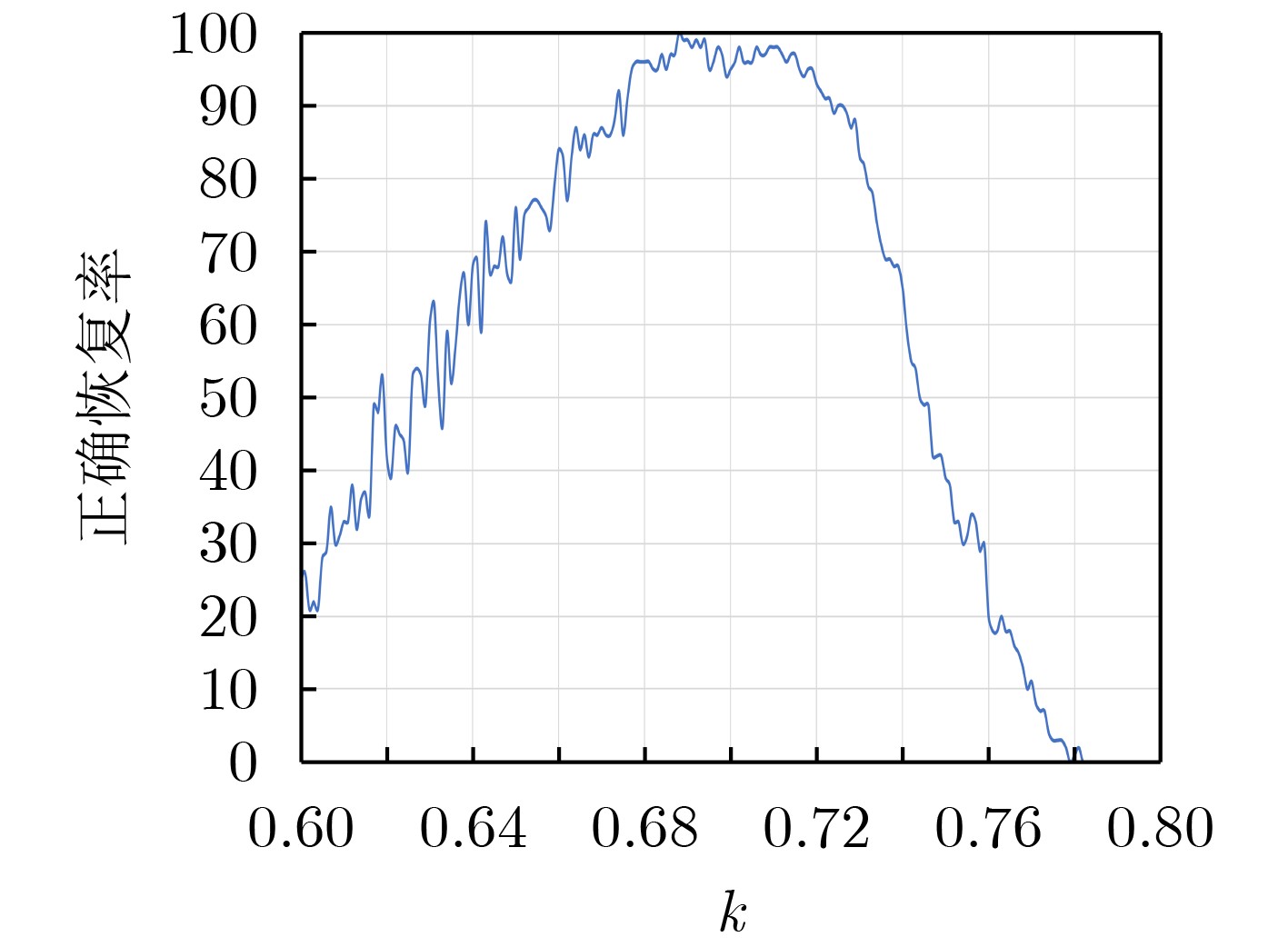
表 1 联合不同数量阵列相机图像的邻近目标超分辨结果正确率
阵列大小 3 $ \times $3 5 $ \times $5 7 $ \times $7 9 $ \times $9 正确恢复率 0.54 0.76 0.95 0.98 -
[1] 林两魁, 徐晖, 安玮, 等. 基于粒子群优化的空间邻近目标红外超分辨算法[J]. 光学学报, 2010, 30(6): 1645–1650. doi: 10.3788/AOS20103006.1645LIN Liangkui, XU Hui, AN Wei, et al. Closely spaced objects infrared super-resolution algorithm based on particle swarm optimization[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2010, 30(6): 1645–1650. doi: 10.3788/AOS20103006.1645 [2] GREEN P J. Reversible jump Markov chain Monte Carlo computation and Bayesian model determination[J]. Biometrika, 1995, 82(4): 711–732. doi: 10.1093/biomet/82.4.711 [3] SUN Guanqun, ZHANG Fangzheng, PAN Shilong, et al. Adaptive super resolution array radar imaging based on sparse reconstruction and effective rank theory[C]. The 24th International Radar Symposium, Berlin, Germany, 2023: 1–7. [4] 张慧, 徐晖, 林两魁. 基于稀疏重构的空间邻近目标红外单帧图像超分辨方法[J]. 光学学报, 2013, 33(4): 0411001. doi: 10.3788/AOS201333.0411001ZHANG Hui, XU Hui, and LIN Liangkui. Super-resolution method of closely spaced objects based on sparse reconstruction using single frame infrared data[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2013, 33(4): 0411001. doi: 10.3788/AOS201333.0411001 [5] LI Xiaosong, ZHOU Fuqiang, and TAN Haishu. Joint image fusion and denoising via three-layer decomposition and sparse representation[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2021, 224: 107087. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2021.107087 [6] XIE Yutong and LI Quanzheng. A review of deep learning methods for compressed sensing image reconstruction and its medical applications[J]. Electronics, 2022, 11(4): 586. doi: 10.3390/electronics11040586 [7] EL MAHDAOUI A, OUAHABI A, and MOULAY M S. Image denoising using a compressive sensing approach based on regularization constraints[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(6): 2199. doi: 10.3390/s22062199 [8] 张熙凡, 于凌志. 基于低秩降维和稀疏重构的图像扰动防御算法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2022, 59(12): 1210004. doi: 10.3788/LOP202259.1210004ZHANG Xifan and YU Lingzhi. Image defense algorithm against adversarial attacks based on low-rank dimensionality reduction and sparse reconstruction[J]. Laser&Optoelectronics Progress, 2022, 59(12): 1210004. doi: 10.3788/LOP202259.1210004 [9] CANDES E J and WAKIN M B. An introduction to compressive sampling[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2008, 25(2): 21–30. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2007.914731 [10] MALLAT S G and ZHANG Zhifeng. Matching pursuits with time-frequency dictionaries[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1993, 41(12): 3397–3415. doi: 10.1109/78.258082 [11] TROPP J A and GILBERT A C. Signal recovery from random measurements via orthogonal matching pursuit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2007, 53(12): 4655–4666. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2007.909108 [12] BLUMENSATH T and DAVIES M E. Iterative hard thresholding for compressed sensing[J]. Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis, 2009, 27(3): 265–274. doi: 10.1016/j.acha.2009.04.002 [13] 贺月, 柳建新, 王显莹, 等. 基于自适应字典学习的插值去噪的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2021, 36(6): 2454–2461. doi: 10.6038/pg2021EE0480HE Yue, LIU Jianxin, WANG Xianying, et al. Application of interpolation denoising based on adaptive dictionary learning[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2021, 36(6): 2454–2461. doi: 10.6038/pg2021EE0480 [14] 潘辉, 印兴耀, 李坤, 等. 基于经验模态分解字典的自适应匹配追踪谱分解方法及其在油气检测中的应用[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2021, 56(5): 1117–1129, 2020–2021.PAN Hui, YIN Xingyao, LI Kun, et al. Spectral decomposition method of adaptive matching pursuit based on empirical mode decomposition dictionary and its application in oil and gas detection[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2021, 56(5): 1117–1129, 2020–2021. [15] FIGUEIREDO M A T, NOWAK R D, and WRIGHT S J. Gradient projection for sparse reconstruction: Application to compressed sensing and other inverse problems[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2007, 1(4): 586–597. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2007.910281 -
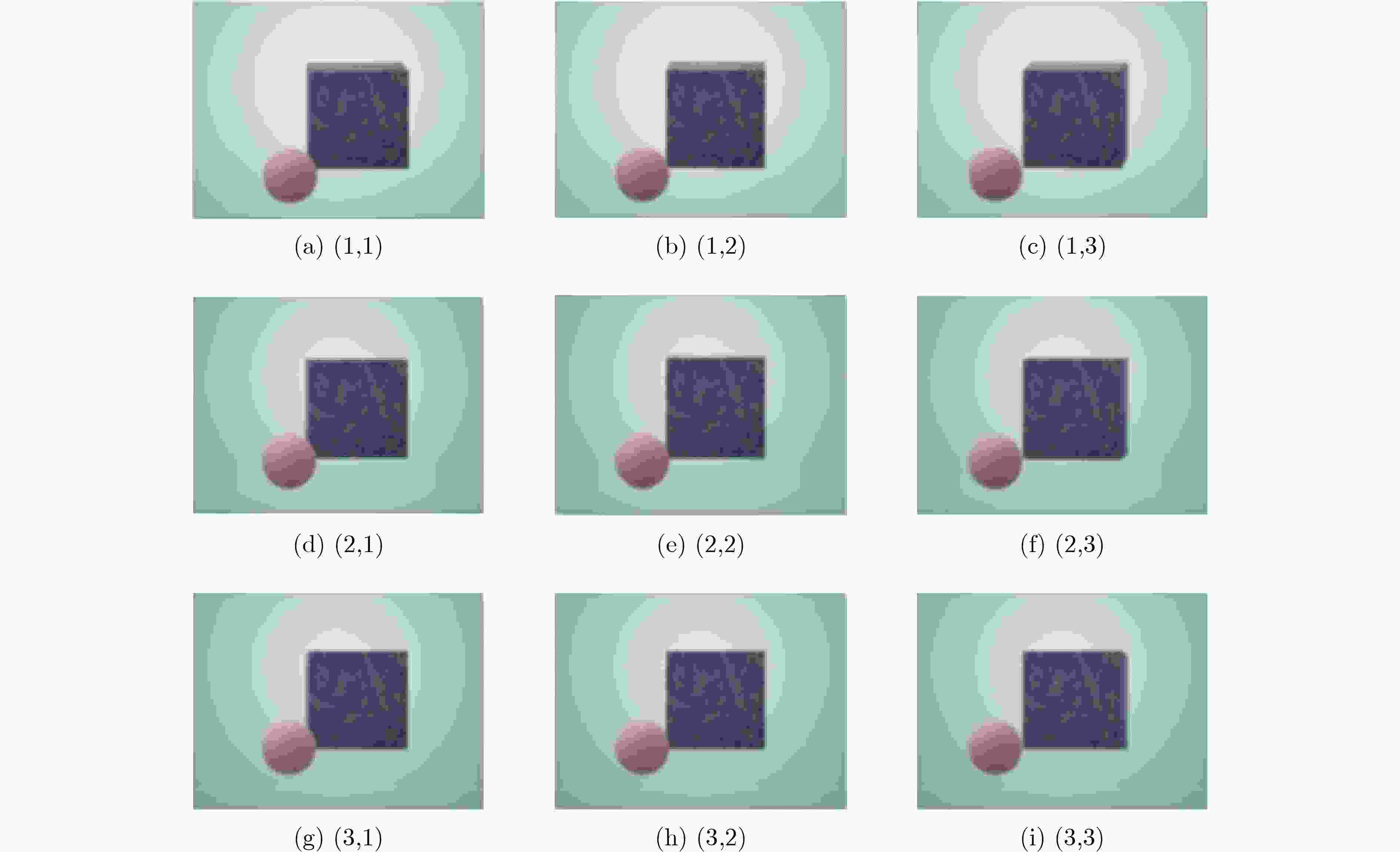






 下载:
下载:

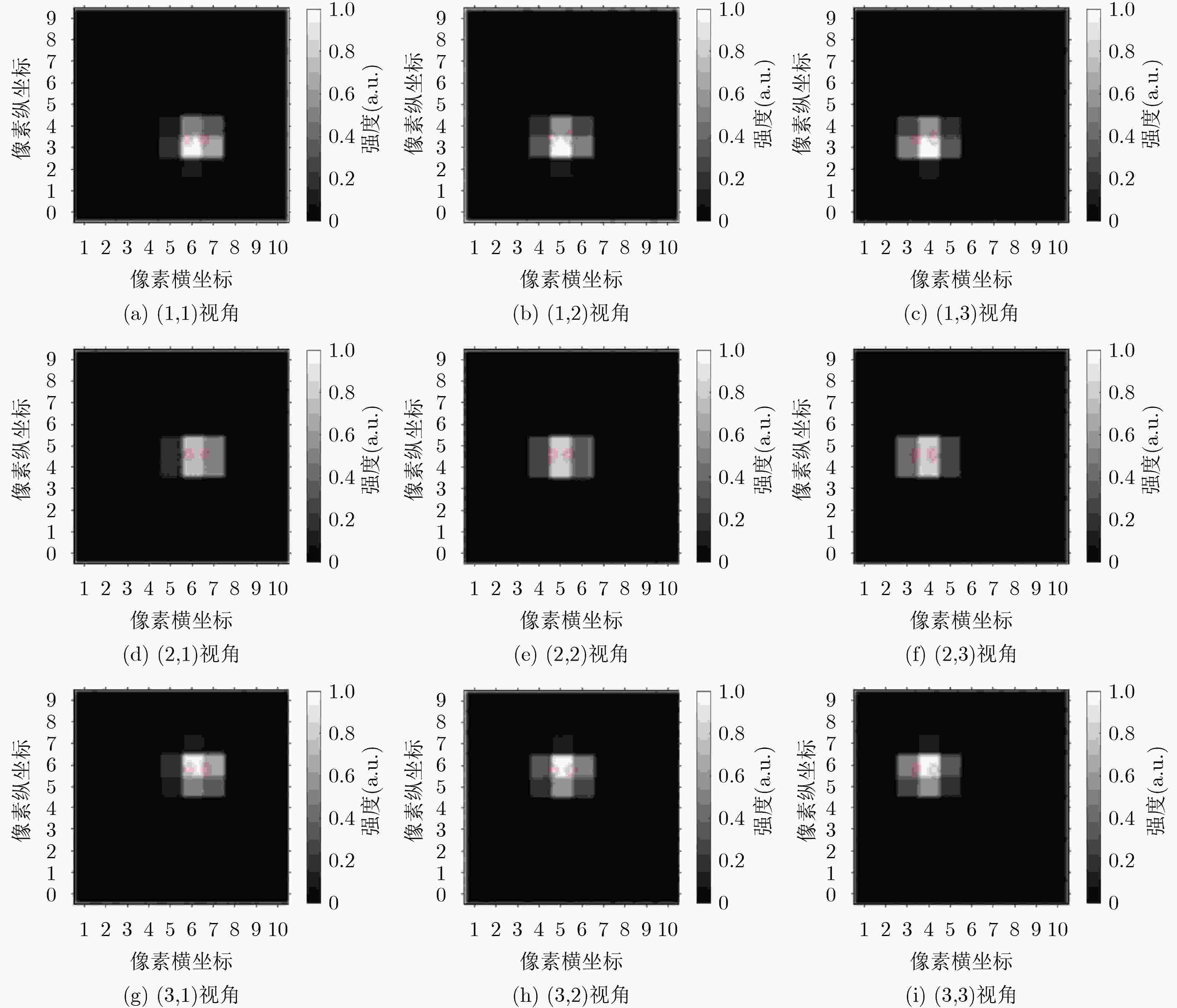
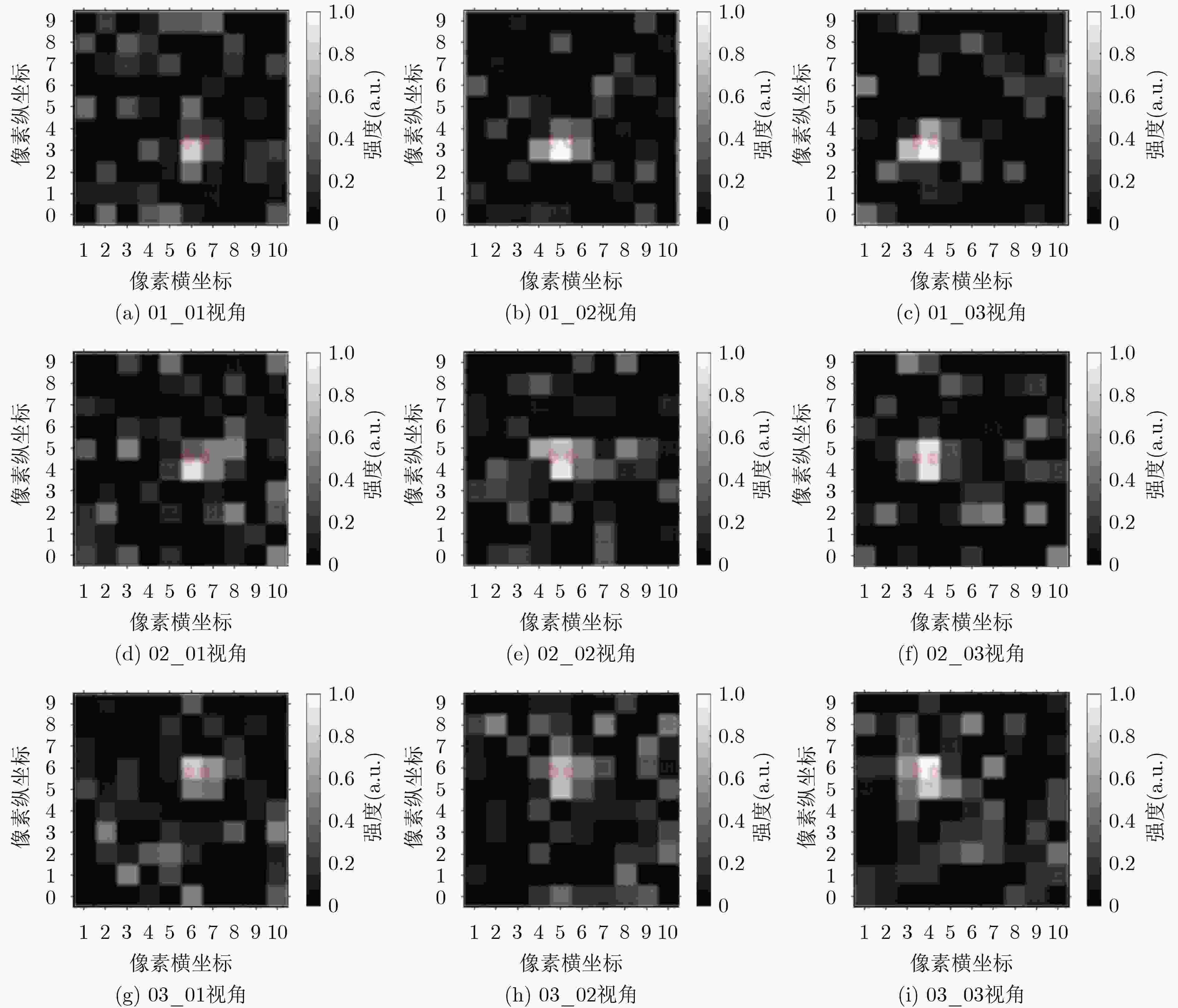
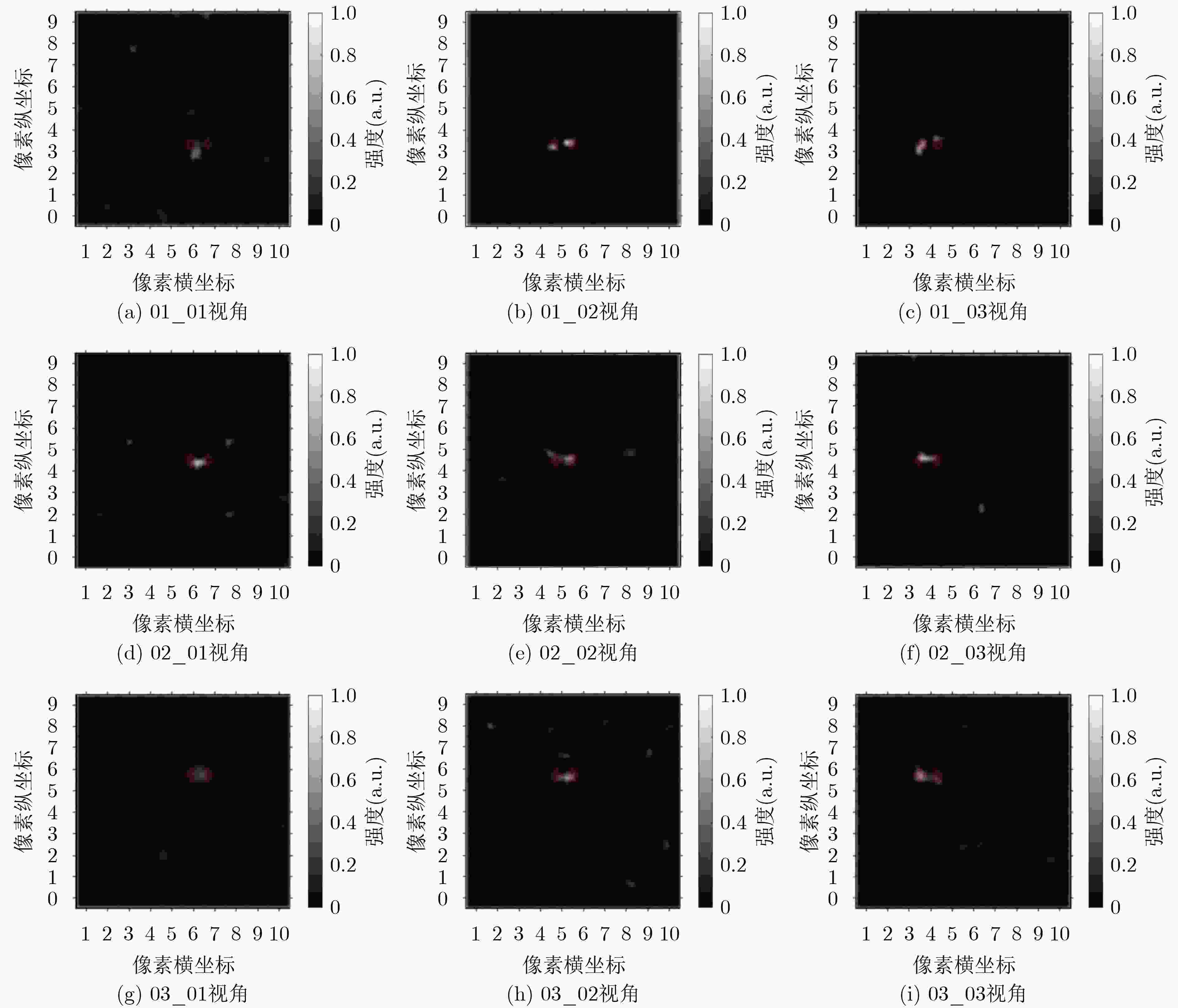
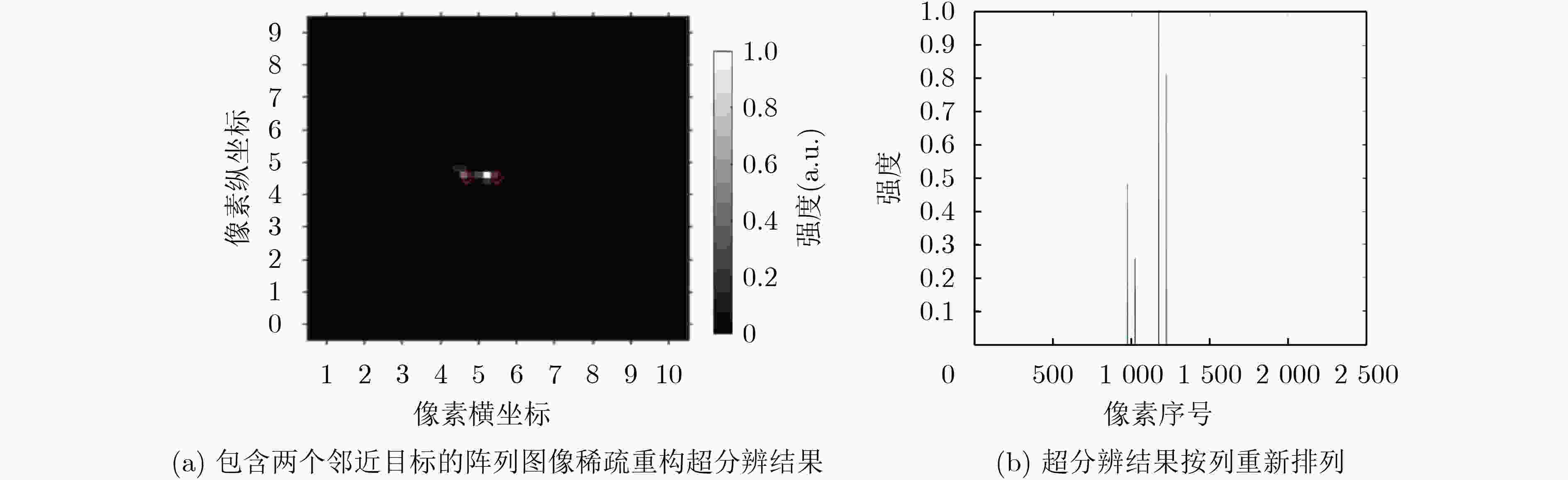


 下载:
下载:
