Resource Scheduling Based on Multi-factor Priority for High Performance Requirements in Wireless Body Area Network
-
摘要: 媒体访问控制(MAC)在确保无线体域网(WBAN)的正常运行方面起着关键的作用。然而,动态环境下紧急数据低延迟和低能耗的高性能需求仍未很好地解决。该文提出一种多因子紧急调度方案(MESS)来满足这样一个严格的需求。首先,针对实际应用场景中数据异质性的特性,设计一种数据分类方法,该方法将数据分为周期数据和紧急数据,这对不同的节点来说更加符合实际情况;其次,设计一种多因子优先级划分方案,包括疾病相关因子、关键程度因子、健康严重程度因子和信息年龄因子,4个因子可以更全面地考虑节点的关键特征;此外,还设计了一种动态时隙分配和排序方法,将节点的时隙依据数据分类和多因子优先级进行动态分配和排序。理论分析和仿真实验结果表明,相较于传统方案所提方案在延迟和能效方面具有明显优势。Abstract: Media Access Control (MAC) plays a pivotal role in ensuring proper operation of Wireless Body Area Networks (WBAN). However, current solutions still cannot satisfy high performance requirements of low latency and energy consumption for emergency data reporting. A Multi-factor Emergency Scheduling Scheme (MESS) is proposed to meeting such a strict demand. First, a data classification method is designed to sort data as periodic data and emergency data, respectively. Unlike consistent data characteristics in other schemes, data heterogeneity is considered in our solution, which is more practical for different nodes. Second, a multi-factor priority division scheme is devised, according to the disease-related factor, critical degree factor, health severity factor and age of information factor. This is a more comprehensive consideration of the key characteristics of the node. In addition, a dynamic slot allocation and sequencing approach is designed, in which time slots of nodes are allocated based on the data classification and multi-factor priority-based ordering. This enhances low latency and guarantees energy efficiency of nodes. Theoretical and simulation results demonstrate the advantages of MESS in terms of delay and energy efficiency.
-
表 1 仿真参数
参数 值 参数 值 接收功率$ {P}_{\mathrm{r}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{c}}\left(\mathrm{m}\mathrm{W}\right) $ $ 35 $ 总节点数 $ m $ $ 3\mathrm{~}8 $ 发送功率$ {P}_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{e}}\left(\mathrm{m}\mathrm{W}\right) $ $ 40 $ 紧急数据节点数 $ n $ $ 2\mathrm{~}8 $ 空闲功率 $ {P}_{\mathrm{i}\mathrm{d}\mathrm{l}}\left(\mathrm{m}\mathrm{W}\right) $ $ 5 $ 最大重传次数 $ r $ $ 3 $ 休眠功率 $ {P}_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{l}\mathrm{p}}\left(\mathrm{m}\mathrm{W}\right) $ $ 2.7\times {10}^{-3} $ 信标数据量 $ {D}_{\mathrm{B}}\left(\mathrm{b}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{t}\right) $ $ 36 $ 信标速率$ {V}_{\mathrm{B}}(\mathrm{k}\mathrm{b}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{t}/\mathrm{s}) $ $ 10 $ ACK数据量 $ {D}_{\mathrm{A}\mathrm{C}\mathrm{K}}\left(\mathrm{b}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{t}\right) $ $ 36 $ ACK速率$ {V}_{\mathrm{A}\mathrm{C}\mathrm{K}}(\mathrm{k}\mathrm{b}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{t}/\mathrm{s}) $ $ 10 $ 数据量$ {D}_{{k}}\left(\mathrm{b}\mathrm{y}\mathrm{t}\mathrm{e}\right) $ $ 32 $ 数据传输速率$ {V}_{k}\left(\mathrm{k}\mathrm{b}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{t}/\mathrm{s}\right) $ $ 320 $ 电池电量 $ {E}_{\mathrm{b}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{t}}\left(\mathrm{m}\mathrm{A}\mathrm{h}\right) $ $ 560 $ 传输分组转换时间pS (μs) $ 75 $ 同步误差容限$ \mathrm{p}\mathrm{E}\mathrm{S} $(μs) $ 10 $ 定时不确定性mCR (μs) $ 4 $ 符号速率$ {V}_{\mathrm{S}\mathrm{r}}\left(\mathrm{k}\mathrm{b}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{t}/\mathrm{s}\right) $ $ 600 $ 物理层前导码数$ {N}_{\mathrm{p}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{e}}\left(\mathrm{b}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{t}\right) $ $ 90 $ PLCP头的负载数$ {N}_{\mathrm{h}\mathrm{d}\mathrm{r}}\left(\mathrm{b}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{t}\right) $ $ 31 $ 扩展因子$ {S}_{\mathrm{h}\mathrm{d}\mathrm{r}} $ $ 4 $ 传递到扩展器的因子$ {S}_{\mathrm{P}\mathrm{S}\mathrm{D}} $ $ 1 $ 扩大因子U $ 1 $ 调制因子$ M $ $ 4 $ -
[1] JAVADPOUR A, SANGAIAH A K, JA'FARI F, et al. Toward a secure industrial wireless body area network focusing MAC layer protocols: An analytical review[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2023, 19(2): 2028–2038. doi: 10.1109/TII.2022.3205361. [2] HU Juncheng, XU Gaochao, HU Liang, et al. An adaptive energy efficient MAC protocol for RF energy harvesting WBANs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2023, 71(1): 473–484. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2022.3222872. [3] KANG T, OH K I, LEE J J, et al. Spiking neural networks-inspired signal detection based on measured body channel response[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2022, 71: 2512816. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2022.3187719. [4] FAN Ling, LIU Xuxun, ZHOU Huan, et al. Efficient resource scheduling for interference alleviation in dynamic coexisting WBANs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2023, 22(3): 1479–1490. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2021.3110235. [5] ZHAO Guichuan, JIANG Qi, LIU Ximeng, et al. Electrocardiogram based group device pairing for wearables[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2023, 22(11): 6394–6409. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2022.3200104. [6] ZHANG Rongrong, YU Jihong, GUAN Yong, et al. A dominating set-based sleep scheduling in energy harvesting WBANs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(11): 11923–11934. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3085833. [7] MOULIK S, MISRA S, and DAS D. AT-MAC: Adaptive MAC-frame payload tuning for reliable communication in wireless body area networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2017, 16(6): 1516–1529. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2016.2598166. [8] LIU Dong, WANG Jingjing, JIANG Chunxiao, et al. A contention-oriented node sleeping MAC protocol for WBAN[C]. 2018 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, Barcelona, Spain, 2018: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/WCNC.2018.8377149. [9] DEEPAK K S and BABU A V. Improving reliability of emergency data frame transmission in IEEE 802.15. 6 wireless body area networks[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2018, 12(3): 2082–2093. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2017.2717189. [10] ZHANG Rongrong, MOUNGLA H, YU Jihong, et al. Medium access for concurrent traffic in wireless body area networks: Protocol design and analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(3): 2586–2599. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2016.2573718. [11] RASHWAND S, MIŠIĆ J, and MIŠIĆ V B. Analysis of CSMA/CA mechanism of IEEE 802.15. 6 under non-saturation regime[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2016, 27(5): 1279–1288. doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2015.2447528. [12] MISRA S, MOULIK S, and CHAO H C. A cooperative bargaining solution for priority-based data-rate tuning in a wireless body area network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2015, 14(5): 2769–2777. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2015.2393303. [13] LIANG Baowen, OBAIDAT M S, LIU Xuxun, et al. Resource scheduling based on priority ladders for multiple performance requirements in wireless body area networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(7): 7027–7036. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3080596. [14] SALAYMA M, AL-DUBAI A, ROMDHANI I, et al. Reliability and energy efficiency enhancement for emergency-aware wireless body area networks (WBANs)[J]. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, 2018, 2(3): 804–816. doi: 10.1109/TGCN.2018.2813060. [15] SUN Gang, WANG Kai, YU Hongfang, et al. Priority-based medium access control for wireless body area networks with high-performance design[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(3): 5363–5375. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2900661. [16] LIANG Baowen, LIU Xuxun, ZHOU Huan, et al. Channel resource scheduling for stringent demand of emergency data transmission in WBANs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(4): 2341–2352. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3041471. [17] RUAN Lihua, DIAS M P I, and WONG E. SmartBAN with periodic monitoring traffic: A performance study on low delay and high energy efficiency[J]. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2018, 22(2): 471–482. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2016.2642220. [18] LIU Bin, YAN Zhisheng, and CHEN Changwen. MAC protocol in wireless body area networks for E-health: Challenges and a context-aware design[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2013, 20(4): 64–72. doi: 10.1109/MWC.2013.6590052. [19] DI FRANCO F, TACHTATZIS C, GRAHAM B, et al. Current characterisation for Ultra Low power wireless body area networks[C]. The 2010 8th Workshop on Intelligent Solutions in Embedded Systems, Heraklion, Greece, 2010: 91–96. doi: 10.1109/WISES.2010.5548422. -





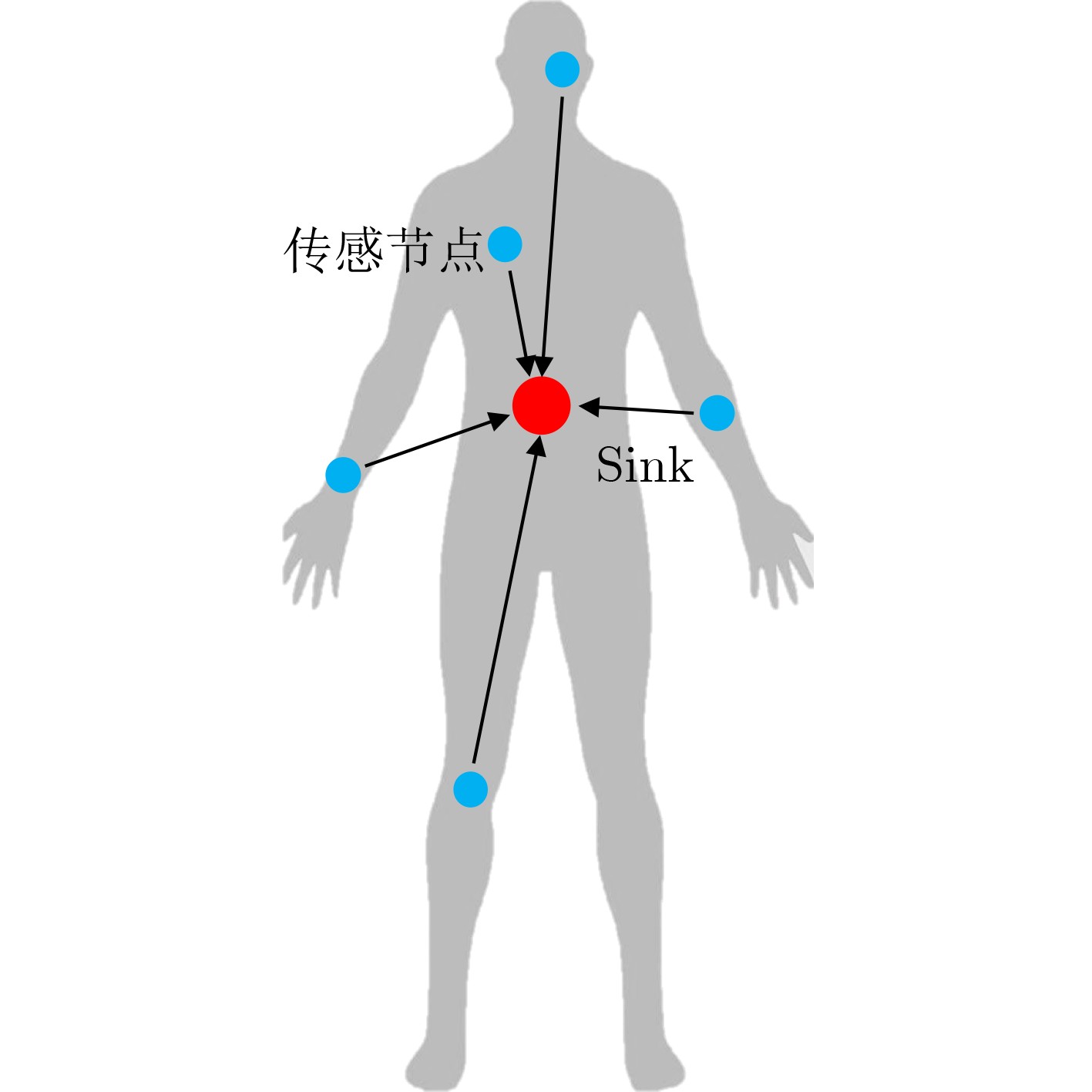
 下载:
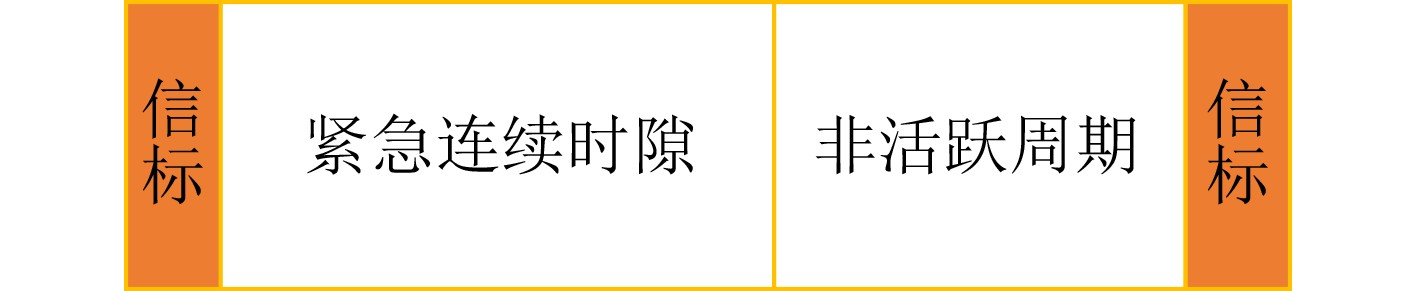
下载:
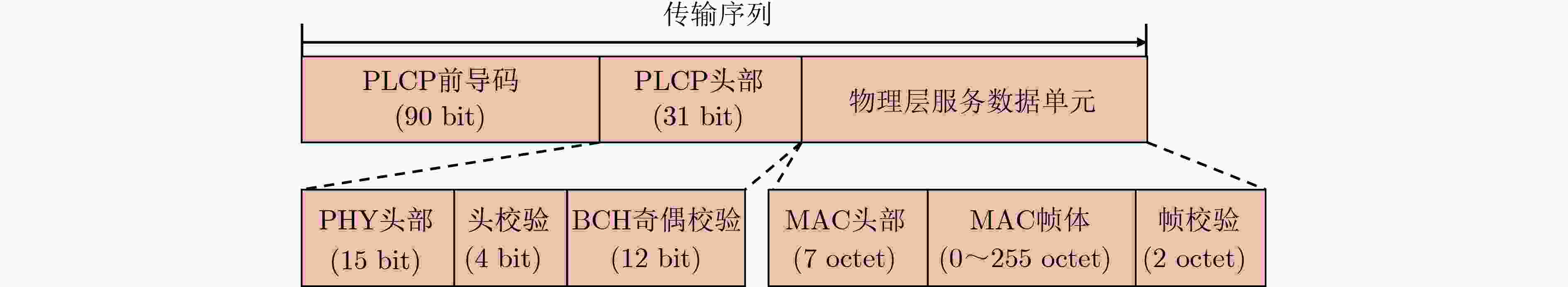

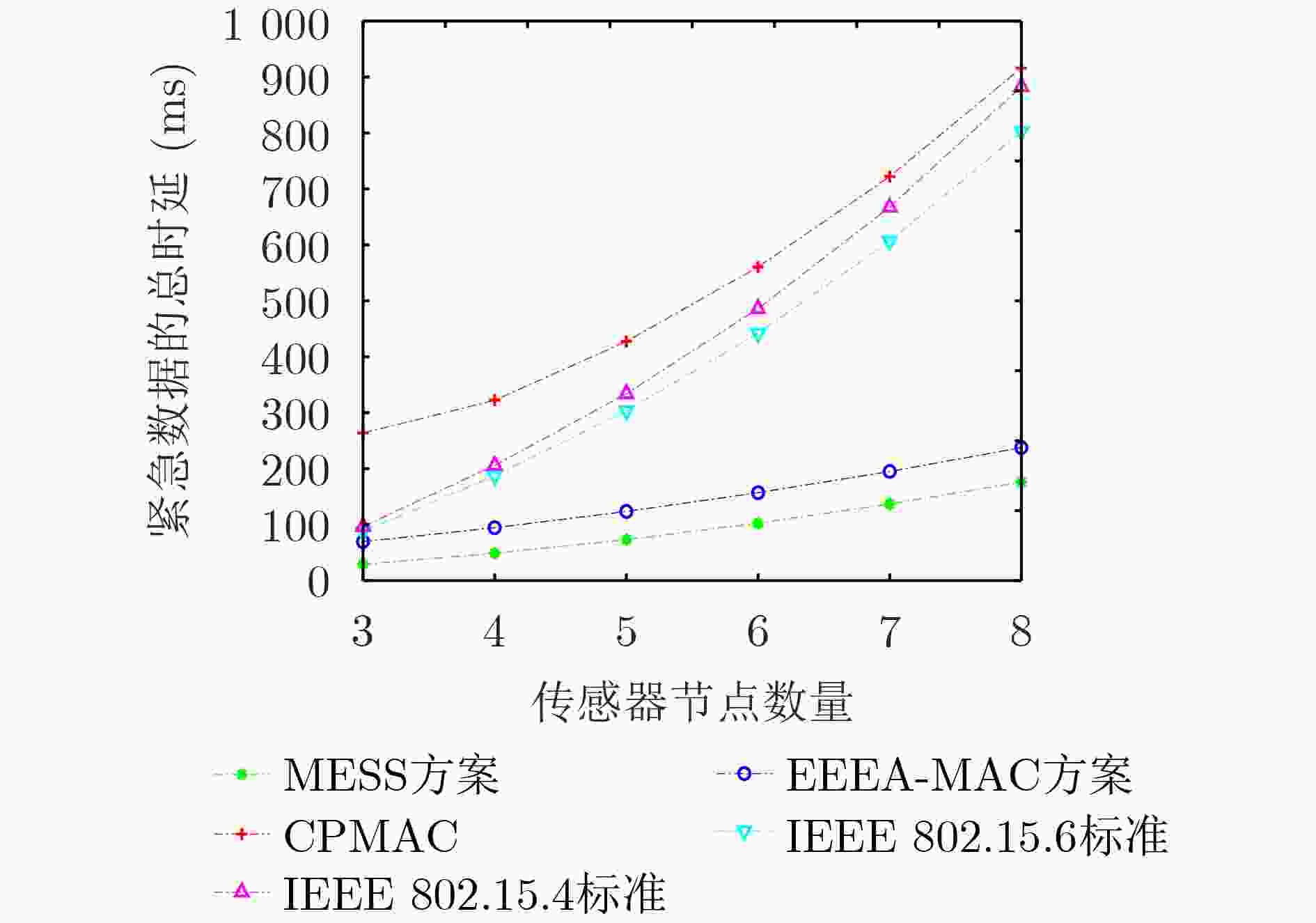
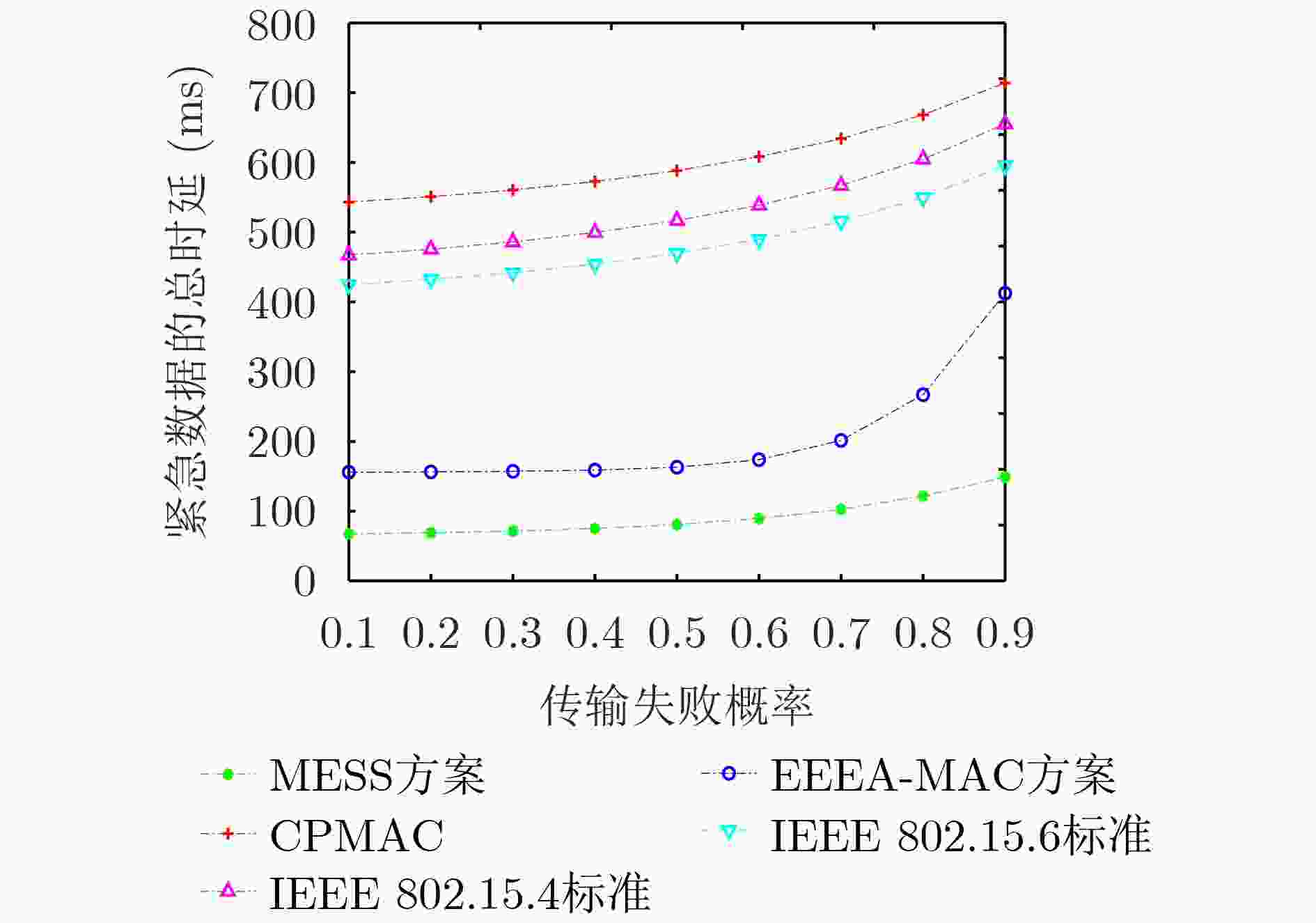
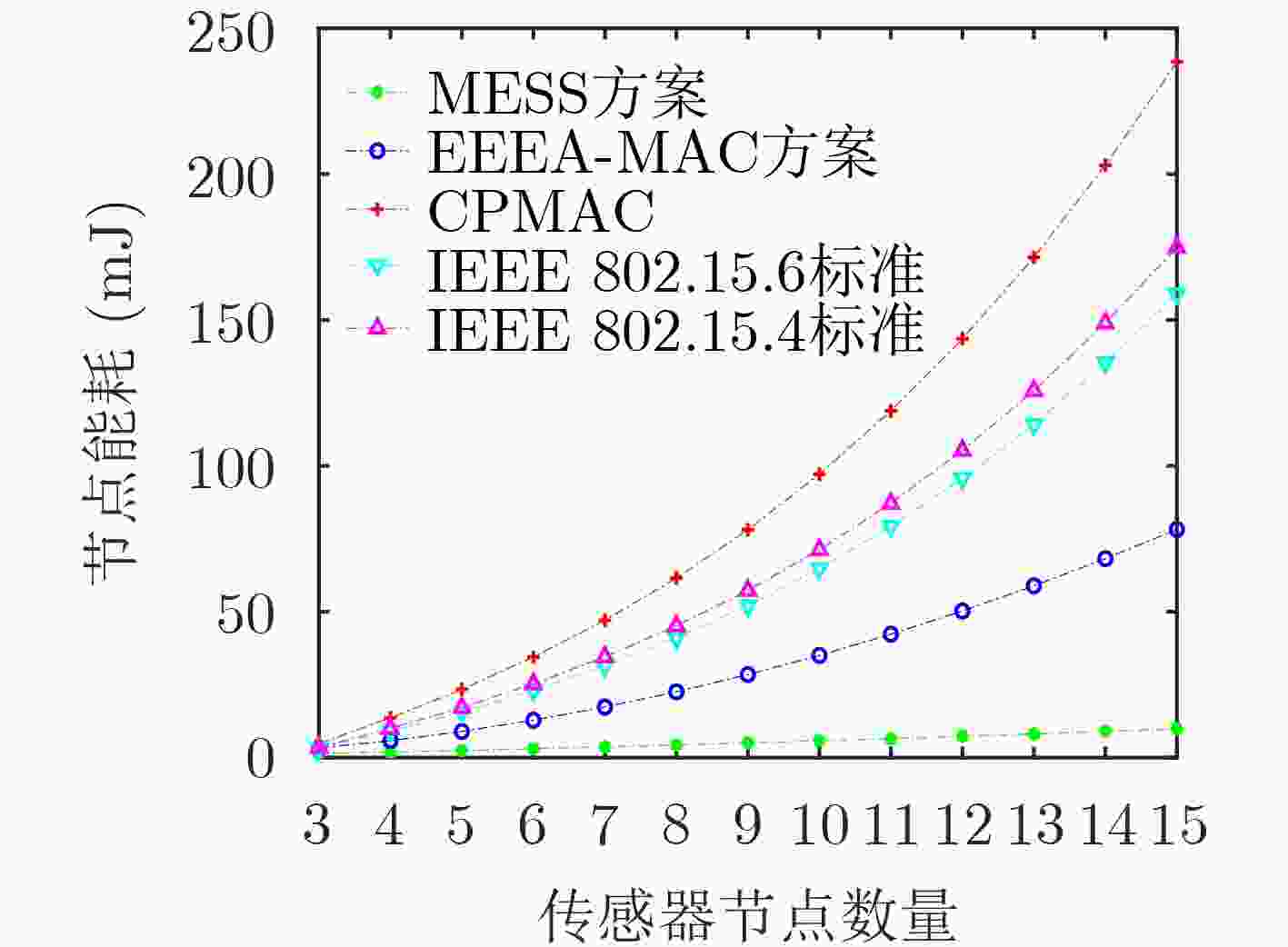
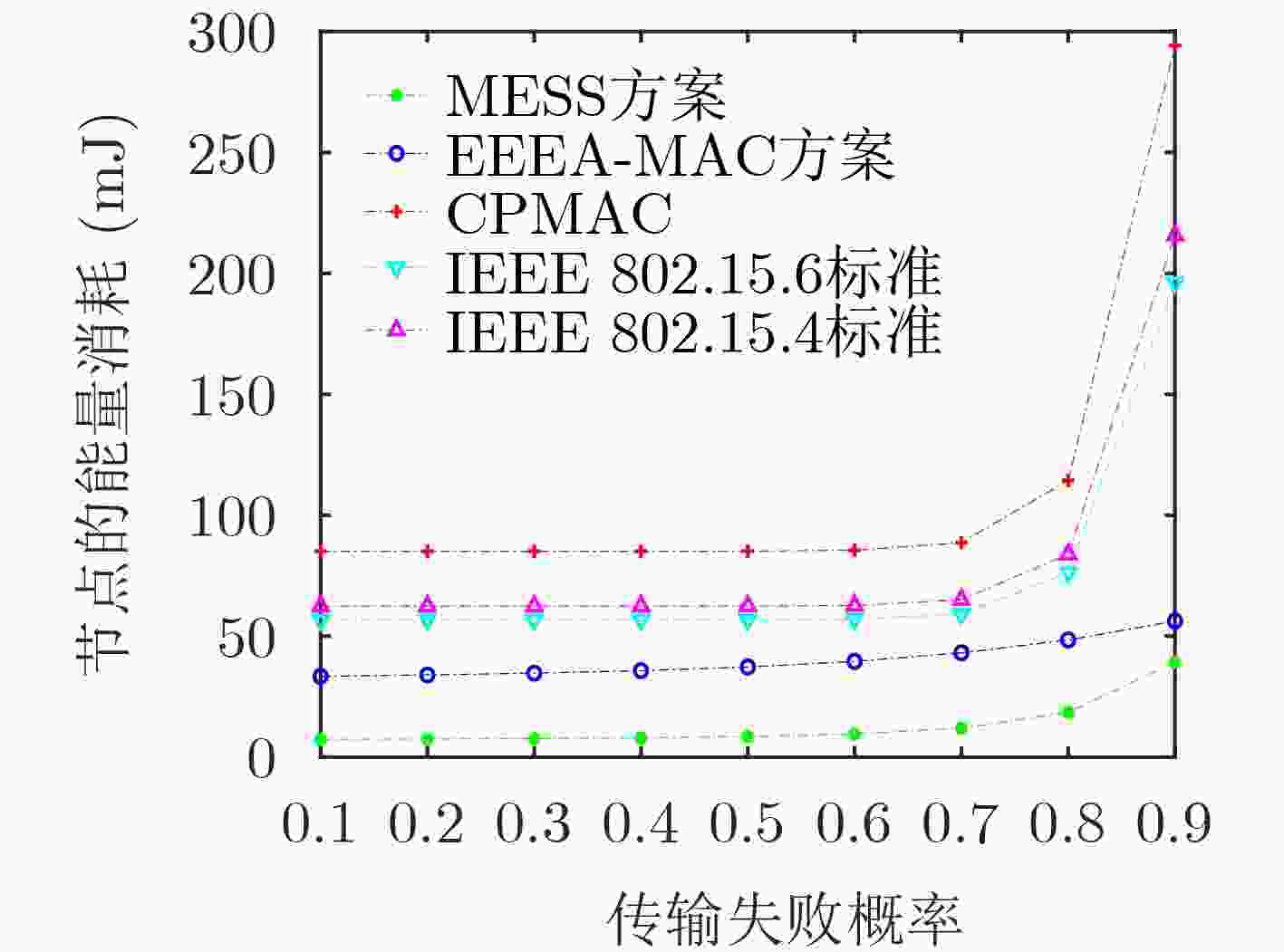


 下载:
下载:
