Channel Estimation of IRS-OTFS Communication System with Meta-learning Algorithm
-
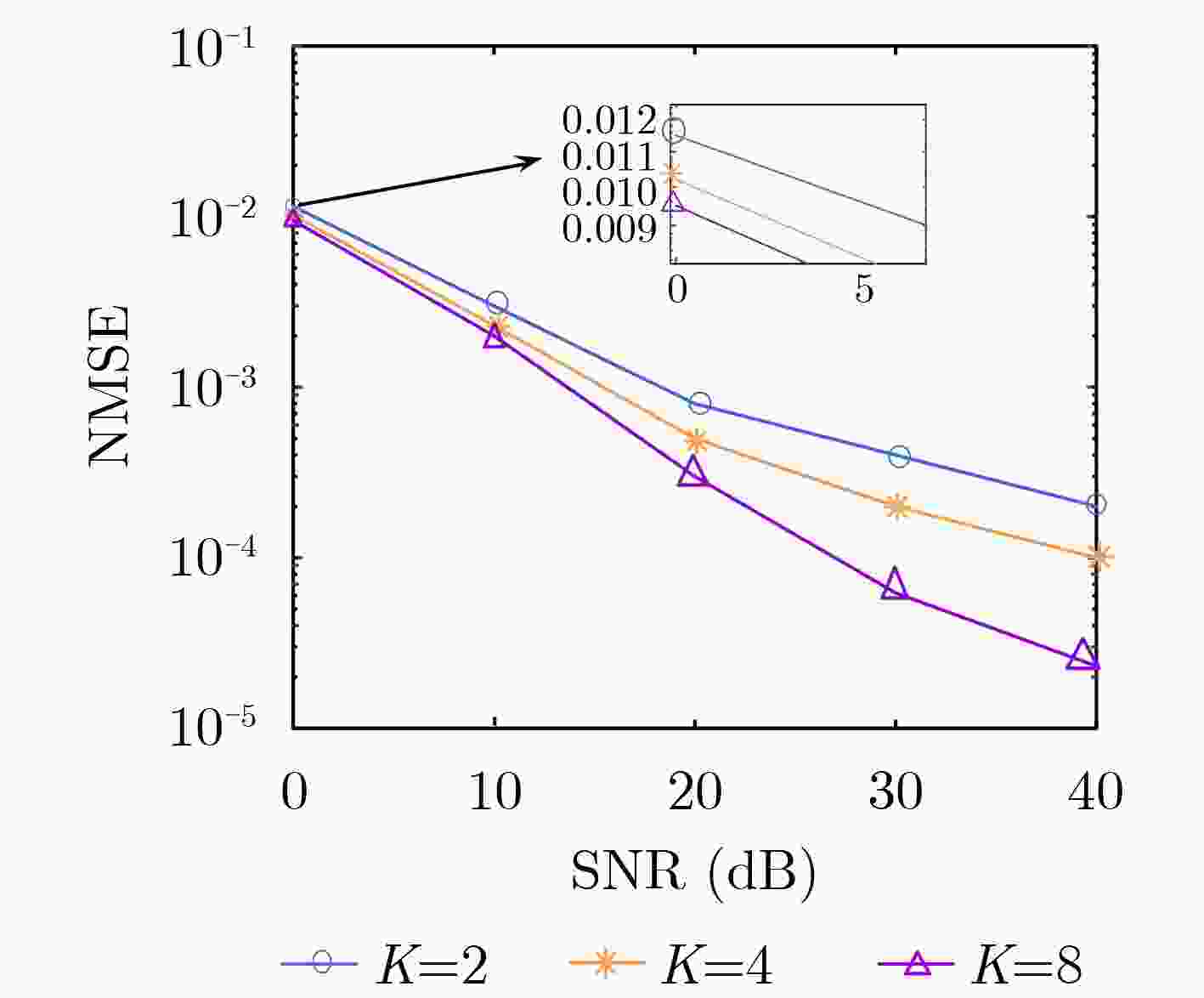
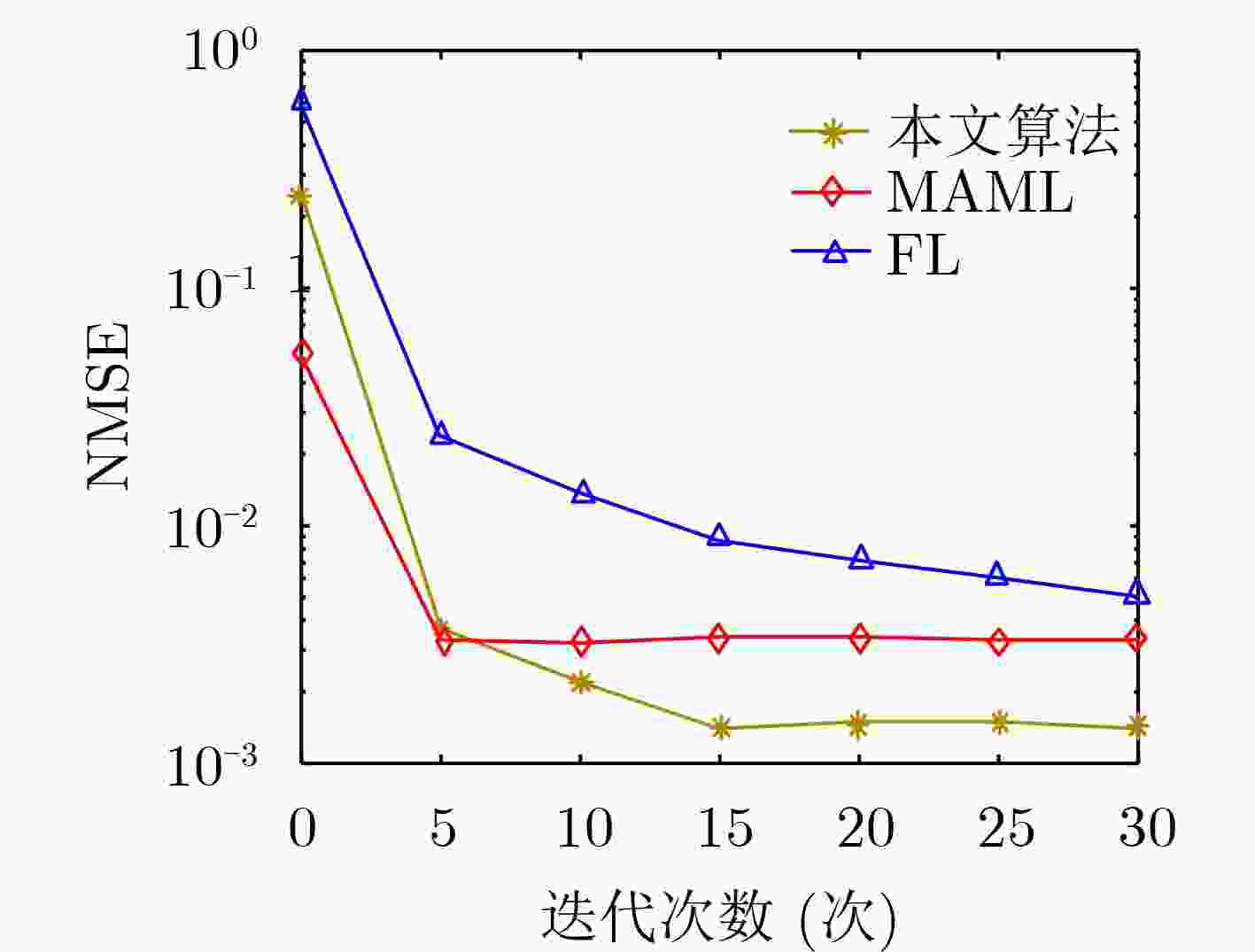
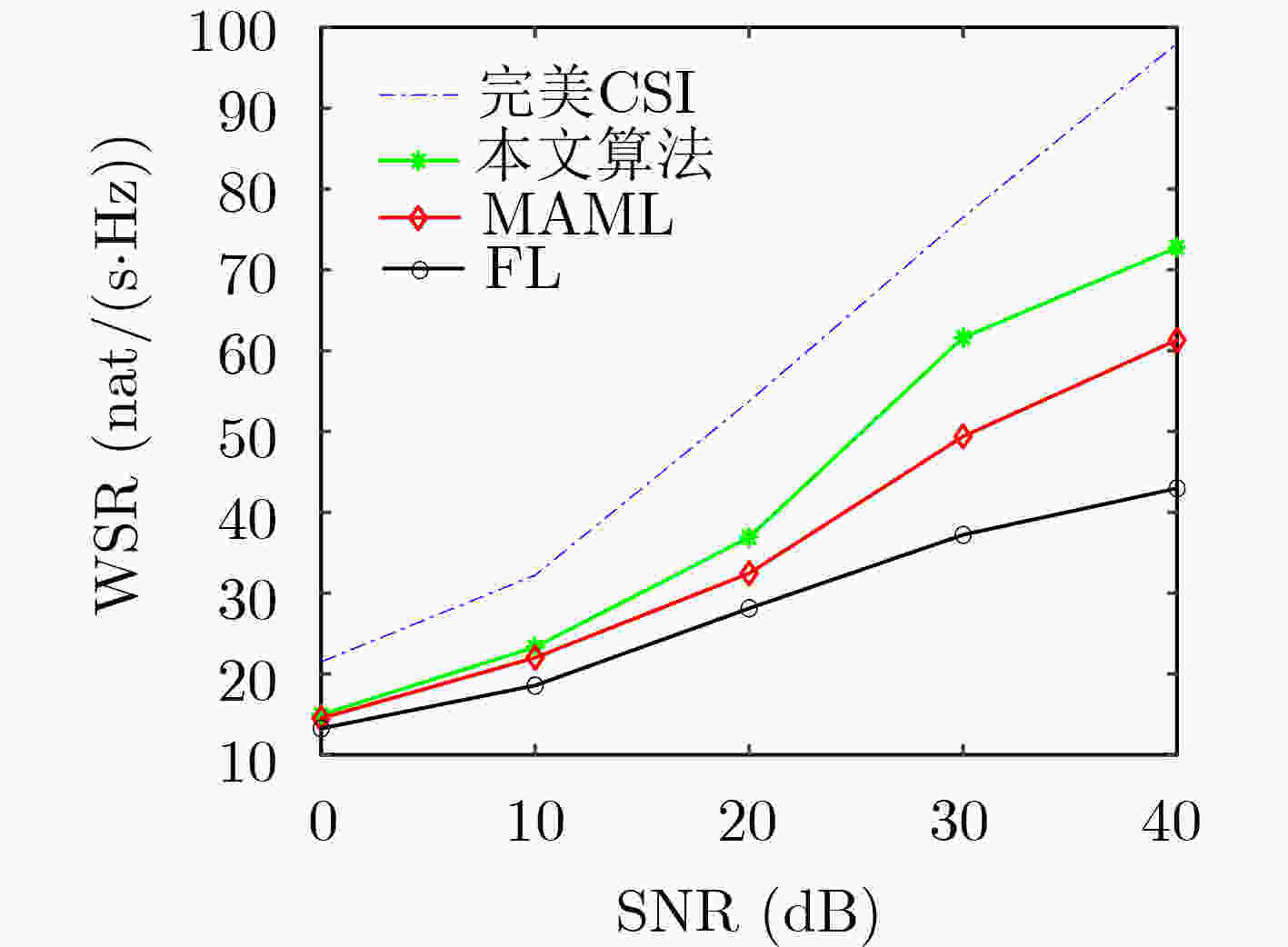
摘要: 针对高多普勒场景下智能反射表面(IRS)辅助多用户通信系统存在的信道估计传输开销大的问题,该文结合正交时频空间(OTFS)调制特点构造一种IRS-OTFS通信系统,充分发挥IRS和OTFS的性能优势,并在此基础上提出一种学习率自适应的模型无关元学习(MAML)算法。对IRS-OTFS多用户信道估计任务做离线训练,根据各任务的收敛速度自适应地调整学习率,防止训练失衡,并利用信道之间的相关性和MAML算法的少样本、泛化特性得到全局模型和适应性模型,快速学习新用户信道的传输特性,降低传输开销,提高信道估计准确性。理论分析和仿真结果表明,该算法在信道传输条件相同的情况下,将传输开销降低了大约50%,并相对于基准算法有4.8 dB左右的性能提升。Abstract: Focusing on the problem of large channel estimation transmission overhead in Intelligent Reflective Surface IRS) assisted multi-user communication system in high Doppler scenario, an IRS-OTFS communication system is constructed based on the characteristics of Orthogonal Time-Frequency Space (OTFS) modulation, which gives full play to the performance advantages of IRS and OTFS, and on this basis, a Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning (MAML) algorithm with adaptive learning rate is proposed. The IRS-OTFS multi-user channel estimation task is trained offline, the learning rate is adaptively adjusted according to the convergence speed of each task to prevent training imbalance, and the correlation between channels and the few samples and generalization characteristics of MAML algorithm are used to obtain global models and adaptive models, so as to quickly learn the transmission characteristics of new user channels, reduce transmission overhead, and improve the accuracy of channel estimation. Theoretical analysis and simulation results show that the algorithm reduces the transmission overhead by about 50% under the same channel transmission conditions, and has a performance improvement of about 4.8 dB compared with the benchmark algorithm.
-
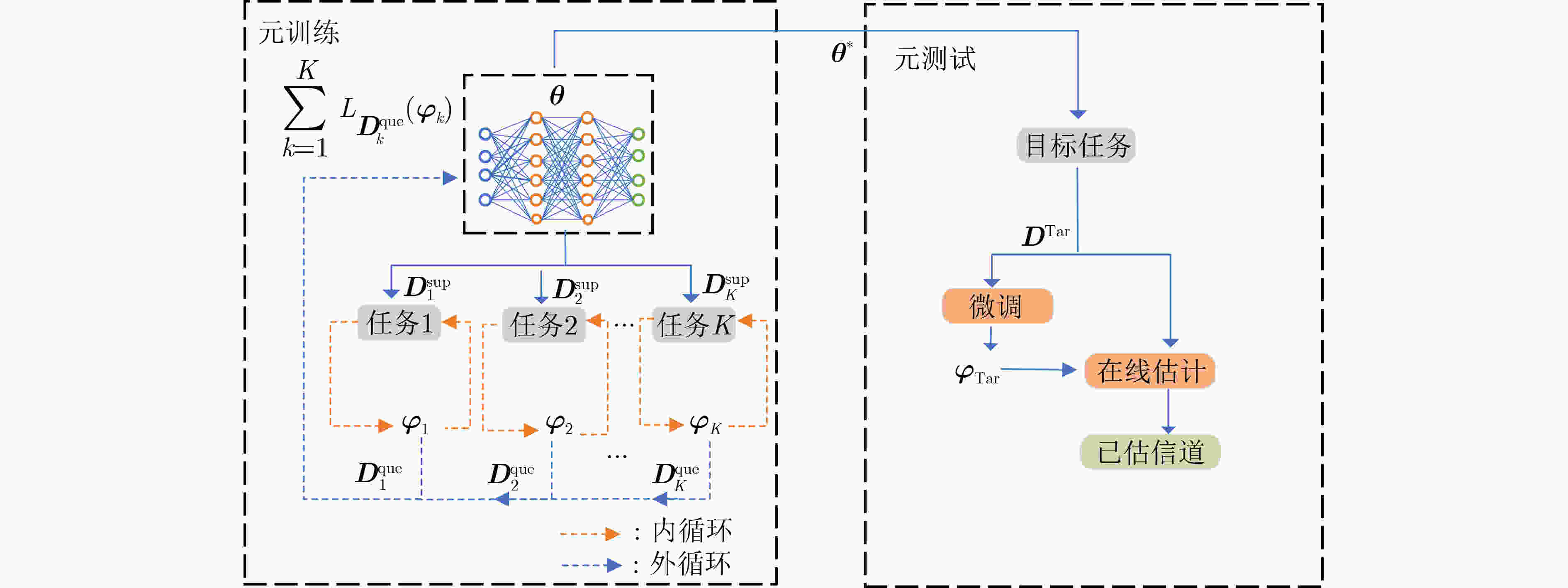
1 学习率自适应的MAML算法信道估计步骤
输入:多用户训练任务集(包括支持集$ {\boldsymbol{D}}_k^{{\mathrm{sup}}} $和查询集$ {\boldsymbol{D}}_k^{{\mathrm{que}}} $),
$ {{\boldsymbol{D}}^{{\mathrm{sup}}}} = {\left\{ {{\boldsymbol{D}}_k^{{\mathrm{sup}}}} \right\}_{k = 1,2, \cdots ,K}} $, $ {{\boldsymbol{D}}^{{\mathrm{que}}}} = {\left\{ {{\boldsymbol{D}}_k^{{\mathrm{que}}}} \right\}_{k = 1,2, \cdots ,K}} $;目标
用户数据集$ {{\boldsymbol{D}}^{\mathrm{Tar}}} $,学习率参数$ \alpha (0) $,$ \beta $,$ \gamma $元训练阶段: 1: for 迭代轮次$ t $ do 2: for 每个信道估计任务$ k $ do 3: 根据式(19)更新当前训练任务的内循环学习率$ {\alpha _k}(t) $ 4: 根据式(21)更新当前用户信道估计任务的适应性参数
$ {{\boldsymbol{\varphi}} _k}(t) $5: end for 6: 根据式(22)更新得到全局模型参数$ {{\boldsymbol{\theta}} ^*} $ 7: end for 针对新用户信道任务的微调阶段: 8: 初始化目标任务的模型参数为$ {{\boldsymbol{\theta}} ^*} $ 9: for 微调次数 do 10: 根据式(23)更新新用户的模型参数$ {{\boldsymbol{\varphi}} _{\mathrm{Tar}}} $ 11:end for 输出:全局模型参数$ {{\boldsymbol{\theta}} ^*} $;目标用户的适应性模型参数$ {{\boldsymbol{\varphi}} _{\mathrm{Tar}}} $ 表 1 仿真参数表
参数 值 载波频率(GHz) 28 BS端天线数 32 IRS无源反射元件数 32 批大小 20 内优化学习率 $ {10^{ - 3}} $ 外优化学习率 $ {10^{ - 4}} $ 卷积层数目 16 表 2 卷积层参数设置表
层数 $ {C^{(l)}} $ $ N_{{\mathrm{SF}}}^{(l)} $ $ W_x^{(l)} $ $ W_y^{(l)} $ conv1,onv9 2 32 3 3 conv2~conv7 32 32 3 3 conv10~conv15 32 32 3 3 conv8, onv16 32 2 3 3 -
[1] HAN Yu, TANG Wankai, JIN Shi, et al. Large intelligent surface-assisted wireless communication exploiting statistical CSI[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(8): 8238–8242. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2923997. [2] HUANG Chongwen, ZAPPONE A, ALEXANDROPOULOS G C, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for energy efficiency in wireless communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(8): 4157–4170. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2922609. [3] WU Qingqing, ZHANG Shuowen, ZHENG Beixiong, et al. Intelligent reflecting surface-aided wireless communications: A tutorial[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(5): 3313–3351. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3051897. [4] NIU Hehao, LIN Zhi, AN Kang, et al. Active RIS assisted rate-splitting multiple access network: Spectral and energy efficiency tradeoff[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2023, 41(5): 1452–1467. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2023.3240718. [5] LIN Zhi, NIU Hehao, AN Kang, et al. Refracting RIS-aided hybrid satellite-terrestrial relay networks: Joint beamforming design and optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(4): 3717–3724. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2022.3155711. [6] ASIF M, IHSAN A, KHAN W U, et al. Energy-efficient beamforming and resource optimization for STAR-IRS enabled hybrid-NOMA 6G communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, 2023, 7(3): 1356–1368. doi: 10.1109/TGCN.2023.3281414. [7] WANG Peilan, FANG Jun, YUAN Xiaojun, et al. Intelligent reflecting surface-assisted millimeter wave communications: Joint active and passive precoding design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(12): 14960–14973. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3031657. [8] CAO Yashuai, LV Tiejun, and NI Wei. Intelligent reflecting surface aided multi-user mmWave communications for coverage enhancement[C]. IEEE 31st Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications, London, UK, 2020: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/PIMRC48278.2020.9217160. [9] WANG Yong, LIN Zhi, NIU Hehao, et al. Secure satellite transmission with active reconfigurable intelligent surface[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2022, 26(12): 3029–3033. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2022.3207190. [10] HADANI R, RAKIB S, TSATSANIS M, et al. Orthogonal time frequency space modulation[C]. IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), San Francisco, USA, 2017: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/WCNC.2017.7925924. [11] HADANI R, RAKIB S, MOLISCH A F, et al. Orthogonal time frequency space (OTFS) modulation for millimeter-wave communications systems[C]. IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium (IMS), Honololu, USA, 2017: 681–683. doi: 10.1109/MWSYM.2017.8058662. [12] THOMAS A, DEKA K, SHARMA S, et al. IRS-assisted OTFS system: Design and analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(3): 3345–3358. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3217140. [13] 蒋占军, 刘庆达. 高速移动通信系统中OTFS信道估计算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(10): 2878–2885. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200683.JIANG Zhanjun and LIU Qingda. Study on OTFS channel estimation algorithms in high-speed mobile communication systems[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2021, 43(10): 2878–2885. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200683. [14] RAVITEJA P, HONG Yi, VITERBO E, et al. Practical pulse-shaping waveforms for reduced-cyclic-prefix OTFS[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(1): 957–961. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2878891. [15] GUNTURU A, GODALA A R, SAHOO A K, et al. Performance analysis of OTFS waveform for 5G NR mmWave communication system[C]. IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Nanjing, China, 2021: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/WCNC49053.2021.9417346. [16] WANG Zhaorui, LIU Liang, and CUI Shuguang. Channel estimation for intelligent reflecting surface assisted multiuser communications: Framework, algorithms, and analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(10): 6607–6620. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3004330. [17] LIU Chang, LIU Xuemeng, NG D W K, et al. Deep residual learning for channel estimation in intelligent reflecting surface-assisted multi-user communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(2): 898–912. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3100148. [18] ELBIR A M and COLERI S. Federated learning for channel estimation in conventional and RIS-assisted massive MIMO[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(6): 4255–4268. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3128392. [19] SINGH G, SRIVASTAVA A, and BOHARA V A. Visible light and reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for beyond 5G V2X communication networks at road intersections[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71(8): 8137–8151. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3174131. [20] MISHRA H B, SINGH P, PRASAD A K, et al. OTFS channel estimation and data detection designs with superimposed pilots[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(4): 2258–2274. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3110659. [21] RAVITEJA P, PHAN K T, and HONG Yi. Embedded pilot-aided channel estimation for OTFS in delay-Doppler channels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(5): 4906–4917. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2906357. [22] BAIK S, OH J, HONG S, et al. Learning to forget for meta-learning via task-and-layer-wise attenuation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(11): 7718–7730. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3102098. [23] LIU Shikun, JOHNS E, and DAVISON A J. End-to-end multi-task learning with attention[C]. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2019: 1871–1880. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00197. [24] PAN Cunhua, REN Hong, WANG Kezhi, et al. Multicell MIMO communications relying on intelligent reflecting surfaces[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(8): 5218–5233. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.2990766. -






 下载:
下载:

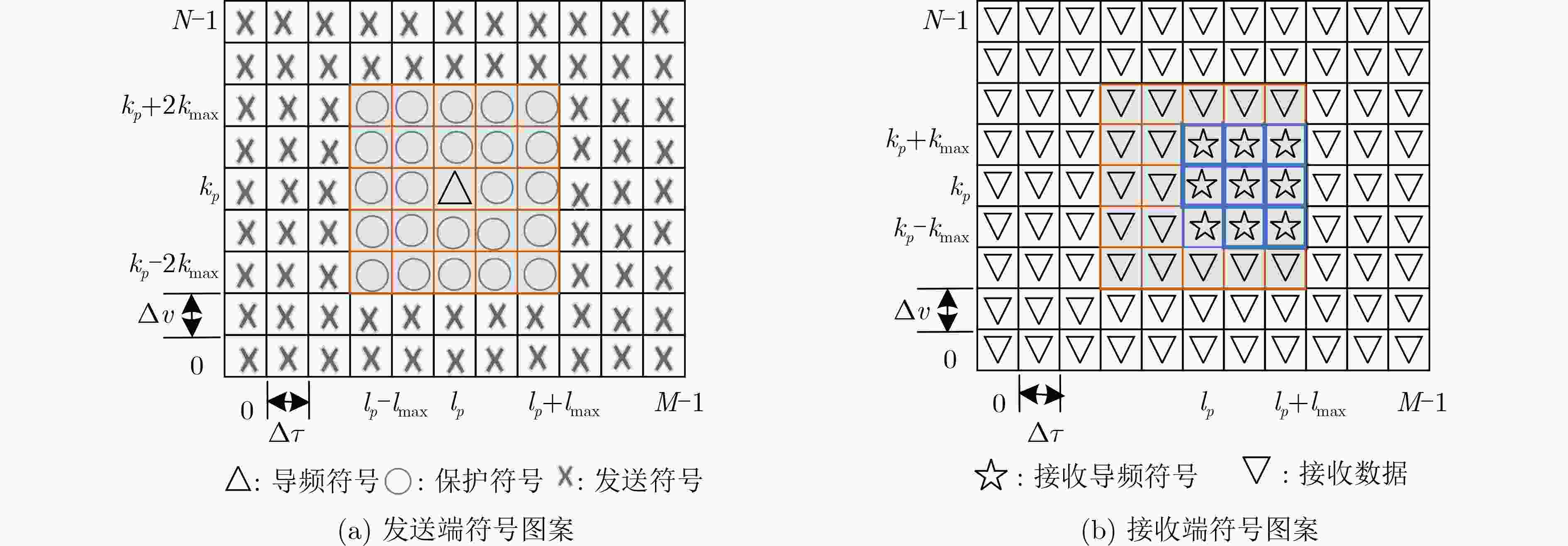
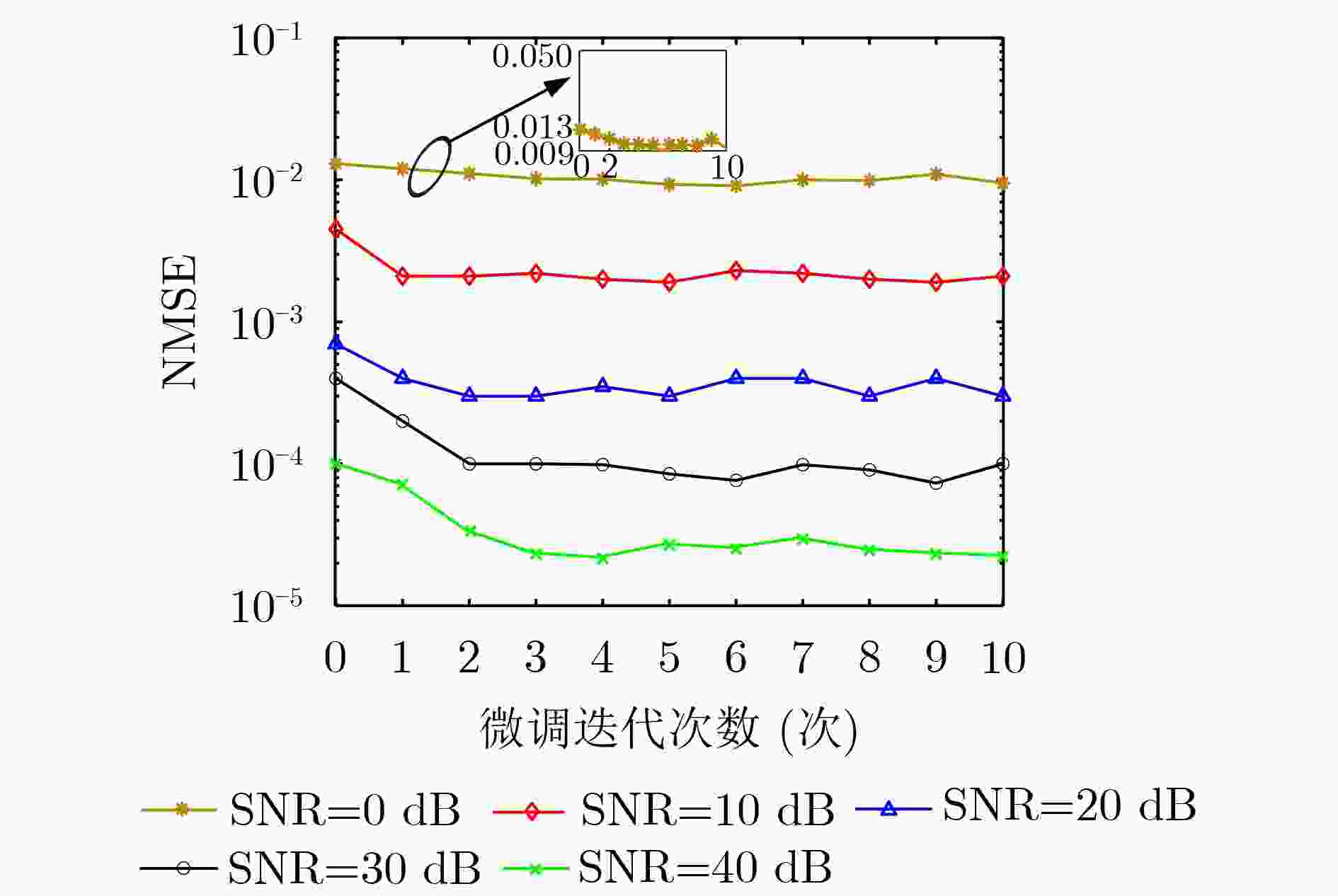
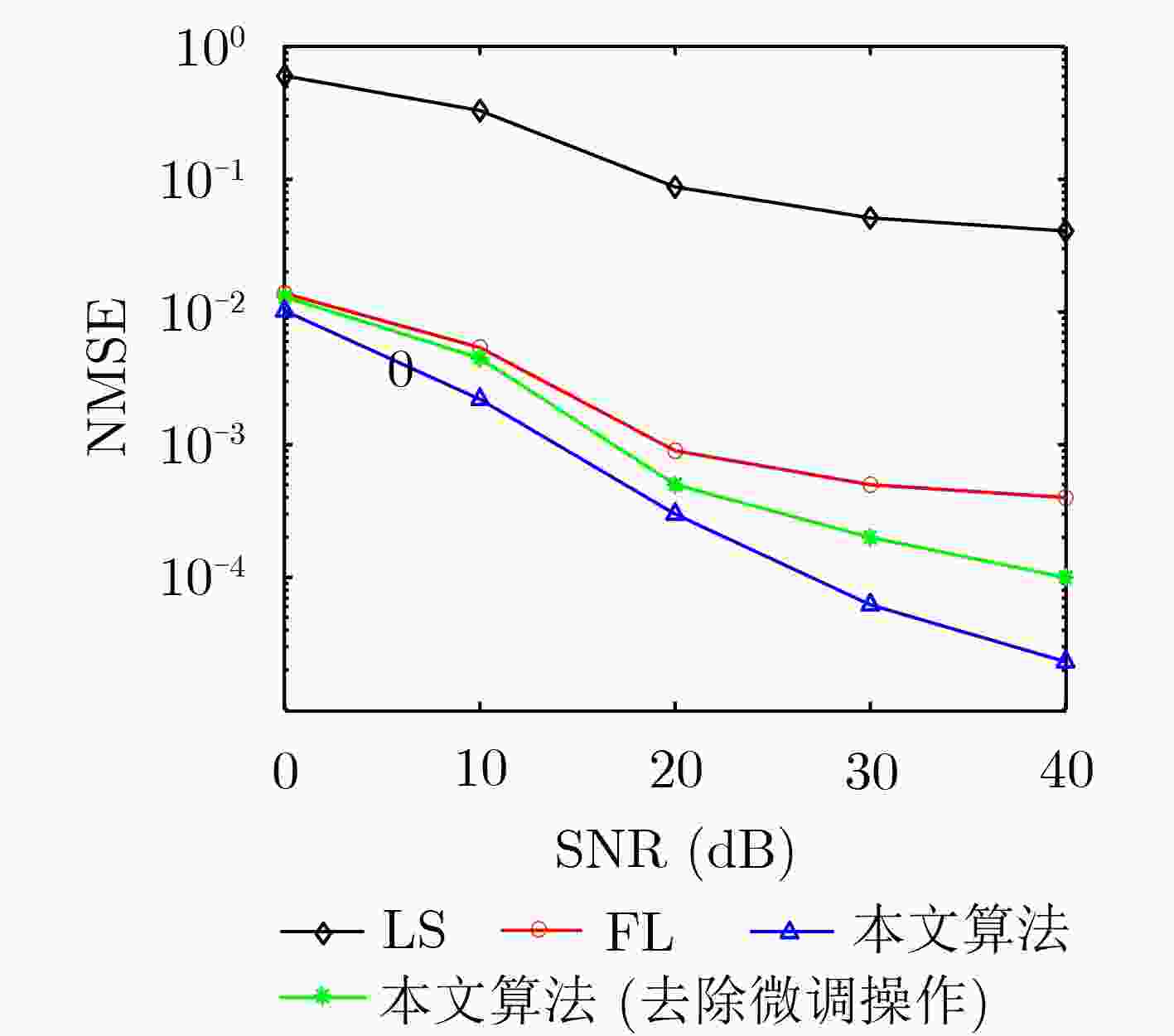


 下载:
下载:
