Improved Meet-in-the-middle Attacks on Reduced-round E2
-
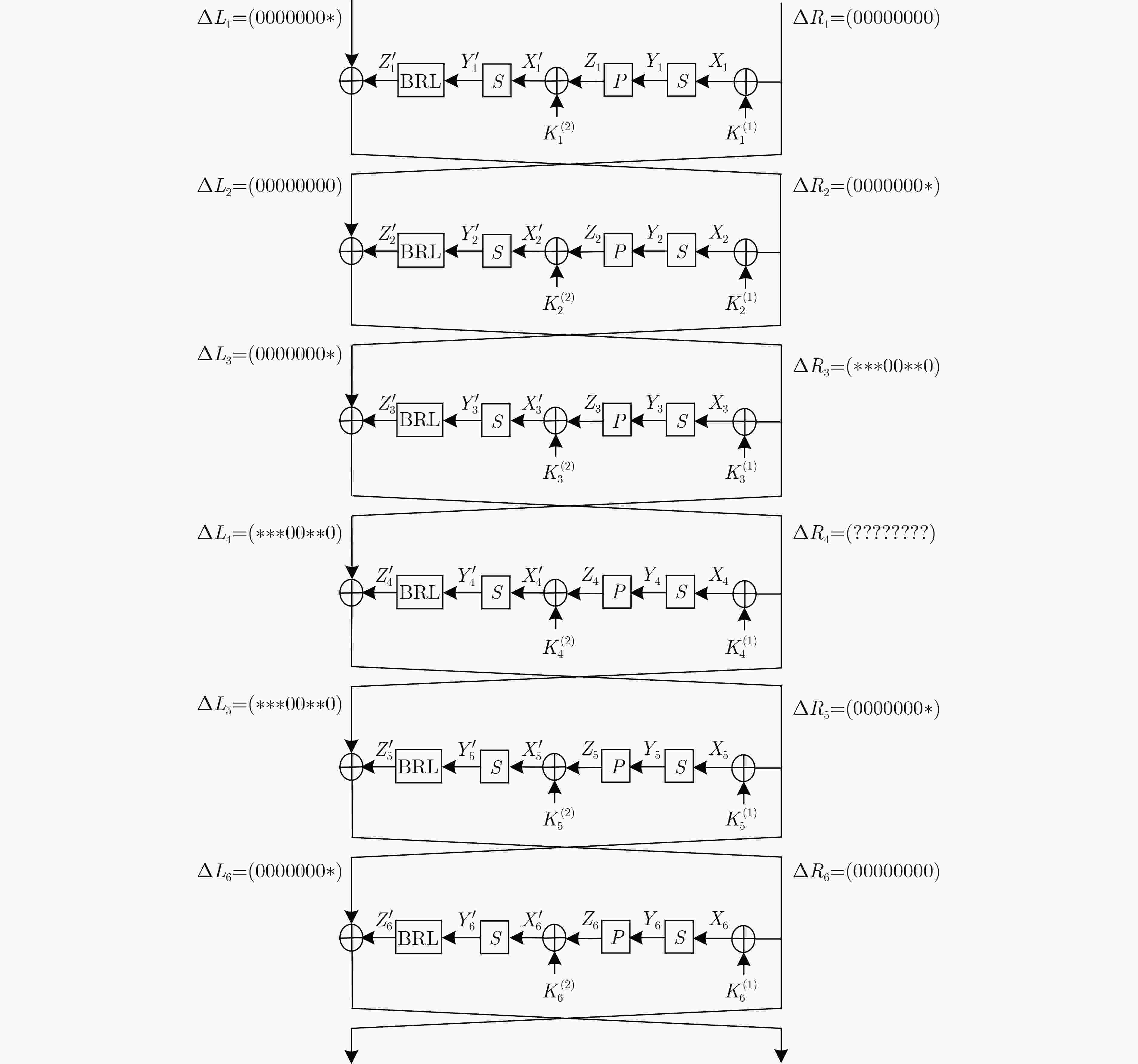
摘要: E2算法是AES首轮征集的15个候选算法之一,具有优良的软硬件实现效率和较强的安全性。该文利用多重集和差分枚举技术,对E2算法进行中间相遇攻击。首先以E2-128为例,改进了已有的4轮中间相遇区分器,将5轮密钥恢复攻击预计算复杂度降低为${2^{31}}$次5轮算法加密。其次针对E2-256,将所得区分器向后增加两轮,构造了6轮中间相遇区分器,并实现了9轮中间相遇攻击,攻击所需的数据复杂度为${2^{105}}$个选择明文,存储复杂度为${2^{200}}$ Byte,时间复杂度为${2^{205}}$次9轮算法加密。与现有对E2算法的安全性分析结果相比,该文实现了对E2-256最长轮数的攻击。Abstract: E2 is one of the 15 candidate algorithms in the first round of AES, which has the characteristics of excellent software and hardware implementation efficiency and strong security. The meet-in-the-middle attacks on E2 are carried out in this paper by using multiset tabulation technique and differential enumeration technique. First, E2-128 is taken as an example to improve the existing 4-round meet-in-the-middle distinguisher, and the pre-computation complexity of 5-round key recovery attack is reduced to ${2^{31}}$ 5-round encryptions. Second, for E2-256, a 6-round distinguisher is constructed from the new 4-round distinguisher by extending two rounds backward, and then a 9-round meet-in-the-middle attack is presented, whose data complexity is ${2^{105}}$ chosen plaintexts, memory complexity is ${2^{200}}$ Byte, and time complexity is ${2^{205}}$ 9-round encryptions. Compared with the existing security analysis results of E2, the scheme achieves the longest number of attack rounds for E2-256.
-
Key words:
- Block cipher /
- E2 /
- Meet-in-the-middle attack /
- Differential enumeration technique
-
表 1 E2算法攻击结果对比
来源 攻击方法 算法版本 轮数 时间复杂度 预计算复杂度 数据复杂度 文献[13] 截断差分 E2-128/E2-128 $ 7/8 $ – – ${2^{91}}/{2^{94}}$ 文献[14] 不可能差分 E2-128/E2-256 $ 7/8 $ ${2^{115.5}}/{2^{214}}$ – ${2^{120}}/{2^{121}}$ 文献[15] 中间相遇攻击 E2-128 5 ${2^{48}}$ ${2^{48}}$ $ 14 $ 本文 中间相遇攻击 E2-128 5 ${2^{47.9}}$ ${2^{31}}$ $ 12 $ 本文 中间相遇攻击 E2-256 9 ${2^{205}}$ ${2^{200.6}}$ ${2^{105}}$ -
[1] WU Wenling and ZHANG Lei. LBlock: A lightweight block cipher[C]. The 9th International Conference on Applied Cryptography and Network Security, Nerja, Spain, 2011: 327–344. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-21554-4_19. [2] GUPTA K C, PANDEY S K, and SAMANTA S. FUTURE: A lightweight block cipher using an optimal diffusion matrix[C]. The 13th International Conference on Cryptology in Africa, Fes, Morocco, 2022: 28–52. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-17433-9_2. [3] 杜小妮, 郑亚楠, 梁丽芳, 等. RAIN-128算法的中间相遇攻击[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(1): 327–334. doi: 10.11999/JEIT221593.DU Xiaoni, ZHENG Yanan, LIANG Lifang, et al. Meet-in-the-middle attack on RAIN-128[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(1): 327–334. doi: 10.11999/JEIT221593. [4] 李超, 孙兵, 李瑞林. 分组密码的攻击方法与实例分析[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010.LI Chao, SUN Bing, and LI Ruilin. Attack Method of Block Cipher and Case Analysis[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2010. [5] 蒋梓龙, 金晨辉. Saturnin算法的不可能差分分析[J]. 通信学报, 2022, 43(3): 53–62. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2022045.JIANG Zilong and JIN Chenhui. Impossible differential cryptanalysis of Saturnin algorithm[J]. Journal on Communications, 2022, 43(3): 53–62. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2022045. [6] DIFFIE W and HELLMAN M. Special feature exhaustive cryptanalysis of the NBS data encryption standard[J]. Computer, 1977, 10(6): 74–84. doi: 10.1109/C-M.1977.217750. [7] DUNKELMAN O, KELLER N, and SHAMIR A. Improved single-key attacks on 8-round AES-192 and AES-256[C]. The 16th International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security, Singapore, 2010: 158–176. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-17373-8_10. [8] SHI Danping, SUN Siwei, DERBEZ P, et al. Programming the Demirci-Selçuk meet-in-the-middle attack with constraints[C]. The 24th International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security, Brisbane, Australia, 2018: 3–34. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-03329-3_1. [9] 任炯炯, 侯泽洲, 李曼曼, 等. 改进的减轮MIBS-80密码的中间相遇攻击[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(8): 2914–2923. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210441.REN Jiongjiong, HOU Zezhou, LI Manman, et al. Improved meet-in-the-middle attacks on reduced-round MIBS-80 cipher[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(8): 2914–2923. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210441. [10] BIRYUKOV A, DERBEZ P, and PERRIN L. Differential analysis and meet-in-the-middle attack against round-reduced TWINE[C]. The 22nd International Workshop on Fast Software Encryption, Istanbul, Turkey, 2015: 3–27. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-48116-5_1. [11] LI Manman and CHEN Shaozhen. Improved meet-in-the-middle attacks on reduced-round Joltik-BC[J]. IET Information Security, 2021, 15(3): 247–255. doi: 10.1049/ise2.12019. [12] KANDA M, MORIAI S, AOKI K, et al. E2-a new 128-bit block cipher[J]. IEICE Transactions on Fundamentals of Electronics, Communications and Computer Sciences, 2000, E83-A(1): 48–59. [13] MORIAI S, SUGITA M, AOKI K, et al. Security of E2 against truncated differential cryptanalysis[C]. The 6th International Conference on Selected Areas in Cryptography, Ontario, Canada, 2000: 106–117. doi: 10.1007/3-540-46513-8_8. [14] WEI Yuechuan, YANG Xiaoyuan, LI Chao, et al. Impossible differential cryptanalysis on tweaked E2[C]. The 6th International Conference on Network and System Security, Wuyishan, China, 2012: 392–404. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-34601-9_30. [15] 官翔, 魏悦川, 杨晓元. E2算法的中间相遇攻击[J]. 计算机工程与科学, 2015, 37(3): 524–528. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-130X.2015.03.019.GUAN Xiang, WEI Yuechuan, and YANG Xiaoyuan. Meet-in-the-middle attacks on E2[J]. Computer Engineering & Science, 2015, 37(3): 524–528. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-130X.2015.03.019. [16] 任炯炯, 陈少真. 11轮3D密码算法的中间相遇攻击[J]. 通信学报, 2015, 36(8): 182–191. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2015131.REN Jiongjiong and CHEN Shaozhen. Meet-in-the-middle attack on 11-round 3D cipher[J]. Journal on Communications, 2015, 36(8): 182–191. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2015131. -






 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:
