Design of Low Offset Temperature Compensation Interface Circuit Based on Magnetic Sensor
-
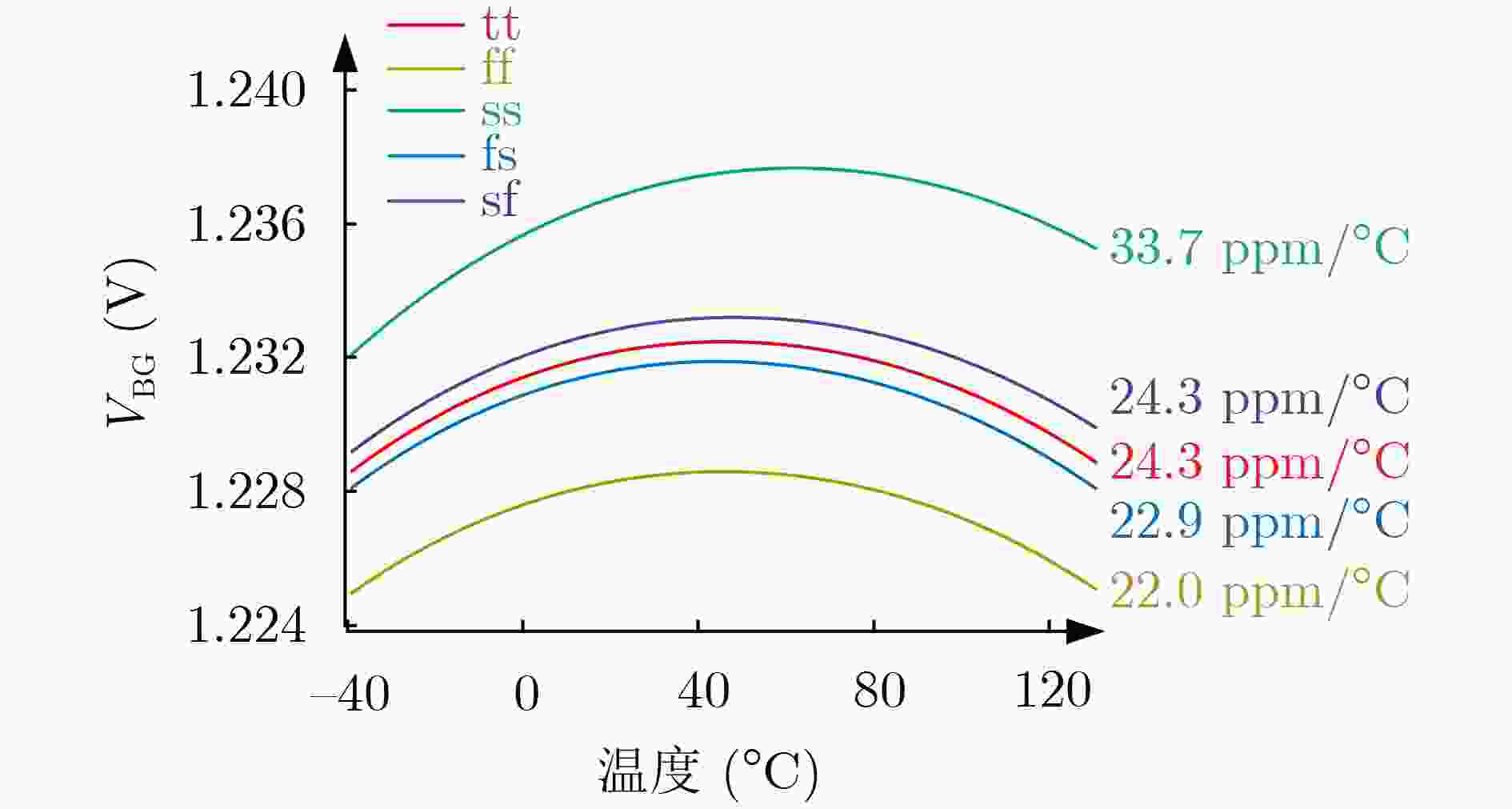
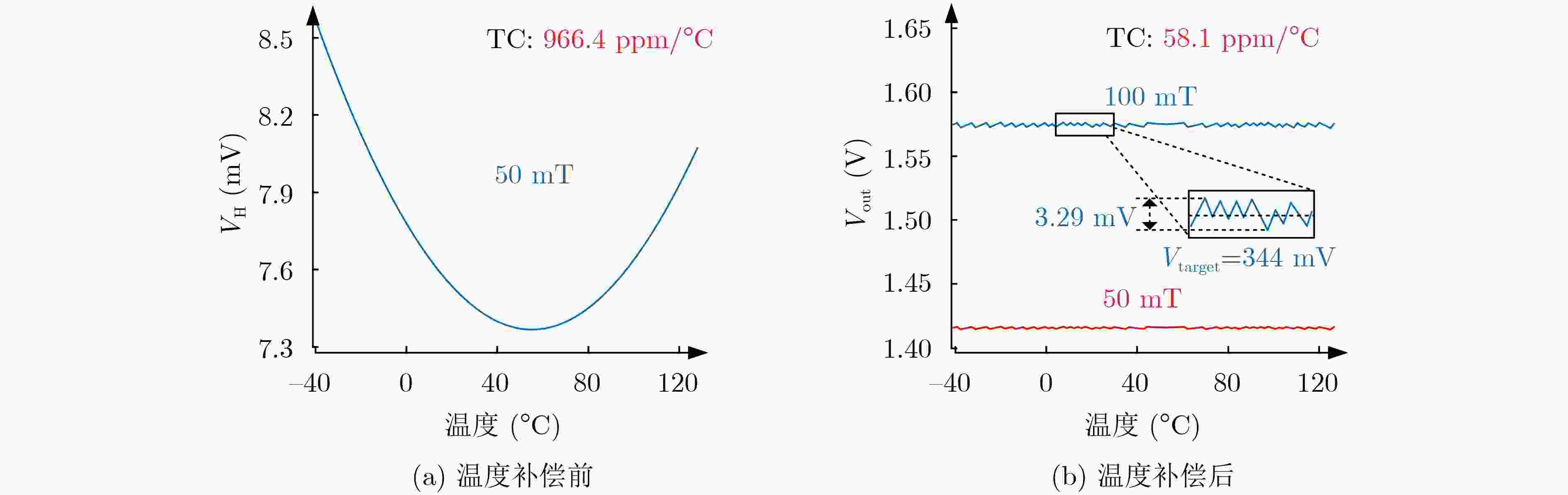
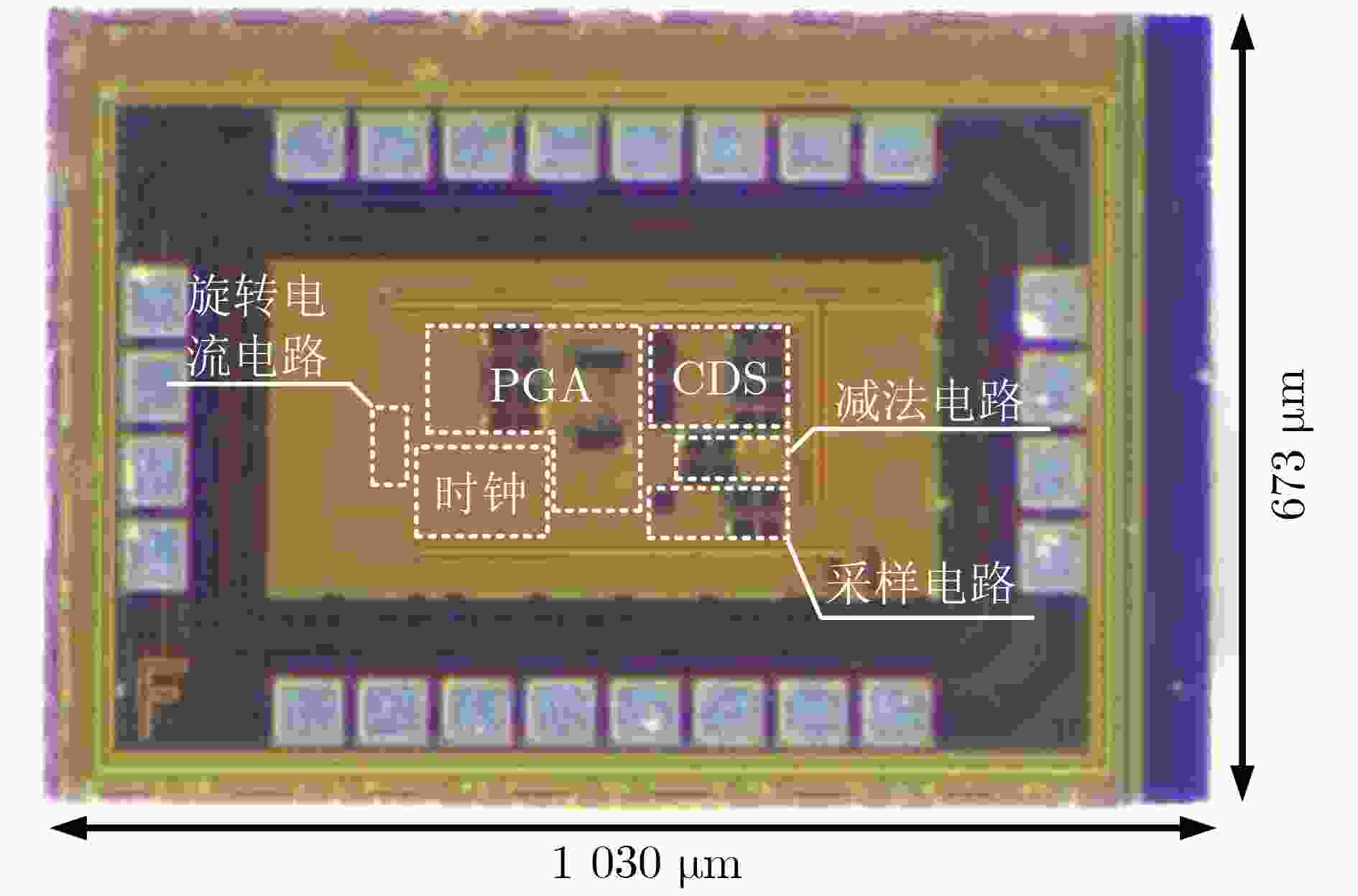
摘要: 面向磁性传感器在物联网(IoT)技术中的广泛应用,该文基于180 nm CMOS工艺设计了一种具有低失调电压,低温度漂移特性的霍尔传感器接口电路。针对霍尔传感器灵敏度的温度漂移特性,该文设计了一种感温电路并与查表法相结合,调节可编程增益放大器 (PGA) 的增益有效地降低了霍尔传感器的温度系数 (TC)。在此基础上,通过在信号主通路中使用相关双采样 (CDS) 技术,极大程度上消除了霍尔传感器的失调电压。仿真结果表明,在–40°C~125°C温度范围内,霍尔传感器的TC从966.4 ppm/°C减小到了58.1 ppm/°C。信号主通路的流片结果表明,霍尔传感器的失调电压从25 mV左右减小到了4 mV左右,霍尔传感器的非线性误差为0.50%。芯片的总面积为0.69 mm2。Abstract: Considering the widespread application of magnetic sensors in the Internet of Things (IoT), a Hall sensor readout interface circuit with low offset voltage and low-temperature drift characteristics based on a 180 nm CMOS process is designed in this work. In response to the temperature drift characteristic of the Hall sensor sensitivity, a temperature sensing circuit that is combined with the table lookup method to adjust the gain of the Programmable Gain Amplifier (PGA) is designed, which effectively reduces the Temperature Coefficient (TC) of the Hall sensor. On this basis, the offset voltage of the Hall sensor is greatly eliminated by the use of Correlated Double Sampling (CDS) technology in the main signal channel. The simulation results show that the TC of the Hall sensor is decreased from 966.4 ppm/°C to 58.1 ppm/°C in the temperature range of –40°C~125°C. The chip measurement results of the main signal channel show that the offset voltage of the Hall sensor is reduced from about 25 mV to about 4 mV and the nonlinear error of the Hall sensor is 0.50%, which occupies an active area of 0.69 mm2.
-
Key words:
- Hall sensor /
- Readout interface circuit /
- Temperature compensation /
- Low offset voltage
-
表 1 各信号对温度的相应
温度范围 (°C) Vtemp范围(V) temp<7:0> VH (mV) 增益 –40~–39.21 1.792~1.806 1001 0110 4.76 31 –20.35~–18.79 1.968~1.982 1010 0011 4.35 35 –1.49~0.07 2.144~2.158 1010 1111 4.06 37 39.36~40.92 2.494~2.508 1100 1001 3.71 40 59.79~61.35 2.668~2.682 1101 0110 3.70 40 78.65~80.21 2.842~2.856 1110 0010 3.79 40 119.52~121.08 3.189~3.203 1111 1100 4.27 35 124.22~125 3.232~3.246 1111 1111 4.35 34 表 2 Voff的高低温测试结果(mV)
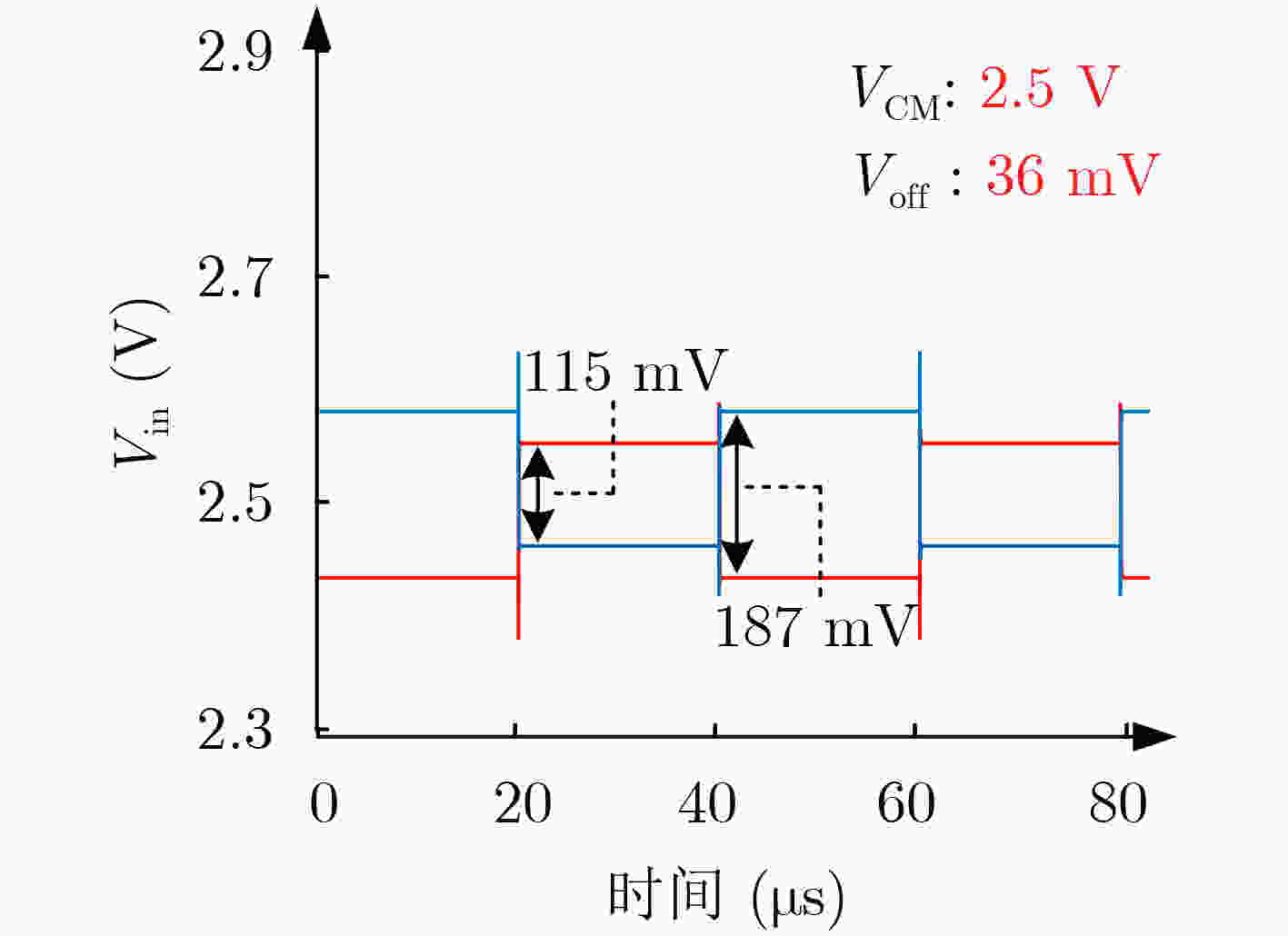
–40°C –20°C 0°C 20°C 40°C Voff1 49.59 42.21 33.05 21.94 11.75 Voff2 72.45 53.87 30.74 20.39 11.32 Voff3 69.15 50.92 33.75 23.05 12.26 表 3 CDS电路测试结果(mV)
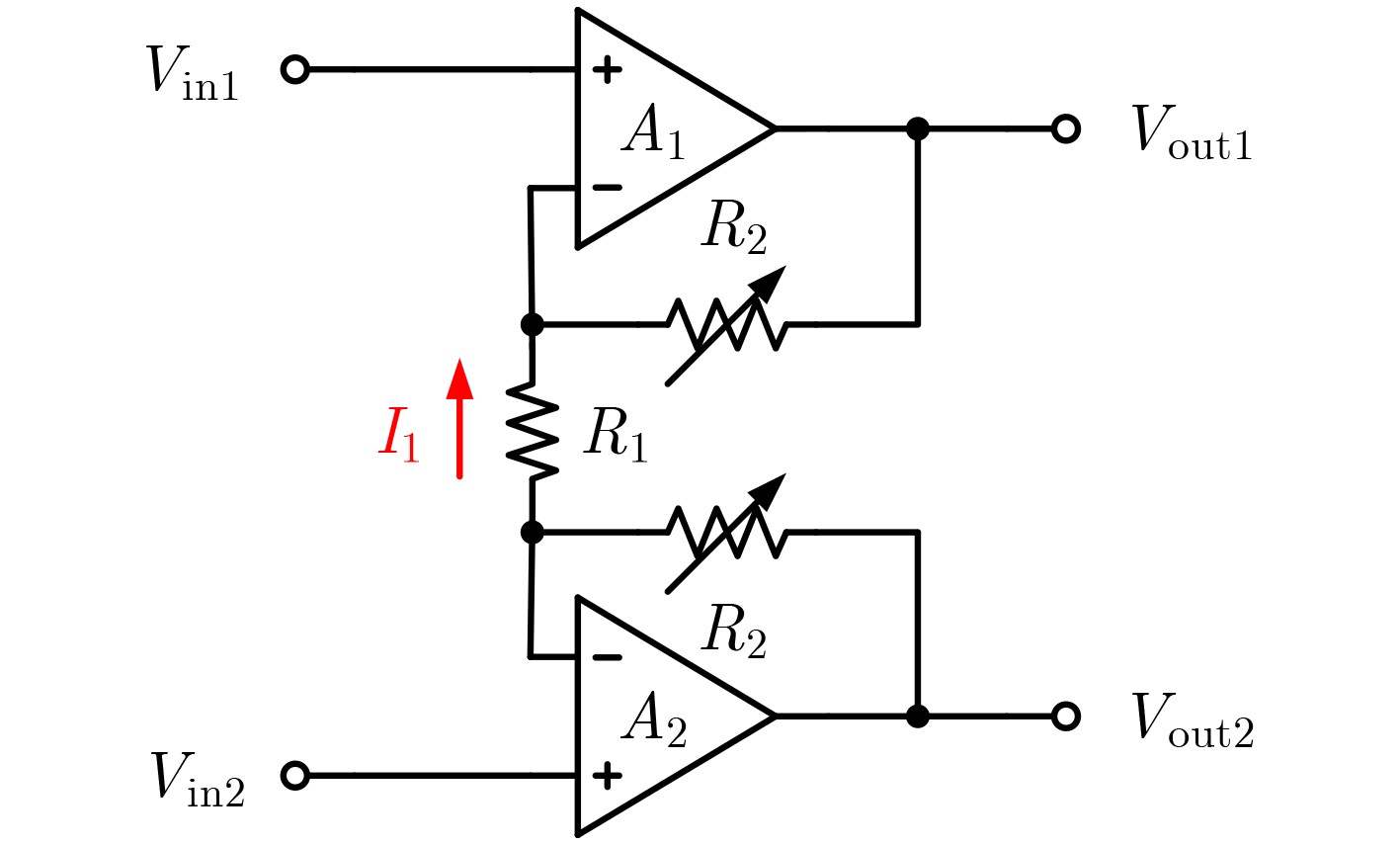
失调电压消除前 失调电压消除后 Voff1 24.9 4 Voff2 25.4 4 Voff3 24.2 2 -
[1] LOZANOVA S V and ROUMENIN C S. Silicon hall-effect multisensor[C]. 2020 XI National Conference with International Participation, Sofia, Bulgaria, 2020: 1–4. [2] CRESCENTINI M, SYEDA S F, and GIBIINO G P. Hall-effect current sensors: Principles of operation and implementation techniques[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(11): 10137–10151. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3119766. [3] DAS P T, NHALIL H, SCHULTZ M, et al. Detection of low-frequency magnetic fields down to sub-pT resolution with planar-hall effect sensors[J]. IEEE Sensors Letters, 2021, 5(1): 1500104. doi: 10.1109/LSENS.2020.3046632. [4] SPINELLI A S, MINOTTI P, LAGHI G, et al. Simple model for the performance of realistic AMR magnetic field sensors[C]. The 18th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems, Anchorage, AK, 2015: 2204–2207. [5] HADJIGEORGIOU N, HRISTOFOROU E, and SOTIRIADIS P P. Closed-loop current-feedback, signal-chopped, low noise AMR sensor with high linearity[C]. The 6th International Conference on Modern Circuits and Systems Technologies, Thessaloniki, Greece, 2017: 1–4. [6] YAN Shaohua, ZHOU Zitong, YANG Yaodi, et al. Developments and applications of tunneling magnetoresistance sensors[J]. Tsinghua Science and Technology, 2022, 27(3): 443–454. doi: 10.26599/TST.2021.9010061. [7] BHASKARRAO N K, ANOOP C S, and DUTTA P K. A novel linearizing signal conditioner for half-bridge-based TMR angle sensor[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(3): 3216–3224. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3023089. [8] XU Xiaopeng, LIU Tingzhang, ZHU Min, et al. New small-volume high-precision TMR busbar DC current sensor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2020, 56(2): 4000105. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2019.2953671. [9] FU Peiyuan and ZHENG Feng. A new GMR sensor based on gradient magnetic field detection for DC and wide-band current measurement[C]. 2022 IEEE Region 10 Symposium, Mumbai, India, 2022: 1–6. [10] STETCO E M, AUREL POP O, and GRAMA A. Simulation model of a GMR based current sensor[C]. 2020 IEEE 26th International Symposium for Design and Technology in Electronic Packaging, Pitesti, Romania, 2020: 17–20. [11] RIPKA P and JANOSEK M. Advances in magnetic field sensors[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2010, 10(6): 1108–1116. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2010.2043429. [12] HALL E H. On a new action of the magnet on electric currents[J]. The London,Edinburgh,and Dublin Philosophical Magazine and Journal of Science, 1880, 9(55): 225–230. doi: 10.1080/14786448008626828. [13] 蔚道嘉. 低噪声线性霍尔传感器的研究与设计[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2020.WEI Daojia. Research on and design of low noise linear hall sensor[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2020. [14] 胡杏杏. 电流模式的高灵敏度CMOS霍尔传感器研究与实现[D]. [硕士论文], 南京邮电大学, 2020.HU Xingxing. Research and implementation of high-sensitivity CMOS integrated hall sensor based on the current-mode[D]. [Master dissertation], Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2020. [15] LEI Kameng, MAK P I, and MARTINS R P. A 0.45-V 3.3-µW resistor-based temperature sensor achieving 10mK resolution in 65-nm CMOS[C]. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Integrated Circuits, Technologies and Applications, Zhuhai, China, 2021: 127–128. [16] WANG Bo, LAW M K, and BERMAK A. A BJT-Based CMOS Temperature Sensor Achieving an Inaccuracy of ± 0.45°C (3σ) from –50°C to 180°C and a resolution-FoM of 7.2 pJ. K2 at 150°C[C]. 2022 IEEE International Solid- State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2022: 72–74. [17] TANG Zhong, FANG Yun, YU Xiaopeng, et al. A 1-V diode-based temperature sensor with a resolution FoM of 3.1pJ·K2 in 55nm CMOS[C]. 2021 IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, Austin, USA, 2021: 1–2. [18] PAUN M A, SALLESE J M, and KAYAL M. Temperature considerations on Hall Effect sensors current-related sensitivity behaviour[C]. The 19th IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits, and Systems, Seville, Spain, 2012: 201–204. [19] CHEN Xiaoqing, XU Yue, XIE Xiaopeng, et al. A novel Hall dynamic offset cancellation circuit based on four-phase spinning current technique[C]. 2015 China Semiconductor Technology International Conference, Shanghai, China, 2015: 1–3. [20] KEIL M, JANSCHITZ J G, and MOTZ M. A Hall effect magnetic sensor with ratiometric output, utilizing a self-regulating chopped amplifier for compensation of offset, temperature and lifetime drift effects[C]. 2022 Austrochip Workshop on Microelectronics, Villach, Austria, 2022: 1–4. -






 下载:
下载:











 下载:
下载:
