Spread Spectrum and Conventional Modulation Signal Recognition Method Based on Generative Adversarial Network and Multi-modal Attention Mechanism
-
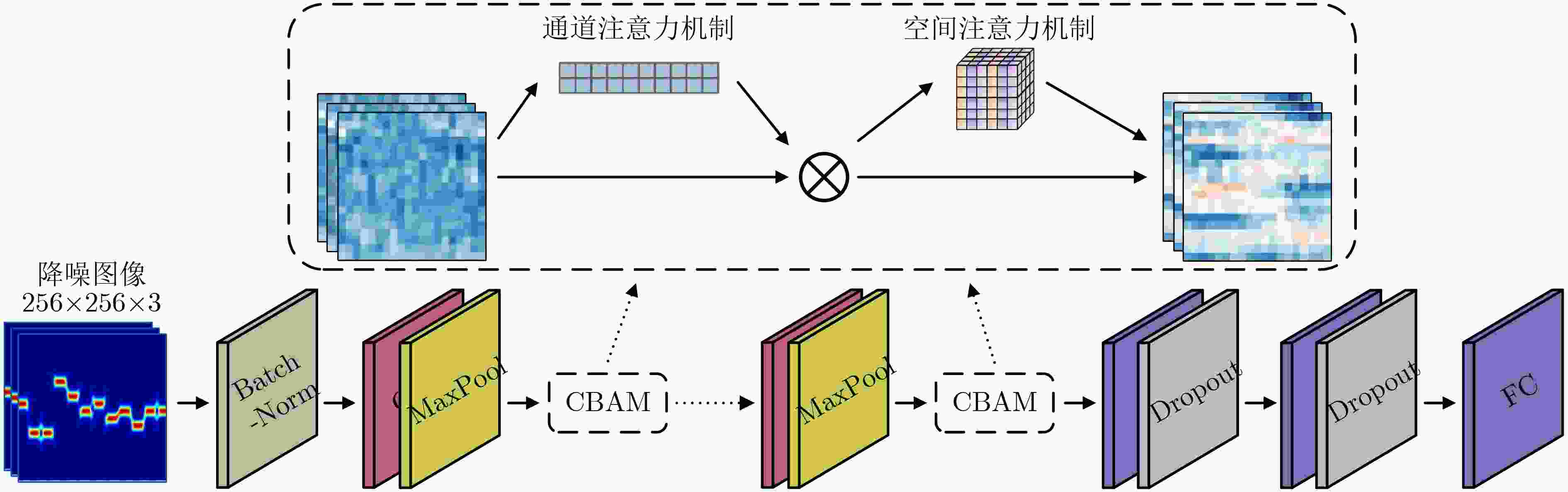
摘要: 针对低信噪比条件下的扩频与常规调制信号分类精度低的问题,该文提出一种基于生成式对抗网络(GAN)、卷积神经网络(CNN)和长短期记忆(LSTM)网络的多模态注意力机制信号调制识别方法。首先生成待识别信号的时频图像(TFIs),并利用GAN实现TFIs降噪处理;然后将信号的同相正交数据(I/Q data)与TFIs作为模型输入,并搭建基于CNN的TFIs识别支路和基于LSTM的I/Q数据识别支路;最后,在模型中添加注意力机制,增强I/Q数据和TFIs中重要特征对分类结果的决定作用。实验结果表明,该文所提方法相较于单模态识别模型以及其它基线模型,整体分类精度有效提升2%~7%,并在低信噪比条件下具备更强的特征表达能力和鲁棒性。
-
关键词:
- 深度学习 /
- 自动调制识别 /
- 生成对抗网络(GAN) /
- 多模态特征 /
- 时频分布
Abstract: Considering the low classification accuracy of spreading and conventional modulated signals under low signal-to-noise ratio conditions, a multimodal attention mechanism signal modulation recognition method based on Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) with Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) network is proposed. Firstly, the Time-Frequency Images (TFIs) of the to-be-recognized signals are generated and the noise reduction process of TFIs is realized by using GAN; Secondly, the In-phase and Quadrature data (I/Q data) of the signals with TFIs are used as model inputs, and the CNN-based TFIs recognition branch and the LSTM-based I/Q data recognition branch are built; Finally, an attentional mechanism is added to the model to enhance the role of important features in I/Q data and TFIs in the determination of classification results. The experimental results show that the proposed method effectively improves the overall classification accuracy by 2% to 7% compared with the unimodal recognition model and other baseline models, and possesses stronger feature expression capability and robustness under low signal-to-noise ratio conditions. -
图 9 SNR=–10 dB条件下,在文献[10]所提数据集上不同模型的分类精度
表 1 数据集相关参数
参数 数值 码元速率(kHz) 2 采样率(kHz) 160 载波频率(kHz) 40 采样点数 960 信号持续时间(ms) 12 TFIs像素(RGB) (256,256)×3 噪声环境 AWGN(–10:2:8 dB) FHSS频点(kHz) 26, 30, 34, 38, 42, 46, 50, 54 表 2 网络相关参数
参数 数值 学习率 0.001 GAN网络中卷积核大小 4×4 CNN-Attention层中卷积核大小 7×7, 5×5, 3×3 LSTM-Attention层中卷积核大小 7×1, 5×1, 3×1 LSTM单元数量 128 丢弃率 0.5 批次大小 32 优化器 Adam -
[1] WANG Yu, LIU Miao, YANG Jie, et al. Data-driven deep learning for automatic modulation recognition in cognitive radios[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(4): 4074–4077. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2900460. [2] MA Kai, ZHOU Yongbin, and CHEN Jianyun. CNN-based automatic modulation recognition of wireless signal[C]. 2020 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Information Systems and Computer Aided Education (ICISCAE), Dalian, China, 2020: 654–659. doi: 10.1109/ICISCAE51034.2020.9236934. [3] HUYNH-THE T, HUA C H, PHAM Q V, et al. MCNet: An efficient CNN architecture for robust automatic modulation classification[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2020, 24(4): 811–815. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2020.2968030. [4] QI Peihan, ZHOU Xiaoyu, ZHENG Shilian, et al. Automatic modulation classification based on deep residual networks with multimodal information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2021, 7(1): 21–33. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2020.3023145. [5] SANG Yujie and LI Li. Application of novel architectures for modulation recognition[C]. 2018 IEEE Asia Pacific Conference on Circuits and Systems (APCCAS), Chengdu, China, 2018: 159-162. doi: 10.1109/APCCAS.2018.8605691. [6] LIAO Kaisheng, ZHAO Yaodong, GU Jie, et al. Sequential convolutional recurrent neural networks for fast automatic modulation classification[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 27182–27188. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3053427. [7] 郭业才, 姚文强. 基于信噪比分类网络的调制信号分类识别算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(10): 3507–3515. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210825.GUO Yecai and YAO Wenqiang. Modulation signal classification and recognition algorithm based on signal to noise ratio classification network[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(10): 3507–3515. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210825. [8] LU Min, PENG Tianjun, YUE Guangxue, et al. Dual-channel hybrid neural network for modulation recognition[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 76260–76269. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3081617. [9] LIANG Zhi, TAO Mingliang, WANG Ling, et al. Automatic modulation recognition based on adaptive attention mechanism and ResNeXt WSL model[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2021, 25(9): 2953–2957. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2021.3093485. [10] 邵凯, 朱苗苗, 王光宇. 基于生成对抗与卷积神经网络的调制识别方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2022, 44(3): 1036–1043. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2022.03.37.SHAO Kai, ZHU Miaomiao, and WANG Guangyu. Modulation recognition method based on generative adversarial and convolutional neural network[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(3): 1036–1043. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2022.03.37. [11] 鲍杰. 扩频信号检测、分类与参数估计研究[D]. [硕士论文], 南京理工大学, 2016. doi: 10.7666/d.Y3044691.BAO Jie. Research on detection, classification and parameter estimation of spread spectrum signals[D]. [Master dissertation], Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2016. doi: 10.7666/d.Y3044691. [12] 占锦敏, 赵知劲. 常规调制信号与扩频信号的调制识别算法[J]. 信号处理, 2020, 36(4): 511–519. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2020.04.005.ZHAN Jinmin and ZHAO Zhijin. Modulation identification algorithm for conventional modulation signals and spread spectrum signals[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2020, 36(4): 511–519. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2020.04.005. [13] ZHANG Ming, DIAO Ming, and GUO Limin. Convolutional neural networks for automatic cognitive radio waveform recognition[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 11074–11082. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2716191. [14] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 2018: 3–19. [15] WEST N E and O'SHEA T. Deep architectures for modulation recognition[C]. 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Dynamic Spectrum Access Networks (DySPAN), Baltimore, MD, USA, 2017: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/DySPAN.2017.7920754. [16] 李红光, 郭英, 眭萍, 等. 基于时频特征的卷积神经网络跳频调制识别[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2020, 54(10): 1945–1954. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2020.10.011.LI Hongguang, GUO Ying, SUI Ping, et al. Frequency hopping modulation recognition of convolutional neural network based on time-frequency characteristics[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2020, 54(10): 1945–1954. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2020.10.011. -






 下载:
下载:










 下载:
下载:
