Elevation-Dependent Stochastic Localization Algorithm for GNSS-based Passive Radar
-
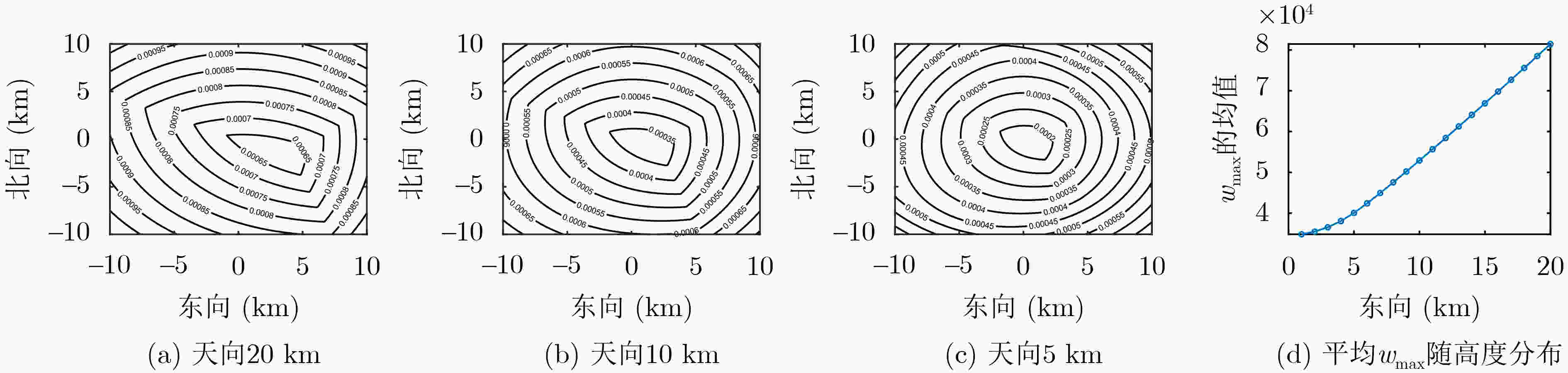
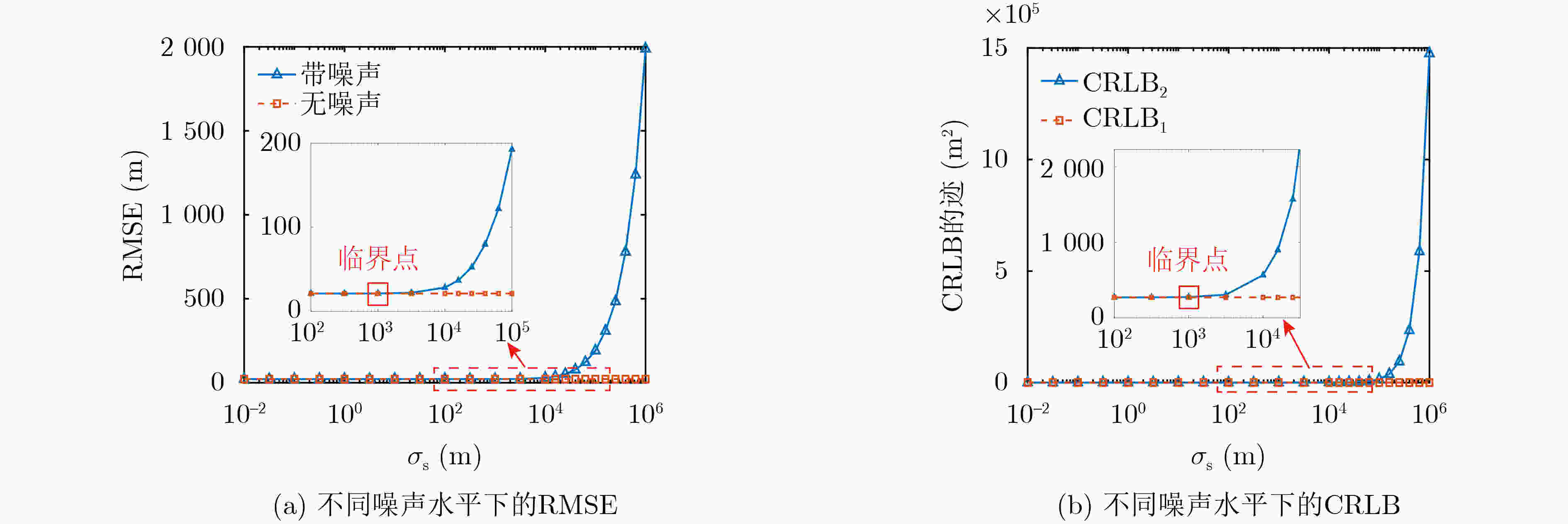
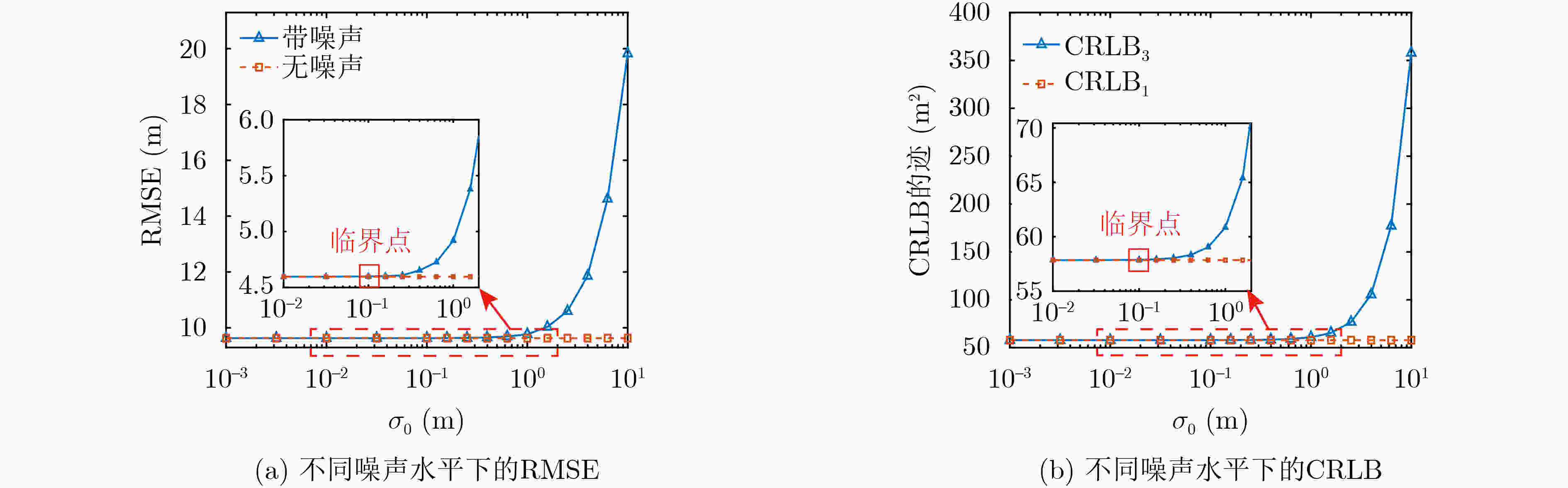
摘要: 针对GNSS外辐射源雷达定位时不同卫星对定位的误差贡献不同的问题,提出基于高度角随机模型的定位算法,理论分析目标位置估计量的克拉美罗界和统计特性,并计算卫星位置误差和地面站位置误差对定位误差的影响。仿真结果表明:所提出算法对不同GNSS卫星的直射、反射路径的伪距差测量值误差进行了合理分配,定位性能达到了克拉美罗界,且不会因为选星方案的改变而大幅恶化。对地面站位置误差和卫星位置误差的分析表明:地面站位置的标准差小于10 cm、卫星位置的标准差小于1 km时对定位总误差的贡献可以忽略不计。Abstract: An elevation-dependent stochastic localization algorithm is proposed to address the problem of different satellites contributing differently to the localization error in Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS)-based passive radar. Herein, the Cramer-Rao Lower Bound (CRLB) and statistical characteristics of the target position estimator are theoretically analyzed, and the contributions of satellite position and ground-station position errors to passive localization error are calculated. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can reasonably distribute the error from the pseudo-range measurements of multiple GNSS satellites with different directions and reflective paths. The localization performance reaches the CRLB but will not deteriorate considerably due to a change in the star selection scheme. Analysis of the ground-station position and satellite position errors show that their contributions to the total positioning error can be ignored if the standard deviation of the ground-station position is less than 10 cm and that of the satellite position is less than 1 km.
-
表 1 目标定位的仿真条件
编号 x(m) y(m) z(m) 高度角(°) 地面站 0 0 0 / 卫星1 2899814.62 18284781.58 12217268.81 60.91 卫星2 –17764738.34 15083494.90 27484289.18 71.13 卫星3 –10828315.49 20312609.37 –3037755.37 42.41 卫星4 –1449209.82 15222521.44 15431127.53 73.64 卫星5 –12017255.44 21647192.40 25857148.55 83.56 卫星6 –18426601.68 32494825.40 –3751263.00 44.14 卫星7 –14055816.53 –1406462.43 18392755.00 42.57 卫星8 –12585819.57 35077860.61 –4631158.40 42.44 卫星9 –2312759.23 22721092.71 28108988.86 71.93 卫星10 –32147920.16 20112722.76 –4037168.82 35.58 表 2 空中目标的位置
名称 空中目标 x(m) 166.12 y(m) –69.15 z(m) 67.10 表 3 目标定位算法对选星方案的敏感性
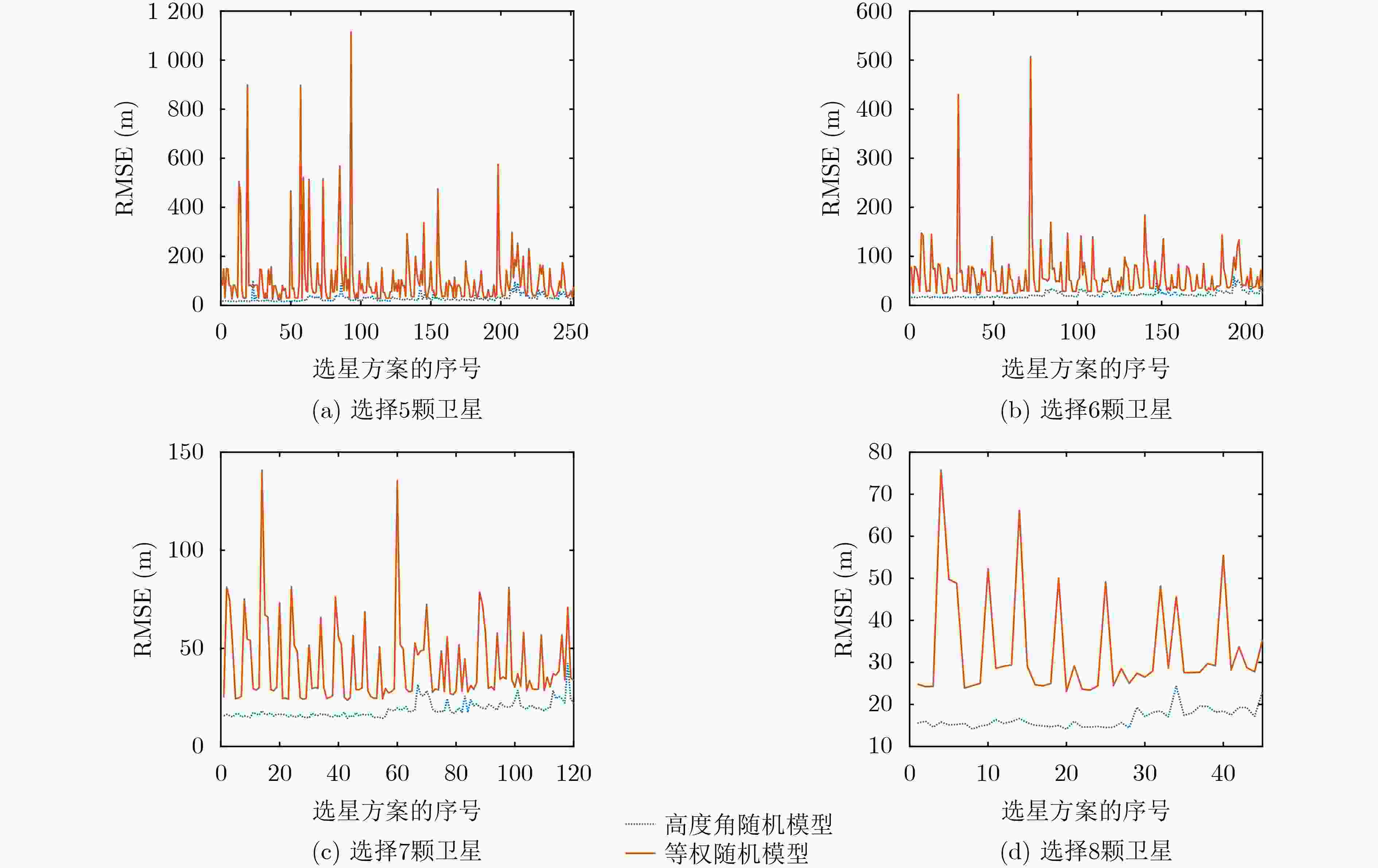
卫星数量 选星方案的总数 RMSE序列的标准差(m) RMSE序列的极差(m) 高度角随机模型 等权随机模型 高度角随机模型 等权随机模型 5 252 13.48 134.20 103.38 1025.10 6 210 6.89 52.74 44.85 495.38 7 120 3.96 20.83 26.36 119.24 8 45 2.24 12.47 9.23 52.37 -
[1] GRIFFITHS H D. From a different perspective: Principles, practice and potential of bistatic radar[C]. 2003 Proceedings of the International Conference on Radar, Adelaide, Australia, 2023: 1–7. [2] 王文钦, 陈慧, 郑植, 等. 频控阵雷达技术及其应用研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(2): 153–166. doi: 10.12000/JR18029.WANG Wenqin, CHEN Hui, ZHENG Zhi, et al. Advances on frequency diverse array radar and its applications[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(2): 153–166. doi: 10.12000/JR18029. [3] 李刚. 新体制雷达及其关键技术[J]. 电子技术与软件工程, 2019(15): 60–62.LI Gang. New system radar and its key technologies[J]. Electronic Technology &Software Engineering, 2019(15): 60–62. [4] 戴文瑞, 王锐, 魏巍. 基于5G基站信号的被动雷达无源定位方法分析[J]. 舰船电子工程, 2022, 42(3): 81–83,141. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9730.2022.03.018.DAI Wenrui, WANG Rui, and WEI Wei. Analysis of passive radar passive location method based on 5G base station signal[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2022, 42(3): 81–83,141. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9730.2022.03.018. [5] TIAN Minghui, WANG Yaqing, WANG Lu, et al. Experimental research on an FM broadcast based TNR passive radar system[C]. IET International Radar Conference (IET IRC 2020), 2020: 1330–1336. [6] MARTELLI T, CABRERA O, COLONE F, et al. Exploitation of long coherent integration times to improve drone detection in DVB-S based passive radar[C]. 2020 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf20), Florence, Italy, 2020: 1–6. [7] 苗铎, 杨东凯, 许志超, 等. GNSS外辐射源雷达低慢小目标探测概率[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2023, 49(3): 657–664. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2021.0271.MIAO Duo, YANG Dongkai, XU Zhichao, et al. Low-altitude, slow speed and small target detection probability of passive radar based on GNSS signals[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2023, 49(3): 657–664. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2021.0271. [8] MA Hui, ANTONIOU M, STOVE A G, et al. Maritime moving target localization using passive GNSS-based multistatic radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(8): 4808–4819. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2838682. [9] NASSO I and SANTI F. A centralized approach for ship target detection and localization with multi-transmitters GNSS-based passive radar[C]. International Conference on Radar Systems (RADAR 2022), Edinburgh, UK, 2022: 202–207. [10] 闫攀, 栗强强, 闫会峰. 基于北斗卫星外辐射源的目标直接定位算法[J]. 无线电工程, 2023, 53(2): 410–416. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2023.02.019.YAN Pan, LI Qiangqiang, and YAN Huifeng. Direct position determination of moving target using BeiDou satellite external illuminators[J]. Radio Engineering, 2023, 53(2): 410–416. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2023.02.019. [11] GRONOWSKI K, SAMCZYŃSKI P, STASIAK K, et al. First results of air target detection using single channel passive radar utilizing GPS illumination[C]. 2019 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Boston, USA, 2019: 1–6. [12] 边少锋, 刘一, 纪兵, 等. 北斗三号卫星观测信息高度角相关随机模型统计特性分析[J]. 武汉大学学报:信息科学版, 2022, 47(10): 1615–1624. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20220021.BIAN Shaofeng, LIU Yi, JI Bing, et al. Analysis of statistic testing of elevation-dependent stochastic models of BDS-3 satellite observation[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2022, 47(10): 1615–1624. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20220021. [13] LI Bofeng, LOU Lizhi, and SHEN Yunzhong. GNSS elevation-dependent stochastic modeling and its impacts on the statistic testing[J]. Journal of Surveying Engineering, 2016, 142(2): 04015012. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)SU.1943-5428.0000156. [14] 孙鹏. 几种随机模型对北斗定位精度影响研究[J]. 矿山测量, 2021, 49(3): 94–98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-358X.2021.03.019.SUN Peng. Study on the influence of several stochastic models on Beidou positioning accuracy[J]. Mine Surveying, 2021, 49(3): 94–98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-358X.2021.03.019. [15] AKHMEDOV D S and RASKALIYEV A S. Localization of an air target by means of GNSS-based multistatic radar[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2016, 1759(1): 020127. doi: 10.1063/1.4959741. [16] 刘琳. GNSS观测值精度估计及随机模型精化方法研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2019.LIU Lin. Research on method of GNSS observation precision estimation and stochastic model refinement[D]. [Master dissertation], Wuhan University, 2019. -





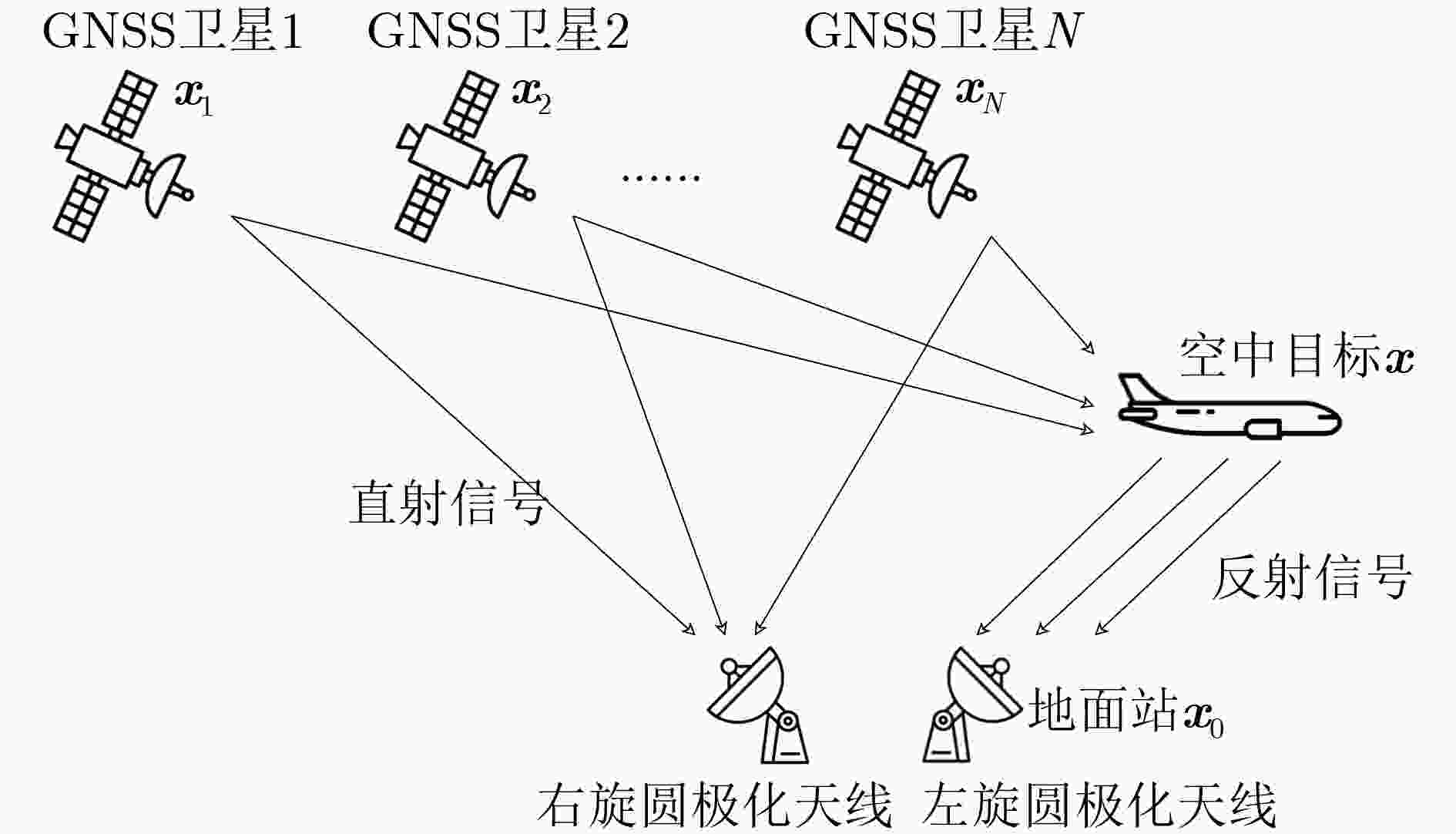
 下载:
下载:
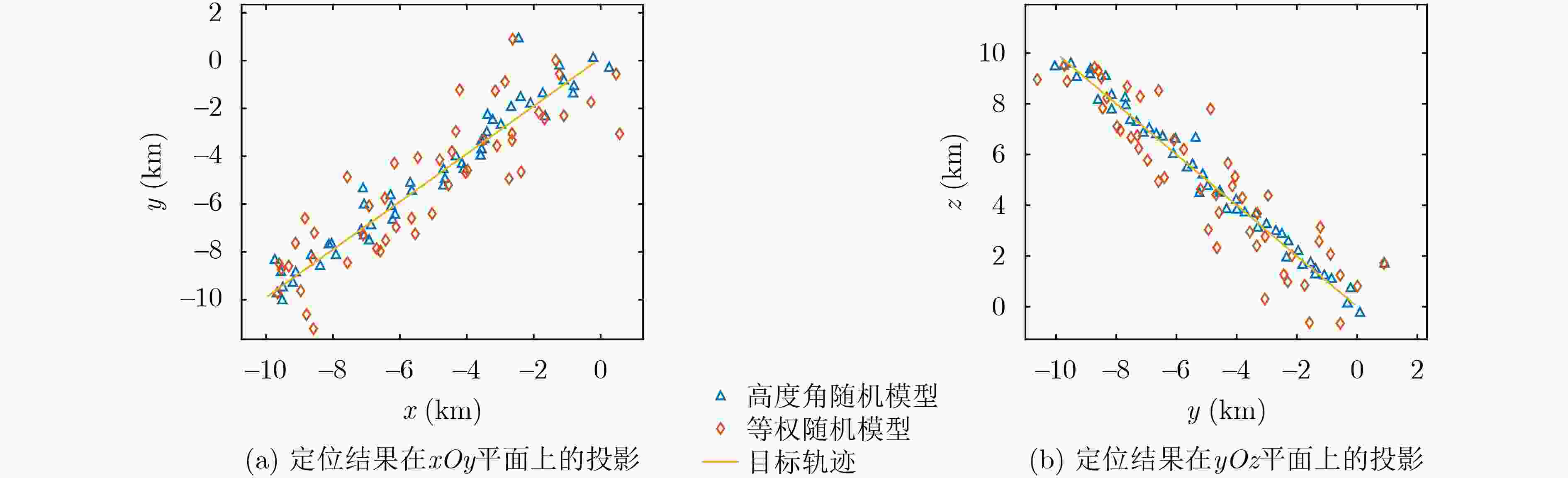
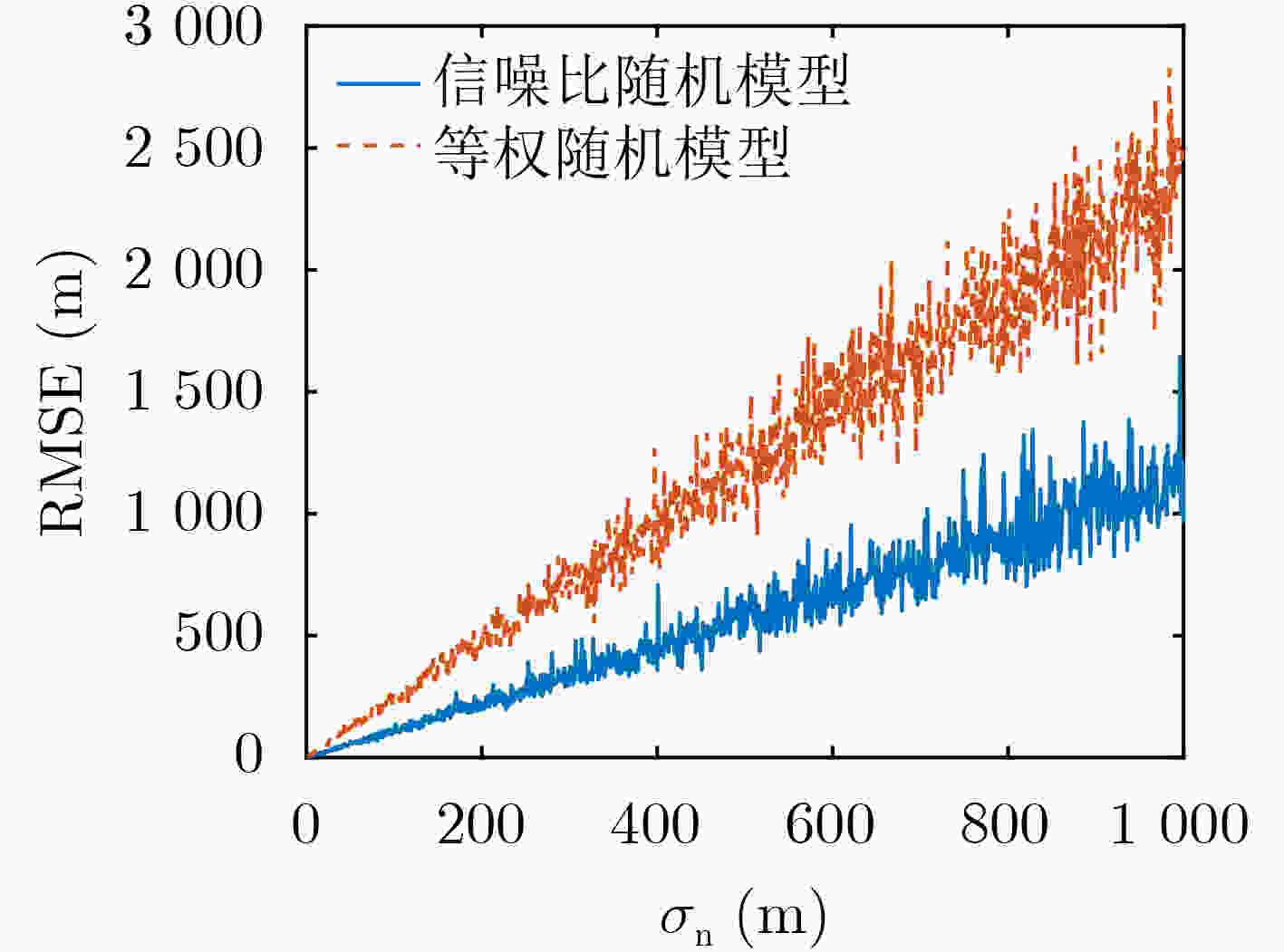
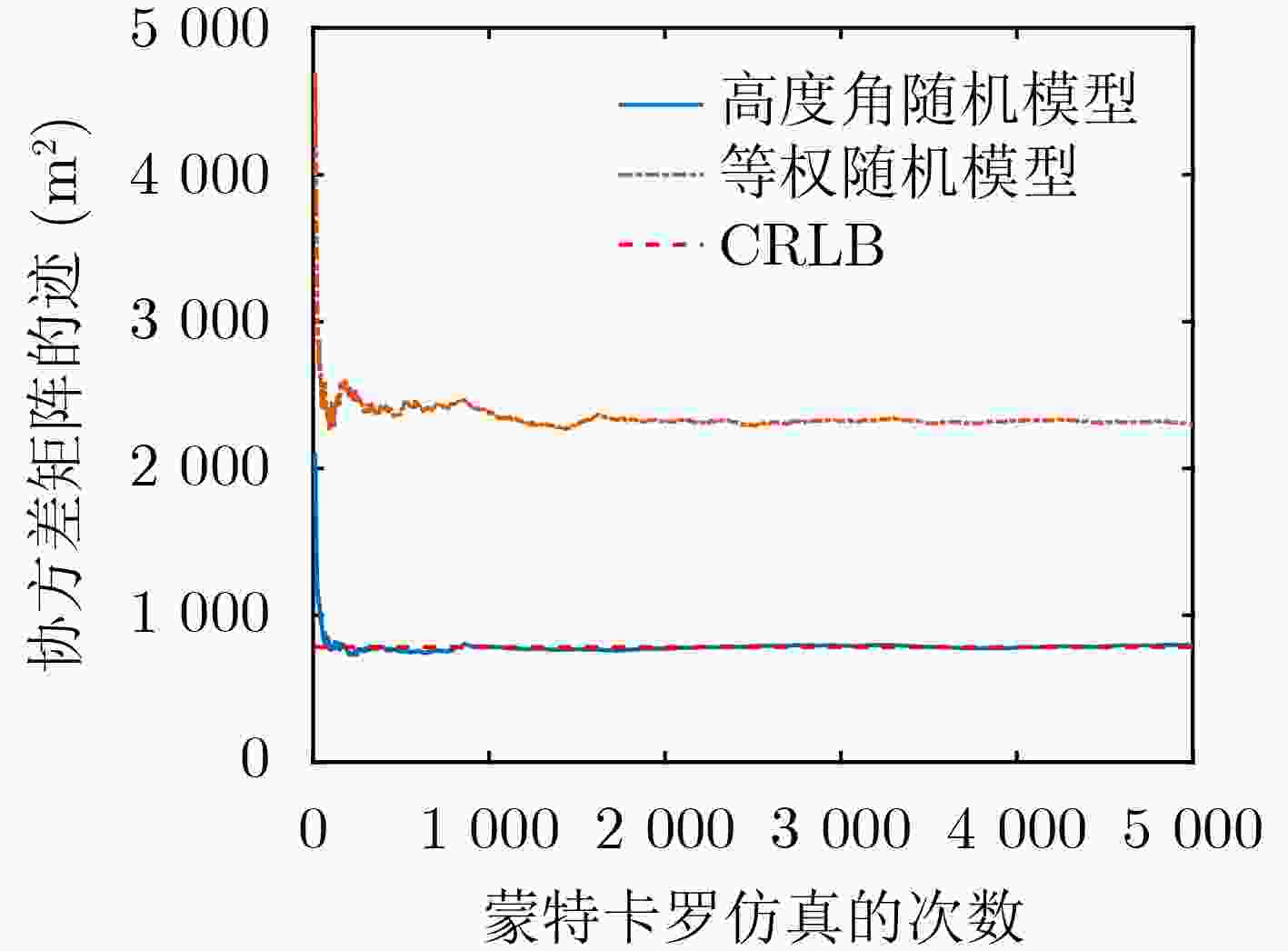



 下载:
下载:
