Optimization of Computation Offloading for UAV-Assisted Intelligent Transportation Systems Considering Age of Information
-
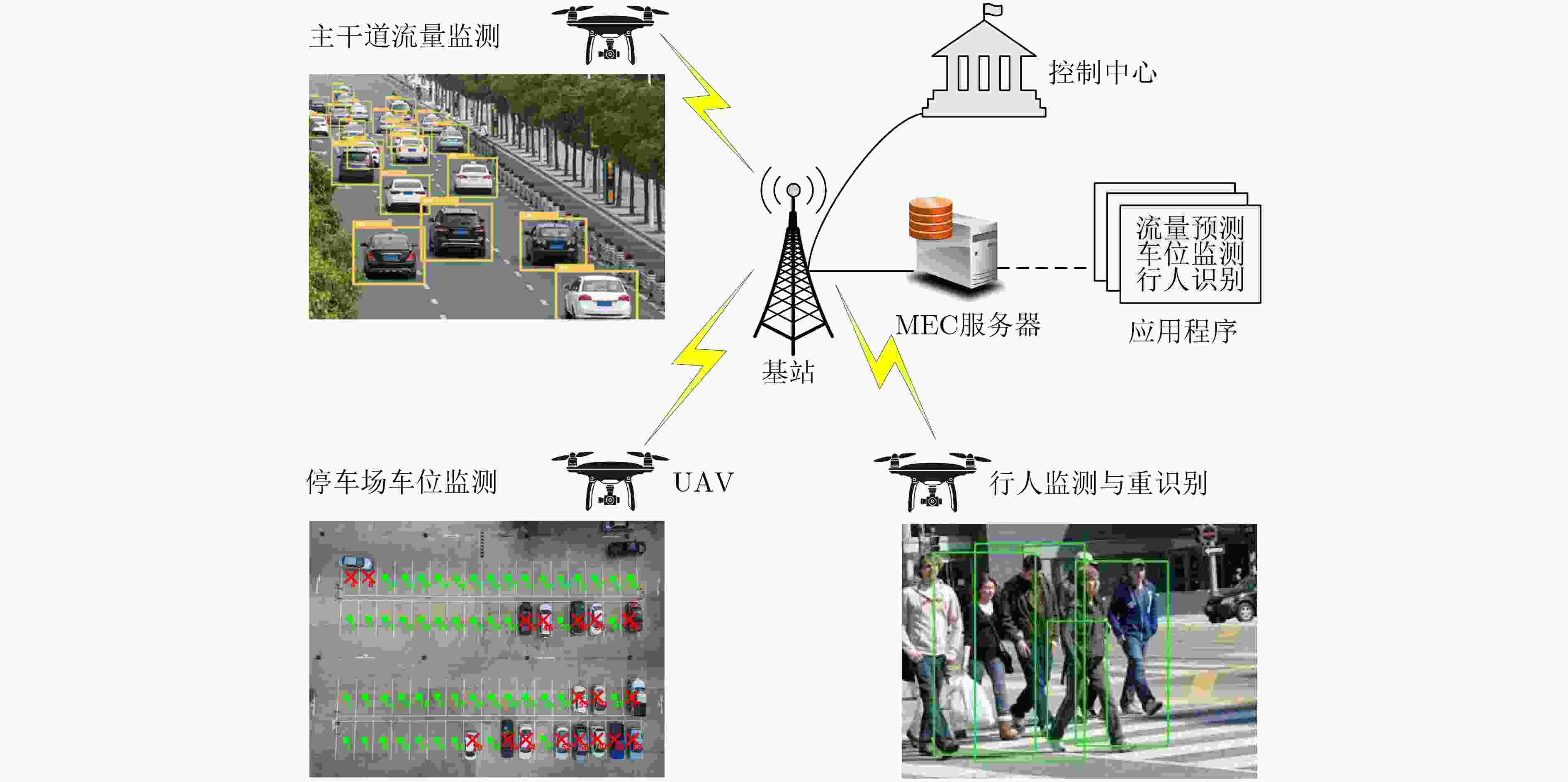
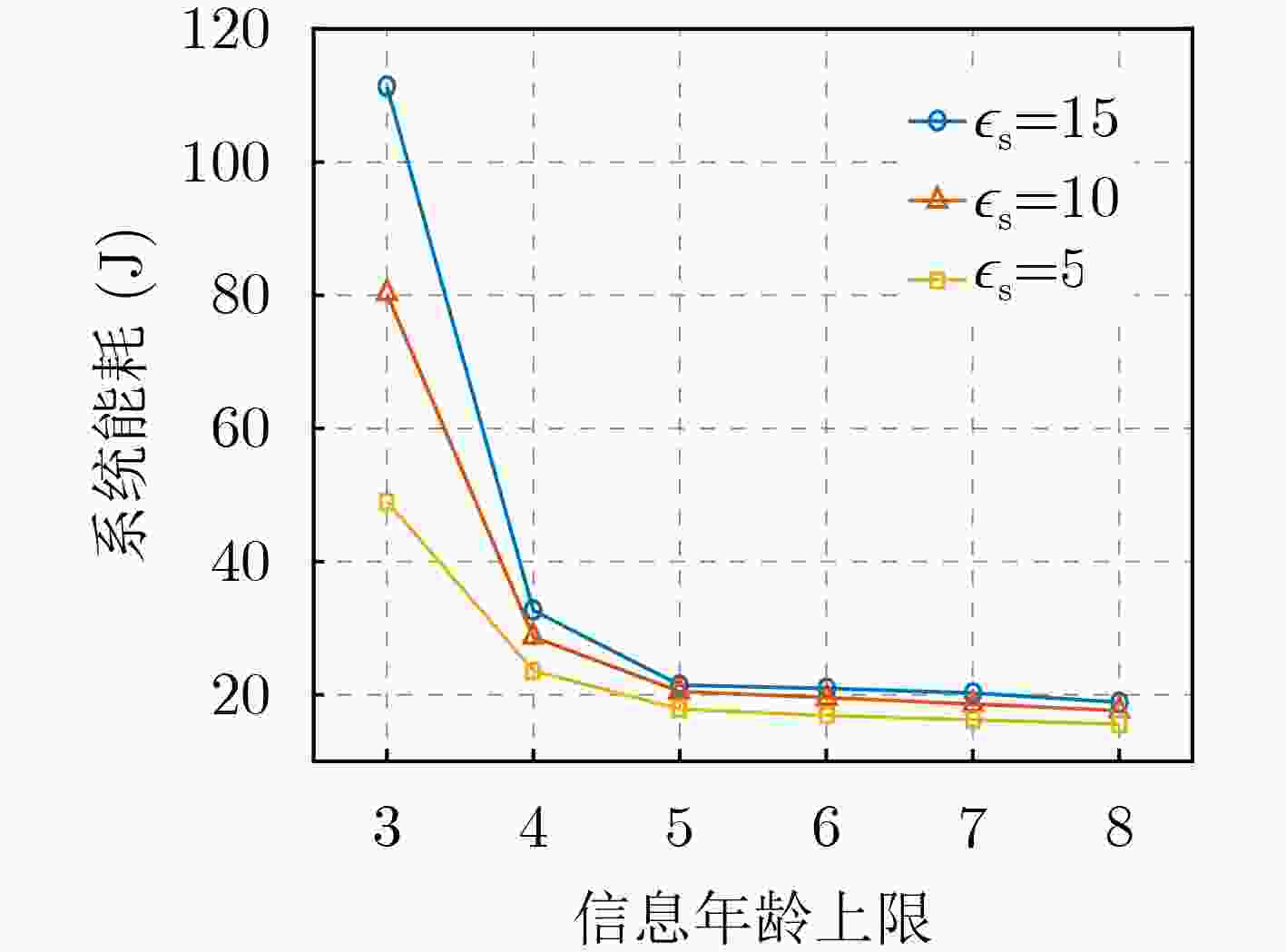
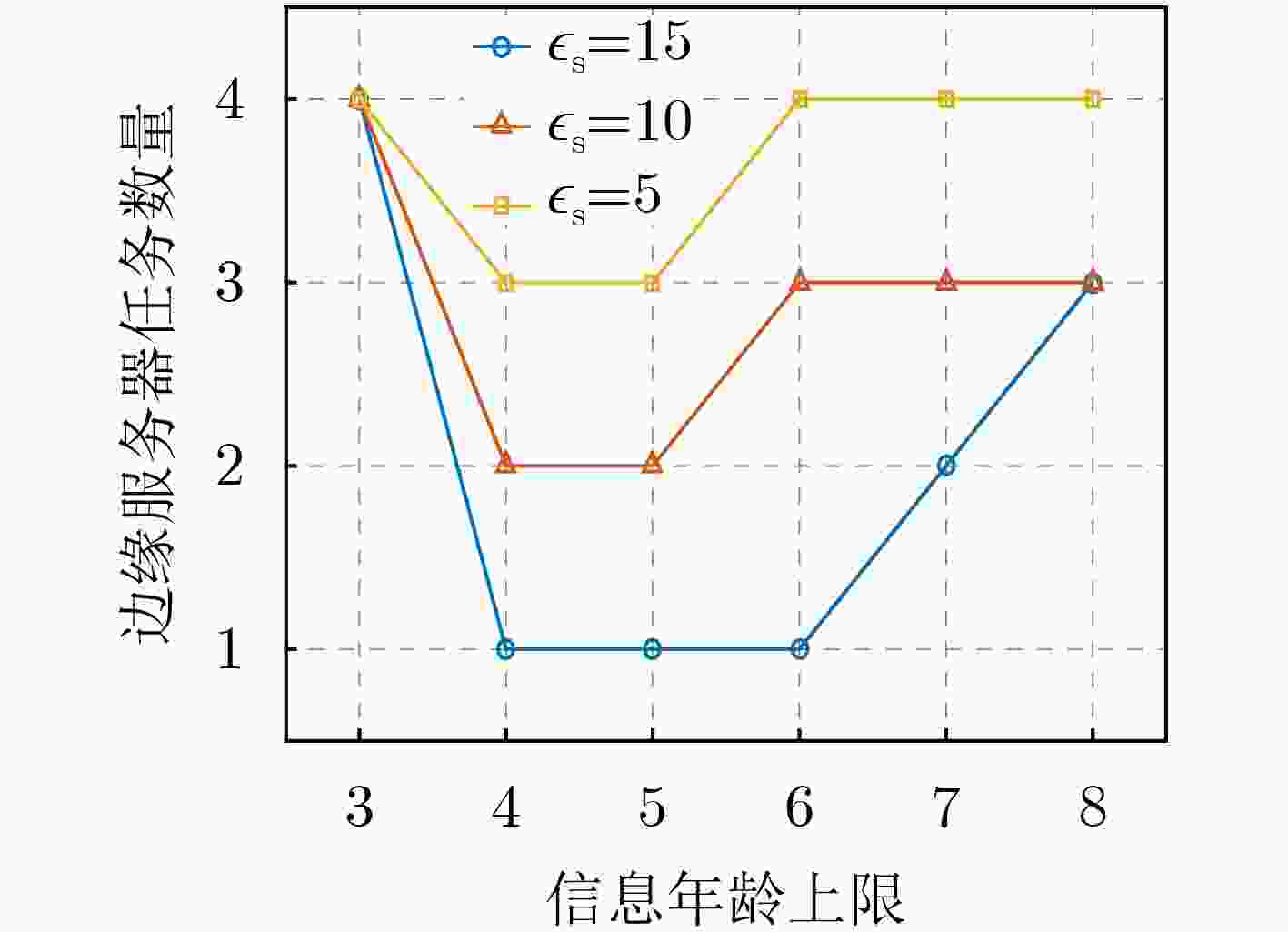
摘要: 该文考虑无人机(UAV)交通监测与移动边缘计算(MEC)技术结合的智能交通系统。为了保障系统中数据时效性并且降低系统能耗,提出计及信息年龄(AoI)的UAV计算卸载优化方法。首先,建立UAV辅助的MEC系统模型,允许MEC服务器缓存常用的应用程序并为UAV提供计算卸载,以支持UAV执行交通监测任务。通过联合优化UAV任务卸载决策、UAV上下行通信带宽分配以及被卸载任务的计算资源分配,最小化所有UAV与MEC服务器的总能耗,同时满足AoI与资源容量等约束条件。其次,系统能耗最小化问题是混合整数非凸优化问题,因此采用离散化和线性化手段,快速获得问题的近似最优解,并设计离散点生成算法来调节近似误差。最后,仿真结果表明,即使对于大型的非凸问题,所提方法也能够快速得到近似最优解,并且可以在不同的任务场景中满足AoI等约束条件,最大限度降低系统能耗。仿真结果验证了所提方法的有效性。Abstract: The intelligent transportation system that combines Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) based traffic monitoring and Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) technologies is considered. In order to ensure the timeliness of data and reduce energy consumption in the system, a UAV computation offloading optimization method considering Age of Information (AoI) is proposed. Firstly, the UAV-assisted MEC system model is established to allow the MEC server to cache commonly used applications and provide UAVs with computation offloading, which supports the UAVs to perform traffic monitoring tasks. By jointly optimizing UAV task offloading decisions, UAV uplink and downlink communication bandwidth allocation, and computing resource allocation of offloaded tasks, the total energy consumption of all UAVs and the MEC server is minimized while satisfying constraints of AoI and resource capacities. Secondly, the system energy consumption minimizing problem is a mixed-integer non-convex optimization problem. Discretization and linearization methods are adopted to quickly obtain an approximately optimal solution to the problem. A discrete point generation algorithm is designed to adjust the approximation error. Finally, simulation results show that even for large non-convex problems, the proposed method can quickly obtain approximately optimal solutions and can satisfy constraints of AoI in different task scenarios, minimizing the system energy consumption as much as possible. The simulation results verify the effectiveness of the proposed method.
-
表 1 P2与P1的关系
P2中的新变量和新函数 与原问题P1的关系 整数变量$ {z_i} $ 用于等价线性化AoI等式(8),见式(18)–式(20) 连续变量$ {a_i}t_i^L,{a_i}t_i^M,{a_i}e_i^L,{a_i}e_i^M,{a_i}r_i^M $ 用于定义凸包络,精确松弛5个双线性项$ {a_i}t_i^L,{a_i}t_i^M,{a_i}e_i^L,{a_i}e_i^M,{a_i}r_i^M $,见式(21)、式(22) 连续变量$ r_i^b,r_i^M $ 用于等价替换$ 1/{b_i} $,$ 1/f_i^M $,见式(23)–式(27) 连续变量$ {m_i} $ 用于等价松弛式(27),见式(28) 直线函数$ l_{k,k + 1}^1(r_i^M) $和连续变量$ {F_i} $ 用于近似函数$ 1/r_i^M $,见式(33)–式(35) 直线函数$ l_{k,k + 1}^2(r_i^M) $ 用于近似函数$ 1/{(r_i^M)^2} $,见式(36) 直线函数$ l_{k,k + 1}^3(r_i^b) $和连续变量$ {B_i} $ 用于近似函数$ 1/r_i^b $,见式(37)、式(38) 算法1 离散点生成算法 输入:$ \delta $, $ f(r) $, $ r \in [{r_{\min }},{r_{\max }}] $, $ {r_1} = {r_{\min }} $, $ R = \{ {r_1}\} $, $ i = 1 $ 输出:$ R $ 1. Repeat 2. 令$ {r_L} = {r_i} $, $ {r_R} = {r_{\max }} $, $ E = \{ {r_L},{r_R}\} $ 3. Repeat 4. $ {r^*} = {f'^{ - 1}}\left( {\frac{{f({r_R}) - f({r_L})}}{{{r_R} - {r_L}}}} \right) $ 5. $ {\varDelta ^*} = {l_{L,R}}({r^*}) - f({r^*}) $ 6. 获得$ \ell $,使得$ E $中第$ \ell $个元素$ {E_\ell } = {r_R} $ 7. If $ {\varDelta ^*} > \delta $ Then 8. $ {r_R} \leftarrow ({E_\ell } + {E_{\ell - 1}})/2 $, $ E \leftarrow E \cup \{ {r_R}\} $ 9. ElseIf $ {\varDelta ^*} < \delta - {\delta _0} $ Then 10. $ {r_R} \leftarrow ({E_\ell } + {E_{\ell + 1}})/2 $, $ E \leftarrow E \cup \{ {r_R}\} $ 11. EndIf 12. 对$ E = \{ {E_1},{E_2}, \cdots \} $排序,使得$ {E_1} < {E_2} < \cdots $ 13. Until $ \delta - {\delta _0} \le {\varDelta ^*} \le \delta $ 14. $ R \leftarrow R \cup \{ {r_R}\} $, $ i \leftarrow i + 1 $ 15. Until $ {r_R} = {r_{\max }} $ 表 2 不同求解方案的运算时间
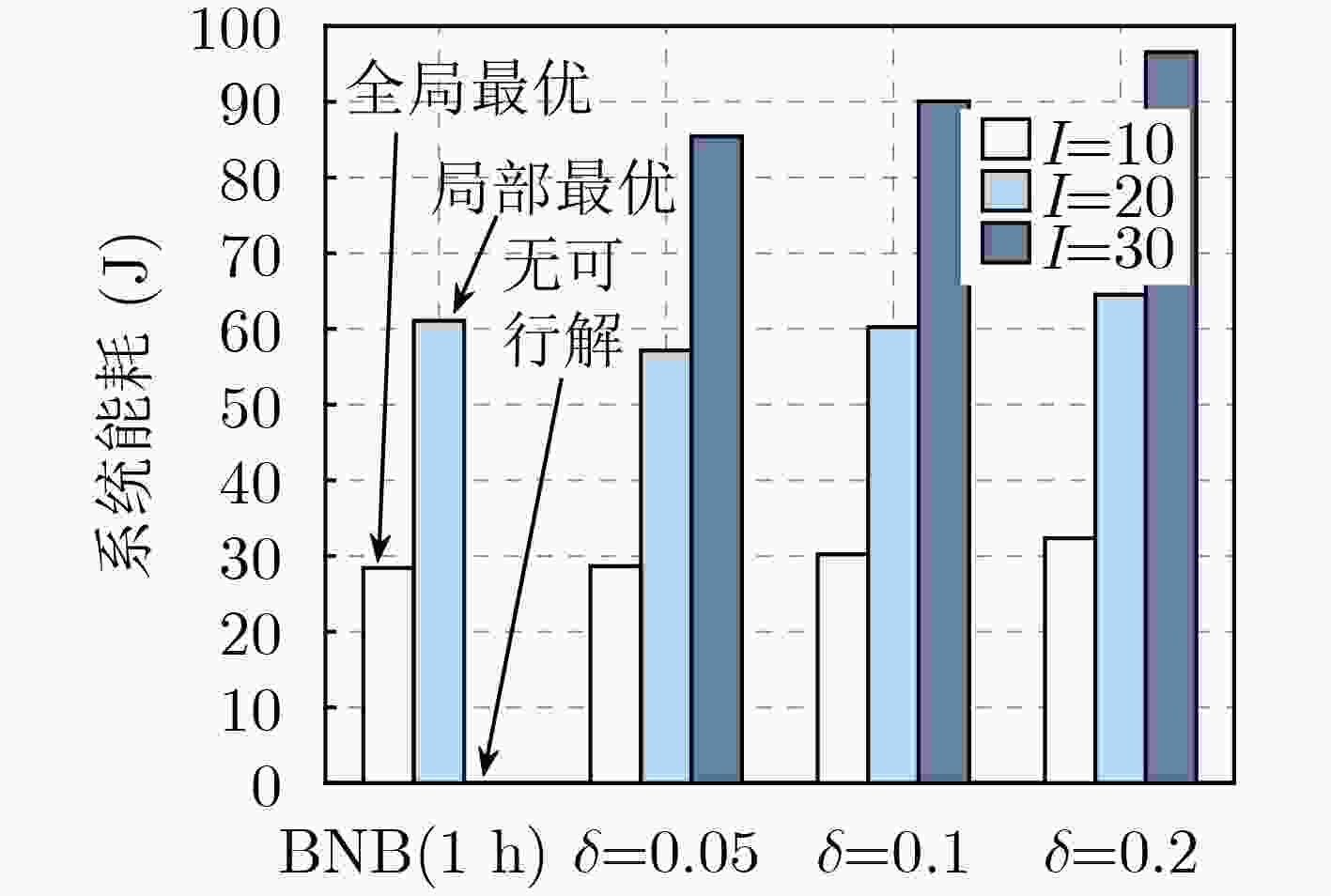
UAV 求解器 本方法 数量 BNB(1 h) δ=0.05 δ=0.1 δ=0.2 I=10 11 min 9 s 5 s 4 s I=20 1 h 28 s 17 s 10 s I=30 1 h 78 s 50 s 31 s -
[1] HU Jinna, CHEN Chen, CAI Lin, et al. UAV-assisted vehicular edge computing for the 6G Internet of vehicles: Architecture, intelligence, and challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Standards Magazine, 2021, 5(2): 12–18. doi: 10.1109/MCOMSTD.001.2000017. [2] LIU Jianyu, WU Jing, and LIU Mingyu. UAV monitoring and forecasting model in intelligent traffic oriented applications[J]. Computer Communications, 2020, 153: 499–506. doi: 10.1016/j.comcom.2020.02.009. [3] 胡硕, 王洁, 孙妍, 等. 无人机视角下的多车辆跟踪算法研究[J]. 智能系统学报, 2022, 17(4): 798–805. doi: 10.11992/tis.202108014.HU Shuo, WANG Jie, SUN Yan, et al. Research on multi-vehicle tracking algorithm from the perspective of UAV[J]. CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems, 2022, 17(4): 798–805. doi: 10.11992/tis.202108014. [4] JIANG Yingying, MIAO Yiming, ALZAHRANI B, et al. Ultra large-scale crowd monitoring system architecture and design issues[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(13): 10356–10366. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3076257. [5] 李新民, 尹宝林, 魏李莉, 等. 强化学习无人机通信系统中的信息年龄优化[J]. 电子科技大学学报, 2022, 51(2): 213–218. doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021128.LI Xinmin, YIN Baolin, WEI Lili, et al. Reinforcement learning-based age of information optimization in UAV-enabled communication system[J]. Journal of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2022, 51(2): 213–218. doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021128. [6] FENG Jialiang and GONG Jie. Joint detection and computation offloading with age of information in mobile edge networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2023, 10(3): 1417–1430. doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2022.3208857. [7] 敬乐天, 贾向东, 曹肖攀, 等. 基于DRL的无人机辅助边缘计算服务质量优化[J]. 信号处理, 2022, 38(6): 1316–1324. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2022.06.018.JING Letian, JIA Xiangdong, CAO Xiaopan, et al. Quality of service optimization in UAV-assisted edge computing based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2022, 38(6): 1316–1324. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2022.06.018. [8] HUANG Jiwei, GAO Han, WAN Shaohua, et al. AoI-aware energy control and computation offloading for industrial IoT[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2023, 139: 29–37. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2022.09.007. [9] DIAO Xianbang, GUAN Xinrong, and CAI Yueming. Joint offloading and trajectory optimization for complex status updates in UAV-assisted Internet of things[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(23): 23881–23896. doi: 10.1109/JIQT.2022.3188608. [10] SUN Mengying, XU Xiaodong, QIN Xiaoqi, et al. AoI-energy-aware UAV-assisted data collection for IoT networks: A deep reinforcement learning method[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(24): 17275–17289. doi: 10.1109/JIQT.2021.3078701. [11] 刘玲珊, 熊轲, 张煜, 等. 信息年龄受限下最小化无人机辅助无线供能网络的能耗: 一种基于DQN的方法[J]. 南京大学学报:自然科学, 2021, 57(5): 847–856. doi: 10.13232/j.cnki.jnju.2021.05.015.LIU Lingshan, XIONG Ke, ZHANG Yu, et al. Energy minimization in UAV-assisted wireless powered sensor networks with AoI constraints: A DQN-based approach[J]. Journal of Nanjing University:Natural Science, 2021, 57(5): 847–856. doi: 10.13232/j.cnki.jnju.2021.05.015. [12] CHEN Xianfu, WU Celimuge, CHEN Tao, et al. Age of information-aware resource management in UAV-assisted mobile-edge computing systems[C]. 2020 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Taipei, China, 2020: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/GLOBECOM42002.2020.9322632. [13] ZHENG Guangyuan, XU Chen, WEN Miaowen, et al. Service caching based aerial cooperative computing and resource allocation in multi-UAV enabled MEC systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71(10): 10934–10947. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3183577. [14] ZHOU Ruiting, WU Xiaoyi, TAN Haisheng, et al. Two time-scale joint service caching and task offloading for UAV-assisted mobile edge computing[C]. 2022 IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, London, United Kingdom, 2022: 1189–1198. doi: 10.1109/INFOCOM48880.2022.9796714. [15] PENG Haixia and SHEN X S. DDPG-based resource management for MEC/UAV-assisted vehicular networks[C]. The 92nd Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2020-Fall), Victoria, Canada, 2020: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/VTC2020-Fall49728.2020.9348633. [16] WANG Yuntao, CHEN Weiwei, LUAN T H. , et al. Task offloading for post-disaster rescue in unmanned aerial vehicles networks[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2022, 30(4): 1525–1539. doi: 10.1109/TNET.2022.3140796. [17] JIANG Xu, SHENG Min, ZHAO Nan, et al. Green UAV communications for 6G: A survey[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2022, 35(9): 19–34. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2021.04.025. [18] 刘漳辉, 郑鸿强, 张建山, 等. 多无人机使能移动边缘计算系统中的计算卸载与部署优化[J]. 计算机科学, 2022, 49(6A): 619–627. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.210600165.LIU Zhanghui, ZHENG Hongqiang, ZHANG Jianshan, et al. Computation offloading and deployment optimization in multi-UAV-enabled mobile edge computing systems[J]. Computer Science, 2022, 49(6A): 619–627. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.210600165. [19] HOANG L T, NGUYEN C T, LI Peng, et al. Joint uplink and downlink resource allocation for UAV-enabled MEC networks under user mobility[C]. 2022 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops, Seoul, Korea, 2022: 1059–1064. doi: 10.1109/ICCWorkshops53468.2022.9814687. [20] EL HABER E, ALAMEDDINE H A, ASSI C, et al. UAV-aided ultra-reliable low-latency computation offloading in future IoT networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(10): 6838–6851. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.309 6559. [21] 卢为党, 詹悦者, 花俏枝, 等. 基于无人机无线能量传输的边缘计算系统能耗优化方法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(3): 899–905. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211314.LU Weidang, ZHAN Yuezhe, HUA Qiaozhi, et al. Energy consumption optimization in UAV wireless power transfer based mobile edge computing system[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(3): 899–905. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211314. [22] BOUKOUVALA F, MISENER R, and FLOUDAS C A. Global optimization advances in mixed-integer nonlinear programming, MINLP, and constrained derivative-free optimization, CDFO[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2016, 252(3): 701–727. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2015.12.018. [23] MCCORMICK G P. Computability of global solutions to factorable nonconvex programs: Part I—Convex underestimating problems[J]. Mathematical Programming, 1976, 10(1): 147–175. doi: 10.1007/BF01580665. [24] ZHONG Weifeng, XIE Shengli, XIE Kan, et al. Cooperative P2P energy trading in active distribution networks: An MILP-based Nash bargaining solution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2021, 12(2): 1264–1276. doi: 10.1109/TSG.2020. 3031013. [25] BOYD S and VANDENBERGHE L. Convex Optimization[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2004. doi: 10.1017/cbo9780511804441. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
