Single Event Transient Analysis and Hardening in a Low-Dropout Regulator
-
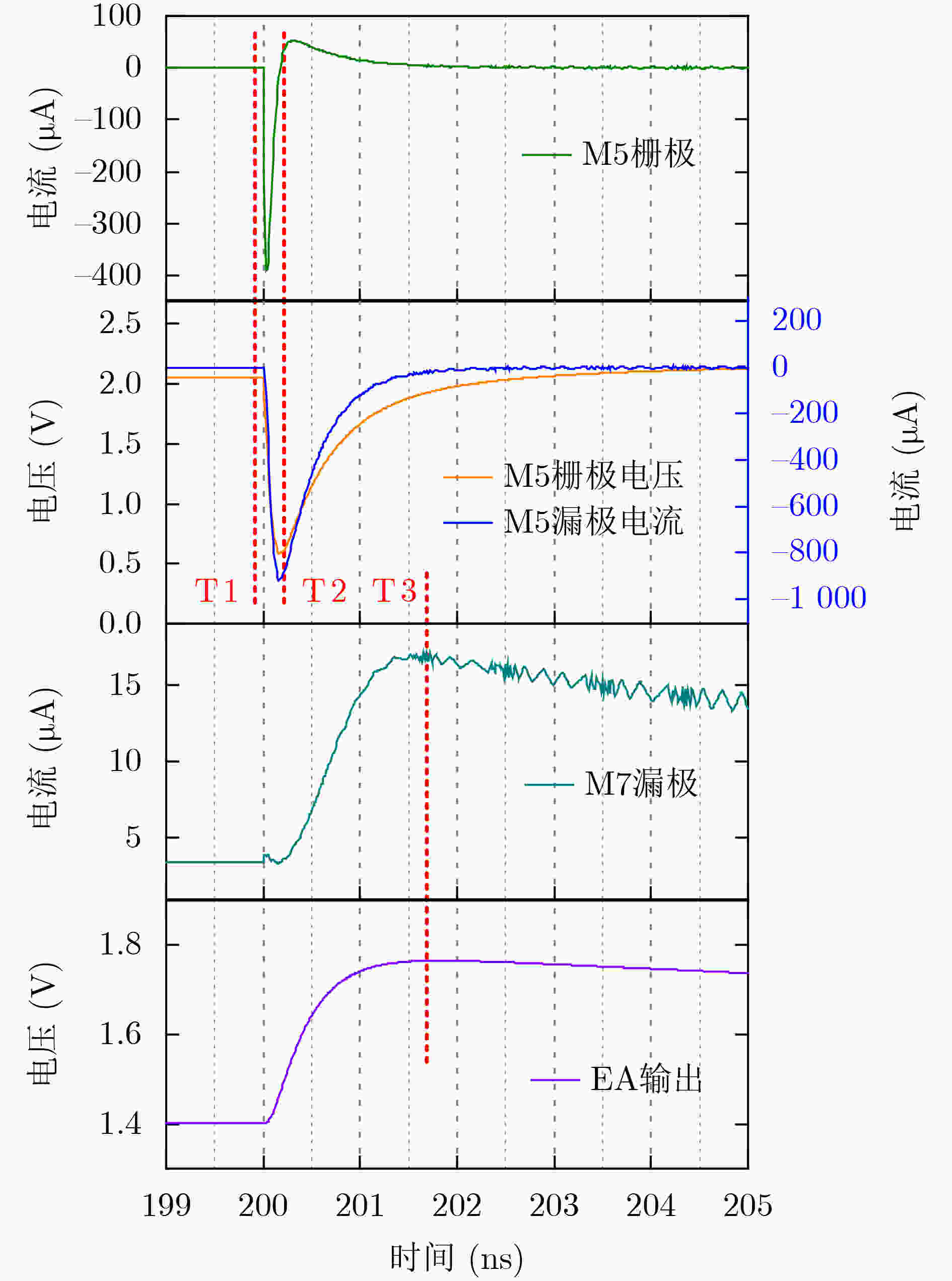
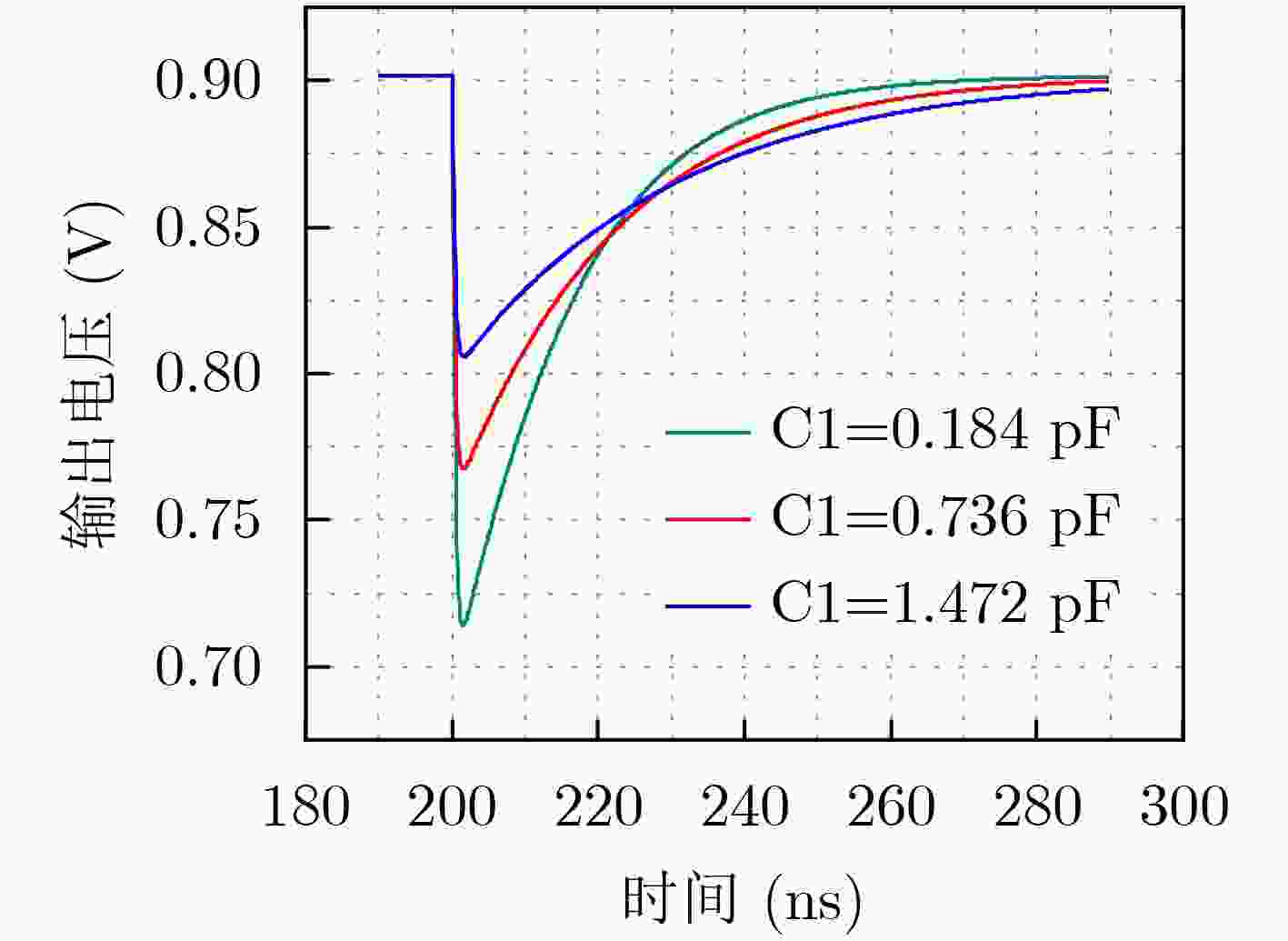
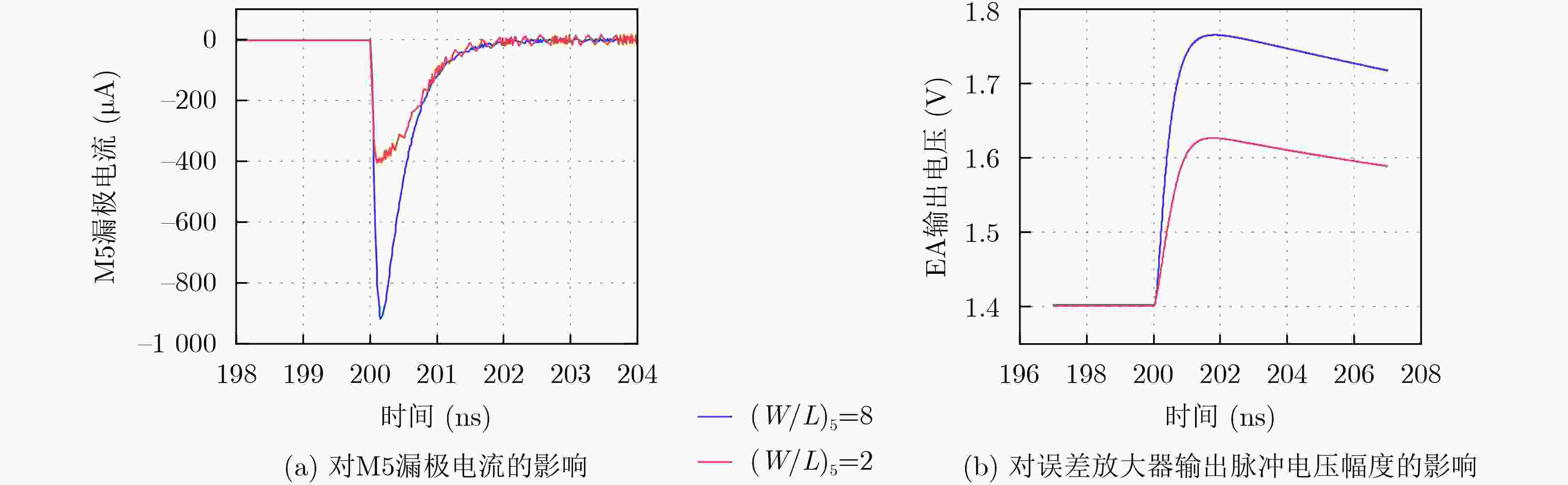
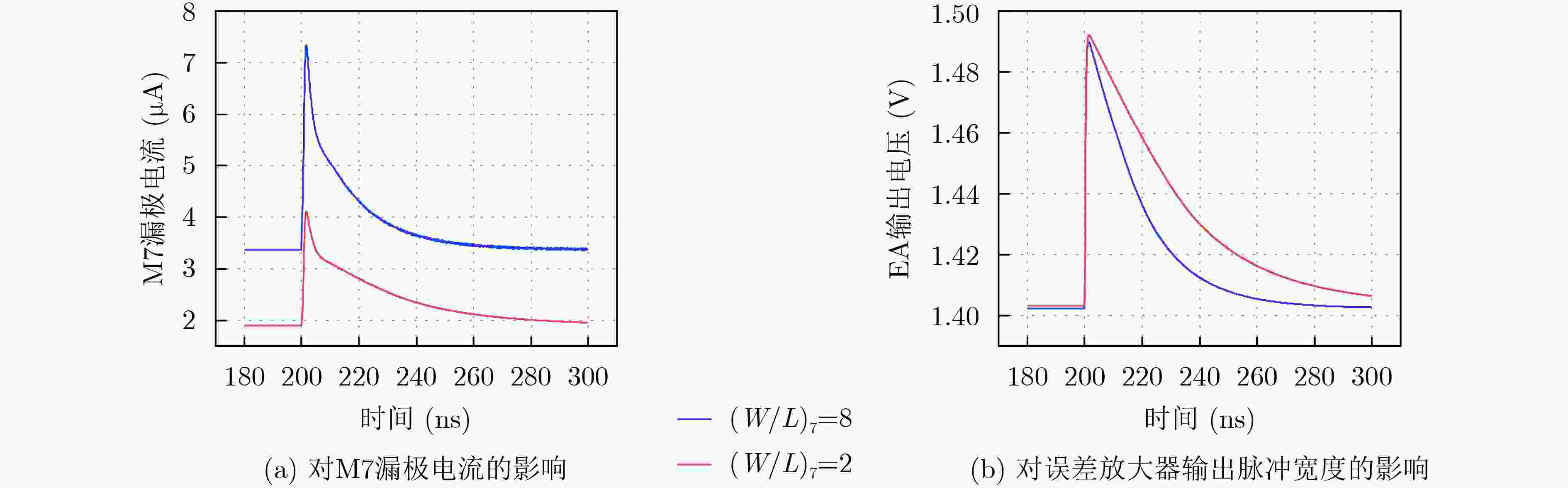
摘要: 随着集成电路特征尺寸的不断缩减,CMOS集成电路的单粒子效应问题越来越严重。为了提高低压差线性稳压器(LDO)的单粒子瞬态(SET)效应加固效果,该文通过SPICE电路仿真和重离子实验研究了一种28 nm CMOS工艺LDO的SET失效机制,并研究了关键器件尺寸大小对SET脉冲的影响,提出一种有效的LDO加固方法。SPICE电路仿真发现这种LDO的敏感节点主要位于误差放大器(EA)内部。功率管(MOSFET)栅极节点的环路滤波电容会明显地影响单粒子瞬态脉冲的幅度,也会轻微地影响单粒子瞬态脉冲的宽度。误差放大器内部关键节点的器件尺寸会影响稳压器输出的单粒子瞬态脉冲的幅度和宽度。通过增加功率管(MOSFET)栅极节点电容和调整误差放大器内部相关节点器件尺寸的方法对LDO进行了SET加固设计。电路仿真和重离子实验结果表明这种加固方法能够有效地降低LDO输出的单粒子瞬态脉冲的幅度和宽度。
-
关键词:
- 单粒子瞬态 /
- 低压差线性稳压器 /
- 重离子实验 /
- SPICE电路仿真 /
- 28 nm CMOS工艺
Abstract: As the feature size of integrated circuits scales down, the problem of the Single Event Transients (SET) in CMOS integrated circuits is becoming more and more serious. In order to improve the hardening effect of the Low-DropOut regulators (LDO), the mechanism of the SET in a LDO fabricated on 28 nm CMOS technology is studied by SPICE circuit simulation and heavy ion experiment. The influence of the size of the key components on the SET in LDO is also studied. The hardening methods for LDO is proposed. The SPICE circuit simulation results show that the most sensitive nodes are located in the Error Amplifier (EA). The equivalent capacitance on the gate node of the power MOSFET can significantly influence the amplitude of the single event transients and slightly influence the width. The size of the relevant devices in the error amplifier can influence both amplitude and width of the SETs. The LDO is hardened by adding the capacitance on the gate node of power MOSFET and adjusting the size of the relevant devices in the error amplifier. The results of the simulation and the experiment show that the hardening method can significantly decrease the amplitude and width of the SETs. -
表 1 重离子参数
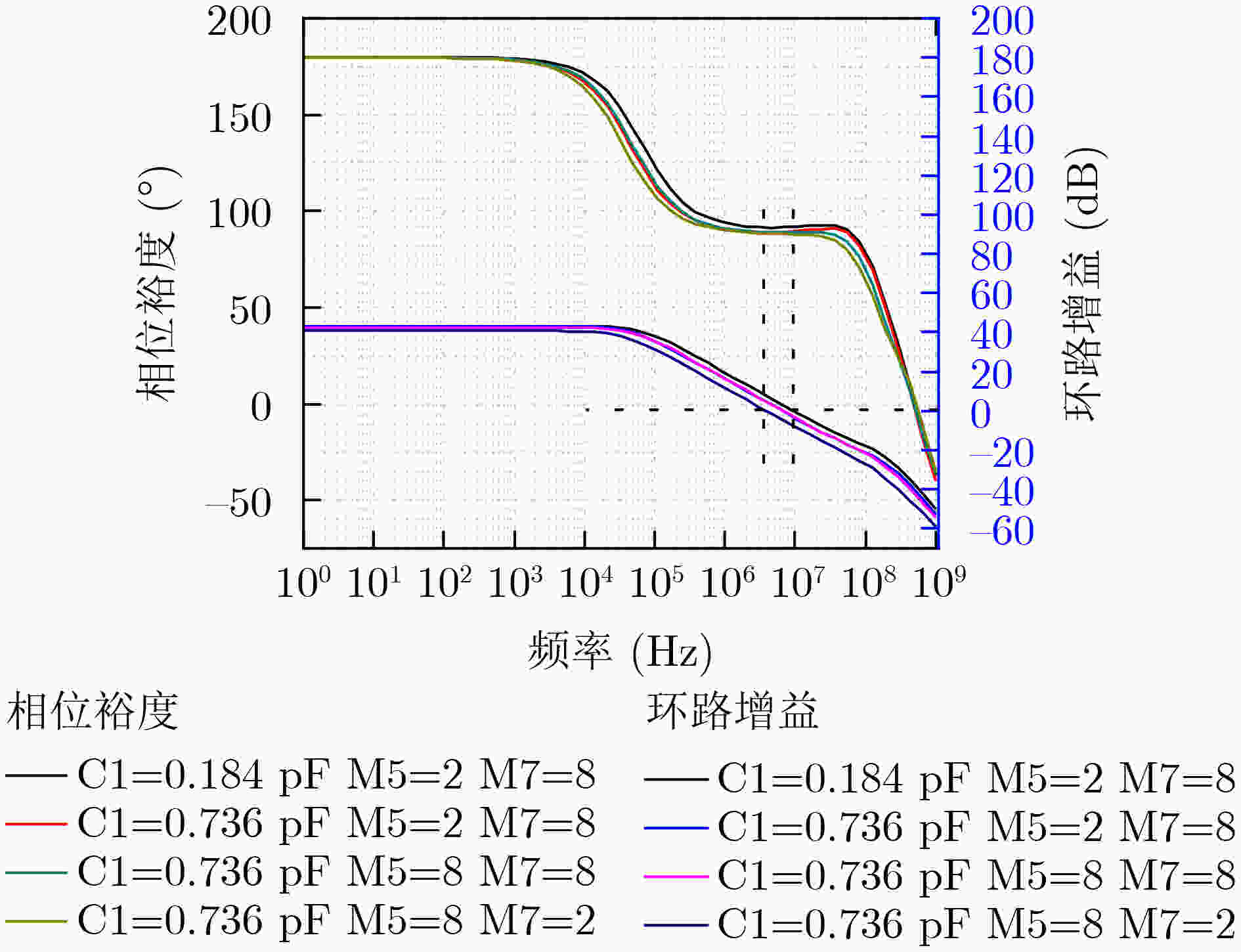
粒子种类 能量(MeV) 射程(μm) LET(MeV·cm2/mg) Cl 150 42.8 13.4 Ti 165 33.9 22.0 Ge 208 30.3 37.3 U 700 41.0 45.0 表 2 C1的值和器件长宽比对LDO功耗的影响
器件宽度 SET宽
度(ns)SET幅
度(mV)EA电源
电流(µA)(W/L)5=2, (W/L)7=2 160 174 49.1 (W/L)5=8, (W/L)7=2 170 272 49.1 (W/L)5=2, (W/L)7=8 100 172 51.6 (W/L)5=8, (W/L)7=8 100 264 51.6 -
[1] ADELL P, SCHRIMPF R D, BARNABY H J, et al. Analysis of single-event transients in analog circuits[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 2000, 47(6): 2616–2623. doi: 10.1109/23.903817 [2] LI Zheyi, BERTI L, WOUTERS J, et al. Characterization of the total charge and time duration for single-event transient voltage pulses in a 65-nm CMOS technology[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 2022, 69(7): 1593–1601. doi: 10.1109/TNS.2022.3141070 [3] CHI Yaqing, WU Zhenyu, HUANG Pengcheng, et al. Characterization of single-event transients induced by high LET heavy ions in 16 nm bulk FinFET inverter chains[J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2022, 130: 114490. doi: 10.1016/j.microrel.2022.114490 [4] SHAH A P and WALTL M. Impact of negative bias temperature instability on single event transients in scaled logic circuits[J]. International Journal of Numerical Modelling:Electronic Networks,Devices and Fields, 2021, 34(3): e2854. doi: 10.1002/jnm.2854 [5] MASSENGILL L W, BHUVA B L, HOLMAN W T, et al. Technology scaling and soft error reliability[C]. 2012 IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium (IRPS), Anaheim, USA, 2012: 3C. 1.1–3C. 1.7. [6] JOHNSTON A H, MIYAHIRA T F, IROM F, et al. Single-event transients in voltage regulators[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 2006, 53(6): 3455–3461. doi: 10.1109/TNS.2006.886215 [7] KELLY A T, ADELL P C, WITULSKI A F, et al. Total dose and single event transients in linear voltage regulators[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 2007, 54(4): 1327–1334. doi: 10.1109/TNS.2007.903243 [8] YAO Ruxue, LU Hongliang, ZHANG Yuming, et al. Radiation-hardened high current low-dropout voltage regulator for space applications[C]. 2022 IEEE 16th International Conference on Solid-State & Integrated Circuit Technology (ICSICT), Nangjing, China, 2022: 1–3. [9] CHEN Xi, GUO Qiancheng, YUAN Hengzhou, et al. A single-event transient radiation hardened low-dropout regulator for LC voltage-controlled oscillator[J]. Symmetry, 2022, 14(4): 788. doi: 10.3390/sym14040788 [10] ADELL P C and SCHEICK L Z. Radiation effects in power systems: A review[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 2013, 60(3): 1929–1952. doi: 10.1109/TNS.2013.2262235 [11] 赵起锋. 线性稳压器电路结构及其抗SET技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 国防科技大学, 2017.ZHAO Q F. Research on the circuit structure and radiation-hardened design of linear regulator[D]. [Master dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2017. [12] 夏鹏. 电源芯片LDO器件的单粒子效应研究[D]. [硕士论文], 广东工业大学, 2019.XIA P. Study on single-event effect of low dropout regulator[D]. [Master dissertation], Guangdong University of Technology, 2019. [13] WANG Liang, HAN Xupeng, ZHAO Yuanfu, et al. Single-event transient analysis and hardening in a 180 nm CMOS embedded low-dropout regulator[C]. 2017 17th European Conference on Radiation and Its Effects on Components and Systems (RADECS), Geneva, Switzerland, 2017: 1–4. [14] ZHAO Qifeng, YANG Guoqing, SUN Yongjie, et al. Research on the effect of single-event transient of an on-chip linear voltage regulator fabricated on 130 nm commercial CMOS technology[J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2017, 73: 116–121. doi: 10.1016/j.microrel.2017.04.030 [15] DUAN Zhikui, DING Yi, LU Chong, et al. A single-event transient hardened LDO regulator with built-in filter[J]. IEICE Electronics Express, 2015, 12(22): 20150850. doi: 10.1587/elex.12.20150850 [16] VAN VONNO N W, PEARCE L W, KNUDSEN K C, et al. Total dose and single event testing of the Intersil ISL75051SRH low dropout regulator[C]. 2012 IEEE Radiation Effects Data Workshop, Miami, USA, 2012: 1–6. [17] VAN VONNO N W, GILL J S, PEARCE L G, et al. Total dose and SEE testing of the Intersil ISL75052SEH low dropout regulator[C]. 2015 15th European Conference on Radiation and its Effects on Components and Systems (RADECS), Moscow, Russia, 2015: 1–6. [18] VAN VONNO N W, MANSILLA O, GILL J S, et al. Single-event effects testing of the Renesas ISL70005SEH dual output point-of-load regulator[C]. 2020 IEEE Radiation Effects Data Workshop (in conjunction with 2020 NSREC), Santa Fe, USA, 2020: 1–7. [19] MESSENGER G C. Collection of charge on junction nodes from ion tracks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 1982, 29(6): 2024–2031. doi: 10.1109/TNS.1982.4336490 [20] XU Changqing, LIU Yi, LIAO Xinfang, et al. Machine learning regression-based single-event transient modeling method for circuit-level simulation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2021, 68(11): 5758–5764. doi: 10.1109/TED.2021.3113884 [21] BLACK D A, ROBINSON W H, WILCOX I Z, et al. Modeling of single event transients with dual double-exponential current sources: Implications for logic cell characterization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 2015, 62(4): 1540–1549. doi: 10.1109/TNS.2015.2449073 [22] RAZAVI B. Design of Analog CMOS Integrated Circuits[M]. 2nd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Education, 2017: 19–20. -





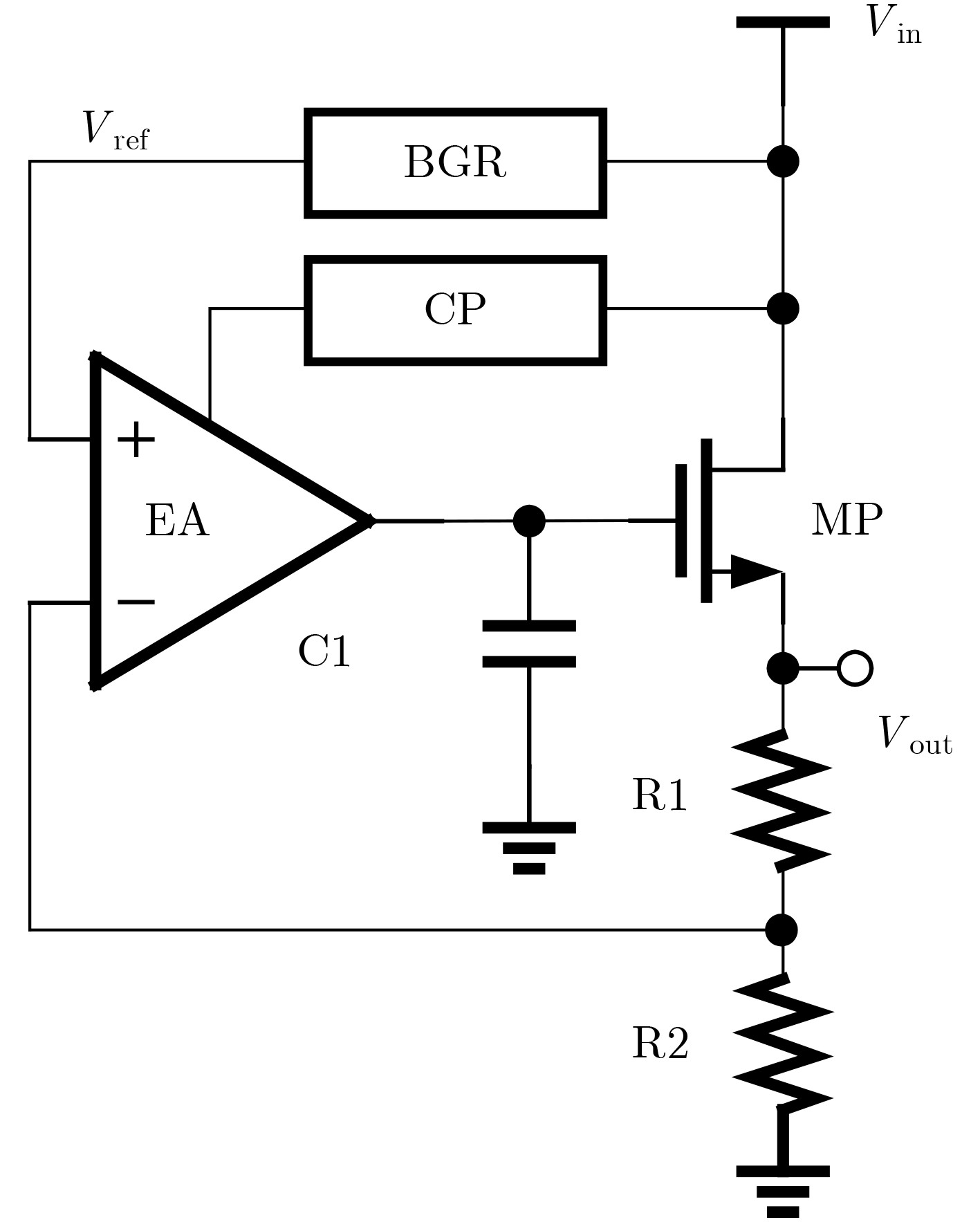
 下载:
下载:
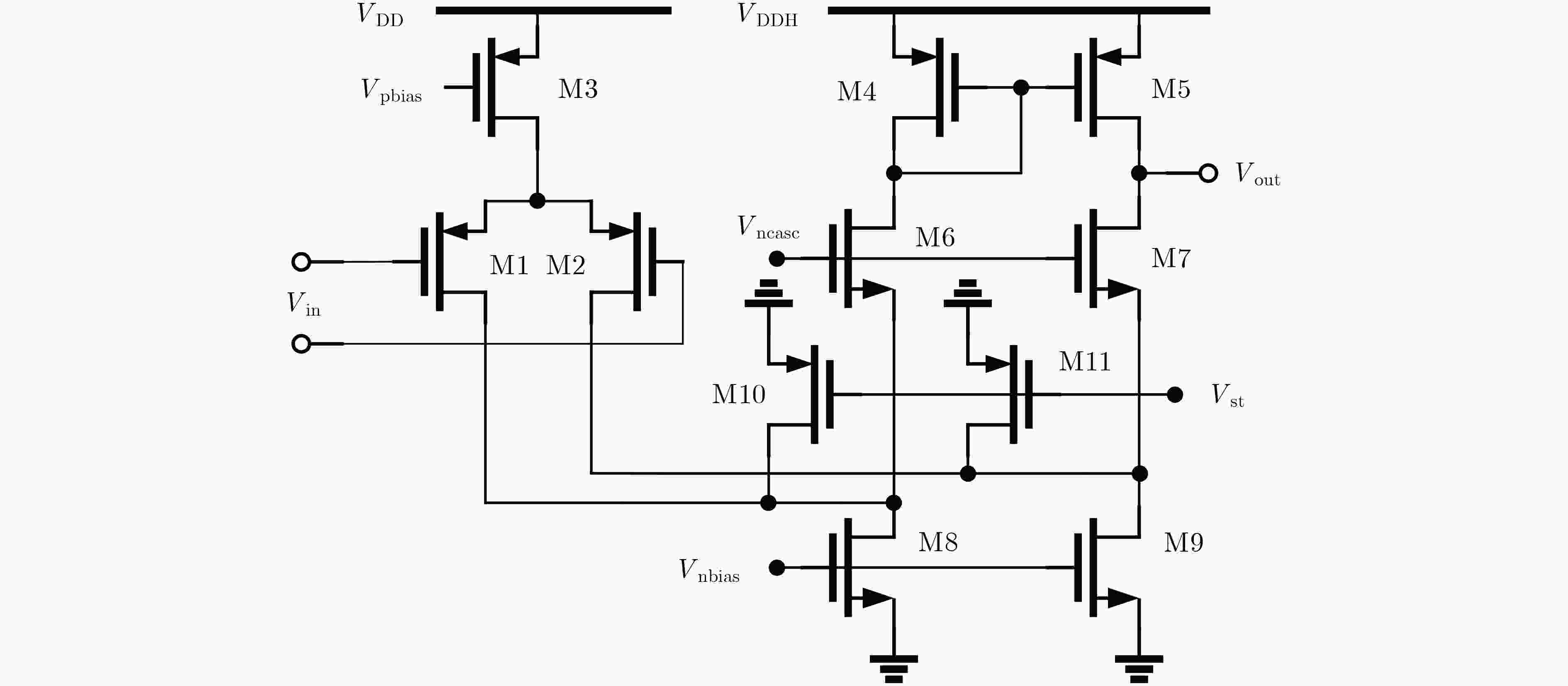
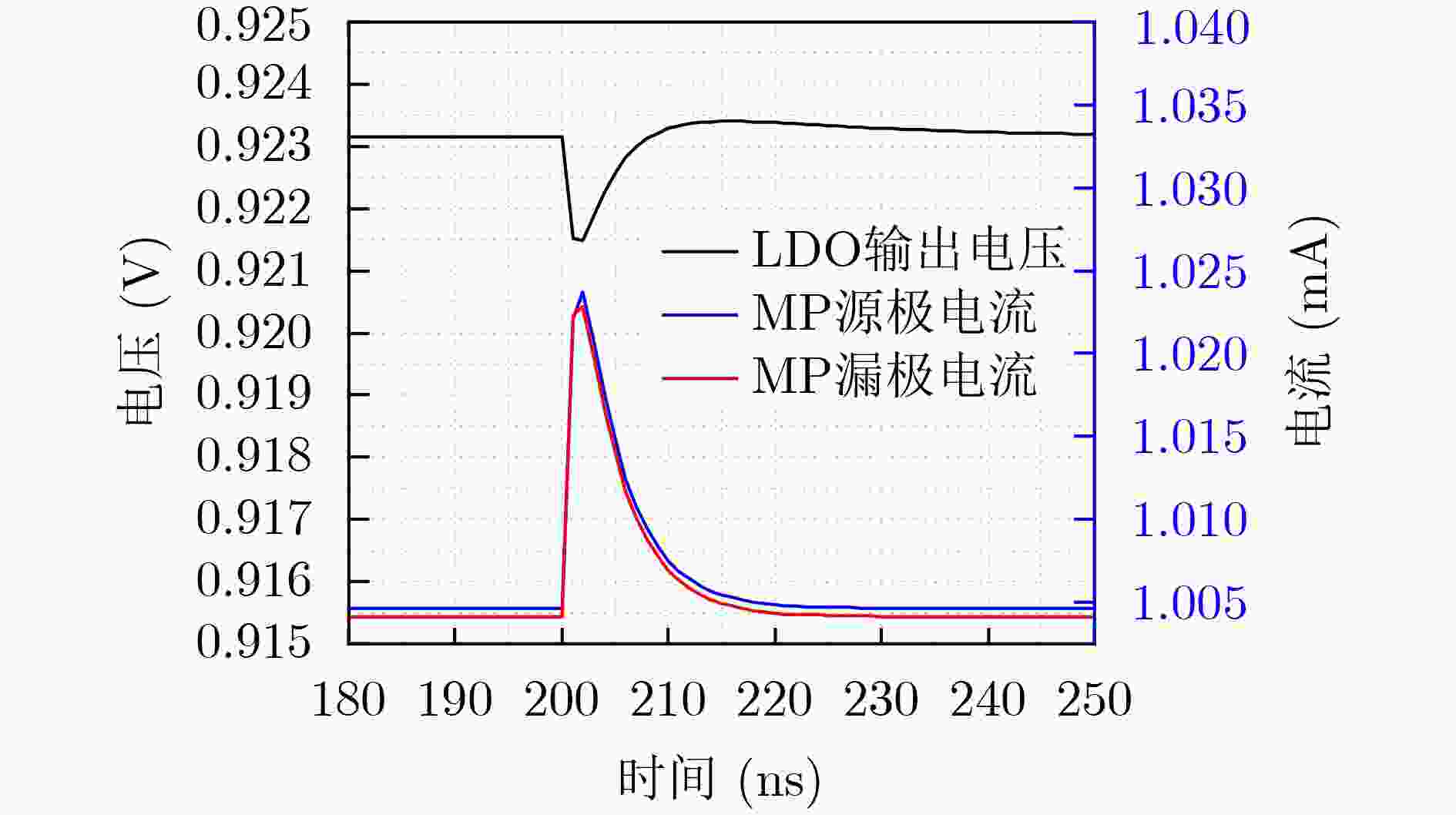
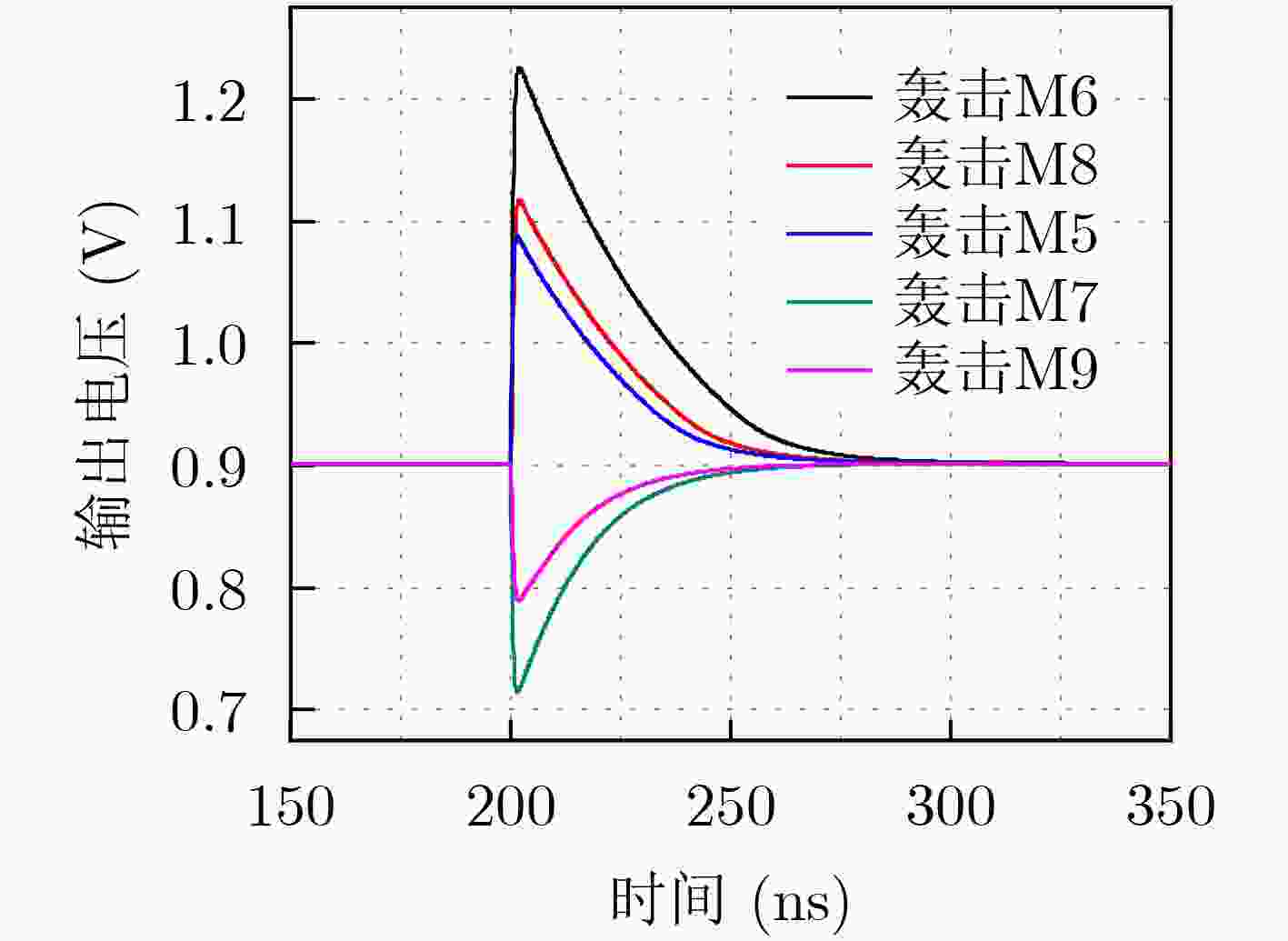
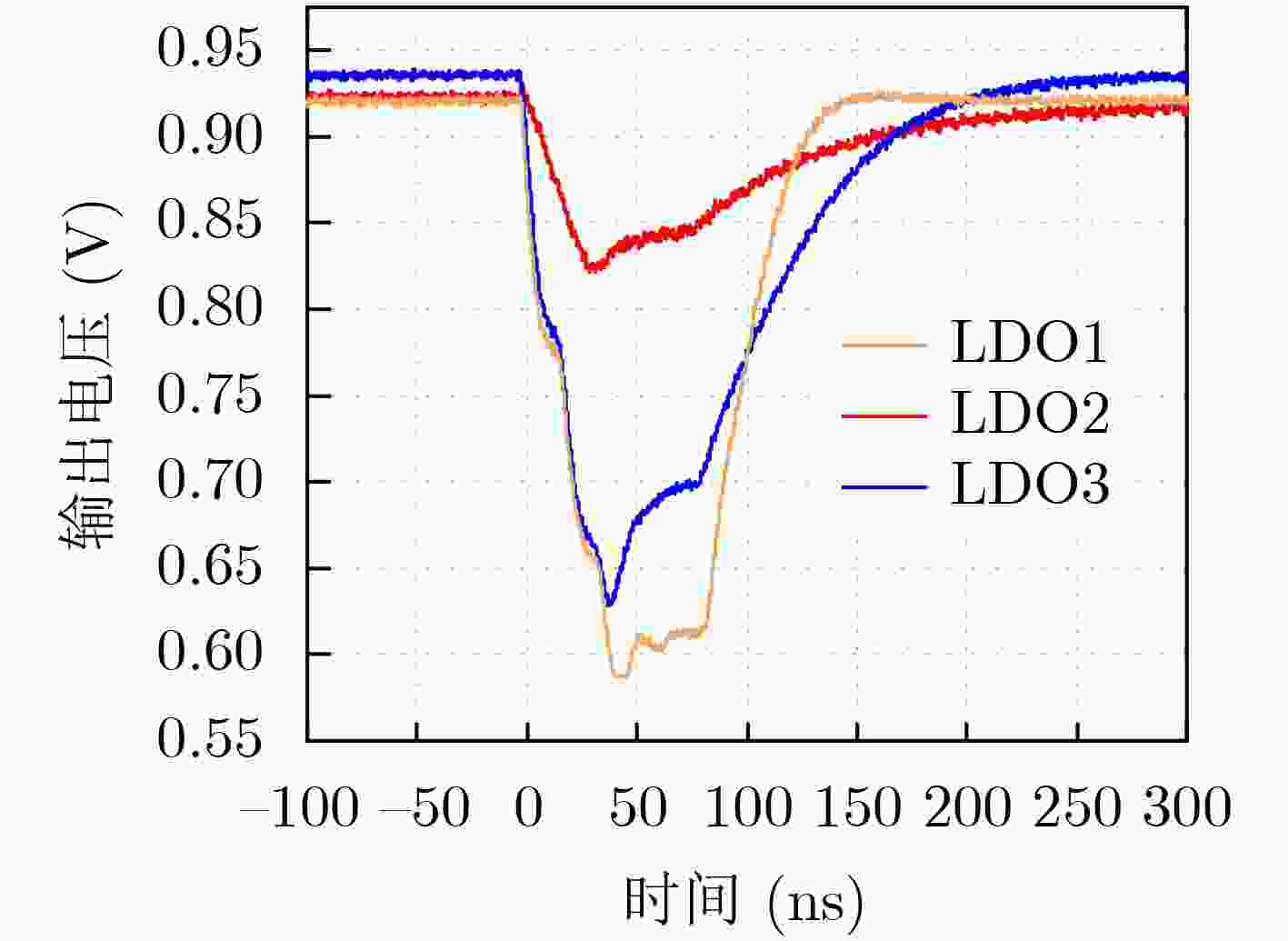
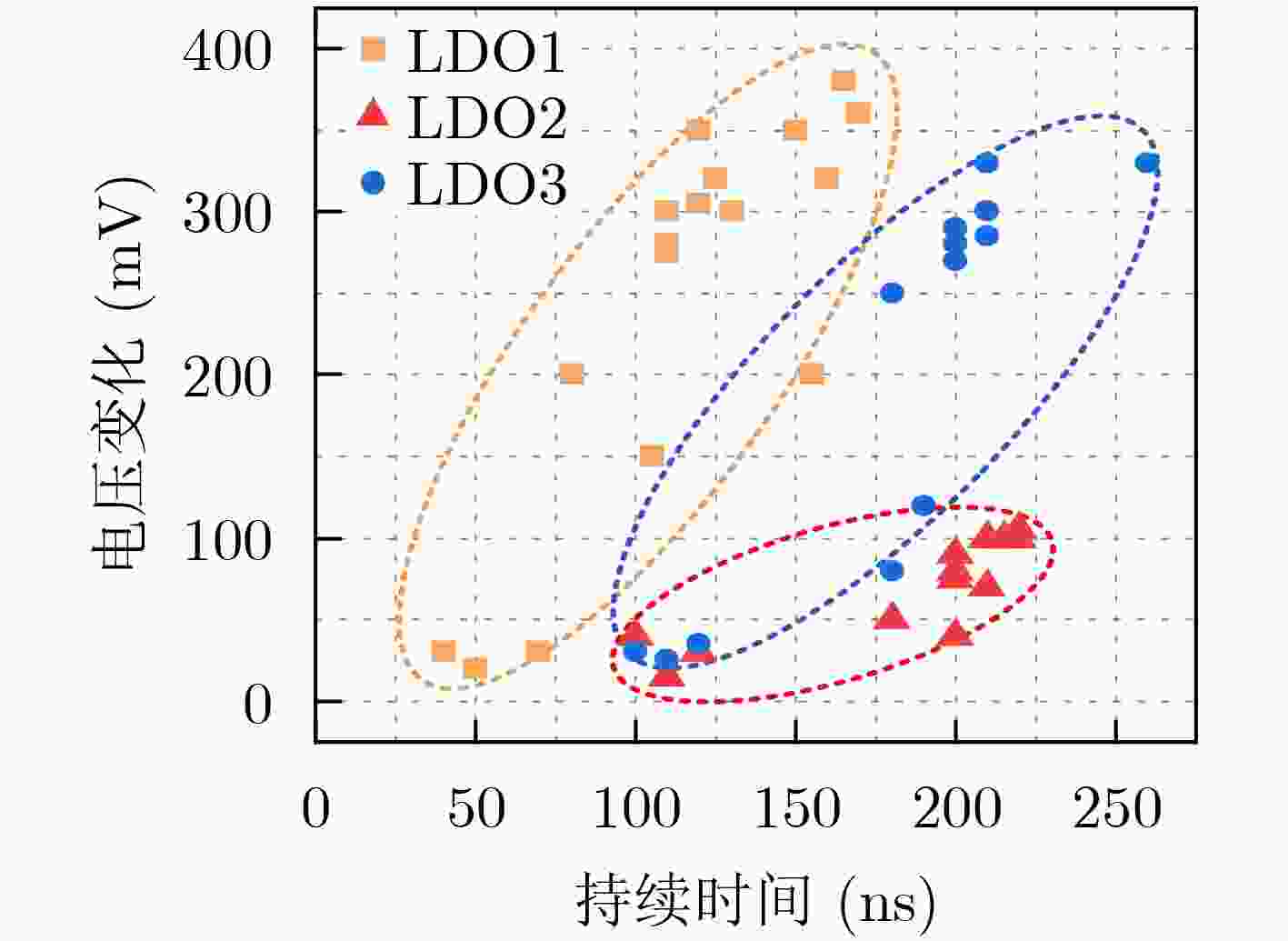
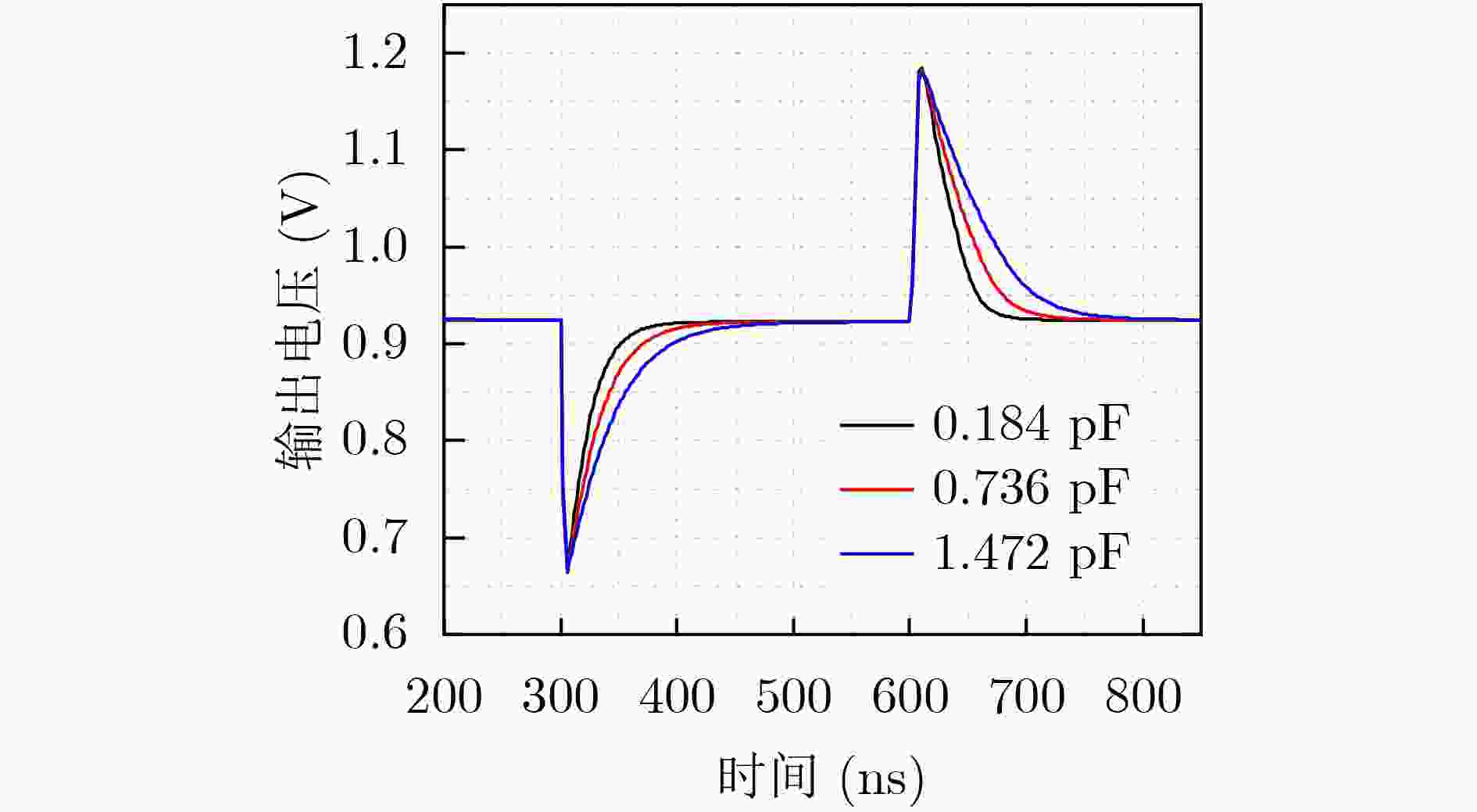
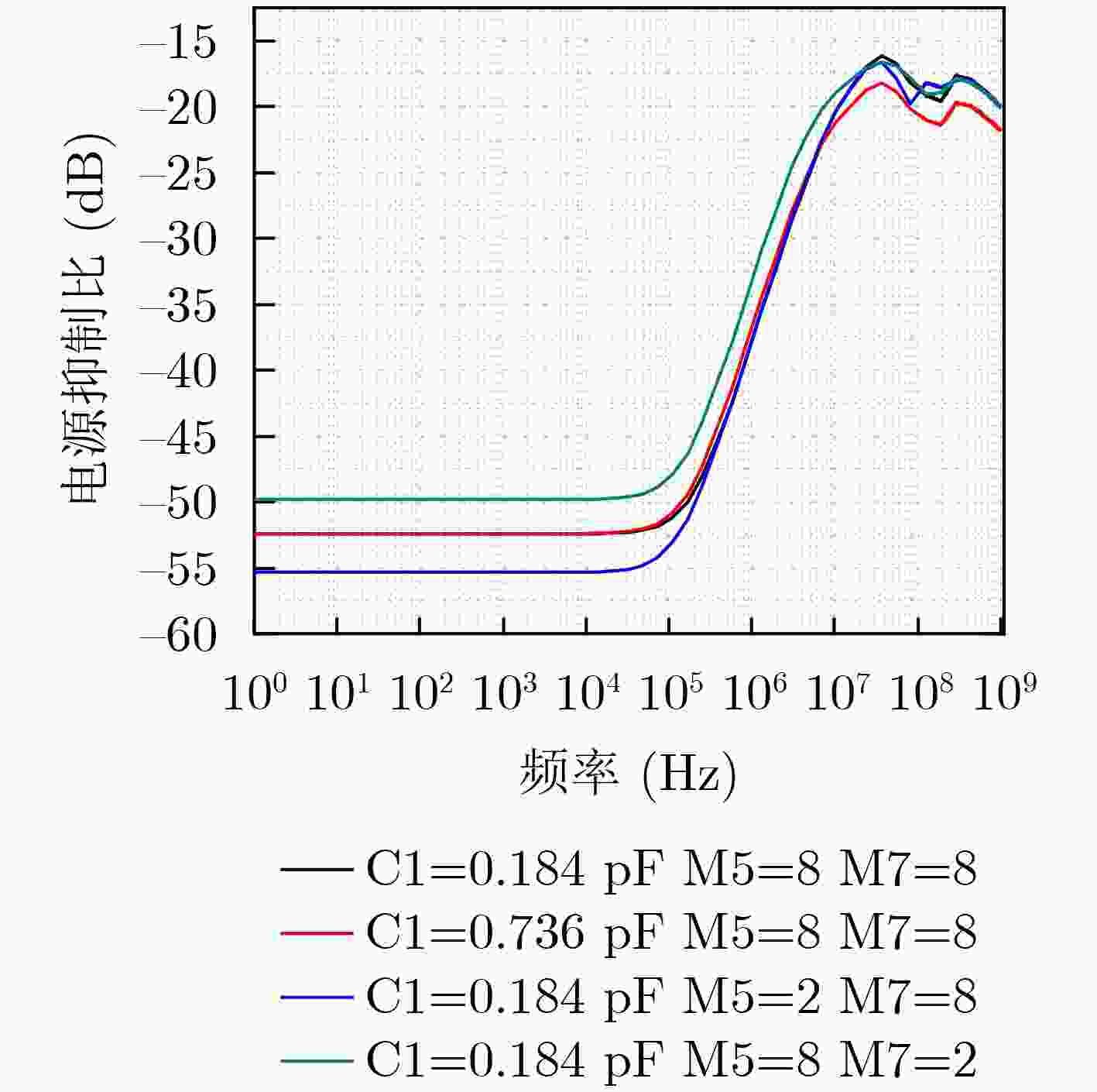


 下载:
下载:
