Robust Power Allocation for Multi-LED Integrated Visible Light Positioning and Communication
-
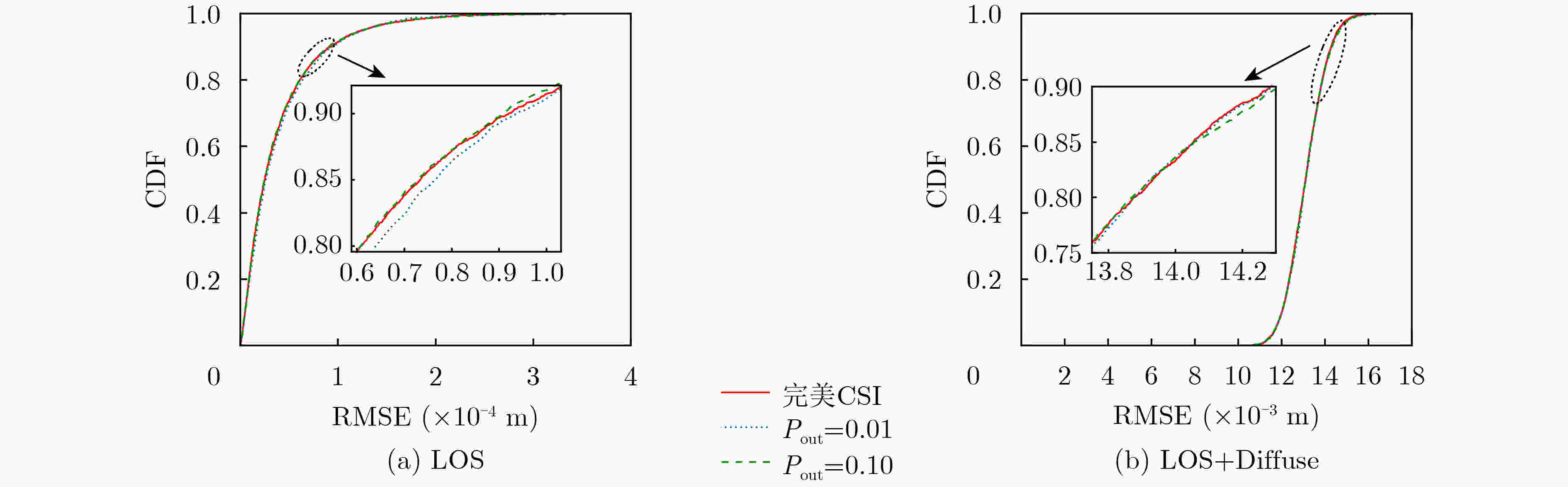
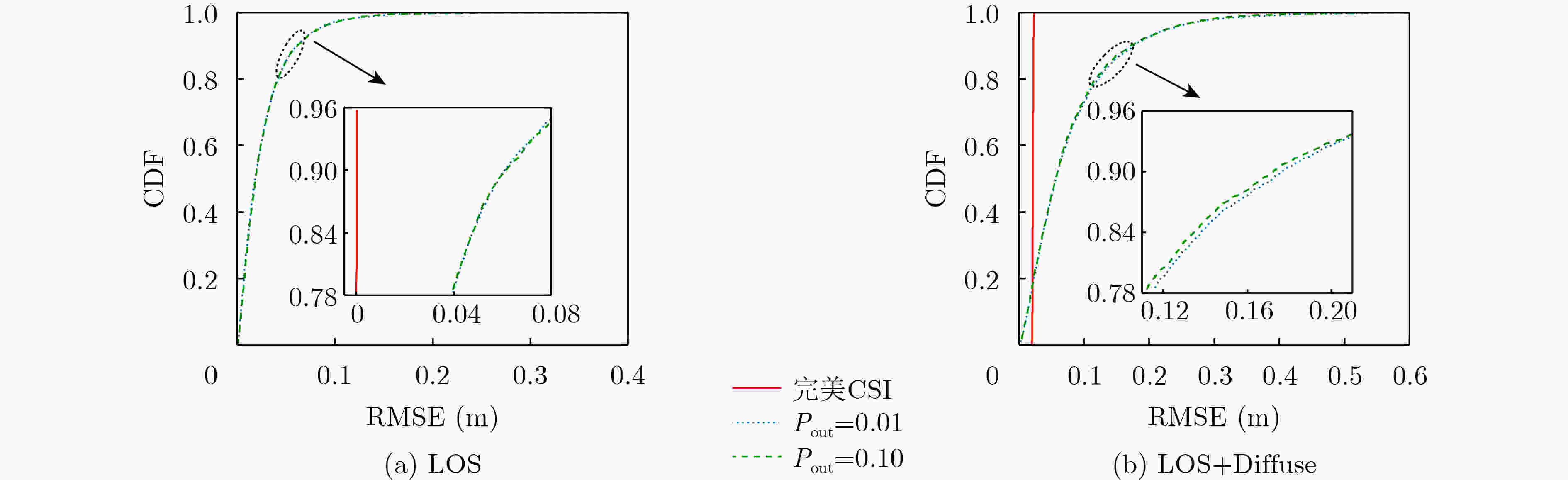
摘要: 为了实现可见光定位(VLP)与可见光通信(VLC)一体化信号传输,保证稳健通信和有效定位,该文提出一种基于频分复用(FDM)的可见光定位通信一体化(VLPC)信号传输方案,并设计了一种多LED VLPC稳健功率分配方案。首先提出了一种基于频分复用的VLPC传输方案,实现两种信号一体化传输,频谱资源独立分配,从而降低传输时延,提高定位实时性;然后基于定位结果进行可见光信道估计,揭示了信道估计误差、通信速率与实际定位误差之间耦合关系与统计特性;更进一步,基于所得到的耦合关系,研究了多LED VLPC联合功率分配问题,从而最小化定位误差克拉默-拉奥下界(CRLB),并满足功率约束和通信速率中断概率约束,并利用半正定松弛、最差情况条件风险值和连续凸近似等方法,将难以求解的非凸问题转化为一系列凸半正定规划问题进行迭代求解,并获得高质量可行解;最后,经过数值仿真验证,所提出的方案能够同时实现稳健通信和有效定位。稳健传输速率超过350 Mbit/s,并且当最小速率门限为200 Mbit/s,最大中断概率门限为0.01时,在直射路径加散射路径场景中,可以实现厘米级定位。Abstract: In order to integrate signals of the Visible Light Positioning (VLP) and Visible Light Communication (VLC), a Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) based signal structure and a robust power allocation scheme for the multi-LED integrated Visible Light Position and Communication (VLPC) system are proposed. Firstly, an FDM-based VLPC signal structure is designed to carry two signals simultaneously with independent spectrum resource allocation, which can reduce transmission delay and improve real-time positioning. Then, the channel estimation based on positioning results is investigated, and the coupling relationship and statistical feature between the channel estimation error and positioning error are revealed. Furthermore, a VLPC robust power allocation problem is proposed to minimize the Cramér-Rao Lower Bound(CRLB) of the VLP under the power constraints and outage chance constraint of the communication rate. This nonconvex problem is transformed into a series of iterative convex semidefinite programming subproblems through semidefinite relaxation, worst-case conditional value-at-risk, and successive convex approximation. Finally, from the simulation results, it is verified that the proposed scheme can simultaneously achieve robust communication and effective positioning. The robust achievable rate exceeds 350 Mbit/s, and the centimeter-level positioning can still be achieved when the minimum rate requirement is 200 Mbit/s, and the maximum tolerable outage probability is 0.01.
-
算法 1 基于CVaR和SCA的多LED VLPC稳健功率分配方法 输入:迭代终止条件$ ϵ\ge 0 $,速率门限$r$和中断概率${P_{{\text{out}}}}$,选择功率分配$ {\mathbf{P}}_{\text{p}}^{\left( 0 \right)} $和${\mathbf{W}}_{\text{c}}^{\left( 0 \right)}$,$k = 0$; (1) 令$k = k + 1$, $ {{\mathbf{p}}_{{\text{p}},0}} = {\mathbf{P}}_{\text{p}}^{\left( {k - 1} \right)} $, ${{\mathbf{W}}_{{\text{c,0}}}} = {\mathbf{W}}_{\text{c}}^{\left( {k - 1} \right)}$,求解问题式(28),得到最优解$ {\mathbf{P}}_{\text{p}}^{\left( k \right)} $和${\mathbf{W}}_{\text{c}}^{\left( k \right)}$; (2) 如果$\left|\text{Tr}\left({{\boldsymbol{J}}}_{{\boldsymbol{u}}}^{-1}\left({{\boldsymbol{P}}}_{\text{p} }^{\left(k\right)}\right)\right)-\text{Tr}\left({{\boldsymbol{J}}}_{{\boldsymbol{u}}}^{-1}\left({{\boldsymbol{P}}}_{\text{p} }^{\left(k-1\right)}\right)\right)\right|\le \epsilon$,则循环结束,否则返回步骤(1); 输出:最优功率分配${{\mathbf{w}}_{\text{c}}}$与${{\mathbf{P}}_{\text{p}}}$。 表 1 仿真参数
视场角ψFOV 半功率角φ1/2 PD物理面积AR 光学前端增益${\eta _{\rm{l}} },{\eta _{\text{c} } }$ 通信信号带宽Bc 定位信号长度Tp 噪声功率谱密度N0 180° 60° 1 cm2 1 40 MHz 0.1 μs 1.336×10–22 A2/Hz -
[1] IMT-2030(6G)推进组. 6G典型场景和关键能力[R]. 2022.IMT-2030(6G) Promotion Group. 6G typical scenarios and key capabilities[R]. 2022. [2] SAAD W, BENNIS M, and CHEN Mingzhe. A vision of 6G wireless systems: Applications, trends, technologies, and open research problems[J]. IEEE Network, 2020, 34(3): 134–142. doi: 10.1109/MNET.001.1900287. [3] 全球6G技术大会. 通感一体化系统架构与关键技术[R]. 2023.Global 6G Conference. System arrchitecture and key technologies of integrated sensing and communication[R]. 2023. [4] MATHEUS L E M, VIEIRA A B, VIEIRA L F M, et al. Visible light communication: Concepts, applications and challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys &Tutorials, 2019, 21(4): 3204–3237. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2019.2913348. [5] MEMEDI A and DRESSLER F. Vehicular visible light communications: A survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys &Tutorials, 2021, 23(1): 161–181. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2020.3034224. [6] KOMINE T and NAKAGAWA M. Fundamental analysis for visible-light communication system using LED lights[J]. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 2004, 50(1): 100–107. doi: 10.1109/TCE.2004.1277847. [7] LI Doupeng, GONG Chen, and XU Zhengyuan. A RSSI-based indoor visible light positioning approach[C]. 2016 10th International Symposium on Communication Systems, Networks and Digital Signal Processing, Prague, Czech Republic, 2016, [8] STEENDAM H, WANG T Q, and ARMSTRONG J. Theoretical lower bound for indoor visible light positioning using received signal strength measurements and an aperture-based receiver[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2017, 35(2): 309–319. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2016.2645603. [9] LIN Bangjiang, TANG Xuan, GHASSEMLOOY Z, et al. Experimental demonstration of an indoor VLC positioning system based on OFDMA[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2017, 9(2): 7902209. doi: 10.1109/JPHOT.2017.2672038. [10] XU Yitong, WANG Zixiong, LIU Peixi, et al. Accuracy analysis and improvement of visible light positioning based on VLC system using orthogonal frequency division multiple access[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(26): 32618–32630. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.032618. [11] YANG Helin, CHEN Chen, ZHONG Wende, et al. Demonstration of a quasi-gapless integrated visible light communication and positioning system[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2018, 30(23): 2001–2004. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2018.2874311. [12] CHEN Danyang, FAN Kai, WANG Jianping, et al. Integrated visible light communication and positioning CDMA system employing modified ZCZ and Walsh code[J]. Optics Express, 2022, 30(22): 40455–40469. doi: 10.1364/OE.474687. [13] SHI Lina, BÉCHADERGUE B, CHASSAGNE L, et al. Joint visible light sensing and communication using m-CAP modulation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting, 2023, 69(1): 276–288. doi: 10.1109/TBC.2022.3201649. [14] JIN Jianli, LU Huimin, WANG Jianping, et al. Adaptive feedback threshold based demodulation for mobile visible light communication and positioning integrated system[J]. Optics Express, 2022, 30(8): 13331–13344. doi: 10.1364/OE.456076. [15] YANG Helin, ZHONG Wende, CHEN Chen, et al. QoS-driven optimized design-based integrated visible light communication and positioning for indoor IoT networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(1): 269–283. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2951396. [16] YANG Helin, ZHONG Wende, CHEN Chen, et al. Coordinated resource allocation-based integrated visible light communication and positioning systems for indoor IoT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(7): 4671–4684. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.2986109. [17] YANG Helin, DU Pengfei, ZHONG Wende, et al. Reinforcement learning-based intelligent resource allocation for integrated VLCP systems[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2019, 8(4): 1204–1207. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2019.2911682. [18] 马帅, 李兵, 盛海鸿, 等. 基于深度强化学习的可见光定位通信一体化功率分配研究[J]. 通信学报, 2022, 43(8): 121–130. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2022163.MA Shuai, LI Bing, SHENG Haihong, et al. Research on power allocation of integrated VLPC based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. Journal on Communications, 2022, 43(8): 121–130. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2022163. [19] MA Shuai, YANG Ruixin, LI Bing, et al. Optimal power allocation for integrated visible light positioning and communication system with a single LED-lamp[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2022, 70(10): 6734–6747. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2022.3204659. [20] KAHN J M and BARRY J R. Wireless infrared communications[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1997, 85(2): 265–298. doi: 10.1109/5.554222. [21] FATH T and HAAS H. Performance comparison of MIMO techniques for optical wireless communications in indoor environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2013, 61(2): 733–742. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2012.120512.110578. [22] WANG T Q, SEKERCIOGLU Y A, and ARMSTRONG J. Analysis of an optical wireless receiver using a hemispherical lens with application in MIMO visible light communications[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2013, 31(11): 1744–1754. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2013.2257685. [23] 马帅, 秦莉莉, 李兵, 等. 可见光与射频聚合系统稳健波束成形设计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(8): 2659–2665. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220142.MA Shuai, QIN Lili, LI Bing, et al. Robust beamforming design for aggregated visible light communication and radio frequency systems[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(8): 2659–2665. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220142. [24] PLETS D, ERYILDIRIM A, BASTIAENS S, et al. A performance comparison of different cost functions for RSS-based visible light positioning under the presence of reflections[C]. The 4th ACM Workshop on Visible Light Communication Systems, Snowbird, USA, 2017. [25] CENGIZ K. Comprehensive analysis on least-squares lateration for indoor positioning systems[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(4): 2842–2856. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3020888. [26] KAY S M, 罗鹏飞, 张文明, 刘忠, 等译. 统计信号处理基础——估计与检测理论(卷Ⅰ、卷Ⅱ合集)[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2014: 22–27.KAY S M, LUO Pengfei, ZHANG Wenming, LIU Zhong, et al. translation. Fundamentals of Statistical Signal Processing, Volume Ⅰ: Estimation Theory, Volume Ⅱ: Detection Theory[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2014: 22–27. [27] WANG Tao, LEUS G, and HUANG Li. Ranging energy optimization for robust sensor positioning based on semidefinite programming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(12): 4777–4787. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2009.2028211. [28] LOTTICI V, D'ANDREA A, and MENGALI U. Channel estimation for ultra-wideband communications[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2002, 20(9): 1638–1645. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2002.805053. [29] KESKIN M F, SEZER A D, and GEZICI S. Optimal and robust power allocation for visible light positioning systems under illumination constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2019, 67(1): 527–542. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2018.2866849. [30] ZYMLER S, KUHN D, and RUSTEM B. Distributionally robust joint chance constraints with second-order moment information[J]. Mathematical Programming, 2013, 137(1/2): 167–198. doi: 10.1007/s10107-011-0494-7. [31] ZHANG Yu, LI Bin, GAO Feifei, et al. A robust design for ultra reliable ambient backscatter communication systems[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(5): 8989–8999. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2925843. [32] LUO Zhiquan, MA W K, SO A M C, et al. Semidefinite relaxation of quadratic optimization problems[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2010, 27(3): 20–34. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2010.936019. [33] GRANT M and BOYD S. CVX: Matlab software for disciplined convex programming, version 2.2[EB/OL]. http://cvxr.com/cvx, 2020. [34] ZHOU Rui and PALOMAR D P. Solving high-order portfolios via successive convex approximation algorithms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2021, 69: 892–904. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2021.3051369. [35] JUNGNICKEL V, POHL V, NONNIG S, et al. A physical model of the wireless infrared communication channel[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2002, 20(3): 631–640. doi: 10.1109/49.995522. [36] MA Shuai, LI Hang, HE Yang, et al. Capacity bounds and interference management for interference channel in visible light communication networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(1): 182–193. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2018.2878585. -





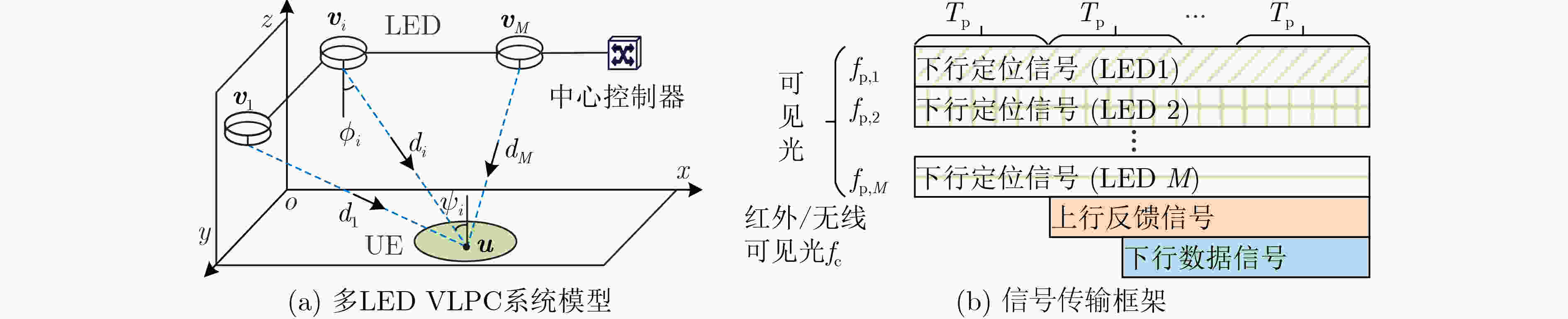
 下载:
下载:
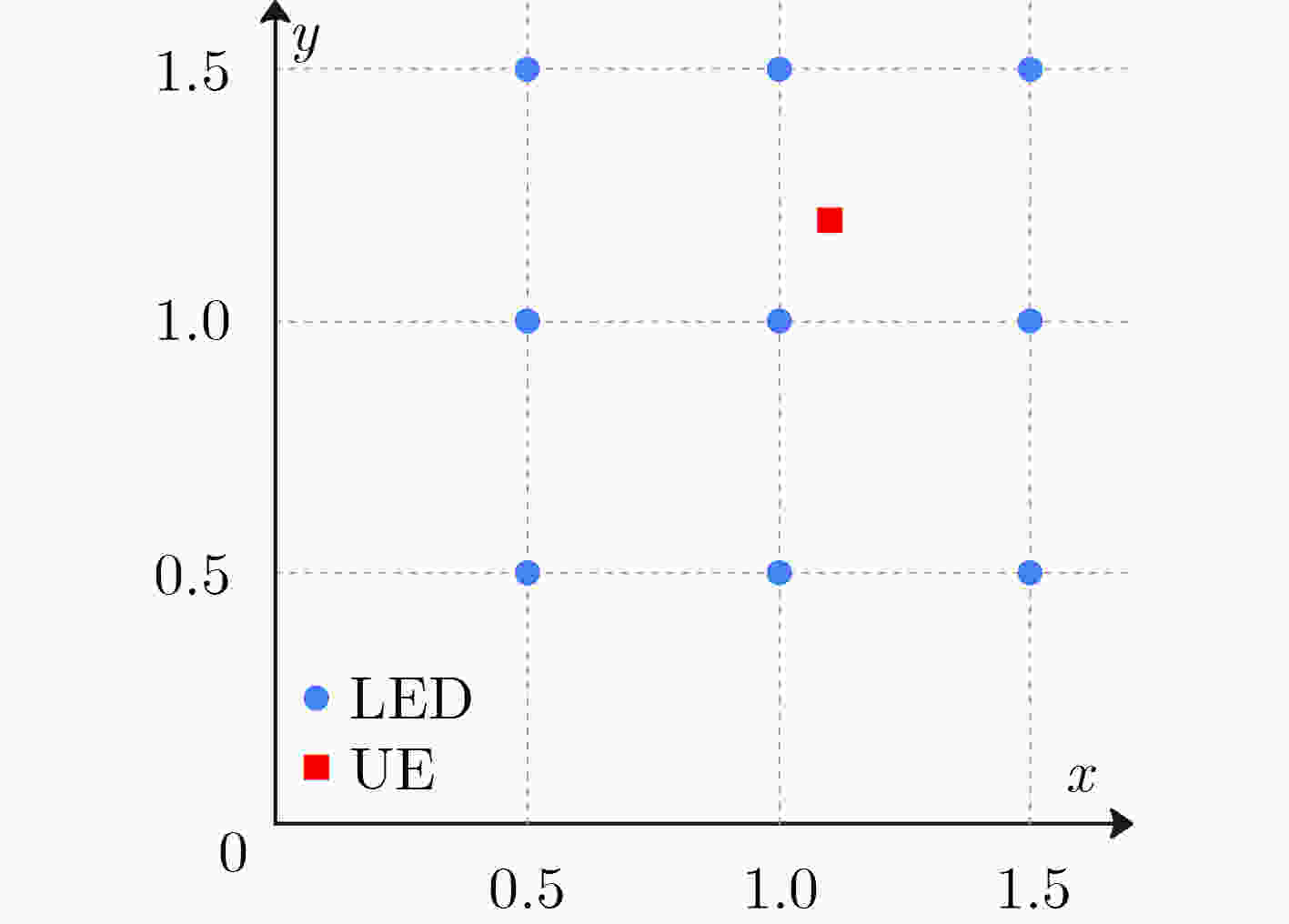
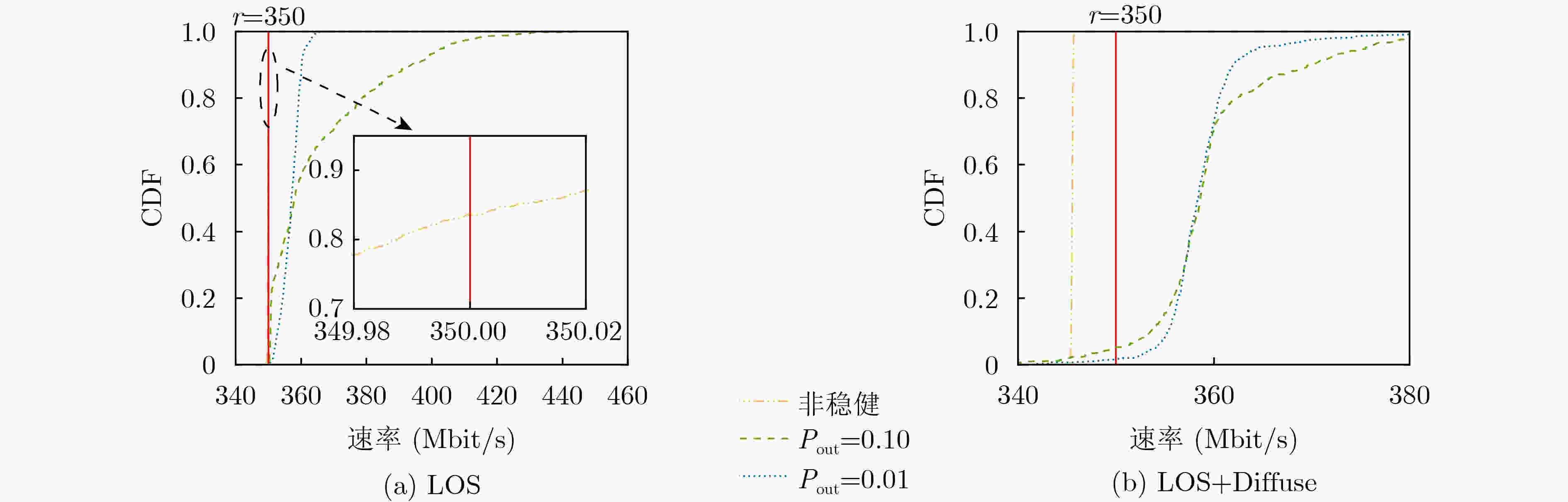
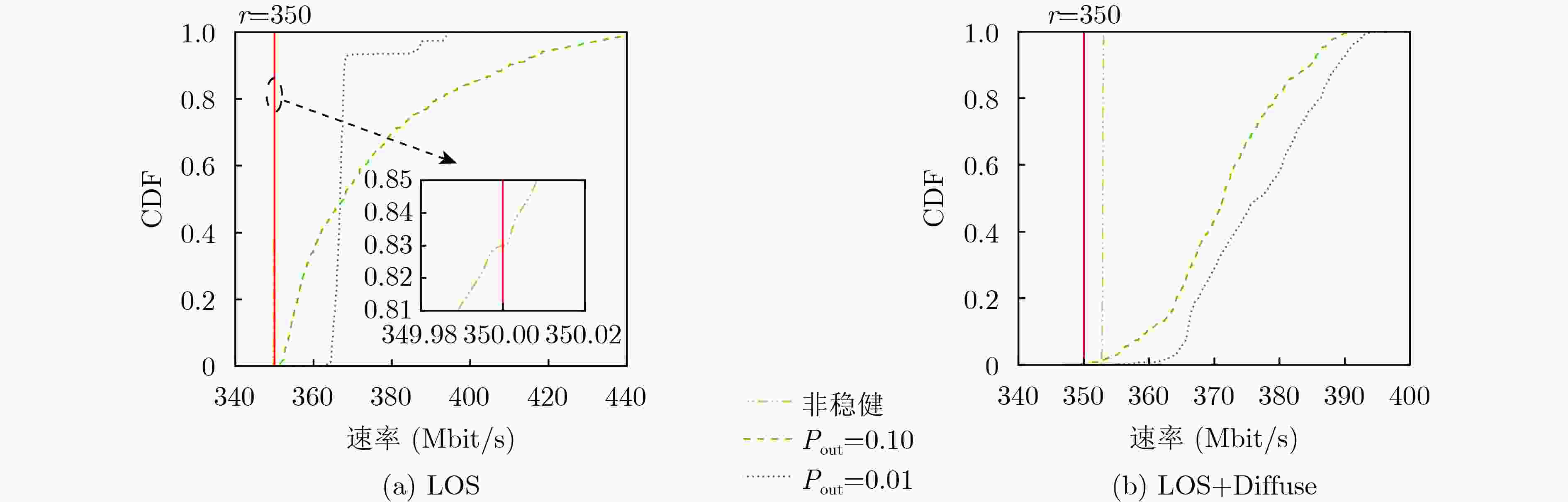


 下载:
下载:
