3D Model Classification Based on Shannon Entropy Representative Feature and Voting Mechanism
-
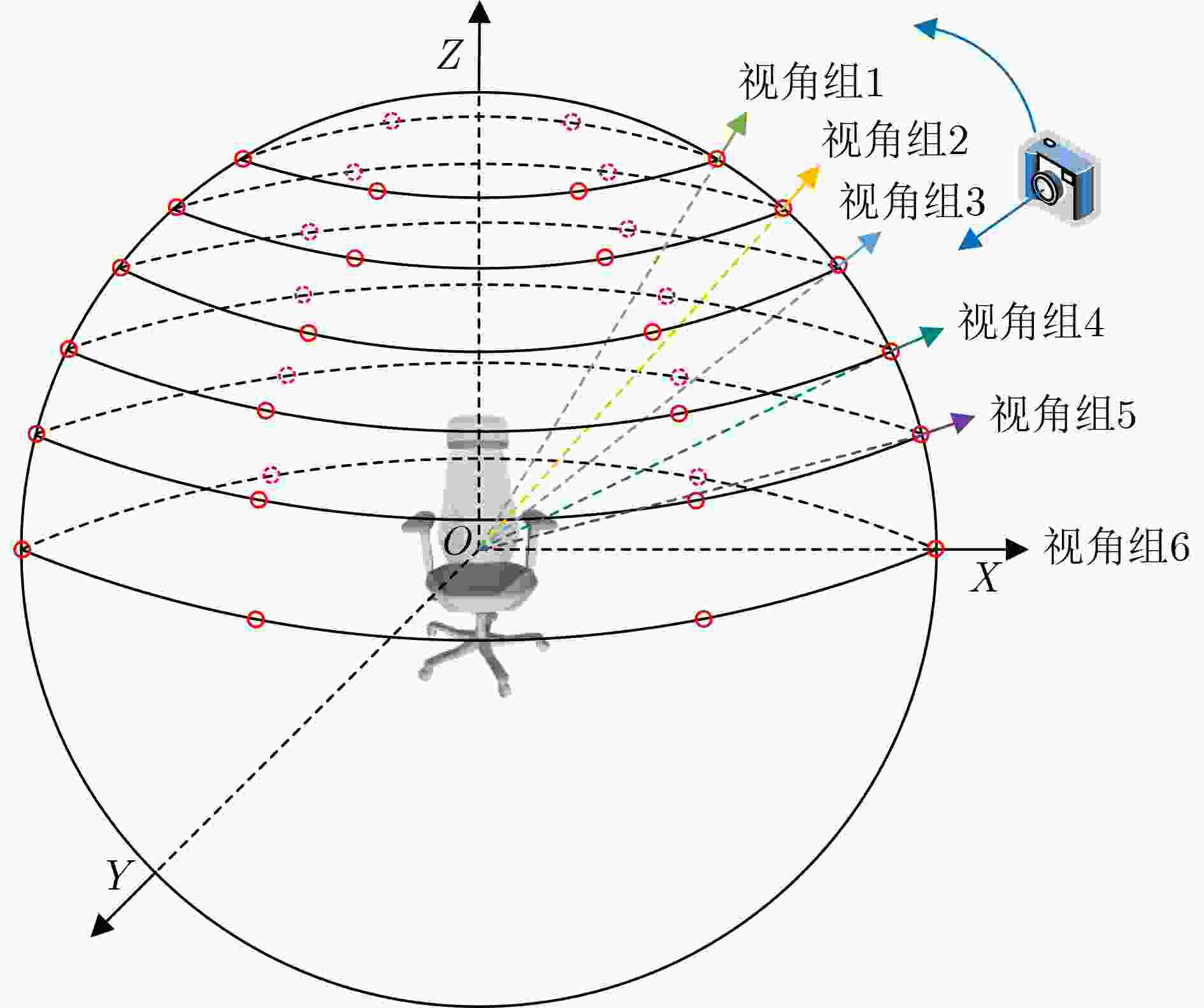
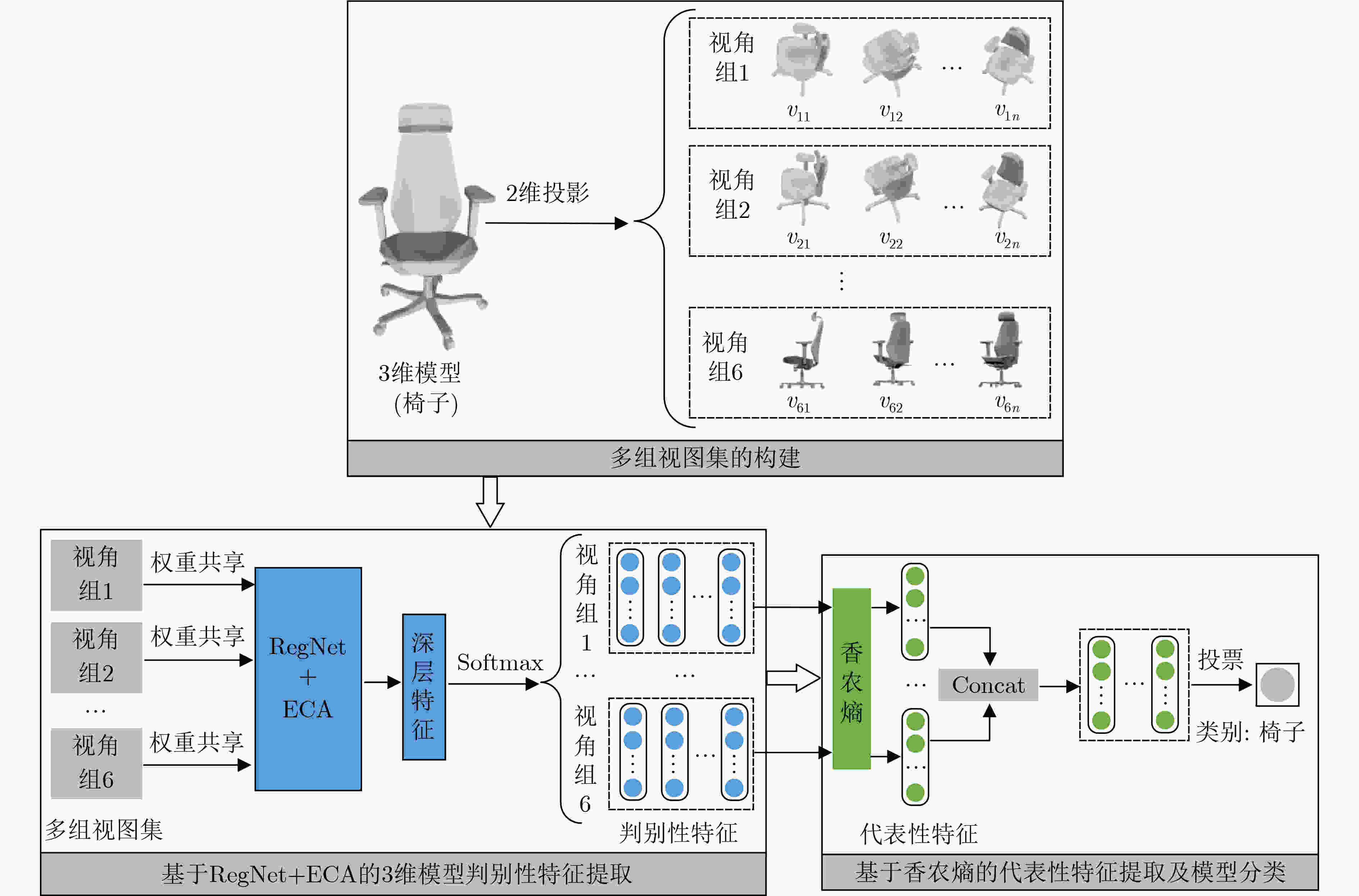
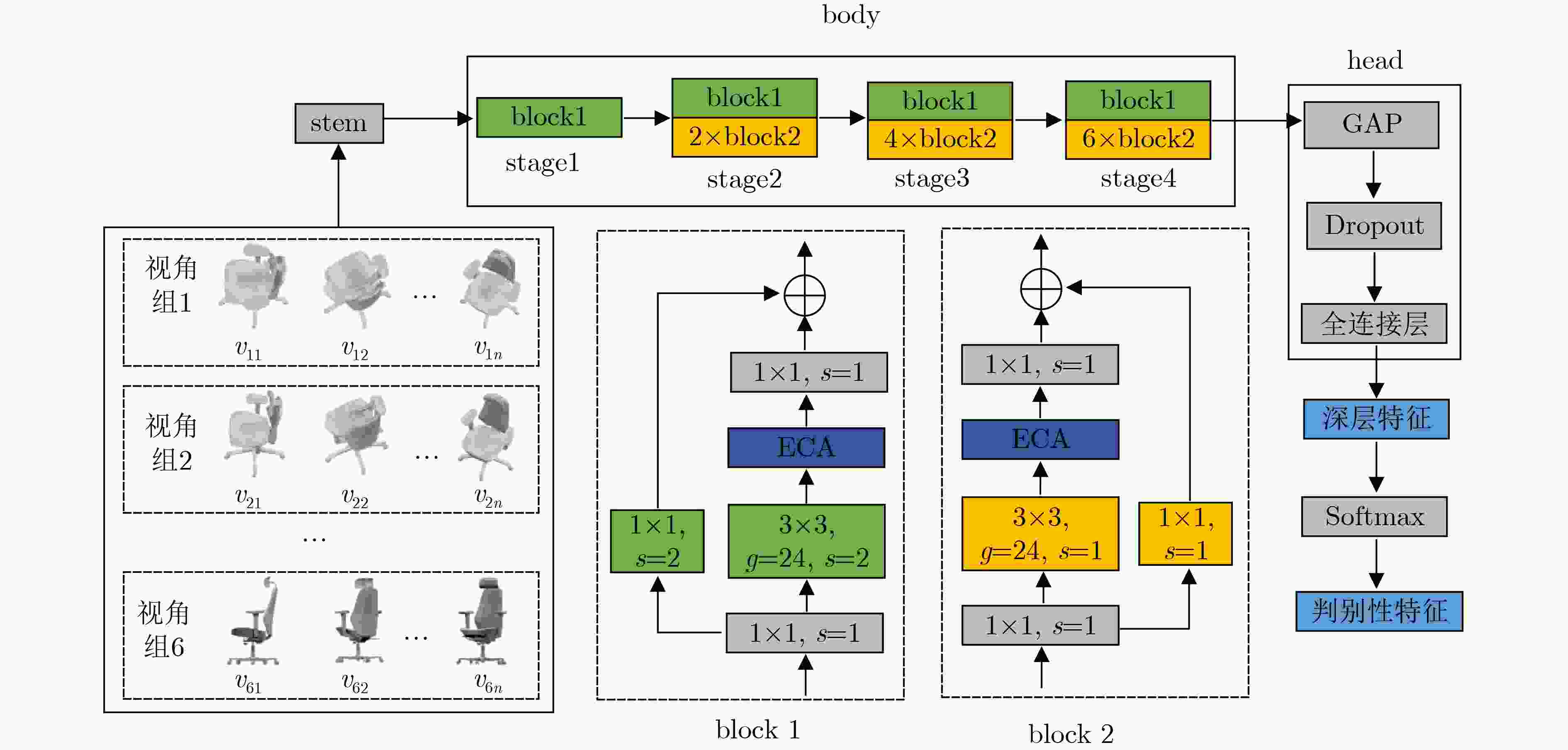
摘要: 目前基于视图的3维模型分类方法存在单视图视觉信息不充分、多视图信息冗余的问题,且同等对待所有视图会忽略不同投影视角之间的差异性。针对上述问题,该文提出一种基于香农熵代表性特征和投票机制的3维模型分类方法。首先,通过在3维模型周围均匀设置多个视角组来获取表征模型的多组视图集。为了有效提取视图深层特征,在特征提取网络中引入通道注意力机制;然后,针对Softmax函数输出的视图判别性特征,使用香农熵来选择代表性特征,从而避免多视图特征冗余;最后,基于多个视角组的代表性特征利用投票机制来完成3维模型分类。实验表明:该方法在3维模型数据集ModelNet10上的分类准确率达到96.48%,分类性能突出。Abstract: At present, view-based 3D model classification has the problems of insufficient visual information for single view and redundant information for multiple views, and treating all views equally will ignore the differences between different projection angles. To solve the above problems, a 3D model classification method based on Shannon entropy representative feature and voting mechanism is proposed. Firstly, multiple angle groups are set uniformly around 3D model, and multiple view sets representing the model are obtained. In order to extract effectively deep features from view, channel attention mechanism is introduced into the feature extraction network. Secondly, based on view discriminative features output from Softmax function, Shannon entropy is used to select representative feature for avoiding redundant feature of multiple views. Finally, based on representative features from multiple angle groups, voting mechanism is used to classify 3D model. Experiments show that the classification accuracy of the proposed method on 3D model dataset ModelNet10 reaches 96.48%, and classification performance is outstanding.
-
表 1 不同视图数目下的分类准确率(%)
网络模型 投票算法 3V 6V 9V 12V 18V RegNet HV 94.05 93.83 93.98 94.82 94.27 SV 94.05 94.60 94.27 94.71 94.60 表 2 不同RegNet网络的分类准确率(%)
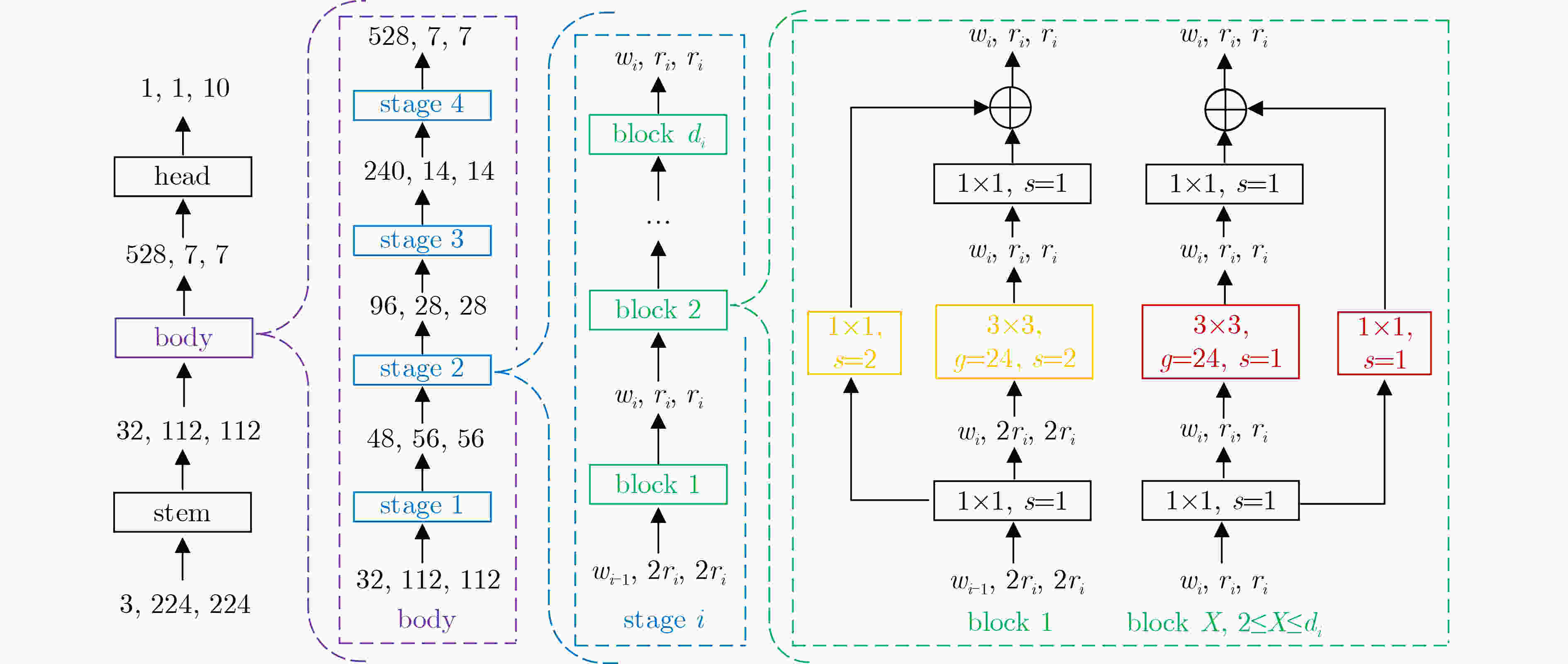
RegNet模型 stage1 stage2 stage3 stage4 flops(B) params(M) HV SV RegNet2X 1×block 1×block 4×block 7×block 0.2 2.7 92.51 93.83 RegNet4X 1×block 2×block 7×block 12×block 0.4 5.2 93.50 94.16 RegNet6X 1×block 3×block 5×block 7×block 0.6 6.2 93.83 94.60 RegNet8X 1×block 3×block 7×block 5×block 0.8 7.3 94.16 94.71 表 3 ECA不同嵌入位置对RegNet分类的影响(%)
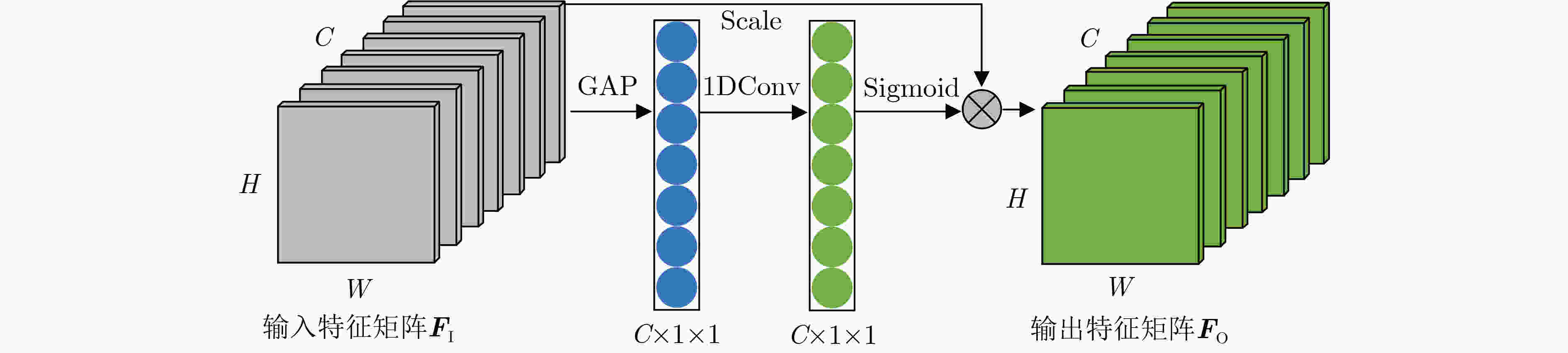
投票算法 ECA1 ECA2 ECA3 ECA4 HV 93.72 93.72 93.94 94.05 SV 94.60 94.49 95.26 94.60 表 4 ECA对RegNet分类的影响(%)
网络模型 投票算法 视角1 视角2 视角3 视角4 视角5 视角6 RegNet HV 92.51 92.95 93.06 93.83 94.05 88.66 SV 93.06 93.94 94.05 94.60 94.49 89.43 RegNet+ECA HV 93.28 94.27 93.39 93.94 94.05 88.88 SV 93.72 94.71 94.93 95.26 95.04 90.42 表 5 多视角代表性特征的对比(%)
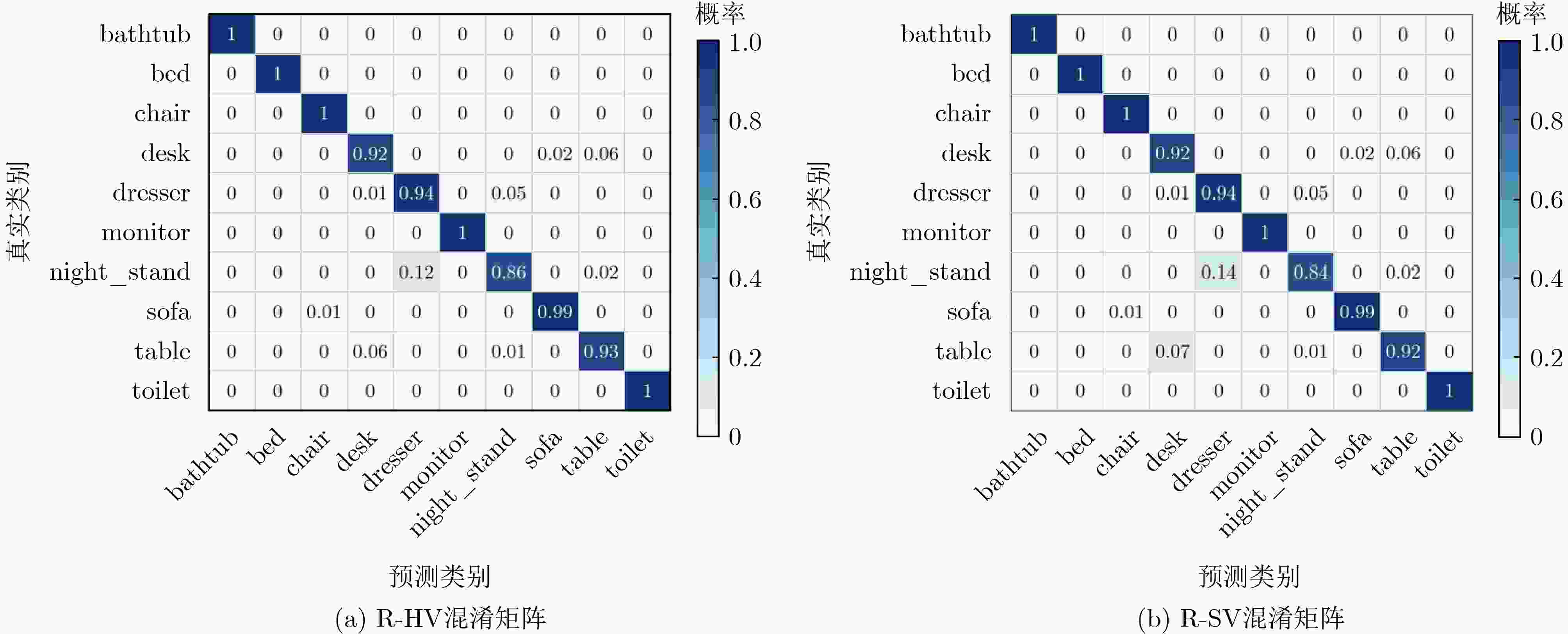
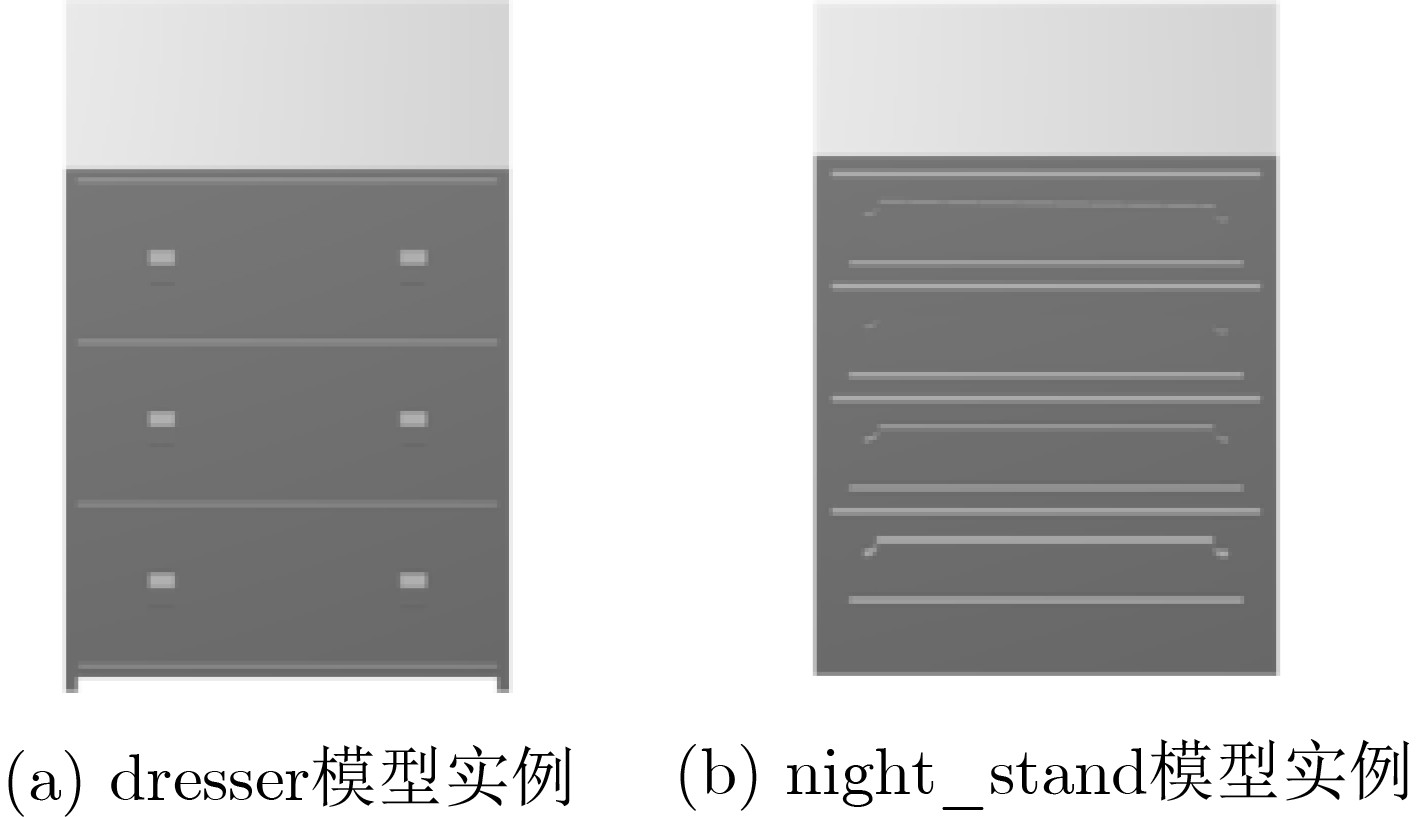
类别 视角1 视角2 视角3 视角4 视角5 视角6 R-SV R-HV bathtub 92.00 98.00 98.00 100.00 96.00 88.00 100.00 100.00 bed 99.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 97.00 100.00 100.00 chair 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 97.00 100.00 100.00 desk 91.86 88.37 89.53 86.05 91.86 75.58 91.86 91.86 dresser 83.72 91.86 95.35 94.19 89.53 87.21 94.19 94.19 monitor 100 99.00 100.00 100.00 99.00 99.00 100.00 100.00 night_stand 89.53 82.56 79.07 82.56 88.37 72.09 83.72 86.05 sofa 99.00 98.00 98.00 99.00 98.00 96.00 99.00 99.00 table 92.00 91.00 85.00 87.00 88.00 87.00 92.00 93.00 toilet 96.00 99.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 平均准确率 94.71 94.93 94.60 94.93 95.26 90.53 96.15 96.48 -
[1] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2017, 60(6): 84–90. doi: 10.1145/3065386. [2] SZEGEDY C, LIU Wei, JIA Yangqing, et al. Going deeper with convolutions[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, USA, 2015: 1–9. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298594. [3] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90. [4] CHARLES R Q, SU Hao, MO Kaichun, et al. PointNet: Deep learning on point sets for 3D classification and segmentation[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 77–85. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.16. [5] QI C R, YI Li, SU Hao, et al. PointNet++: Deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space[C]. Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 5105–5114. [6] SONG Yupeng, HE Fazhi, DUAN Yansong, et al. A kernel correlation-based approach to adaptively acquire local features for learning 3D point clouds[J]. Computer-Aided Design, 2022, 146: 103196. doi: 10.1016/j.cad.2022.103196. [7] 张溯, 杨军. 利用空间结构信息的三维点云模型分类[J]. 小型微型计算机系统, 2021, 42(4): 779–784. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1220.2021.04.018.ZHANG Su and YANG Jun. 3D model classification using spatial structure information[J]. Journal of Chinese Computer Systems, 2021, 42(4): 779–784. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1220.2021.04.018. [8] HASSAN R, FRAZ M M, RAJPUT A, et al. Residual learning with annularly convolutional neural networks for classification and segmentation of 3D point clouds[J]. Neurocomputing, 2023, 526: 96–108. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2023.01.026. [9] ZHOU Ruqin, LI Xixing, and JIANG Wanshou. SCANet: A spatial and channel attention based network for partial-to-partial point cloud registration[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2021, 151: 120–126. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2021.08.002. [10] WU Zhirong, SONG Shuran, KHOSLA A, et al. 3D ShapeNets: A deep representation for volumetric shapes[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, USA, 2015: 1912–1920. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298801. [11] XU Xu and TODOROVIC S. Beam search for learning a deep convolutional neural network of 3D shapes[C]. 2016 23rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Cancun, Mexico, 2016: 3506–3511. doi: 10.1109/ICPR.2016.7900177. [12] KIM S, CHI H G, and RAMANI K. Object synthesis by learning part geometry with surface and volumetric representations[J]. Computer-Aided Design, 2021, 130: 102932. doi: 10.1016/j.cad.2020.102932. [13] MA Ziping, ZHOU Jie, MA Jinlin, et al. A novel 3D shape recognition method based on double-channel attention residual network[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2022, 81(22): 32519–32548. doi: 10.1007/s11042-022-12041-9. [14] CAI Weiwei, LIU Dong, NING Xin, et al. Voxel-based three-view hybrid parallel network for 3D object classification[J]. Displays, 2021, 69: 102076. doi: 10.1016/j.displa.2021.102076. [15] HE Yunqian, XIA Guihua, LUO Yongkang, et al. DVFENet: Dual-branch voxel feature extraction network for 3D object detection[J]. Neurocomputing, 2021, 459: 201–211. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.06.046. [16] SHI Baoguang, BAI Song, ZHOU Zhichao, et al. DeepPano: Deep panoramic representation for 3-D shape recognition[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2015, 22(12): 2339–2343. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2015.2480802. [17] SINHA A, BAI Jing, and RAMANI K. Deep learning 3D shape surfaces using geometry images[C]. The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 223–240. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46466-4_14. [18] SU Hang, MAJI S, KALOGERAKIS E, et al. Multi-view convolutional neural networks for 3D shape recognition[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 2015: 945–953. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2015.114. [19] LIANG Qi, WANG Yixin, NIE Weizhi, et al. MVCLN: Multi-view convolutional LSTM network for cross-media 3D shape recognition[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 139792–139802. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3012692. [20] 白静, 司庆龙, 秦飞巍. 基于卷积神经网络和投票机制的三维模型分类与检索[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2019, 31(2): 303–314. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1089.2019.17160.BAI Jing, SI Qinglong, and QIN Feiwei. 3D model classification and retrieval based on CNN and voting scheme[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics, 2019, 31(2): 303–314. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1089.2019.17160. [21] HEGDE V and ZADEH R. FusionNet: 3D object classification using multiple data representations[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1607.05695, 2016. [22] JIN Xun and LI De. Rotation prediction based representative view locating framework for 3D object recognition[J]. Computer-Aided Design, 2022, 150: 103279. doi: 10.1016/j.cad.2022.103279. [23] ZHU Feng, XU Junyu, and YAO Chuanming. Local information fusion network for 3D shape classification and retrieval[J]. Image and Vision Computing, 2022, 121: 104405. doi: 10.1016/j.imavis.2022.104405. [24] RADOSAVOVIC I, KOSARAJU R P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Designing network design spaces[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2020: 10425–10433. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01044. [25] WANG Qilong, WU Banggu, ZHU Pengfei, et al. ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2020: 11531–11539. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01155. -





 下载:
下载:
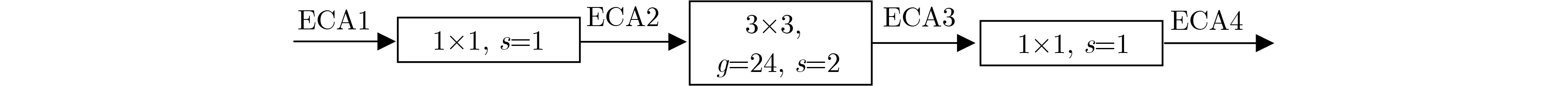


 下载:
下载:
