A Survey of Key Issues in Edge Intelligent Computing Under Cloud-Edge-Terminal Architecture: Computing Optimization and Computing Offloading
-
摘要: 近年来,随着入网设备数量与数据体量的急剧增加,以云计算为代表的中心式计算模式的缺点越来越显露出来。边缘计算,即让计算尽量靠近数据源,以减少数据传输时间和网络延迟,作为云计算的补充,已经成为学术界和工业界关注的焦点。该文面向边缘计算中应用较广的实例架构—云边端架构,以及边缘计算的典型应用—边缘智能计算,讨论云边端架构下边缘智能计算的两大关键问题:计算优化和计算卸载。首先分析和梳理了云边端架构下边缘智能计算优化的应用与研究现状。然后讨论了云边端架构下计算卸载的研究思路和现状。最后,总结提出了目前云边端架构下边缘智能计算业务所面临的挑战和未来研究趋势。Abstract: With the rapid increase in the number of network access devices and the volume of network access data currently, the shortcomings of the centralized computing architecture represented by cloud computing are increasingly exposed. Edge computing, that is making computing as close to the data source as possible to reduce data transmission time and network delay, has become the focus of academia and industry as a supplement to cloud computing. An instance architecture widely used in edge computing: Cloud-Edge-Terminal architecture, and a typical application of edge computing: edge intelligent computing is focused on in this paper. Two key issues of edge intelligent computing under Cloud-Edge-Terminal architecture: computing optimization and computing offloading is analyzed. First, the research focus of edge intelligent computing is analyzed, and the application and research status of intelligent computing optimization under Cloud-Edge-Terminal architecture is combed. Then the research ideas and current situation of computing offloading under Cloud-Edge-Terminal architecture is discussed. Finally, the challenges and research trends of edge intelligent computing under Cloud-Edge-Terminal architecture is summarized.
-
表 1 边缘智能计算框架对比
TensorFlow Lite PyTorch Mobile MindSpore Lite Paddle Lite 开发者 谷歌 Linux基金会 华为 百度 支持功能 推理 训练+推理 训练+推理 推理 支持的操作系统 Android
iOS
LinuxiOS
AndroidAndroid
iOS
OpenHarmony
Linux
WindowsAndroid
iOS
Linux
Windows
macOS -
[1] 工业和信息化部. 2022年通信业统计公报[EB/OL]. https://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2023-02/02/content_5739680.htm, 2023.Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of the People’s Republic of China. 2022 Communication industry Statistical Bulletin[EB/OL]. https://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2023-02/02/content_5739680.htm, 2023. [2] 刘俊旭, 孟小峰. 机器学习的隐私保护研究综述[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2020, 57(2): 346–362. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2020.20190455.LIU Junxu and MENG Xiaofeng. Survey on privacy-preserving machine learning[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2020, 57(2): 346–362. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2020.20190455. [3] XING Tong, BARBALACE A, OLIVIER P, et al. H-container: Enabling heterogeneous-ISA container migration in edge computing[J]. ACM Transactions on Computer Systems, 2021, 39(1/4): 5. doi: 10.1145/3524452. [4] CHEN Ying, ZHAO Fengjun, CHEN Xin, et al. Efficient multi-vehicle task offloading for mobile edge computing in 6G networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71(5): 4584–4595. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3133586. [5] LIU Chunyu, WANG Kailin, ZHANG Heli, et al. Rendered tile reuse scheme based on FoV prediction for MEC-assisted wireless VR service[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2023, 10(3): 1709–1721. doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2023.3234029. [6] HAZRA A, RANA P, ADHIKARI M, et al. Fog computing for next-generation internet of things: Fundamental, state-of-the-art and research challenges[J]. Computer Science Review, 2023, 48: 100549. doi: 10.1016/j.cosrev.2023.100549. [7] BHARANY S, SHARMA S, KHALAF O I, et al. A systematic survey on energy-efficient techniques in sustainable cloud computing[J]. Sustainability, 2022, 14(10): 6256. doi: 10.3390/su14106256. [8] DAMSGAARD H J, OMETOV A, and NURMI J. Approximation opportunities in edge computing hardware: A systematic literature review[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2023, 55(12): 252. doi: 10.1145/3572772. [9] SHI Weisong, CAO Jie, ZHANG Quan, et al. Edge computing: Vision and challenges[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2016, 3(5): 637–646. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2016.2579198. [10] 朱特浩. 边缘计算在军事信息系统智能化发展中的应用[J]. 火力与指挥控制, 2021, 46(8): 5–11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2021.08.002.ZHU Tehao. Analysis of the application of edge computing in the intelligent development of military information system[J]. Fire Control &Command Control, 2021, 46(8): 5–11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2021.08.002. [11] CONTRERAS L M, SOLANO A, CANO F, et al. Analysis of network function sharing in content delivery network-as-a-service slicing scenarios[J]. International Journal of Network Management, 2023, 33(4): e2221. doi: 10.1002/nem.2221. [12] KHAN L U, YAQOOB I, TRAN N H, et al. Edge-computing-enabled smart cities: A comprehensive survey[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(10): 10200–10232. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.2987070. [13] LIN Jie, YANG Peng, ZHANG Ning, et al. Low-latency edge video analytics for on-road perception of autonomous ground vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2023, 19(2): 1512–1523. doi: 10.1109/TII.2022.3181986. [14] 刘子杰, 王凯, 王亚刚, 等. 工业互联网端边云协同数据同步方案设计与实现[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2022, 39(3): 821–825. doi: 10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2021.09.0349.LIU Zijie, WANG Kai, WANG Yagang, et al. Design and implementation of end-to-end cloud collaborative data synchronization scheme for industrial Internet[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2022, 39(3): 821–825. doi: 10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2021.09.0349. [15] SHARMA V, TRIPATHI A K, and MITTAL H. Technological revolutions in smart farming: Current trends, challenges & future directions[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2022, 201: 107217. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2022.107217. [16] 周锦雯, 刘乃金, 陈清霞. 基于分布式深度学习的多星计算卸载策略[J]. 中国空间科学技术, 2023, 43(2): 73–80. doi: 10.16708/j.cnki.1000-758X.2023.0022.ZHOU Jinwen, LIU Naijin, and CHEN Qingxia. Multi-satellite task offloading method based on distributed deep learning[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2023, 43(2): 73–80. doi: 10.16708/j.cnki.1000-758X.2023.0022. [17] SUN Cjuan, LI Xiuhua, WEN Junhao, et al. Federated deep reinforcement learning for recommendation-enabled edge caching in mobile edge-cloud computing networks[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2023, 41(3): 690–705. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2023.3235443. [18] DENG Shuiguang, ZHAO Hailiang, FANG Weijia, et al. Edge intelligence: The confluence of edge computing and artificial intelligence[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(8): 7457–7469. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.2984887. [19] Clarivate. Document search - web of science core collection[EB/OL]. https://www.webofscience.com/wos/woscc/basic-search, 2023. [20] CHEN Jiasi and RAN Xukan. Deep learning with edge computing: A review[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2019, 107(8): 1655–1674. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2019.2921977. [21] ZHANG Jing and TAO Dacheng. Empowering things with intelligence: A survey of the progress, challenges, and opportunities in artificial intelligence of things[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(10): 7789–7817. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3039359. [22] 张晓东, 张朝昆, 赵继军. 边缘智能研究进展[J/OL]. 计算机研究与发展: 1–22. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1777.tp.20230310.1731.006.html, 2023.ZHANG Xiaodong, ZHANG Chaokun, and ZHAO Jijun. State-of-the-art survey on edge intelligence[J/OL]. Journal of Computer Research and Development: 1–22. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1777.tp.20230310.1731.006.html, 2023. [23] ZHOU Zhi, CHEN Xu, LI En, et al. Edge intelligence: Paving the last mile of artificial intelligence with edge computing[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2019, 107(8): 1738–1762. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2019.2918951. [24] HU Haizhou and JIANG Congfeng. Edge intelligence: Challenges and opportunities[C]. 2020 International Conference on Computer, Information and Telecommunication Systems (CITS), Hangzhou, China, 2020: 1–5. [25] XU Dianlei, LI Tong, LI Yong, et al. Edge intelligence: Empowering intelligence to the edge of network[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2021, 109(11): 1778–1837. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2021.3119950. [26] KHAN W Z, AHMED E, HAKAK S, et al. Edge computing: A survey[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2019, 97: 219–235. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2019.02.050. [27] 刘通, 方璐, 高洪皓. 边缘计算中任务卸载研究综述[J]. 计算机科学, 2021, 48(1): 11–15. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.200900217.LIU Tong, FANG Lu, and GAO Honghao. Survey of task offloading in edge computing[J]. Computer Science, 2021, 48(1): 11–15. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.200900217. [28] 中国信通院. AI框架发展白皮书[M]. 北京: 中国信通院, 2022: 35–36.China Academy of Information and Communications Technology. White Paper on AI Framework Development[M]. Beijing: China Academy of Information and Communications Technology, 2022: 35–36. [29] TensorFlow. TensorFlow lite[EB/OL]. https://tensorflow.google.cn/lite/guide?hl=zh-cn, 2021. [30] The Linux Foundation. PYTORCH MOBILE[EB/OL]. https://pytorch.org/mobile/home/, 2023. [31] MindSpore. MindSpore lite[EB/OL]. https://www.mindspore.cn/lite?version=/master/, 2023. [32] PaddlePaddle Developers. Paddle lite - 端侧轻量化推理引擎[EB/OL]. https://paddlelite.paddlepaddle.org.cn/, 2023.PaddlePaddle Developers. Paddle lite-End-side lightweight inference engine[EB/OL]. https://paddlelite.paddlepaddle.org.cn/, 2023 [33] 李博闻. 深度神经网络量化及其硬件加速研究[D]. [博士论文], 浙江大学, 2022.LI Bowen. Quantization and hardware acceleration for deep neural network[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Zhejiang University, 2022. [34] 林景栋, 吴欣怡, 柴毅, 等. 卷积神经网络结构优化综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(1): 24–37. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c180275.LIN Jingdong, WU Xinyi, CHAI Yi, et al. Structure optimization of convolutional neural networks: A survey[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(1): 24–37. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c180275. [35] ZOUMPEKAS T, SALAMÓ M, and PUIG A. effective early stopping of point cloud neural networks[C]. The 19th International Conference on Modeling Decisions for Artificial Intelligence (MDAI), Sant Cugat, Spain, 2022: 156–167. [36] MEI Shaohui, CHEN Xiaofeng, ZHANG Yifan, et al. Accelerating convolutional neural network-based hyperspectral image classification by step activation quantization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5502012. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3058321. [37] WANG Peisong, CHEN Weihan, HE Xianyu, et al. Optimization-based post-training quantization with bit-split and stitching[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(2): 2119–2135. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3159369. [38] LI Guangli, MA Xiu, WANG Xueying, et al. Optimizing deep neural networks on intelligent edge accelerators via flexible-rate filter pruning[J]. Journal of Systems Architecture, 2022, 124: 102431. doi: 10.1016/j.sysarc.2022.102431. [39] YU Fang, CUI Li, WANG Pengcheng, et al. EasiEdge: A novel global deep neural networks pruning method for efficient edge computing[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(3): 1259–1271. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3034925. [40] BAKHTIARNIA A, ZHANG Qi, and IOSIFIDIS A. Single-layer vision transformers for more accurate early exits with less overhead?[J]. Neural Networks, 2022, 153: 461–473. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2022.06.038. [41] QIU Han, ZHANG Tianwei, ZHANG Tianzhu, et al. DefQ: Defensive quantization against inference slow-down attack for edge computing[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(4): 3243–3251. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3138935. [42] HOWARD A G, ZHU Menglong, CHEN Bo, et al. MobileNets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.04861, 2017. [43] ZHANG Xiangyu, ZHOU Xinyu, LIN Mengxiao, et al. ShuffleNet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 6848–6856. [44] 王健宗, 孔令炜, 黄章成, 等. 联邦学习算法综述[J]. 大数据, 2020, 6(6): 64–82. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-0271.2020055.WANG Jianzong, KONG Lingwei, HUANG Zhangcheng, et al. Research review of federated learning algorithms[J]. Big Data Research, 2020, 6(6): 64–82. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-0271.2020055. [45] LIU Lumin, CHANG Jun, SONG S H, et al. Client-edge-cloud hierarchical federated learning[C]. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Dublin, Ireland 2020: 1–6. [46] LIU Lumin, ZHANG Jun, SONG Shenghui, et al. Hierarchical federated learning with quantization: Convergence analysis and system design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2023, 22(1): 2–18. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2022.3190512. [47] ZHOU Hongliang, ZHENG Yifeng, HUANG Hejiao, et al. Toward robust hierarchical federated learning in internet of vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2023, 24(5): 5600–5614. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2023.3243003. [48] REN Jinke, HE Yinghui, WEN Dingzhu, et al. Scheduling for cellular federated edge learning with importance and channel awareness[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(11): 7690–7703. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3015671. [49] FENG Wenjun and ZHANG Xian. Wireless federated learning with dynamic quantization and bandwidth adaptation[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2022, 11(11): 2335–2339. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2022.3202645. [50] REN Jinke, YU Guanding, and DING Guangyao. Accelerating DNN training in wireless federated edge learning systems[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2021, 39(1): 219–232. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2020.3036971. [51] ZHU Hangyu, XU Jinjin, LIU Shiqing, et al. Federated learning on non-IID data: A survey[J]. Neurocomputing, 2021, 465: 371–390. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.07.098. [52] ZHAO Yue, LI Meng, LAI Liangzhen, et al. Federated learning with non-IID data[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1806.00582, 2022. [53] CHEN Aiguo, FU Yang, WANG Lingfu, et al. DWFed: A statistical-heterogeneity-based dynamic weighted model aggregation algorithm for federated learning[J]. Frontiers in Neurorobotics, 2022, 16: 1041553. doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2022.1041553. [54] JAMALI-RAD H, ABDIZADEH M, and SINGH A. Federated learning with taskonomy for non-IID data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022: 1–12. [55] XU Yawen, LI Xiaojun, YANG Zeyu, et al. Robust communication strategy for federated learning by incorporating self-attention[C]. SPIE 11584, 2020 International Conference on Image, Video Processing and Artificial Intelligence, Shanghai, China, 2020: 115841F. [56] ARAFEH M, OULD-SLIMANE H, OTROK H, et al. Data independent warmup scheme for non-IID federated learning[J]. Information Sciences, 2023, 623: 342–360. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2022.12.045. [57] LU C H and LIN Xiaozong. Toward direct edge-to-edge transfer learning for IoT-enabled edge cameras[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(6): 4931–4943. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3034153. [58] LU C H and ZHOU Yangming. Direct edge-to-edge many-to-many latent feature transfer learning[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(12): 10048–10060. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3117991. [59] HSU T H, WANG Zhihao, and SEE A R. A Cloud-edge-smart IoT architecture for speeding up the deployment of neural network models with transfer learning techniques[J]. Electronics, 2022, 11(14): 2255. doi: 10.3390/electronics11142255. [60] CHEN Dawei, LIU Yinchen, KIM B, et al. Edge computing resources reservation in vehicular networks: A meta-learning approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(5): 5634–5646. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.2983445. [61] DONG Fang, GE Xinghua, LI Qinya, et al. PADP-FedMeta: A personalized and adaptive differentially private federated meta learning mechanism for AIoT[J]. Journal of Systems Architecture, 2023, 134: 102754. doi: 10.1016/j.sysarc.2022.102754. [62] LIU Yi, PENG Jialiang, KANG Jiawen, et al. A secure federated learning framework for 5G networks[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2020, 27(4): 24–31. doi: 10.1109/MWC.01.1900525. [63] CHENG Yanyu, LU Jianyuan, NIYATO D, et al. Federated transfer learning with client selection for intrusion detection in mobile edge computing[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2022, 26(3): 552–556. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2022.3140273. [64] 李强, 杜婷婷, 童钊, 等. 移动边缘计算中基于深度强化学习的依赖任务卸载研究[J/OL]. 小型微型计算机系统: 1–8. https://doi.org/10.20009/j.cnki.21-1106/TP.2021-0823, 2023.LI Qiang, DU Tingting, TONG Zhao, et al. Dependent task offload based on deep reinforcement learning in mobile edge computing[J/OL]. Journal of Chinese Computer Systems: 1–8. https://doi.org/10.20009/j.cnki.21-1106/TP.2021-0823, 2023. [65] WU Chao, ZHANG Yaoxue, and DENG Yongheng. Toward fast and distributed computation migration system for edge computing in IoT[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(6): 10041–10052. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2935120. [66] TANG Ming and WONG V W S. Deep reinforcement learning for task offloading in mobile edge computing systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2022, 21(6): 1985–1997. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2020.3036871. [67] BABAR M and KHAN M S. ScalEdge: A framework for scalable edge computing in Internet of things-based smart systems[J]. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2021, 17(7). [68] HAN Dongsheng, LIU Yu, and NI Junhong. Research on multinode collaborative computing offloading algorithm based on minimization of energy consumption[J]. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 2020, 2020: 8858298. doi: 10.1155/2020/8858298. [69] 胡世红. 边缘计算中资源动态调度的QoS优化技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 江南大学, 2021.HU Shihong. Research on QoS optimization technologies of dynamic resource scheduling in edge computing[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Jiangnan University, 2021. [70] 张成虎, 李鹏旭, 王琪. 网络金融犯罪预警系统研究——基于区块链和边缘计算[J]. 情报杂志, 2023, 42(1): 59–65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1965.2023.01.009.ZHANG Chenghu, LI Pengxu, and WANG Qi. Research on network financial crime early warning system——based on blockchain and edge computing[J]. Journal of Intelligence, 2023, 42(1): 59–65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1965.2023.01.009. [71] 张俊娜, 鲍想, 陈家伟, 等. 一种联合时延和能耗的依赖性任务卸载方法[J/OL]. 计算机研究与发展, 1–13. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1777.TP.20230213.0839.002.html, 2023.ZHANG Junna, BAO Xiang, CHENG Jiawei, et al. A dependent task offloading method for joint delay and energy consumption[J/OL]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 1–13. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1777.TP.20230213.0839.002.html, 2023. [72] DING Xinhui and ZHANG Wenjuan. Computing unloading strategy of massive internet of things devices based on game theory in mobile edge computing[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2021, 2021: 2163965. doi: 10.1155/2021/2163965. [73] 马勇, 戴梦轩, 夏云霓, 等. 一种基于人群分类的边缘计算任务卸载方法[P]. 中国, 115878227A, 2023.MA Yong, DAI Mengxuan, XIA Yunni, et al. A method of edge computing task unloading based on crowd classification[P]. CN, 115878227A, 2023. [74] REN Jinke, YU Guanding, HE Yinghui, et al. Collaborative cloud and edge computing for latency minimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(5): 5031–5044. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2904244. [75] LIN Li, LI Peng, XIONG Jinbo, et al. Distributed and application-aware task scheduling in edge-clouds[C]. 2018 14th International Conference on Mobile Ad-Hoc and Sensor Networks (MSN), Shenyang, China, 2018: 165–170. [76] REN Jinke, YU Guanding, CAI Yunlong, et al. Latency optimization for resource allocation in mobile-edge computation offloading[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2018, 17(8): 5506–5519. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2018.2845360. [77] 徐佳, 李学俊, 丁瑞苗, 等. 移动边缘计算中能耗优化的多重资源计算卸载策略[J]. 计算机集成制造系统, 2019, 25(4): 954–961. doi: 10.13196/j.cims.2019.04.018.XU Jia, LI Xuejun, DING Ruimiao, et al. Energy efficient multi-resource computation offloading strategy in mobile edge computing[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2019, 25(4): 954–961. doi: 10.13196/j.cims.2019.04.018. [78] 李强, 仪晋辉, 杜婷婷, 等. 移动边缘计算中基于A3C的依赖任务卸载与资源分配[J]. 计算机工程, 2023, 49(6): 42–52. doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0066095.LI Qiang, YI Jinhui, DU Tingting, et al. Dependent task offloading and resource allocation based on A3C in mobile edge computing[J]. Computer Engineering, 2023, 49(6): 42–52. doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0066095. [79] 彭昇, 赵建保, 魏敏捷, 等. 基于移动边缘计算的任务卸载优化[J]. 计算机系统应用, 2023, 32(4): 262–267. doi: 10.15888/j.cnki.csa.009013.PENG Sheng, ZHAO Jianbao, WEI Minjie, et al. Task offload optimization based on mobile edge computing[J]. Computer Systems &Applications, 2023, 32(4): 262–267. doi: 10.15888/j.cnki.csa.009013. -





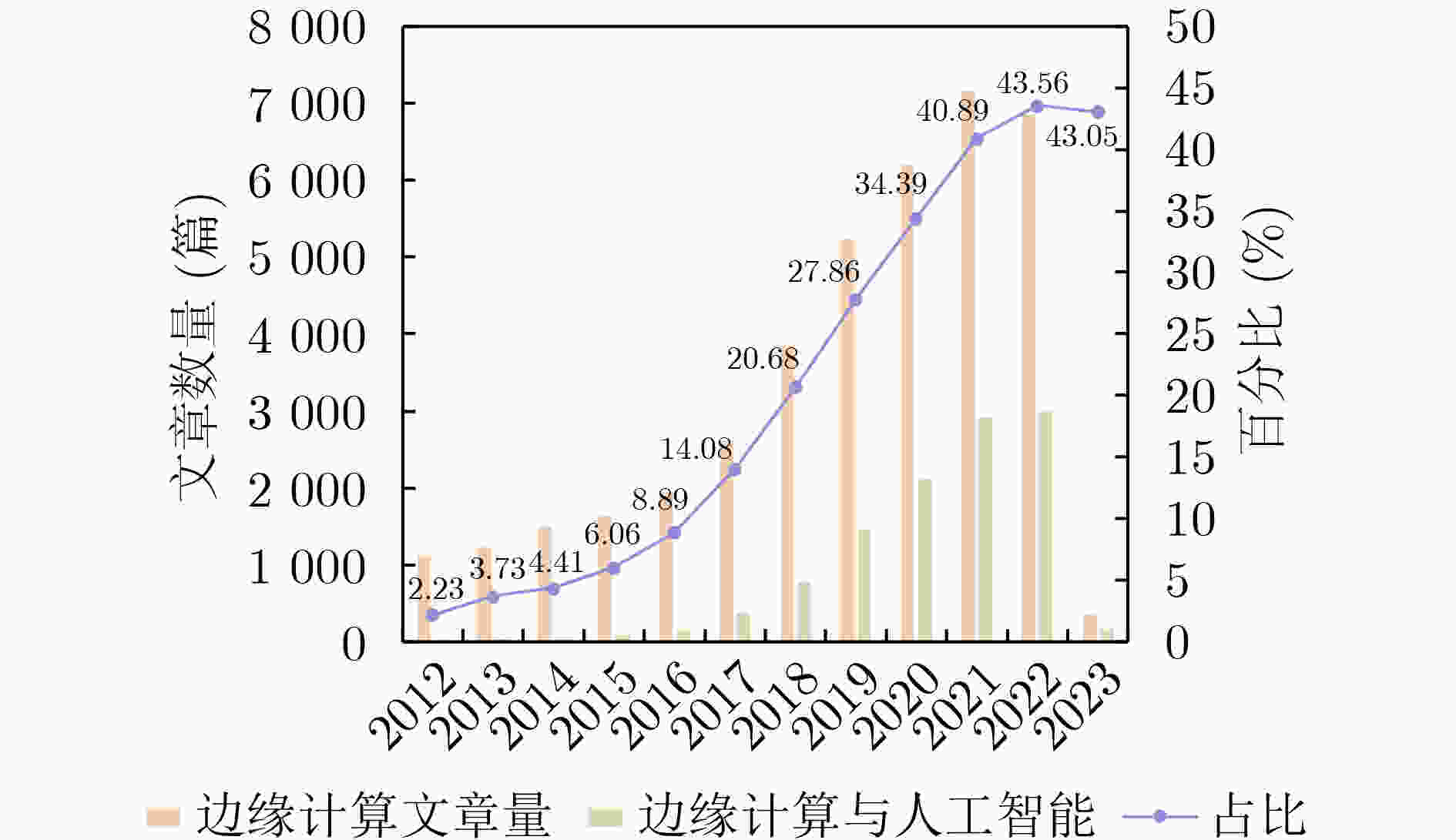
 下载:
下载:
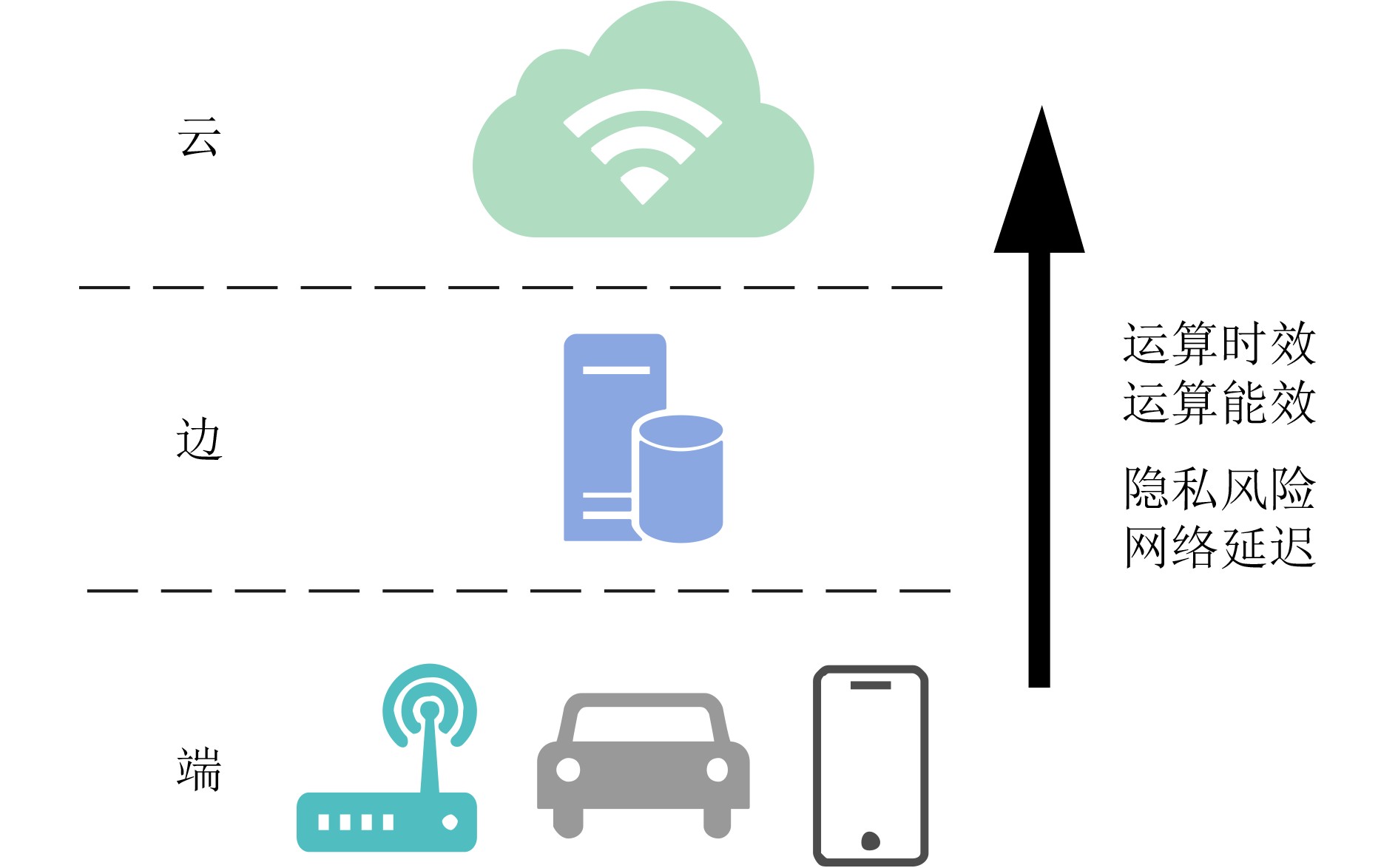
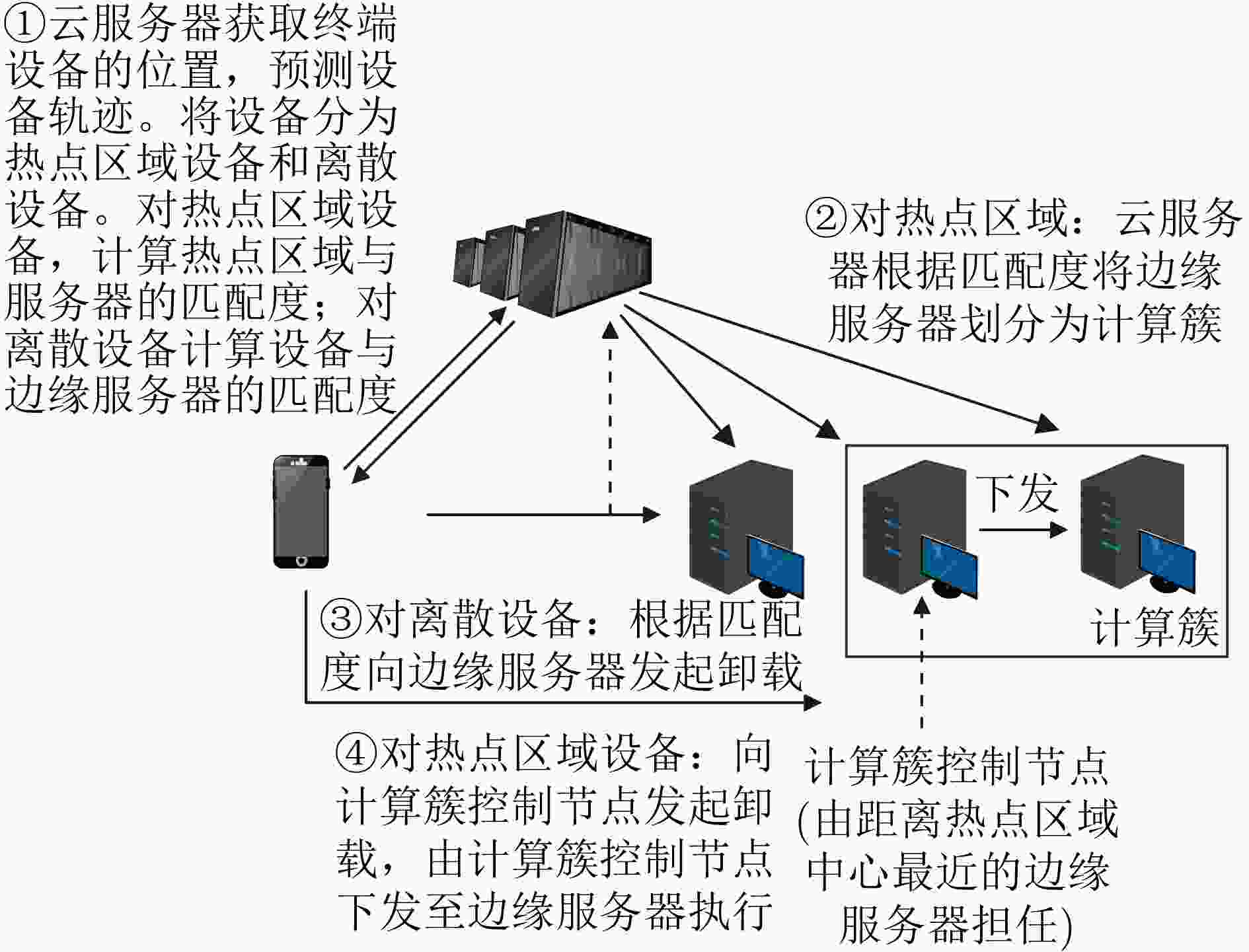
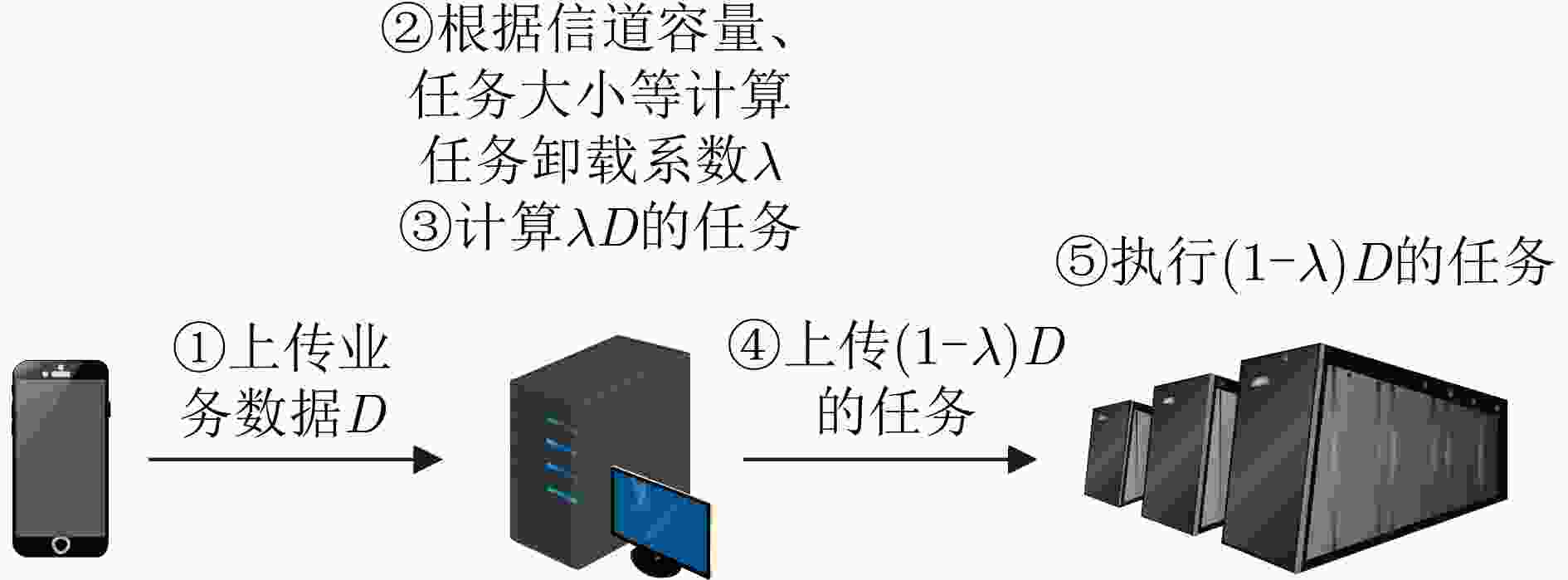
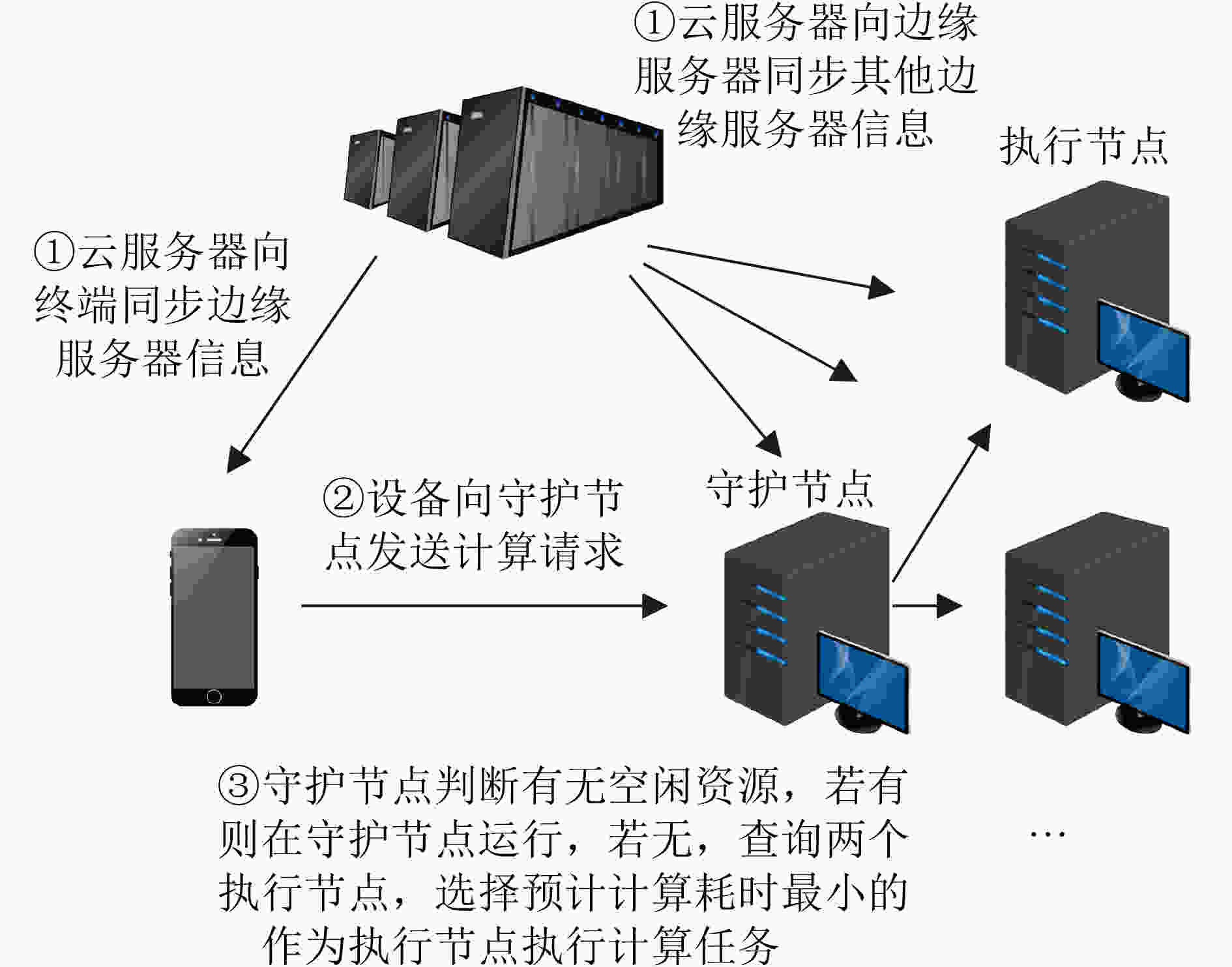


 下载:
下载:
