Ultrasound Image Lesion Detection Algorithm Optimized by Feature Feedback Mechanism
-
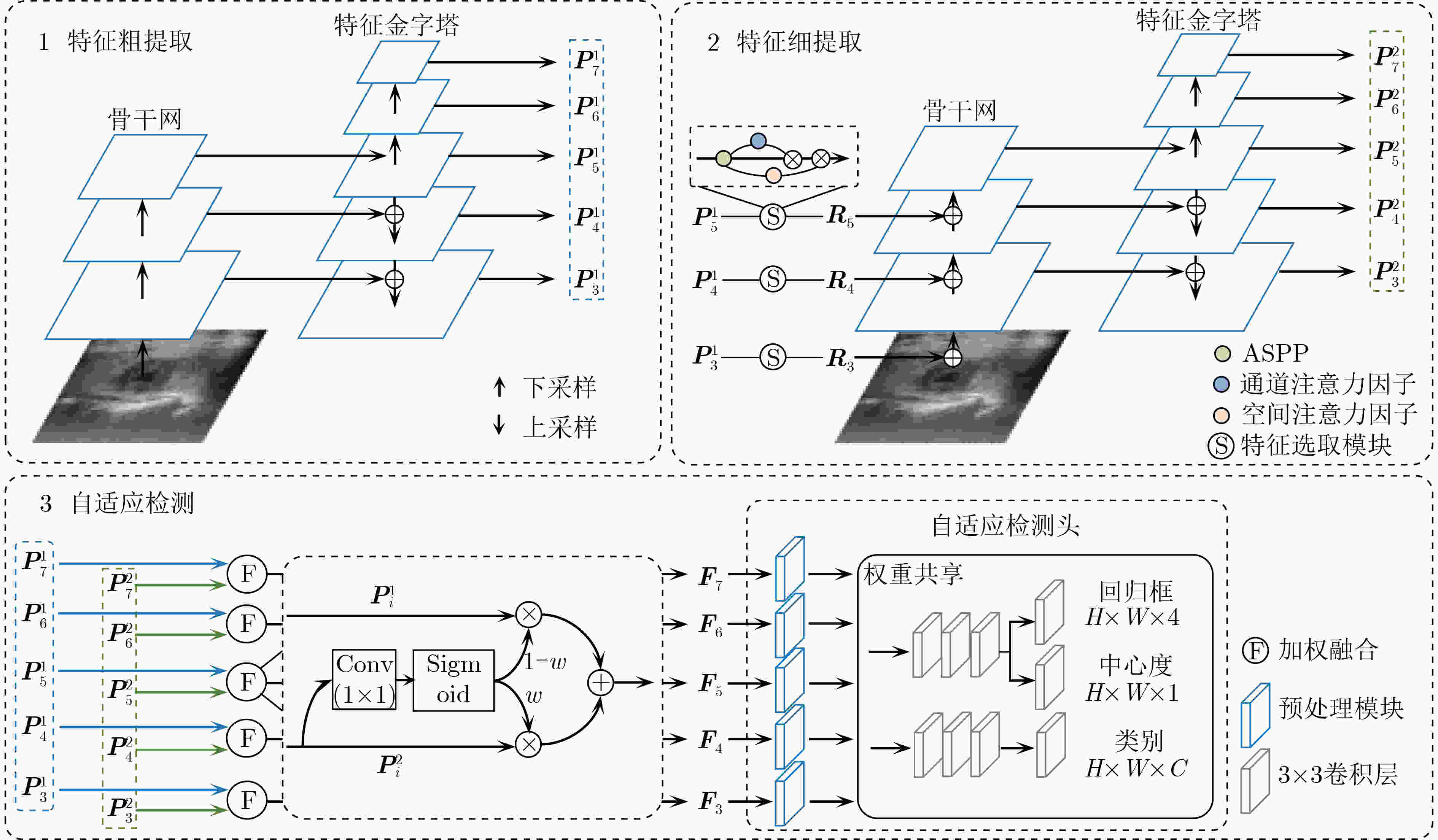
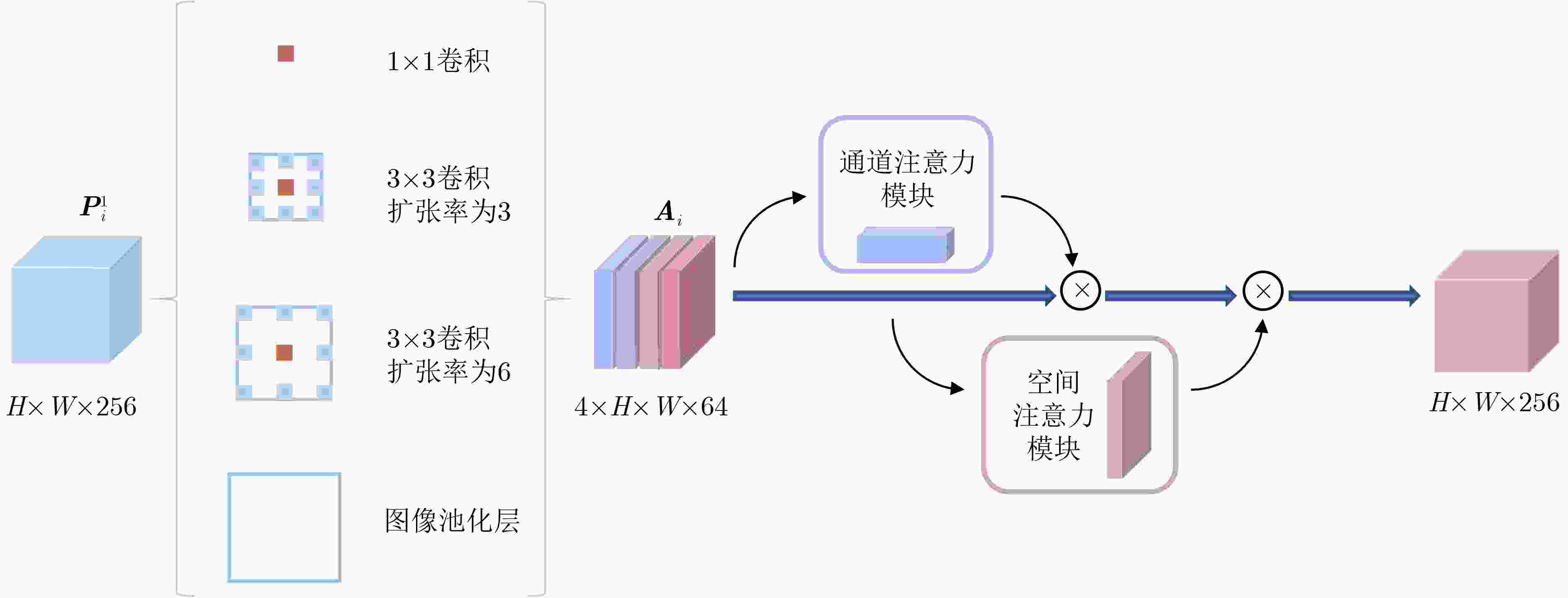
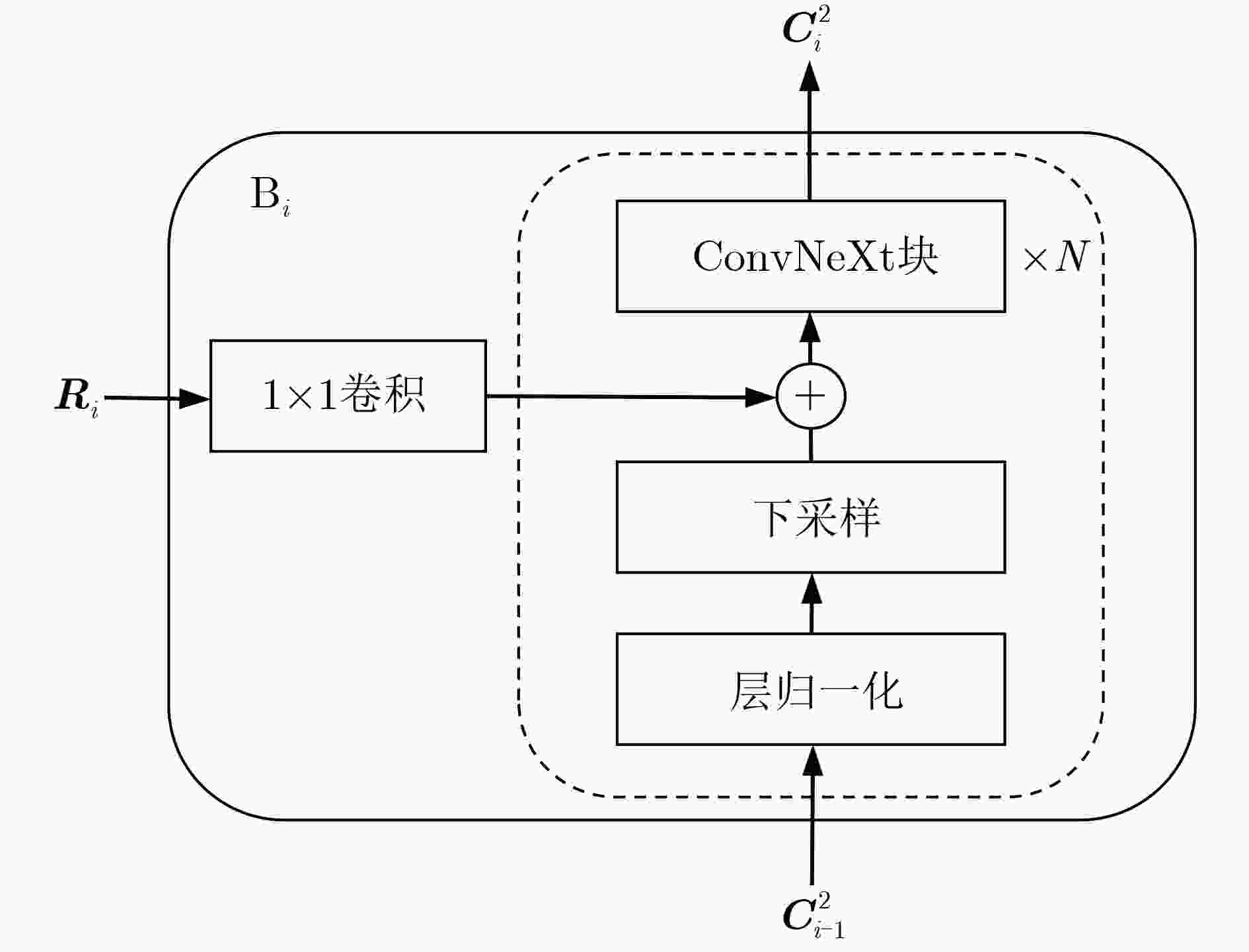
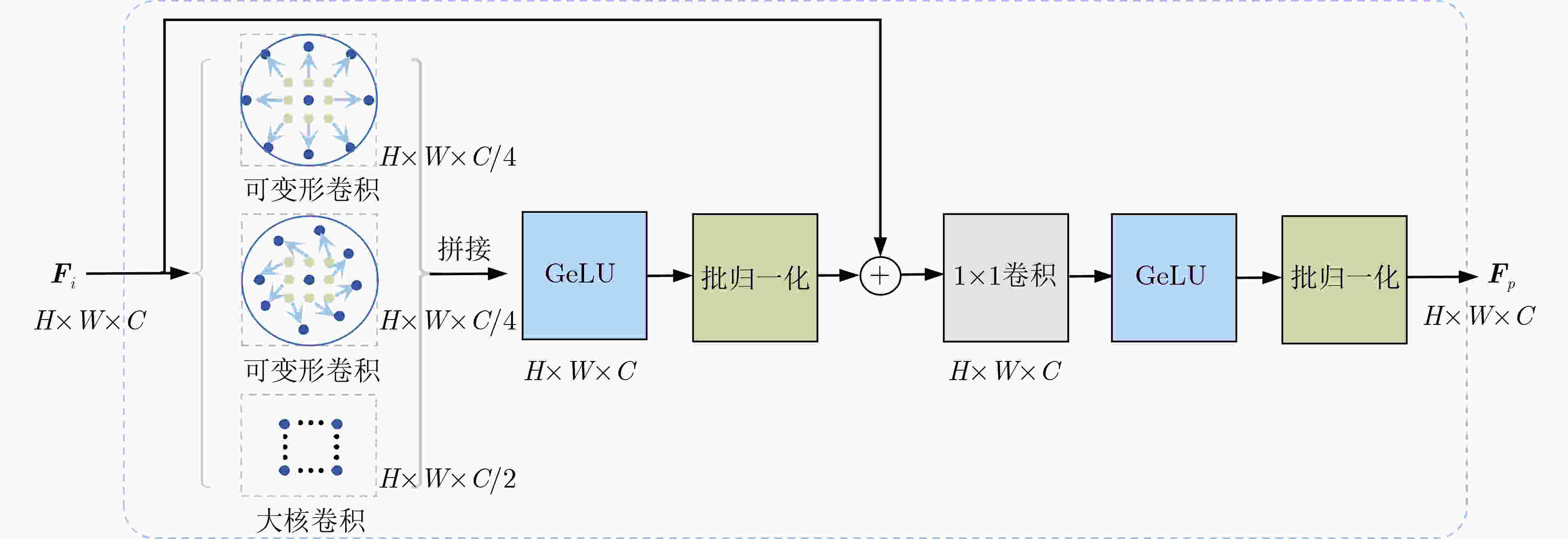
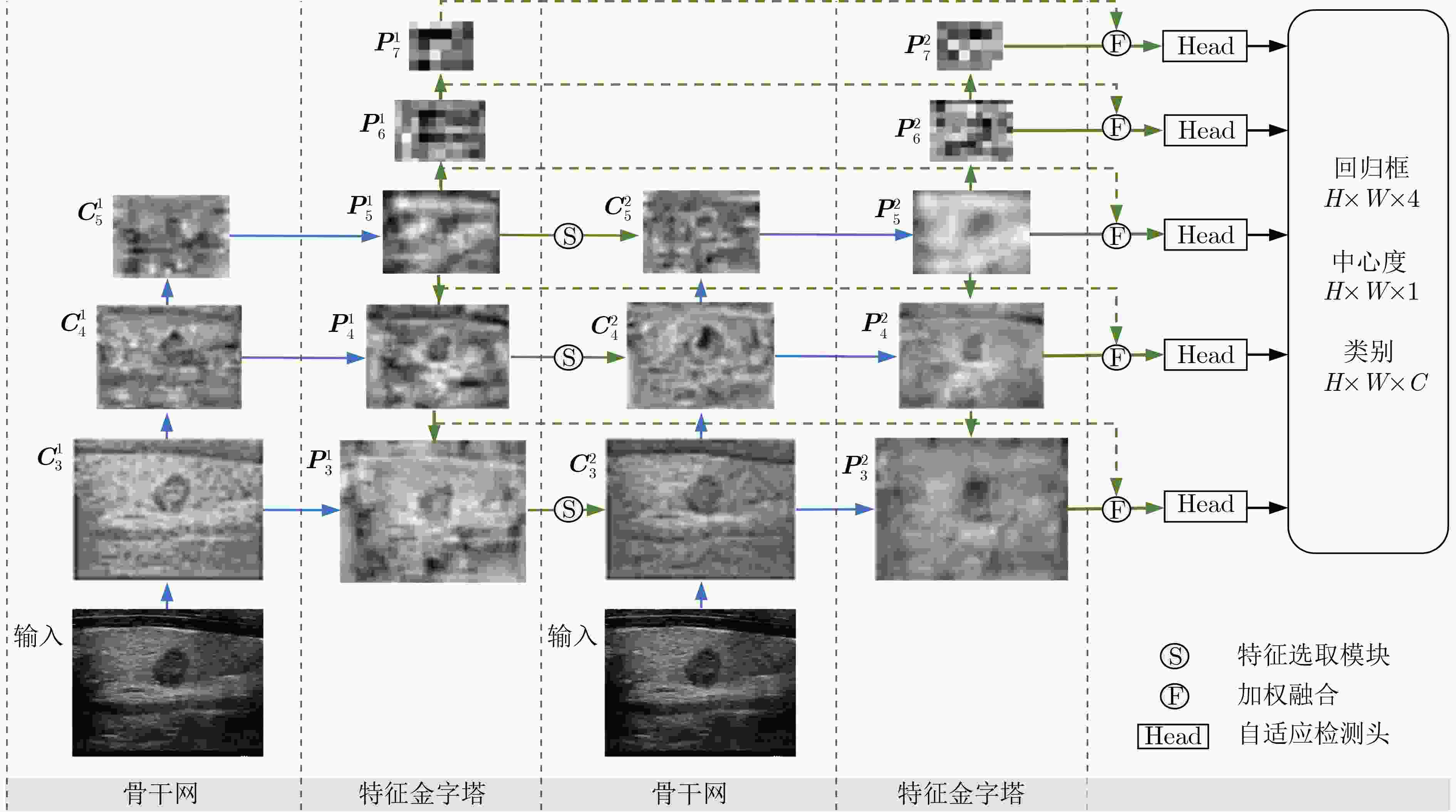
摘要: 该文提出一种基于特征反馈机制的超声图像病灶检测方法,以实现超声病灶的实时精确定位与检测。所提方法由基于特征反馈机制的特征提取网络和基于分治策略的自适应检测头两部分组成。特征反馈网络通过反馈特征选取和加权融合计算,充分学习超声图像的全局上下文信息和局部低级语义细节以提高局部病灶特征的识别能力。自适应检测头对特征反馈网络所提取的多级特征进行分治预处理,通过将生理先验知识与特征卷积相结合的方式对各级特征分别进行病灶形状和尺度特征的自适应建模,增强检测头对不同大小病灶在多级特征下的检测效果。所提方法在甲状腺超声图像数据集上进行了测试,得到了70.3%的AP,99.0%的AP50和88.4%的AP75,实验结果表明,相较于主流检测算法,所提算法能实现更精准的实时超声图像病灶检测和定位。Abstract: A lesion detection method in ultrasound images based on feature feedback mechanism is proposed to realize real-time accurate localization and detection of ultrasound lesions. The proposed method consists of two parts: feature extraction network based on feature feedback mechanism and adaptive detection head based on divide-and-conquer strategy. The feature feedback network fully learns the global context information and local low-level semantic details of ultrasound images through feedback feature selection and weighted fusion calculation to improve the recognition ability of local lesion features. The adaptive detection head performs divide-and-conquer preprocessing on the multi-level features extracted by the feature feedback network. By combining physiological prior knowledge and feature convolution, adaptive modeling of lesion shape and scale features is performed on features at all levels to enhance the detection effect of the detection head on lesions of different sizes under multi-level features. The proposed method is tested on the thyroid ultrasound image dataset, and 70.3% AP, 99.0% AP50 and 88.4% AP75 are obtained. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can achieve more accurate real-time detection and positioning of ultrasound image lesions in comparison with mainstream detection algorithm.
-
Key words:
- Lesion detection /
- Feature feedback /
- Adaptive detection head
-
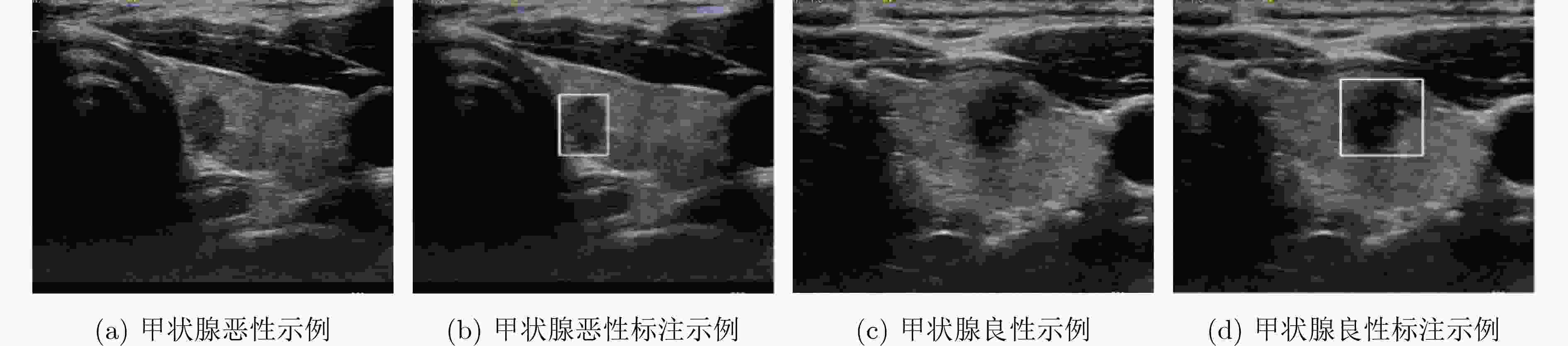
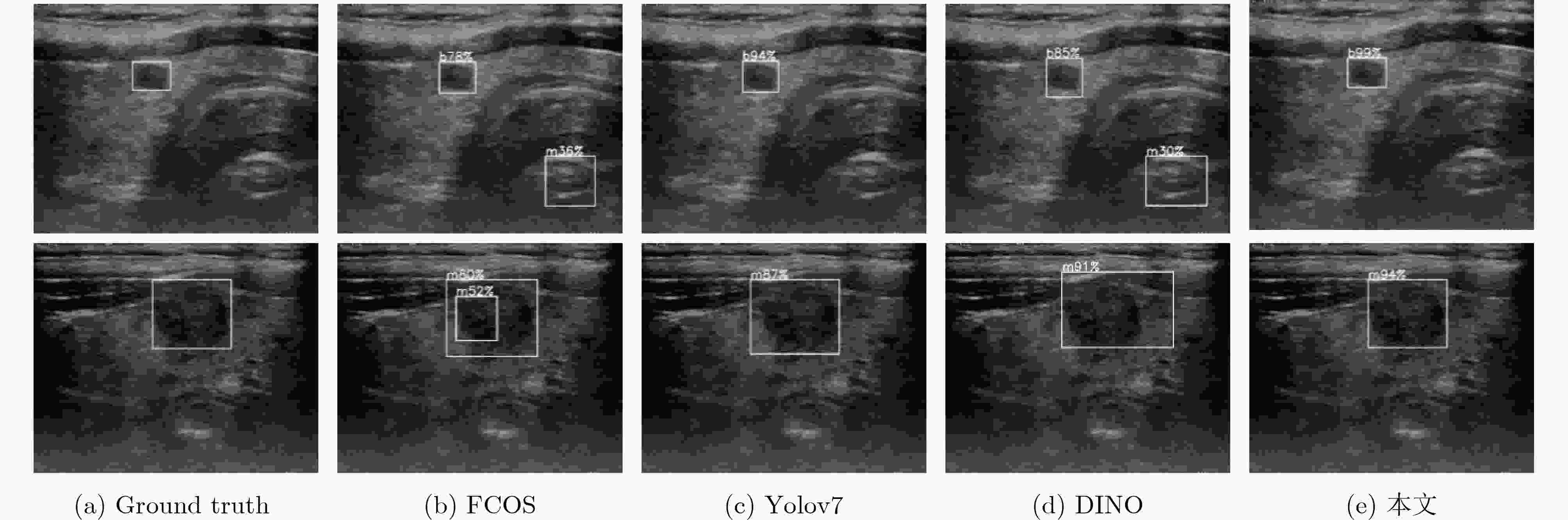
表 1 甲状腺超声病灶检测精度对比(%)
方法 骨干网 AP AP50 AP75 AP良性 AP恶性 Faster RCNN[7] ResNet50 64.3 96.6 79.2 61.5 67.1 RetinaNet[10] ResNet50 65.2 97.6 80.3 62.4 67.9 Yolov3[11] Darknet53 64.7 95.2 81.5 62.5 66.8 FCOS[12] ResNet50 65.8 95.5 80.8 63.5 68.2 EfficientDet[26] EfficientNet-B1 66.1 98.7 77.1 63.8 68.5 VarifocalNet[13] ResNet50 64.5 97.3 78.5 64.4 64.6 Yolof[14] ResNet50 65.9 99.2 81.4 64.8 66.9 Yolox[16] Darknet53 67.0 98.1 83.4 64.4 69.5 Yolov7[17] CBS+ELAN 67.3 98.3 84.0 65.3 69.2 DETR[20] ResNet50 63.4 93.6 76.2 61.2 65.7 DAB-DETR[21] ResNet50 64.9 96.3 78.9 64.1 65.8 DINO[22] ResNet50 66.1 95.8 83.6 62.5 69.7 本文 ResNet50 69.6 99.0 87.7 68.2 71.0 本文 ConvNeXt-tiny 70.3 99.0 88.4 68.9 71.6 表 2 病灶检测精度消融实验(%)
方法 AP AP50 AP75 Baseline 65.8 95.5 80.8 +ConvNeXt 67.5 98.7 84.8 +ConvNeXt+自适应检测头 68.5 98.6 86.8 +ConvNeXt+自适应检测头+特征反馈网络 70.3 99.0 88.4 表 3 不同检测头对比(%)
方法 AP AP50 AP75 基线检测头(FCOS) 67.5 98.7 84.8 耦合检测头(Yolov3) 65.6 97.1 82.0 解耦合检测头(Yolox) 67.1 98.5 87.0 自适应检测头(本文) 68.5 98.6 86.8 表 4 不同反馈方式对比
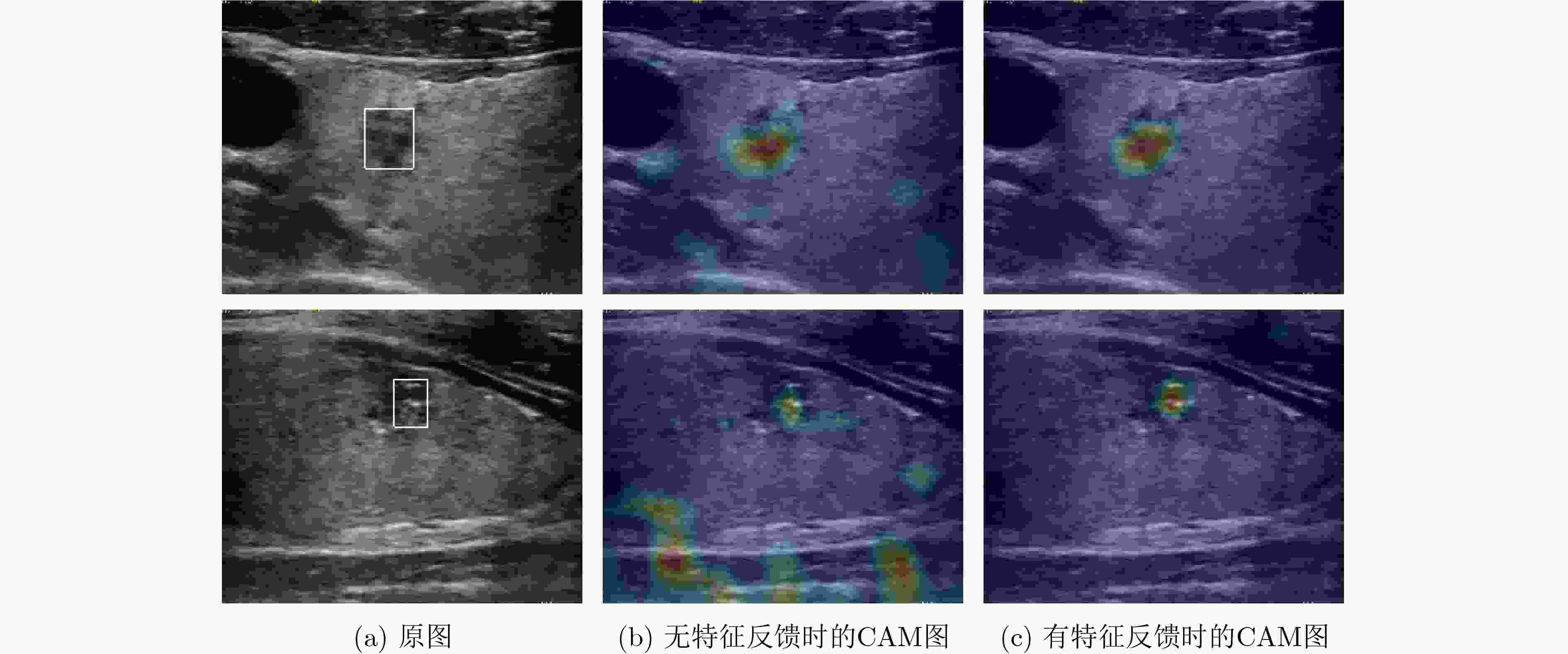
方法 AP(%) AP50(%) AP75(%) FPS(帧/s) 无反馈网络 68.5 98.6 86.8 46 $ {\boldsymbol{P}}_3^1 $至$ {\boldsymbol{P}}_5^1 $反馈网络+ASPP 69.6 98.6 87.4 40 $ {\boldsymbol{P}}_3^1 $至$ {\boldsymbol{P}}_7^1 $反馈网络+ASPP 69.6 98.4 87.8 34 $ {\boldsymbol{P}}_3^1 $至$ {\boldsymbol{P}}_5^1 $反馈网络+反馈特征
选取模块(本文)70.3 99.0 88.4 39 $ {\boldsymbol{P}}_3^1 $至$ {\boldsymbol{P}}_7^1 $反馈网络+反馈特征
选取模块70.1 98.5 88.2 30 -
[1] WATAYA T, YANAGAWA M, TSUBAMOTO M, et al. Radiologists with and without deep learning–based computer-aided diagnosis: Comparison of performance and interobserver agreement for characterizing and diagnosing pulmonary nodules/masses[J]. European Radiology, 2023, 33(1): 348–359. doi: 10.1007/s00330-022-08948-4. [2] SOLYMOSI T, HEGEDŰS L, BONNEMA S J, et al. Considerable interobserver variation calls for unambiguous definitions of thyroid nodule ultrasound characteristics[J]. European Thyroid Journal, 2023, 12(2): e220134. doi: 10.1530/ETJ-22-0134. [3] YAP M H, GOYAL M, OSMAN F, et al. Breast ultrasound region of interest detection and lesion localisation[J]. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, 2020, 107: 101880. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2020.101880. [4] LI Yujie, GU Hong, WANG Hongyu, et al. BUSnet: A deep learning model of breast tumor lesion detection for ultrasound images[J]. Frontiers in Oncology, 2022, 12: 848271. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.848271. [5] MENG Hui, LIU Xuefeng, NIU Jianwei, et al. DGANet: A dual global attention neural network for breast lesion detection in ultrasound images[J]. Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology, 2023, 49(1): 31–44. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2022.07.006. [6] GIRSHICK R, DONAHUE J, DARRELL T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]. 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 580–587. [7] REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137–1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031. [8] LIANG Tingting, CHU Xiaojie, LIU Yudong, et al. CBNet: A composite backbone network architecture for object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022, 31: 6893–6906. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2022.3216771. [9] QIAO Siyuan, CHEN L C, and YUILLE A. DetectoRS: Detecting objects with recursive feature pyramid and switchable atrous convolution[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 10208–10219. [10] LIN T Y, GOYAL P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 2999–3007. [11] REDMON J and FARHADI A. YOLOv3: An incremental improvement[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1804.02767, 2018. [12] TIAN Zhi, SHEN Chunhua, CHEN Hao, et al. FCOS: Fully convolutional one-stage object detection[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 2019: 9626–9635. [13] ZHANG Haoyang, WANG Ying, DAYOUB F, et al. VarifocalNet: An IoU-aware dense object detector[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 8510–8519. [14] CHEN Qiang, WANG Yingming, YANG Tong, et al. You only look one-level feature[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 13034–13043. [15] TAN Mingxing, PANG Ruoming, and LE Q V. EfficientDet: Scalable and efficient object detection[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 10778–10787. [16] GE Zheng, LIU Songtao, WANG Feng, et al. YOLOX: Exceeding YOLO series in 2021[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2107.08430, 2021. [17] WANG C Y, BOCHKOVSKIY A, and LIAO H Y M. YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2207.02696, 2022. [18] WANG Wen, ZHANG Jing, CAO Yang, et al. Towards data-efficient detection transformers[C]. The 17th European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 2022: 88–105. [19] CHEN Xiangyu, HU Qinghao, LI Kaidong, et al. Accumulated trivial attention matters in vision transformers on small datasets[C]. 2023 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, USA, 2023: 3973–3981. [20] CARION N, MASSA F, SYNNAEVE G, et al. End-to-end object detection with transformers[C]. Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 213–229. [21] LIU Shilong, LI Feng, ZHANG Hao, et al. DAB-DETR: Dynamic anchor boxes are better queries for DETR[C]. The Tenth International Conference on Learning Representations (Virtual), 2022: 1–20. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2201.12329. [22] ZHANG Hao, LI Feng, LIU Shilong, et al. DINO: DETR with improved DeNoising anchor boxes for end-to-end object detection[C]. The Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations, Kigali, Rwanda, 2023: 1–19. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2203.03605. [23] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. [24] LIU Zhuang, MAO Hanzi, WU Chaoyuan, et al. A ConvNet for the 2020s[C]. 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 11966–11976. [25] PENG Zhiliang, GUO Zonghao, HUANG Wei, et al. Conformer: Local features coupling global representations for recognition and detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(8): 9454–9468. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2023.3243048. [26] WANG W, DAI J, CHEN Z, et al. Internimage: Exploring large-scale vision foundation models with deformable convolutions[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, Canada, 2023: 14408–14419. [27] SELVARAJU R R, COGSWELL M, DAS A, et al. Grad-CAM: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 618–626. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
