Optimization of User Pairing, Beamforming and Phase-shifting for Intelligent Reflecting Surface Assisted Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access Systems
-
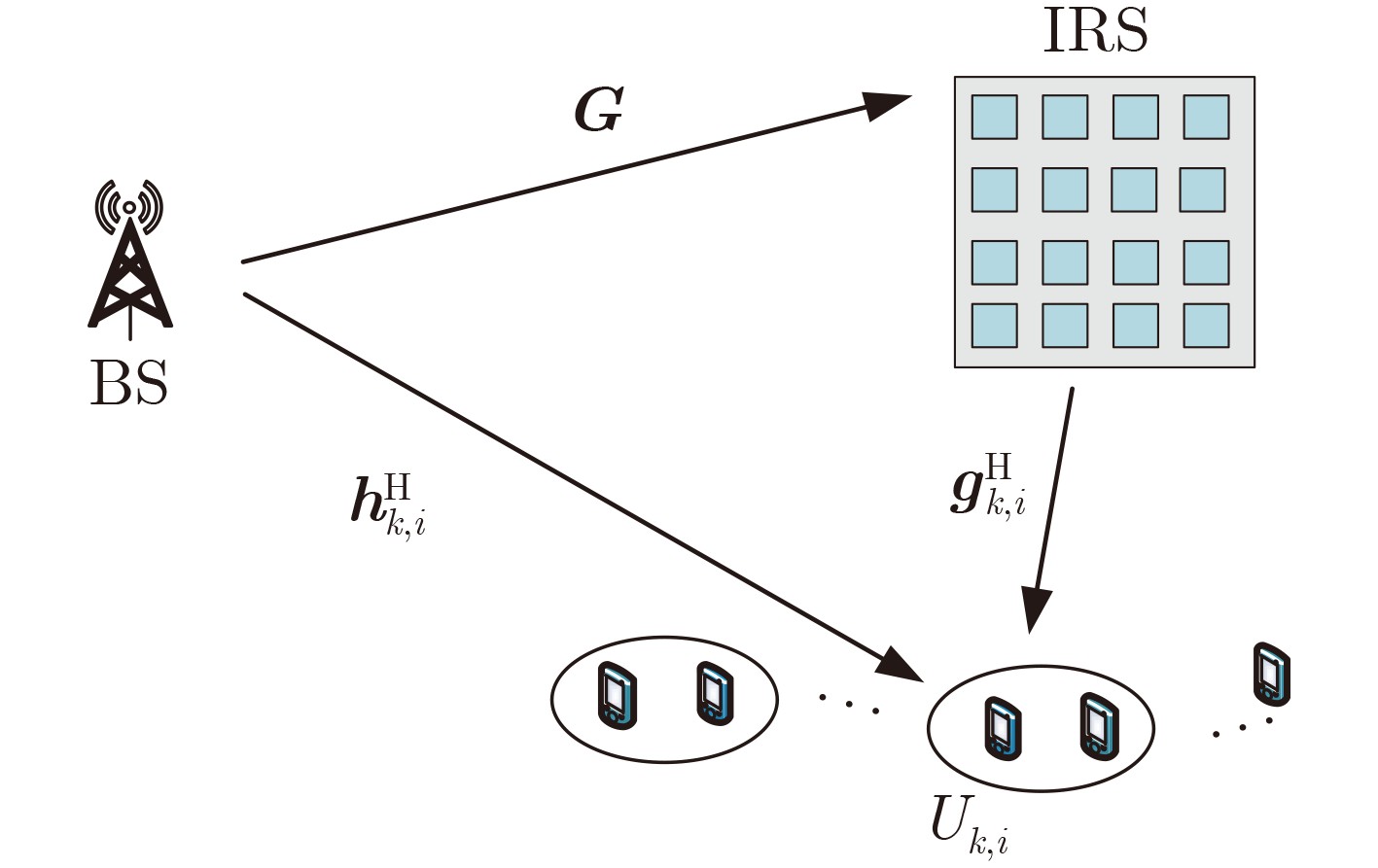
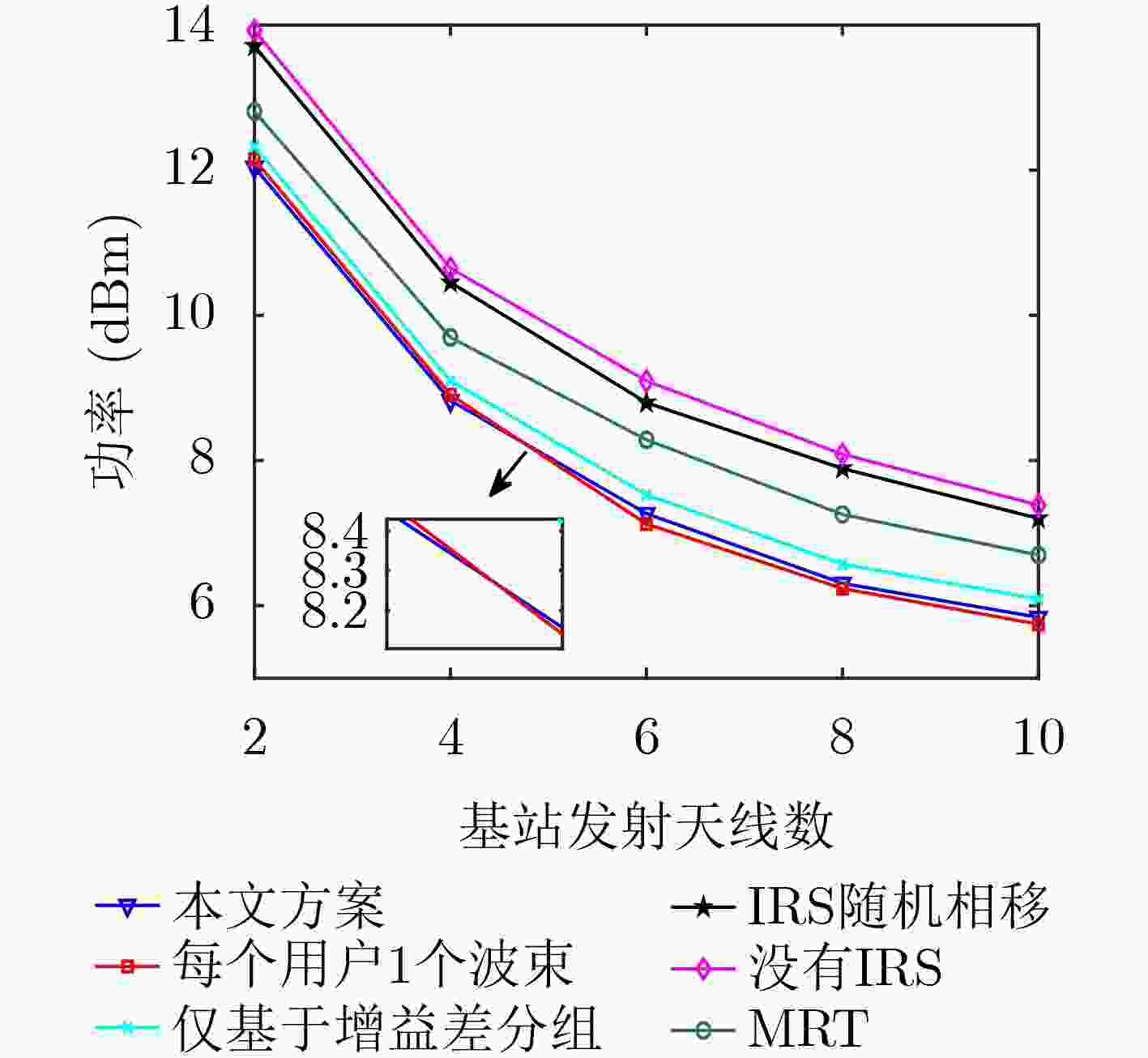
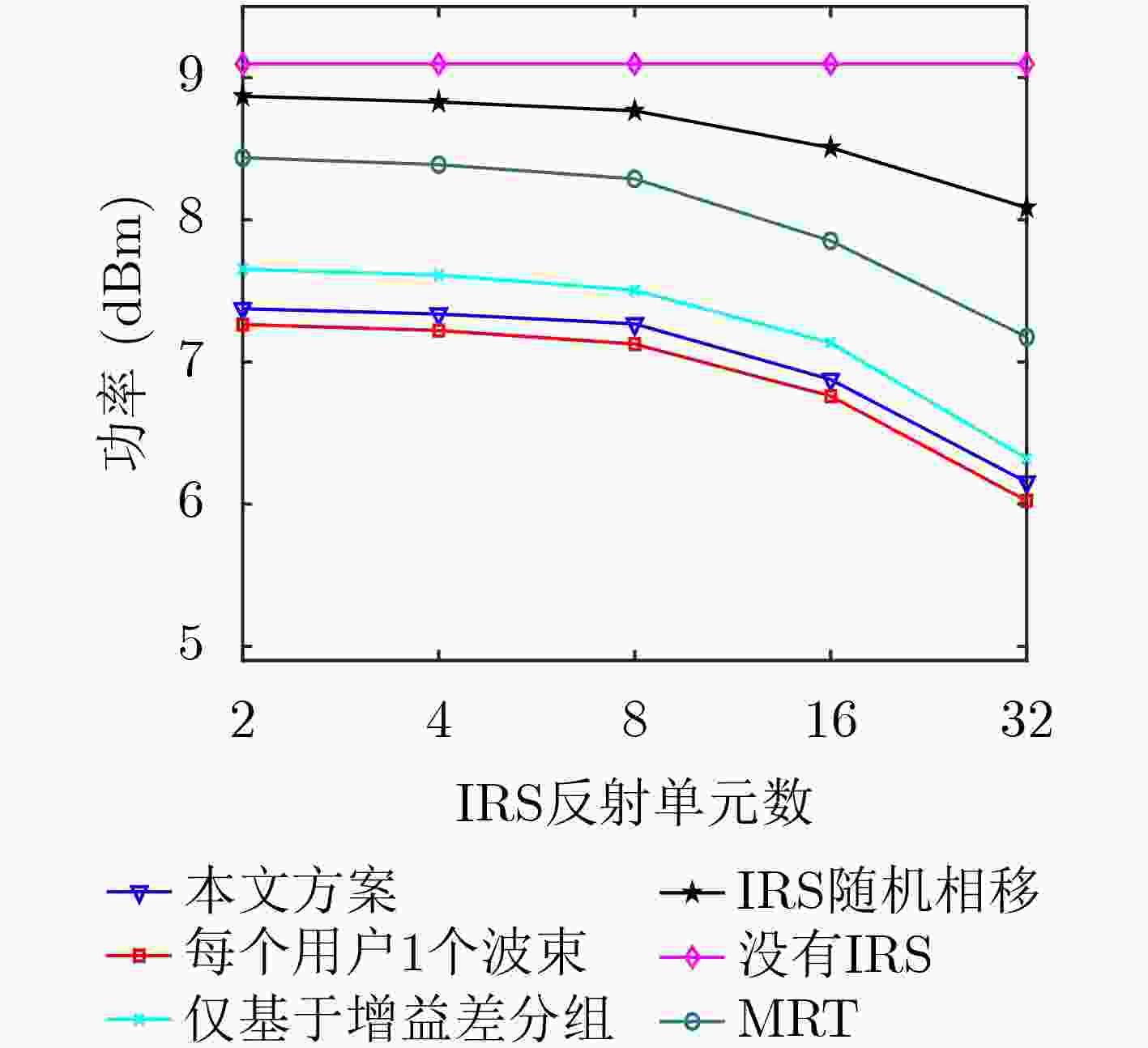
摘要: 该文研究智能反射表面(IRS)辅助的多天线非正交多址接入(NOMA)网络中用户分组、发送波束赋形、相移等的联合优化问题。系统中1个分组分配1个波束并在组内进行连续干扰消除检测。该文提出一种不依赖于发送波束赋形和IRS相移的用户分组配对策略,将用户分组与其他优化分离,显著降低了优化问题求解的难度和计算复杂度。进一步,联合优化基站发送波束赋形、功率分配和IRS相移矩阵,最小化基站的总发送功率。原始优化问题是一个多变量相互耦合的非凸优化问题,利用松弛变量、连续凸逼近、半定松弛、交替迭代优化等方法将原问题转化为凸问题并求解。仿真结果显示,相较于1个用户1个波束的方案,所提方案在基站天线数较少时性能更优,而在天线数较多时也与该对比方案非常接近,但所提方案的优化计算复杂度更低。而对比采用不同分组算法、随机IRS相移方案、最大比发射方案,以及无IRS的方案,所提方案的性能始终更优。Abstract: The joint optimization of user pairing, beamforming and phase shifting in a Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access(NOMA) network assisted by Intelligent Reflecting Surface(IRS) is studied in this paper. In the system, each pair is assigned with one beam and the intra-group successive interference cancellation in the signal detection is adopted. A user pairing strategy independent of transmit beamforming and IRS phase shift is proposed, so the user pairing is separated from the joint optimization and the difficulty and complexity in the solving of the optimization is significantly reduced. Then, the transmit beamforming, power allocation and IRS phase shift are jointly optimized to minimize the total transmission power of the base station. The original optimization problem is non-convex. By using the methods such as slack variables, successive convex approximation, semidefinite relaxation and alternative optimization, the original problem is transformed into a convex problem and solved. Simulation results show that the performance of the proposed scheme is better than that of the scheme that one user is assigned with one beam when the number of the transmit antennas is less than that of the users, and is very close to the scheme that one user is assigned with one beam when the number of antennas is more than that of the users, while the computational complexity of the proposed scheme is lower. Compared with the schemes that employ different user pairing strategy, random IRS phase shift, maximum ratio transmission beamforming, or that without IRS, the proposed scheme is always superior in performance.
-
算法1 优化问题P1的求解算法 (1) 初始化参数:$c=0 $, ${\lambda _1} $, ${\lambda _2} $,随机取值相移矩阵${\boldsymbol{\varPhi}}^{(0)} $,和
波束赋形矢量${\boldsymbol{w}}_k^{(0)}$,求解问题P2,$P_{l,i}^{(0)} $得到和$P_{m,1}^{(0)} $(2) while; (3) ${c_1} = {c_1} + 1 $ (4)初始化参数:${c_2} = 0 $, ${P_{l,i}} = P_{l,i}^{(0)} $, $ {P_{m,1}} = P_{m,1}^{(0)} $ (5) while; (6) ${c_2} = {c_2} + 1 $ (7)令${\boldsymbol{ \varPhi}} = {{\boldsymbol{\varPhi}} ^{({c_2} - 1)}} $,求解问题P6,得到${\boldsymbol{W}}_k^{({c_2})} $ (8)对$ {\boldsymbol{W}}_k^{({c_2})} $进行特征值分解可得${\boldsymbol{w} }_k^{({c_2})}$ (9)令${ {\boldsymbol{w} }_k} = {\boldsymbol{w} }_k^{({c_2})}$,求解问题P8,得到${{\boldsymbol{V}}^{({c_2})}} $ (10)对${{\boldsymbol{V}}^{({c_2})}} $进行特征值分解,再对角化得到${{\boldsymbol{\varPhi}} ^{({c_2})}} $ (11) 由${{\boldsymbol{\varPhi}} ^{({c_2})}} $和${\boldsymbol{w}}_k^{({c_2})} $计算$R_{{\rm{toll}}}^{({c_2})} $ (12) until ${ {R_{ {\rm{toll} } }^{({c_2})} - R_{ {\rm{toll} } }^{({c_2} - 1)} } / {R_{ {\rm{toll} } }^{({c_2} - 1)} } } \le {\lambda _2}$ (13) 输出${\boldsymbol{w} }_k^{({c_1})} = {\boldsymbol{w} }_k^{({c_2})}$, $ {{\boldsymbol{\varPhi}} ^{({c_1})}} = {{\boldsymbol{\varPhi}} ^{({c_2})}} $。 (14)令${{\boldsymbol{w}}_k} = {\boldsymbol{w}}_k^{({c_1})} $, ${\boldsymbol{\varPhi}} = {{\boldsymbol{\varPhi}} ^{({c_1})}} $,求解问题P2,得到$P_{l,i}^{({c_1})} $和
$P_{m,1}^{({c_1})} $,更新$P_{{\rm{toll} } }^{({c_1})}$。(15) until ${ {P_{ {\rm{toll} } }^{({c_1})} - P_{ {\rm{toll} } }^{({c_1} - 1)} } / {P_{ {\rm{toll} } }^{({c_1} - 1)} } } \le {\lambda _1}$ -
[1] SAAD W, BENNIS M, and CHEN Mingzhe. A vision of 6G wireless systems: Applications, trends, technologies, and open research problems[J]. IEEE Network, 2020, 34(3): 134–142. doi: 10.1109/MNET.001.1900287. [2] DING Zhiguo, LV Lu, FANG Fang, et al. A state-of-the-art survey on reconfigurable intelligent surface-assisted non-orthogonal multiple access networks[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2022, 110(9): 1358–1379. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2022.3174140. [3] 冯友宏, 张彦峨, 董国青. 基于分布式智能反射面的物理层安全通信研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(6): 2081–2088. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220659.FENG Youhong, ZHANG Yan’e, and DONG Guoqing. Research on physical layer security communication based on distributed intelligent reflective surface[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2023, 45(6): 2081–2088. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220659. [4] WU Qingqing and ZHANG Rui. Towards smart and reconfigurable environment: Intelligent reflecting surface aided wireless network[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2020, 58(1): 106–112. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.1900107. [5] LIU Xiao, LIU Yuanwei, CHEN Yue, et al. RIS enhanced massive non-orthogonal multiple access networks: Deployment and passive beamforming design[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2021, 39(4): 1057–1071. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2020.3018823. [6] LI Yiqing, JIANG Miao, ZHANG Qi, et al. Joint beamforming design in multi-cluster MISO NOMA reconfigurable intelligent surface-aided downlink communication networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(1): 664–674. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2020.3032695. [7] XIE Ximing, FANG Fang, and DING Zhiguo. Joint optimization of beamforming, phase-shifting and power allocation in a multi-cluster IRS-NOMA network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(8): 7705–7717. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3090255. [8] ZUO Jiakuo, LIU Yuanwei, BASAR E, et al. Intelligent reflecting surface enhanced millimeter-wave NOMA systems[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2020, 24(11): 2632–2636. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2020.3009158. [9] KIMY B, LIM S, KIM H, et al. Non-orthogonal multiple access in a downlink multiuser beamforming system[C]. 2013 IEEE Military Communications Conference, San Diego, USA, 2013: 1278–1283. [10] ZHU Lipeng, ZHANG Jun, XIAO Zhenyu, et al. Optimal user pairing for downlink non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA)[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2019, 8(2): 328–331. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2018.2853741. [11] DING Zhiguo, FAN Pingzhi, and POOR H V. Impact of user pairing on 5G nonorthogonal multiple-access downlink transmissions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2016, 65(8): 6010–6023. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2015.2480766. [12] CHI C Y, LI W C, and LIN C H. Convex Optimization for Signal Processing and Communications: From Fundamentals to Applications[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2017: 217–218. [13] BOYD S and VANDENBERGHE L. Convex Optimization[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2009: 131–133. [14] YAN Wenjing, YUAN Xiaojun, HE Zhenqing, et al. Passive beamforming and information transfer design for reconfigurable intelligent surfaces aided multiuser MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2020, 38(8): 1793–1808. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2020.3000811. [15] WU Qingqing and ZHANG Rui. Intelligent reflecting surface enhanced wireless network via joint active and passive beamforming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(11): 5394–5409. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2936025. -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
