Combined Positioning of High-Speed Train Based on Improved Adaptive IMM Algorithm
-
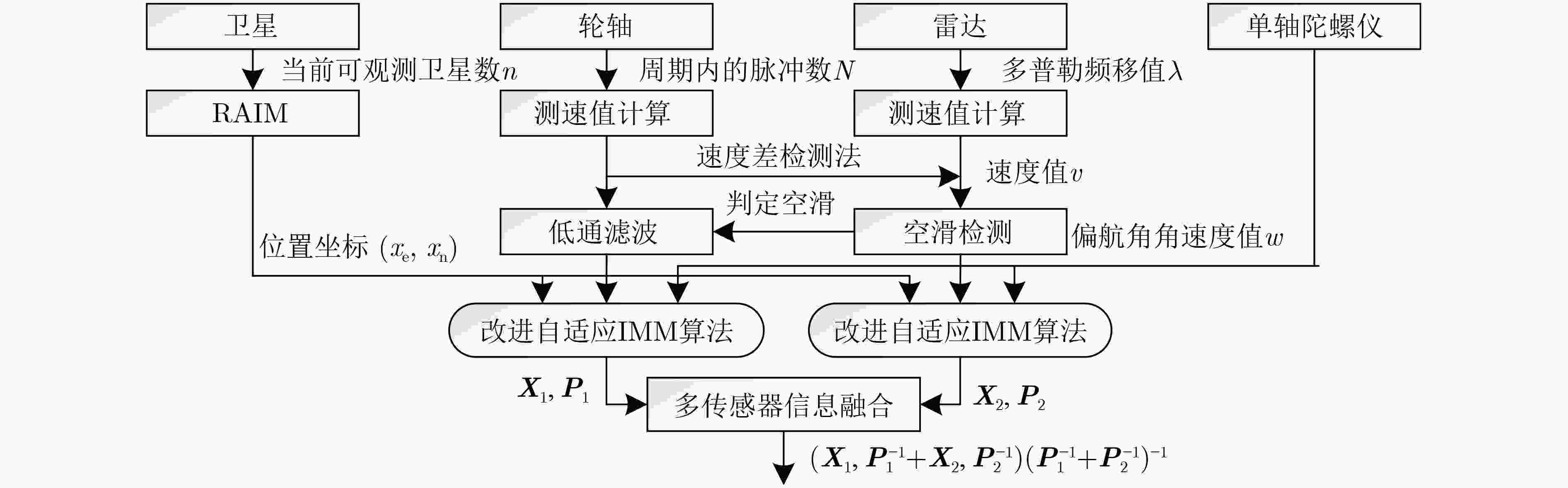
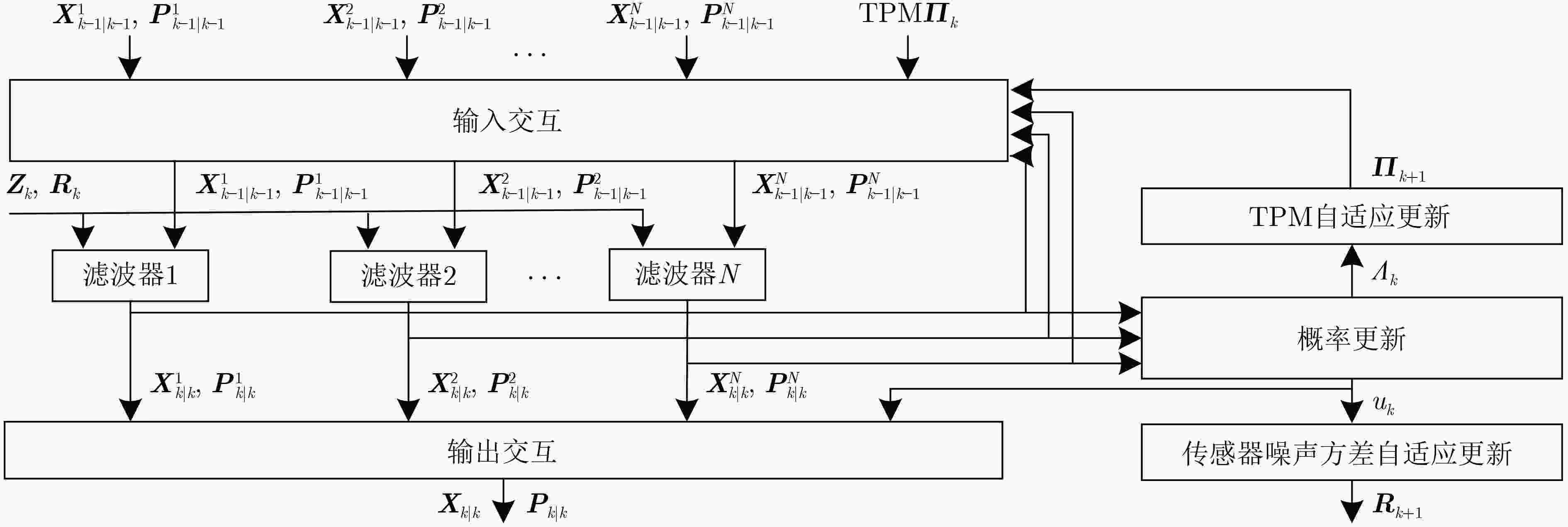
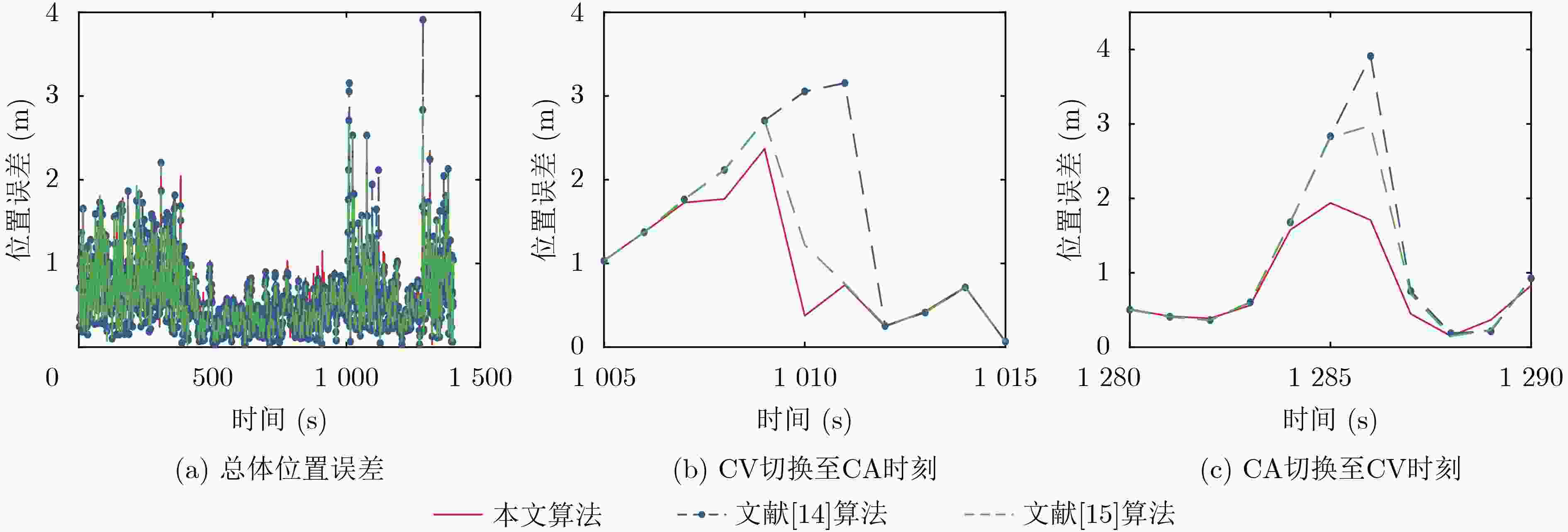
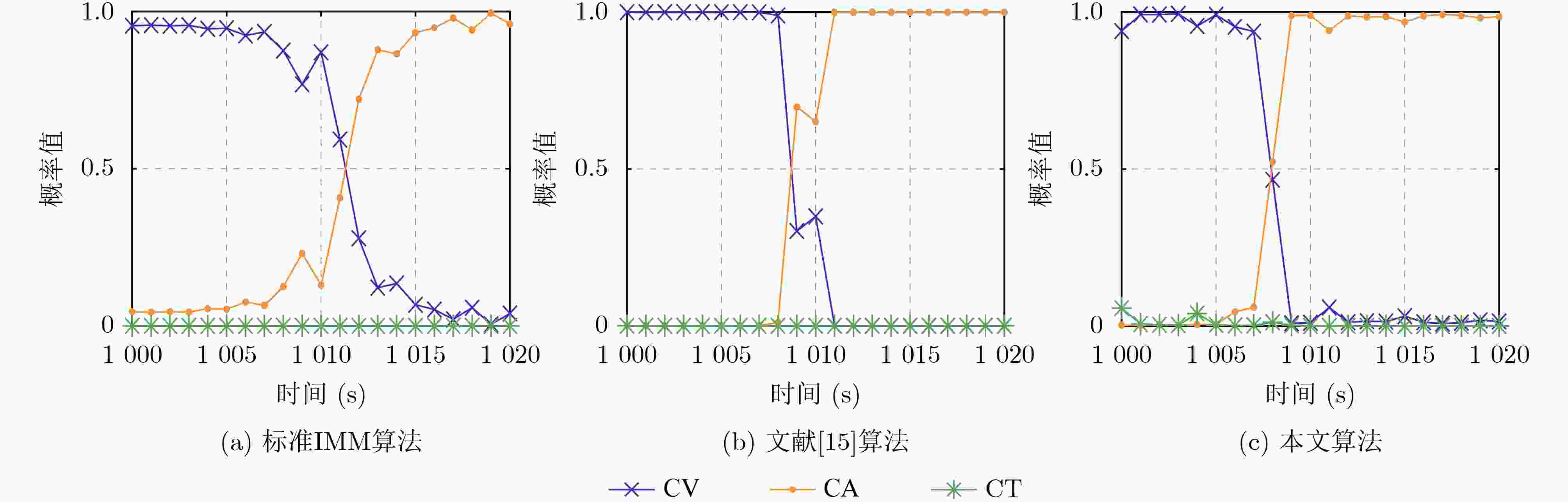
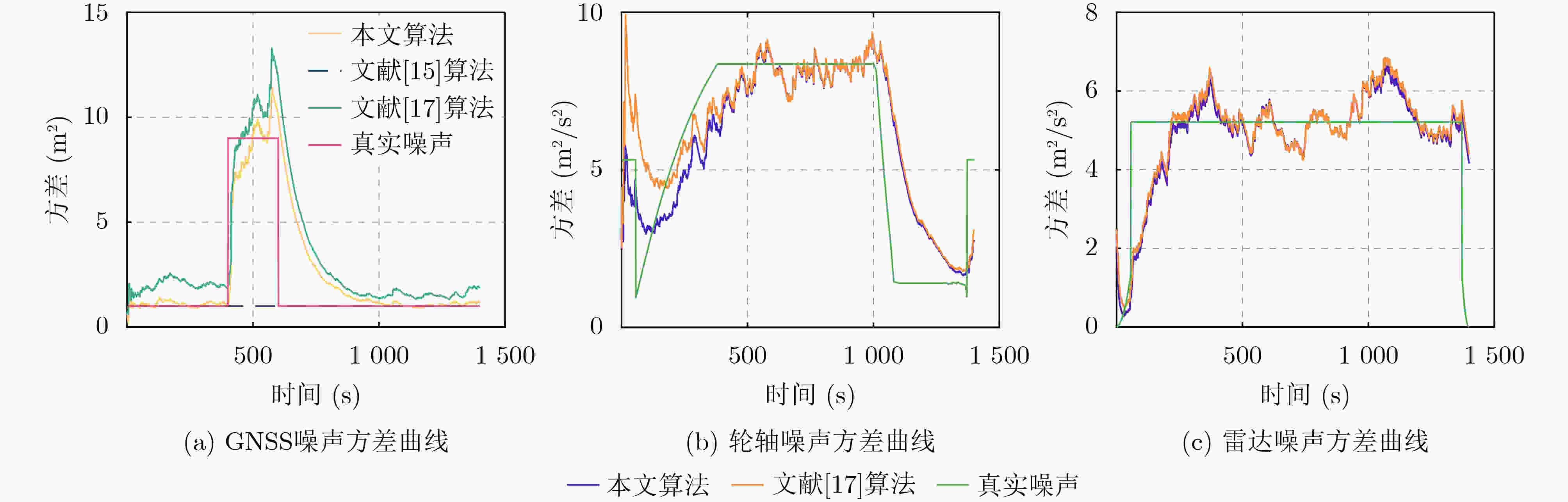
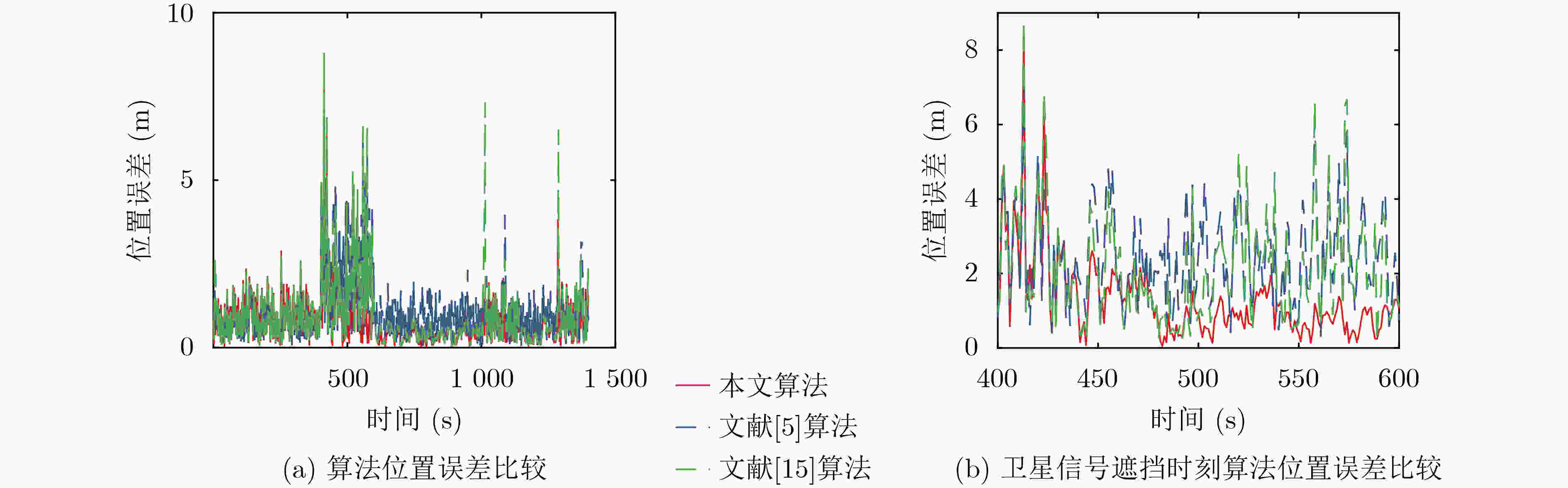
摘要: 针对列车高精度定位问题,该文提出基于改进自适应交互多模型(IMM)的高速列车高精度组合定位方法。首先,根据列车定位需求和各传感器特点,设计了卫星接收器、轮轴测速传感器、测速雷达以及单轴陀螺仪4种传感器的组合定位方案。然后,针对IMM融合滤波算法因先验信息不准导致固定参数设置不当的问题,引入Sage-Husa自适应滤波和转移概率矩阵(TPM)自适应更新集成为自适应IMM算法。针对多模型切换的滞后问题,利用子模型似然函数值能快速反映模型变化趋势的特点,将似然函数值设为判定标志,并引入判定窗对TPM矩阵元素进行修正,有效提升了模型的切换速度。最后,基于改进自适应IMM算法对4种传感器定位信息进行融合滤波,实现高速列车的高精度组合定位。仿真结果表明:改进后的算法相比其他自适应IMM算法提升定位精度1.6%~14.7%,并且能通过提高模型间切换速度来有效降低位置误差峰值,同时具备较好的抗噪性能。
-
关键词:
- 列车定位 /
- 交互式多模型 /
- Sage-Husa自适应滤波算法 /
- 马尔可夫转移概率矩阵 /
- 判定窗
Abstract: A high accuracy combined positioning method for high-speed trains based on the Improved Adaptive Interacting Multiple Model (IMM) is proposed for the high-precision positioning problem of trains. Firstly, a combined positioning scheme of four sensors, namely, satellite receiver, wheel speed sensor, speed radar and single-axis gyroscope, is designed according to the train positioning requirements and the characteristics of each sensor. Next, to address the issue that the IMM fusion filtering algorithm has improper fixed parameter settings due to inaccurate a priori information, the Sage-Husa adaptive filtering and the Transition Probability Matrix (TPM) adaptive update set are introduced to become the adaptive IMM algorithm. To solve the lag problem of multi-model switching, the likelihood function value is set as the judgment flag by using the feature that sub-model likelihood function value can quickly respond to the model change trend, and the judgment window is introduced to correct the TPM matrix elements, which effectively improves the model switching speed. Finally, based on the improved adaptive IMM algorithm, the fusion filtering of four sensor positioning information is carried out to realize the high-precision combined positioning of high-speed trains. Simulation results show that the enhanced algorithm improves the positioning accuracy by 1.6%~14.7% compared with other adaptive IMM algorithms, and it can effectively reduce the peak positional error by increasing the switching speed between models, and it also has a better anti-noise performance. -
表 1 列车定位传感器特性
传感器 类别 提供的信息 精度下降的场景 优势 误差来源 轮轴测速传感器 相对定位 速度 车轮粘着不良 低成本、高可靠 空转打滑、轮径磨损 车载多普勒雷达 相对定位 速度 极端积水 高精度 安装误差、车体振动 卫星接收器 直接定位 位置/速度 封闭空间 低成本、高精度 受卫星接收条件影响 INS 相对定位 加速度/角速度 无 高精度、高可靠 累计误差 表 2 CRH3型车的动力学参数
参数 取值 轮径(mm) 920 牵引质量(t) 536 回转系数 0.08 基本阻力(N) 0.79+0.0064v+0.000115v2 牵引(kN) –0.285v+300, v≤119 km/h, 31500/v, v>119 km/h 制动加速度(m/s2) –0.00043v+0.7105, v>210 km/h
, –0.0021v+1.0612, 172 km/h<v≤210 km/h
, –0.025v+5, 160 km/h<v≤172 km/h, 1 km/h<v≤160 km/h, 0表 3 各滤波算法的定位性能比较
算法 东方向位移MAE(m) 东方向位移最大偏差(m) 北方向位移MAE(m) 北方向位移最大偏差(m) 位置MAE(m) 位置RMSE(m) 最大位置偏差(m) 文献[5] 0.5090 2.1361 0.4788 2.0156 0.7690 0.8707 2.8537 标准IMM 0.4304 2.2686 0.4278 2.4337 0.6719 0.7801 2.9912 文献[13] 0.4244 2.4353 0.4147 2.9316 0.6551 0.7628 3.1984 文献[16] 0.4729 2.1850 0.4743 2.3048 0.7411 0.8456 2.6531 文献[14] 0.3892 2.3567 0.3876 2.8491 0.6082 0.7360 3.6359 文献[15] 0.3865 2.7326 0.3849 2.9204 0.6040 0.7325 3.5502 本文 0.3874 2.1912 0.3765 2.3092 0.5964 0.7209 2.7817 表 4 传感器实际精度
传感器 雷达(m/s) 轮轴测速传感器(m/s) 卫星(m) 噪声标准差(V≥100 km/h) $\dfrac{{{\text{0}}{\text{.4}}{f_0}\cos \theta }}{{3{\text{c}} \cdot 3.6}}$ $\dfrac{{0.2\% NV\Delta t}}{{3\pi D \cdot 3.6}}$ 1 噪声标准差(V<100 km/h) $\dfrac{{{\text{0}}{\text{.2\% }}V{f_0}\cos \theta }}{{3{\text{c}} \cdot 3.6}}$ $\dfrac{{0.6N\Delta t}}{{3\pi D \cdot 3.6}}$ 1 -
[1] OTEGUI J, BAHILLO A, LOPETEGI I, et al. A survey of train positioning solutions[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2017, 17(20): 6788–6797. doi: 10.1109/jsen.2017.2747137. [2] MARAIS J, BEUGIN J, and BERBINEAU M. A survey of GNSS-based research and developments for the European railway signaling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2017, 18(10): 2602–2618. doi: 10.1109/tits.2017.2658179. [3] 蔡煊, 陶汉卿, 侯宇婷, 等. 北斗卫星导航系统在列车定位中的应用研究与发展[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2022, 19(8): 2417–2427. doi: 10.19713/j.cnki.43-1423/u.t20211086.CAI Xuan, TAO Hanqing, HOU Yuting, et al. Application research and development of Beidou navigation satellite system in train positioning[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2022, 19(8): 2417–2427. doi: 10.19713/j.cnki.43-1423/u.t20211086. [4] JIANG Wei, CHEN Sirui, CAI Baigen, et al. A multi-sensor positioning method-based train localization system for Low Density Line[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(11): 10425–10437. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2869157. [5] 莫志松, 安鸿飞. 新型列控系统列车综合自主定位技术研究[J]. 铁道学报, 2022, 44(1): 56–64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2022.01.008.MO Zhisong and AN Hongfei. Research on comprehensive autonomous positioning technology of new train control system[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2022, 44(1): 56–64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2022.01.008. [6] KIM K, KONG S H, and JEON S Y. Slip and slide detection and adaptive information sharing algorithms for high-speed train navigation systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2015, 16(6): 3193–3203. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2015.2437899. [7] MAZOR E, AVERBUCH A, BAR-SHALOM Y, et al. Interacting multiple model methods in target tracking: A survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1998, 34(1): 103–123. doi: 10.1109/7.640267. [8] ZENG Yuan, LU Wenbin, YU Bo, et al. Improved IMM algorithm based on support vector regression for UAV tracking[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 33(4): 867–876. doi: 10.23919/JSEE.2022.000075. [9] 曾浩, 母王强, 杨顺平. 高机动目标跟踪ATPM-IMM算法[J]. 通信学报, 2022, 43(7): 93–101. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2022135.ZENG Hao, MU Wangqiang, and YANG Shunping. High maneuvering target tracking ATPM-IMM algorithm[J]. Journal on Communications, 2022, 43(7): 93–101. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2022135. [10] 彭滔, 张亚, 李世中. 基于航向角辅助的IMM-CKF雷达/红外跟踪算法[J]. 探测与控制学报, 2022, 44(2): 48–53. doi: 10.11812/j.issn.1008-1194.2022.2.tcykzxb202202009.PENG Tao, ZHANG Ya, and LI Shizhong. IMM-CKF Radar/IR tracking algorithm based on course angle aids[J]. Journal of Detection &Control, 2022, 44(2): 48–53. doi: 10.11812/j.issn.1008-1194.2022.2.tcykzxb202202009. [11] YAO Yiqing, XU Xiaosu, YANG Dongrui, et al. An IMM-UKF aided SINS/USBL calibration solution for underwater vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(4): 3740–3747. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.2972526. [12] 高学泽, 魏文军. 马尔可夫参数自适应IMM算法在列车定位中的应用[J]. 传感器与微系统, 2019, 38(1): 155–157,160. doi: 10.13873/J.1000-9787(2019)01-0155-03.GAO Xueze and WEI Wenjun. Application of Markov parameter adaptive IMM algorithm in train positioning[J]. Transducer and Microsystem Technologies, 2019, 38(1): 155–157,160. doi: 10.13873/J.1000-9787(2019)01-0155-03. [13] 戴定成, 姚敏立, 蔡宗平, 等. 改进的马尔可夫参数自适应IMM算法[J]. 电子学报, 2017, 45(5): 1198–1205. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2017.05.024.DAI Dingcheng, YAO Minli, CAI Zongping, et al. Improved adaptive Markov IMM algorithm[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2017, 45(5): 1198–1205. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2017.05.024. [14] 叶瑾, 许枫, 杨娟, 等. 一种改进的时变转移概率AIMM跟踪算法[J]. 应用声学, 2020, 39(2): 246–252. doi: 10.11684/j.issn.1000-310X.2020.02.011.YE Jin, XU Feng, YANG Juan, et al. An improved AIMM tracking algorithm based on adaptive transition probability[J]. Journal of Applied Acoustics, 2020, 39(2): 246–252. doi: 10.11684/j.issn.1000-310X.2020.02.011. [15] 王平波, 刘杨. 基于改进自适应IMM-UKF算法的水下目标跟踪[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(6): 1999–2005. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211128.WANG Pingbo and LIU Yang. Underwater target tracking algorithm based on improved adaptive IMM-UKF[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(6): 1999–2005. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211128. [16] 邓雯琪, 黄景春, 康灿, 等. 基于交互式多模型滤波算法机车车速估计[J]. 传感器与微系统, 2022, 41(7): 122–125. doi: 10.13873/J.1000-9787(2022)07-0122-04.DENG Wenqi, HUANG Jingchun, KANG Can, et al. Locomotive speed estimation based on interactive multi-model filtering algorithm[J]. Transducer and Microsystem Technologies, 2022, 41(7): 122–125. doi: 10.13873/J.1000-9787(2022)07-0122-04. [17] XU Shuqing, ZHOU Haiyin, WANG Jiongqi, et al. SINS/CNS/GNSS integrated navigation based on an improved federated Sage–Husa adaptive filter[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(17): 3812. doi: 10.3390/s19173812. [18] 李飞, 段哲民, 龚诚, 等. GNSS接收机自主完好性监测算法研究[J]. 测绘通报, 2007(8): 14–15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0494-0911.2007.08.005.LI Fei, DUAN Zhemin, GONG Cheng, et al. Research on RAIM Algorithm of GNSS[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2007(8): 14–15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0494-0911.2007.08.005. [19] 杨栋, 王思明, 许建玉. CRH3型动车组牵引制动模式曲线的算法研究[J]. 城市轨道交通研究, 2013, 16(12): 94–98. doi: 10.16037/j.1007-869x.2013.12.025.YANG Dong, WANG Siming, and XU Jianyu. On algorithm of traction and braking mode curve for CRH3 multiple unit[J]. Urban Mass Transit, 2013, 16(12): 94–98. doi: 10.16037/j.1007-869x.2013.12.025. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
