Human Activities Recognition Based on Two-stream NonLocal Spatial Temporal Residual Convolution Neural Network
-
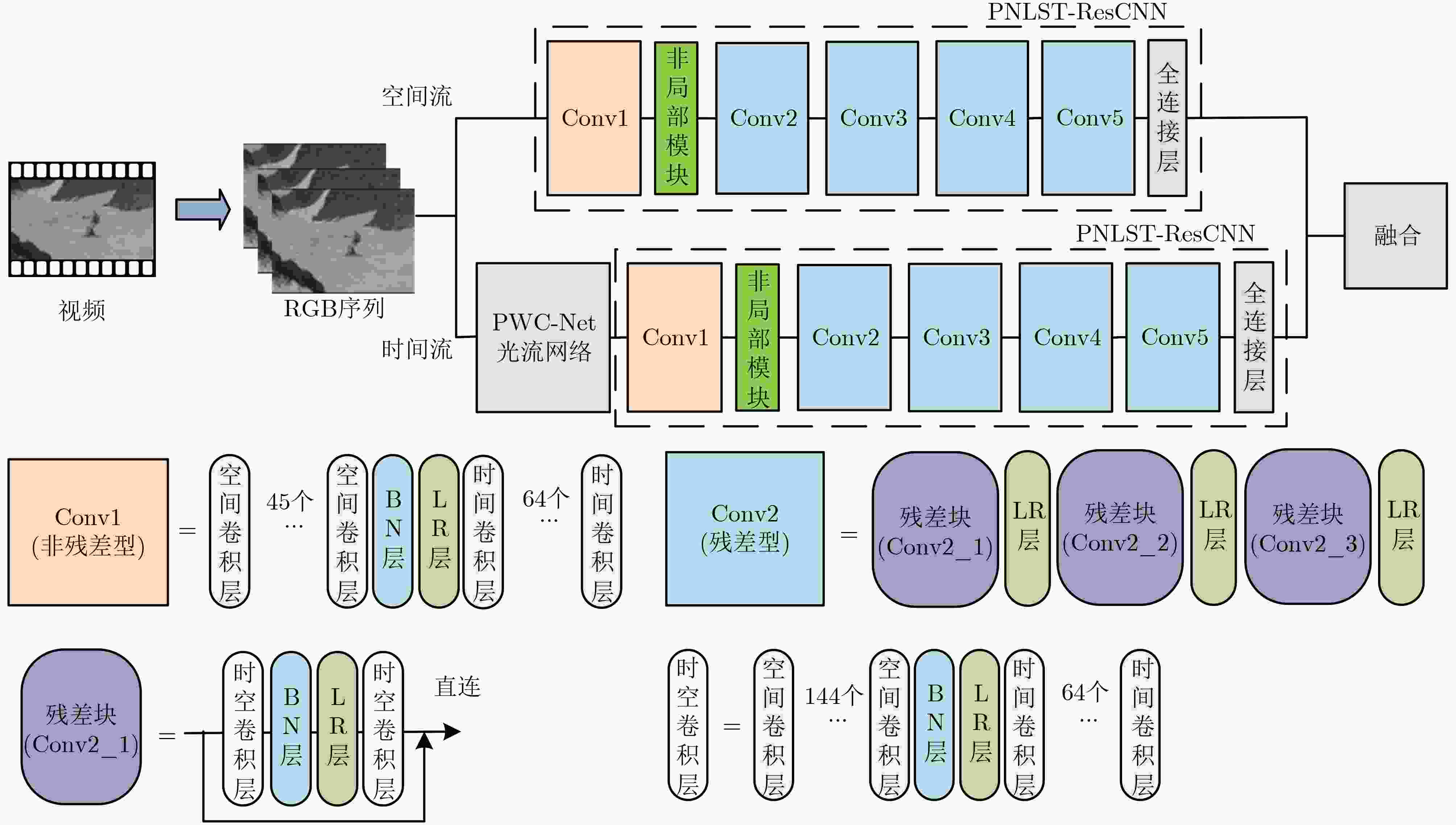
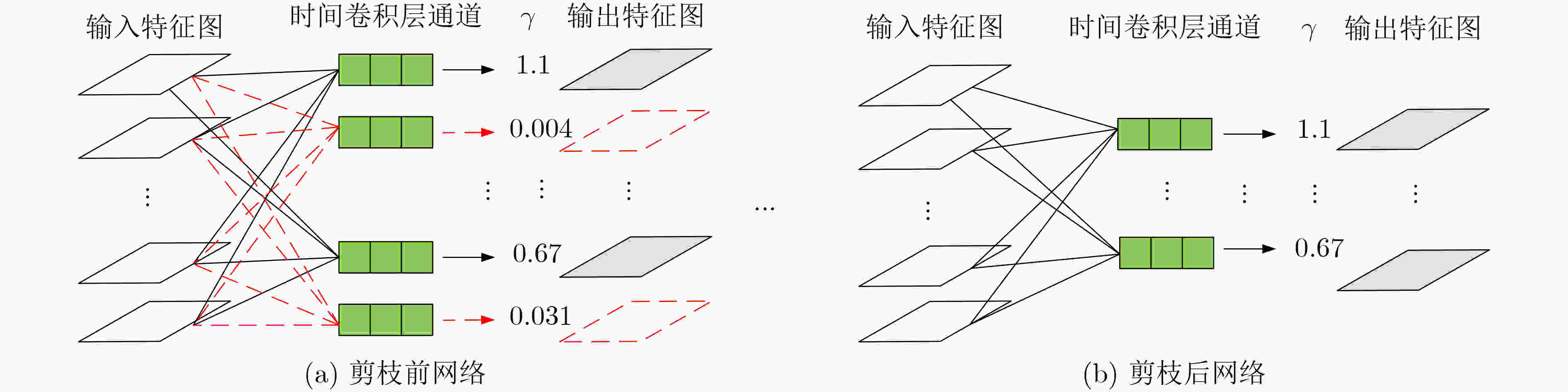
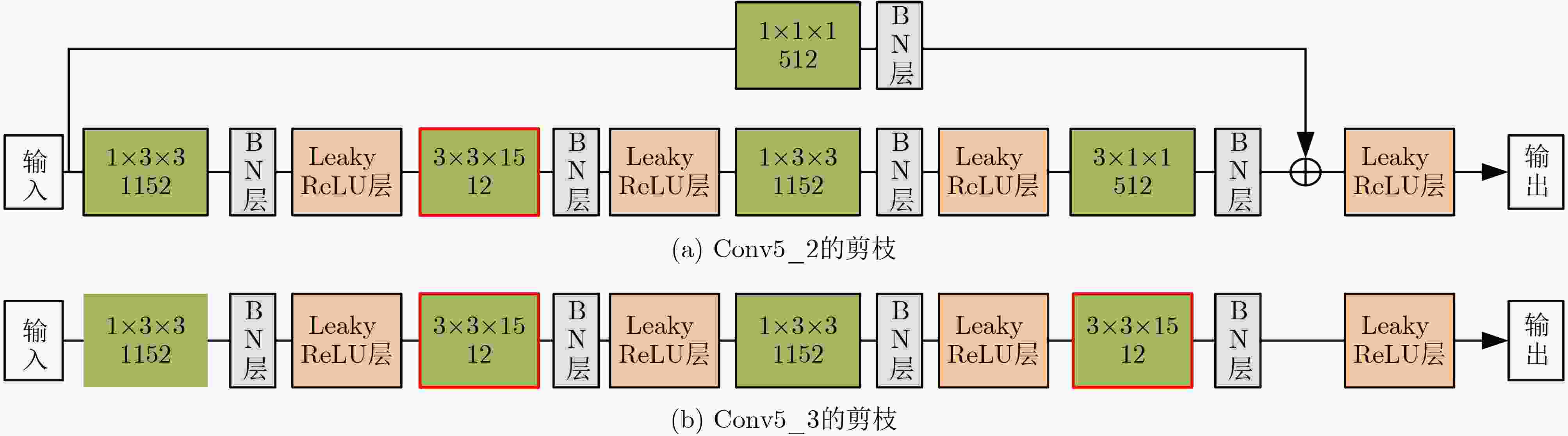
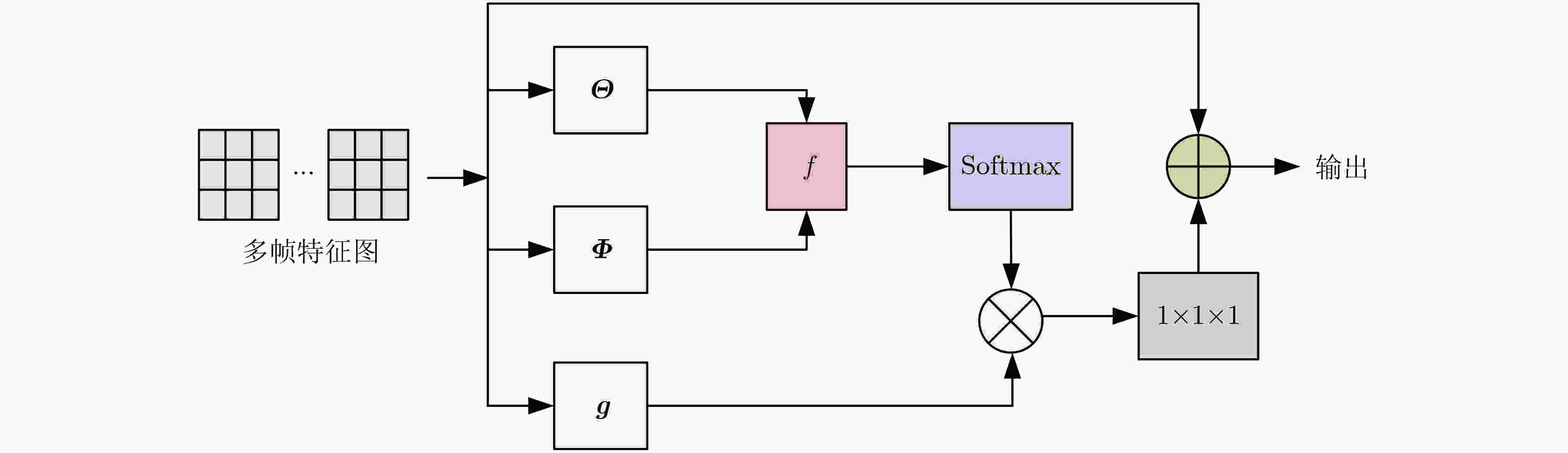
摘要: 3维卷积神经网络(3D CNN)与双流卷积神经网络(two-stream CNN)是视频中人体行为识别研究的常用架构,且各有优势。该文旨在研究结合两种架构且复杂度低、识别精度高的人体行为识别模型。具体地,该文提出基于通道剪枝的双流-非局部时空残差卷积神经网络(TPNLST-ResCNN),该网络采用双流架构,分别在时间流子网络和空间流子网络采用时空残差卷积神经网络(ST-ResCNN),并采用均值融合算法融合两个子网络的识别结果。进一步地,为了降低网络的复杂度,该文提出了针对时空残差卷积神经网络的通道剪枝方案,在实现模型压缩的同时,可基本保持模型的识别精度;为了使得压缩后网络能更好地学习到输入视频中人体行为变化的长距离时空依赖关系,提高网络的识别精度,该文提出在剪枝后网络的首个残差型时空卷积块前引入一个非局部模块。实验结果表明,该文提出的人体行为识别模型在公共数据集UCF101和HMDB51上的识别准确率分别为98.33%和74.63%。与现有方法相比,该文模型具有参数量小、识别精度高的优点。Abstract: Three-Dimensional Convolution Neural Network (3D CNN) and two-stream Convolution Neural Network (two-stream CNN) are commonly-used for human activities recognition, and each has its own advantages. A human activities recognition model with low complexity and high recognition accuracy is proposed by combining the two architectures. Specifically, a Two-stream NonLocal Spatial Temporal Residual Convolution Neural Network based onchannel Pruning (TPNLST-ResCNN) is proposed in this paper. And Spatial Temporal Residual Convolution Neural Networks (ST-ResCNN) are used both in the temporal stream subnetwork and the spatial stream subnetwork. The final recognition results are acquired by fusing the recognition results of the two subnetworks under a mean fusion algorithm. Furthermore, in order to reduce the complexity of the network, a channel pruning scheme for ST-ResCNN is presented to achieve model compression. In order to enable the compressed network to learn the long-distance spatiotemporal dependencies of human activity changes better and improve the recognition accuracy of the network, a nonlocal block is introduced before the first residual spatial temporal convolution block of the pruned network. The experimental results show that the recognition accuracies of the proposed human activity recognition model are 98.33% and 74.63% on the public dataset UCF101 and HMDB51, respectively. Compared with the existed algorithms, the proposed model in this paper has fewer parameters and higher recognition accuracy.
-
表 1 不同网络深度ST-ResCNN的结构及其识别精度
网络模型 网络层数 参数量(M) Conv2(个) Conv3(个) Conv4(个) Conv5(个) 精度(%) A 10 14.38 1 1 1 1 57.70 B 12 15.26 1 2 1 1 55.65 C 12 17.92 1 1 2 1 55.80 D 12 28.54 1 1 1 2 55.17 表 2 融合实验结果对比(%)
数据集 空间流 时间流 最大值融合 均值融合 UCF101 94.60 85.67 97.70 98.00 HMDB51 58.63 50.15 62.80 69.20 表 3 UCF101和HMDB51上剪枝的实验结果(%)
数据集 子网络 剪枝阈值 模型压缩 精度 融合精度 UCF101 空间流 70 41.70 92.13 96.83 时间流 80 41.70 81.96 HMDB51 空间流 40 37.97 59.11 72.27 时间流 30 27.89 54.97 表 4 提高输入帧长后网络的识别精度对比
数据集 输入帧长 剪枝前的精度(%) 剪枝后的精度(%) UCF101 8 96.88 96.83 16 98.00 97.75 HMDB51 8 62.10 72.27 16 69.20 73.01 表 5 3种网络的对比实验(输入帧长为16、均值融合)
网络名称 数据集 参数量(M) 精度(%) 精度变化(%) ST-ResCNN HMDB51 28.76 69.20 +7.10 UCF101 127.08 98.00 +1.12 PST-ResCNN HMDB51 19.29 73.01 +0.74 UCF101 70.29 97.75 +0.92 PNLST-ResCNN HMDB51 20.11 74.63 +1.53 UCF101 71.68 98.33 +4.67 表 6 本文算法与现有算法的比较
算法 输入 预训练数据集 参数量(M) 精度(%) UCF101 HMDB51 C3D[2] RGB Sports-1M 61.63 82.3 56.8 P3D[5] RGB Sports-1M – 88.6 – R3D-34[21] RGB Kinetics-700 63.52 88.8 59.5 R(2+1)D-50[21] RGB Kinetics-700+Sports1M 53.95 93.4 69.4 CIDC[11] RGB – 103.00 97.9 75.2 ActionCLIP[22] RGB 网络数据 85.58 97.1 76.2 STM(ResNet-50)[23] RGB ImageNet+Kinetics – 96.2 72.2 TDN(ResNet-50) [11] RGB ImageNet+Kinetics – 97.4 76.3 R(2+1)D-34[24] 双流 Sports-1M 127.08 95.0 72.7 本文PNLST-ResCNN-34 双流 Kineticts-400 71.68 98.3 – 本文PNLST-ResCNN-10 双流 – 20.11 – 74.6 -
[1] 白静, 杨瞻源, 彭斌, 等. 三维卷积神经网络及其在视频理解领域中的应用研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(6): 2273–2283. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220596.BAI Jing, YANG Zhanyuan, PENG Bin, et al. Research on 3D convolutional neural network and its application to video understanding[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2023, 45(6): 2273–2283. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220596. [2] CARREIRA J and ZISSERMAN A. QUO Vadis, action recognition? A new model and the kinetics dataset[C]. The 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 6299–6308. [3] QIU Zhaofan, YAO Ting, and MEI Tao. Learning spatio-temporal representation with pseudo-3D residual networks[C]. The 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 5534–5542. [4] 王粉花, 张强, 黄超, 等. 融合双流三维卷积和注意力机制的动态手势识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(5): 1389–1396. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200065.WANG Fenhua, ZHANG Qiang, HUANG Chao, et al. Dynamic gesture recognition combining two-stream 3D convolution with attention mechanisms[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(5): 1389–1396. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200065. [5] PANG Chen, LU Xuequan, and LYU Lei. Skeleton-based action recognition through contrasting two-stream spatial-temporal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2023, 1520–9210. [6] VARSHNEY N and BAKARIYA B. Deep convolutional neural model for human activities recognition in a sequence of video by combining multiple CNN streams[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2022, 81(29): 42117–42129. doi: 10.1007/s11042-021-11220-4. [7] LI Bing, CUI Wei, WANG Wei, et al. Two-stream convolution augmented transformer for human activity recognition[C]. The 35th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2021: 286–293. [8] ILG E, MAYER N, SAIKIA T, et al. Flownet 2.0: Evolution of optical flow estimation with deep networks[C]. The 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 1647–1655. [9] SUN Deqing, YANG Xiaodong, LIU Mingyu, et al. PWC-net: CNNs for optical flow using pyramid, warping, and cost volume[C]. The 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 8934–8943. [10] WEI S E, RAMAKRISHNA V, KANADE T, et al. Convolutional pose machines[C]. The 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 4724–4732. [11] LI Xinyu, SHUAI Bing, and TIGHE J. Directional temporal modeling for action recognition[C]. The 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 275–291. [12] WANG Xiaolong, GIRSHICK R, GUPTA A, et al. Non-local neural networks[C]. The 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7794–7803. [13] HUANG Min, QIAN Huimin, HAN Yi, et al. R(2+1)D-based two-stream CNN for human activities recognition in videos[C]. The 40th Chinese Control Conference, Shanghai, China, 2021: 7932–7937. [14] LIU Zhuang, LI Jianguo, SHEN Zhiqiang, et al. Learning efficient convolutional networks through network slimming[C]. The 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 2755–2763. [15] VAROL G, LAPTEV I, and SCHMID C. Long-term temporal convolutions for action recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(6): 1510–1517. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2712608. [16] SOOMRO K, ZAMIR A R, and SHAH M. UCF101: A dataset of 101 human actions classes from videos in the wild[OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1907.06987, 2012. [17] KUEHNE H, JHUANG H, GARROTE E, et al. HMDB: A large video database for human motion recognition[C]. The 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 2011: 2556−2563. [18] KAY W, CARREIRA J, SIMONYAN K, et al. The kinetics human action video dataset[OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1705.06950, 2017. [19] CARREIRA J, NOLAND E, HILLIER C, et al. A short note on the kinetics-700 human action dataset[OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1907.06987, 2019. [20] KARPATHY A, TODERICI G, SHETTY S, et al. Large-scale video classification with convolutional neural networks[C]. The 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 1725–1732. [21] KATAOKA H, WAKAMIYA T, HARA K, et al. Would mega-scale datasets further enhance spatiotemporal 3D CNNs?[OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2004.04968, 2020. [22] WANG Mengmeng, XING Jiazheng, and LIU Yong. ActionCLIP: A new paradigm for video action recognition[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2109.08472, 2021. [23] JIANG Boyuan, WANG Mengmeng, GAN Weihao, et al. STM: SpatioTemporal and motion encoding for action recognition[C]. The 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 2000–2009. [24] TRAN D, WANG Heng, TORRESANI L, et al. A closer look at spatiotemporal convolutions for action recognition[C]. The 2018 IEEE/CVF conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 6450–6459. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
