Robust Secure Resource Allocation Algorithm for Cognitive Backscatter Communication with Hardware Impairment
-
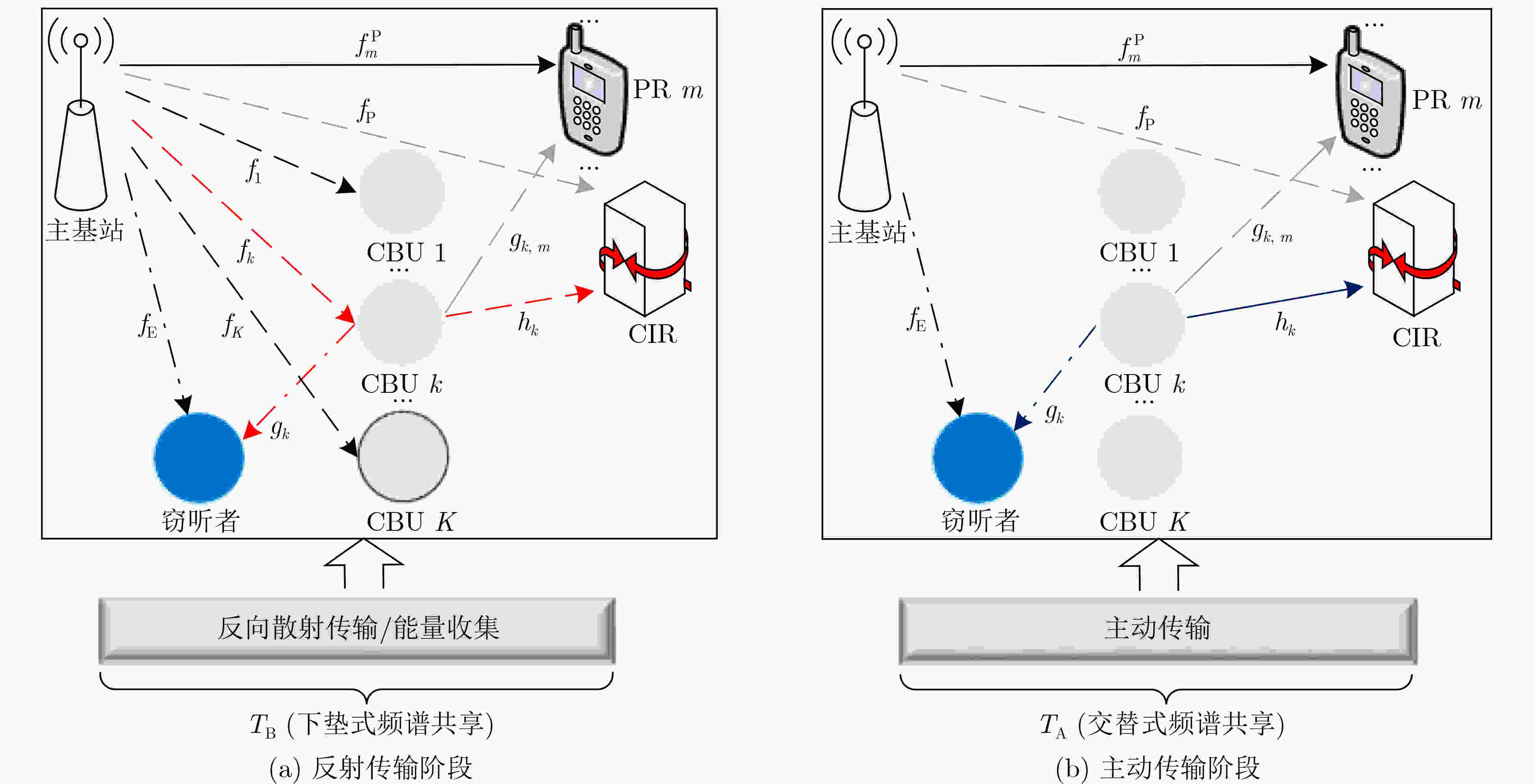
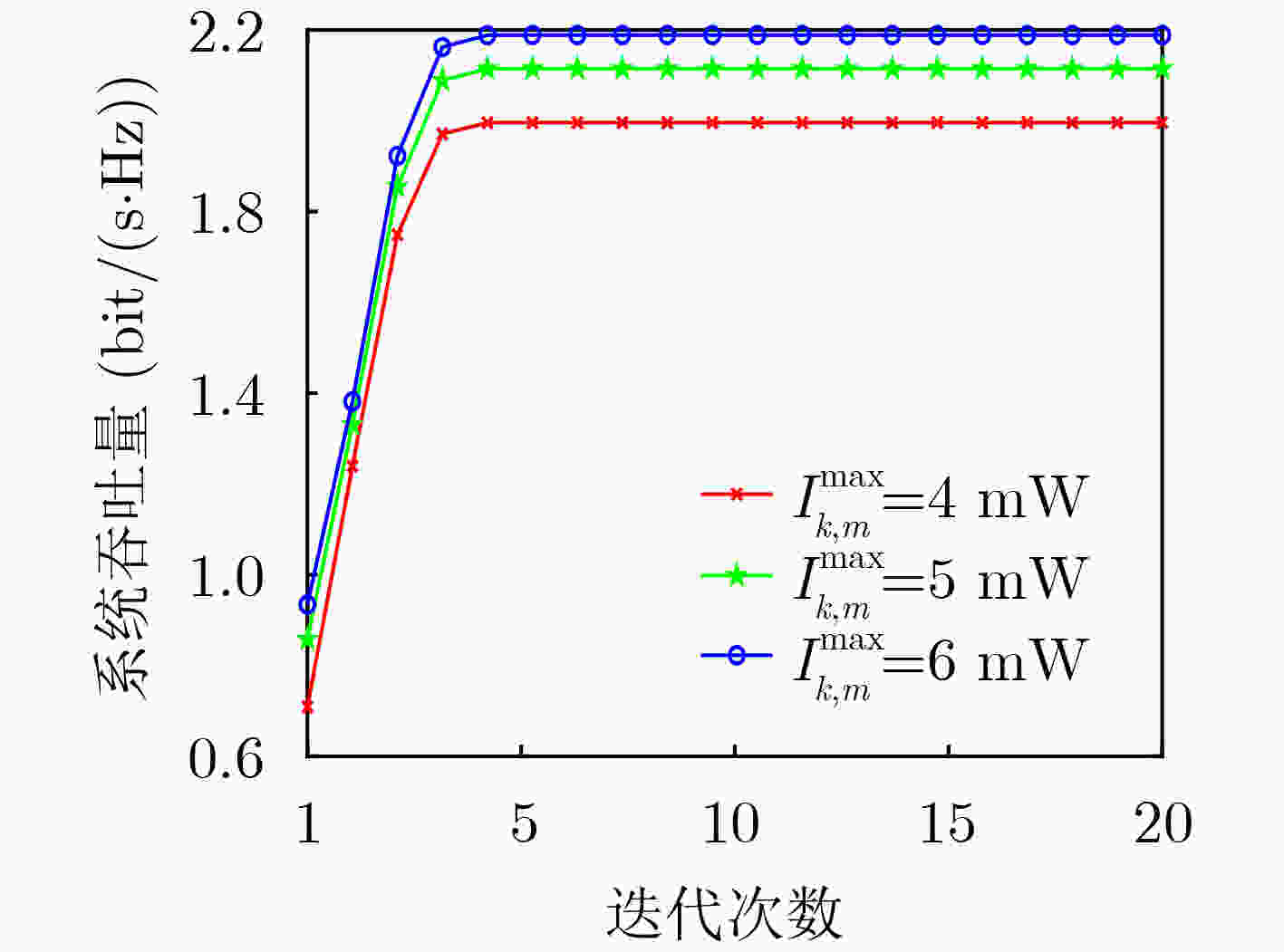
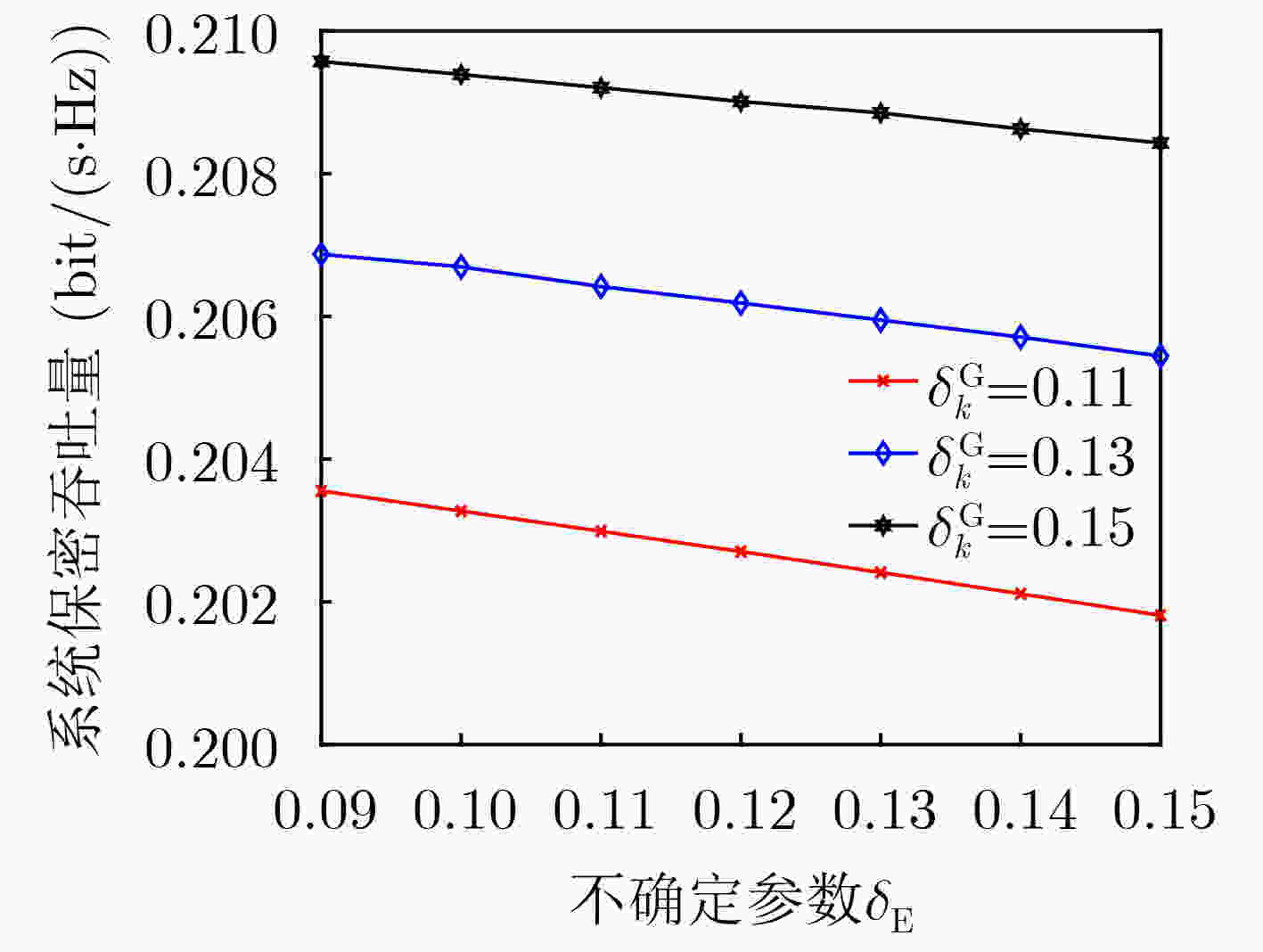
摘要: 为了提高反向散射通信网络频谱效率、传输鲁棒性及信息安全性,该文提出一种基于硬件损伤的认知反向散射通信网络鲁棒安全资源分配算法。首先,考虑认知反向散射用户的最小安全速率、传输时间、能量收集和反射系数等约束,基于有界信道不确定性和频谱感知误差模型,建立一个多变量耦合的吞吐量最大化非凸资源分配问题。其次,利用最坏准则、连续凸近似和交替优化方法,将原问题转换为凸优化问题,并提出一种基于迭代的鲁棒资源分配算法。仿真结果表明,与现有算法对比,所提算法具有较好的鲁棒性。Abstract: To improve spectral efficiency, transmission robustness, and information security of backscatter communication networks, a robust secure resource allocation algorithm is proposed for cognitive backscatter communication networks with hardware impairments. Firstly, considering the constraints of the minimum secure rate of each cognitive backscatter user, transmission time, energy harvesting, and reflection coefficients, a multivariable coupled resource allocation problem with throughput maximization is established under bounded channel uncertainties and spectrum sensing errors. Secondly, the original problem is transformed into a convex problem by using a worst-case approach, successive convex approximation, alternating optimization, and an iteration-based robust resource allocation algorithm is proposed to solve it. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm has better robustness by comparing it with the existing algorithms.
-
表 1 频谱检测情况
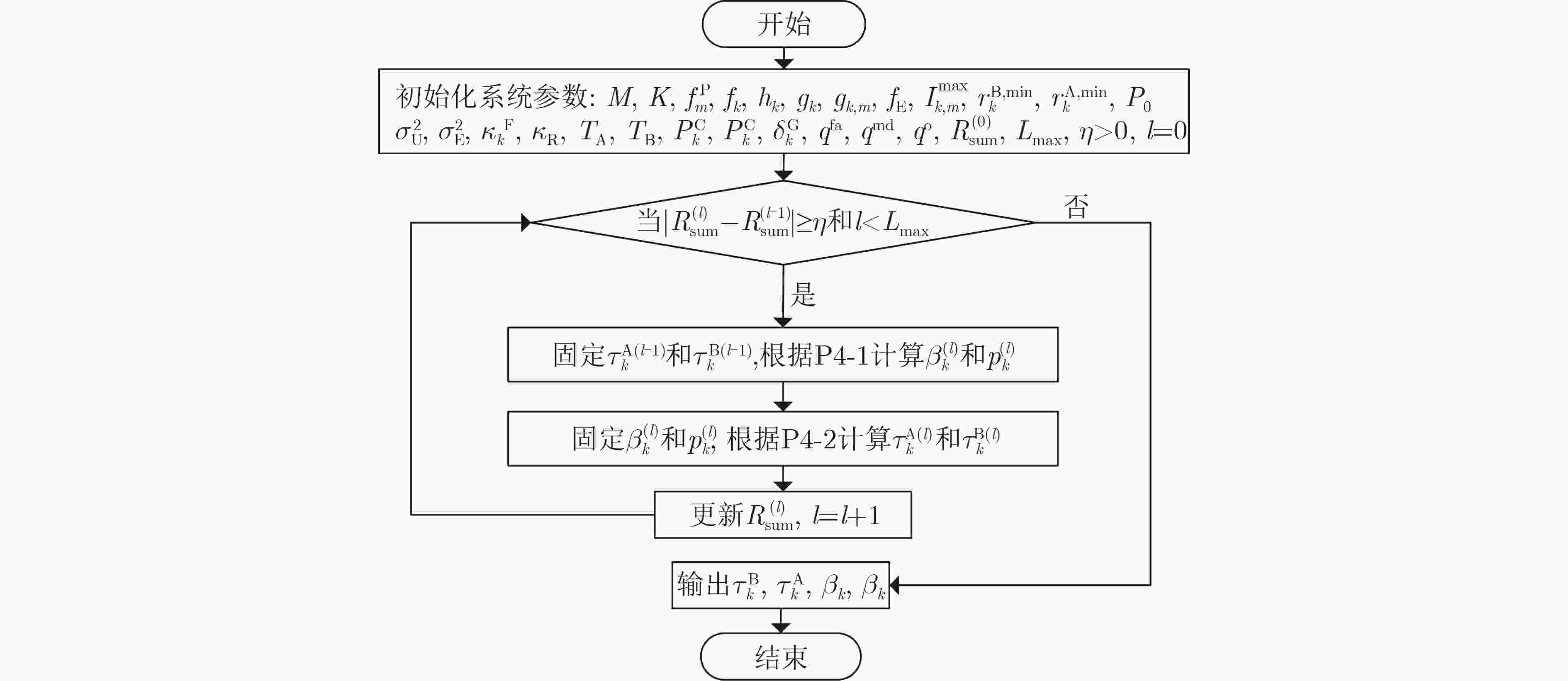
授权频谱状态 授权频谱感知结果 条件感知概率 占用$ \left( O \right) $ 占用$ \left( {\tilde O} \right) $ ${\rho ^1} = \Pr \{ O|\tilde O\} = \dfrac{ {\left( {1 - {q^{ {\text{md} } } }} \right){q^{\text{o} } } }}{ { {q^{ {\text{fa} } } }\left( {1 - {q^{\text{o} } } } \right) + \left( {1 - {q^{ {\text{md} } } }} \right){q^{\text{o} } } }}$ 空闲$ \left( V \right) $ 占用$ \left( {\tilde O} \right) $ ${\rho ^2} = \Pr \{ V|\tilde O\} = \dfrac{ { {q^{ {\text{fa} } } }\left( {1 - {q^{\text{o} } } } \right)} }{ { {q^{ {\text{fa} } } }\left( {1 - {q^{\text{o} } } } \right) + \left( {1 - {q^{ {\text{md} } } }} \right){q^{\text{o} } } }}$ 占用$ \left( O \right) $ 空闲$ \left( {\tilde V} \right) $ ${\rho ^3} = \Pr \{ O|\tilde V\} = \dfrac{ { {q^{ {\text{md} } } }{q^{\text{o} } } }}{ {\left( {1 - {q^{ {\text{fa} } } }} \right)\left( {1 - {q^{\text{o} } } } \right) + {q^{ {\text{md} } } }{q^{\text{o} } } }}$ 空闲$ \left( V \right) $ 空闲$ \left( {\tilde V} \right) $ ${\rho ^4} = \Pr \{ V|\tilde V\} = \dfrac{ {\left( {1 - {q^{ {\text{fa} } } }} \right)\left( {1 - {q^{\text{o} } } } \right)} }{ {\left( {1 - {q^{ {\text{fa} } } }} \right)\left( {1 - {q^{\text{o} } } } \right) + {q^{ {\text{md} } } }{q^{\text{o} } } }}$ 算法1 基于迭代的鲁棒资源分配算法 初始化系统参数:$ {P_0} $, $ M $, $ K $, $ f_m^{\text{P}} $, $ {f_{\text{P}}} $, $ {f_k} $, $ {h_k} $, $ {g_k} $, $ {g_{k,m}} $, $ {f_{\text{E}}} $, $ I_{k,m}^{{\text{max}}} $, $ r_k^{{\text{B,min}}} $, $ r_k^{{\text{A,min}}} $, $ \sigma _{\text{U}}^2 $, $ \sigma _{\text{E}}^2 $, $ \kappa _k^{\text{F}} $, $ {\kappa _{\text{R}}} $, ${T_{\rm{A}}}$, ${T_{\rm{B}}}$, $P_k^{\text{C}}$, $p_k^{\text{C}}$, $ \delta _k^{\text{G}} $, $ {\delta _{\text{E}}} $, $ {q^{{\text{fa}}}} $,
$ {q^{{\text{md}}}} $, $ {q^{\text{o}}} $, $R_{{\text{sum}}}^{\left( 0 \right)}$;定义算法收敛精度$\eta > 0$和外层最大迭代次数${L_{\max }}$;初始化外层迭代次数$l = 0$;(1) while$|R_{ {\text{sum} } }^{\left( l \right)} - R_{ {\text{sum} } }^{\left( {l - 1} \right)}| \ge \eta$或$l \le {L_{\max } }$,do; (2) 定义迭代次数$l = l + 1$; (3) 给定${ \tau_k^{{\rm{B}}{\left( {l - 1} \right)} } }$和${\tau_k^{ {\text{A} }{\left( {l - 1} \right)} } }$的值,根据P4-1计算$ \beta _k^{(l)} $和$ p_k^{(l)} $; (4) 固定$ \beta _k^{(l)} $和$ p_k^{(l)} $,根据P4-2计算${\tau_k^{{\rm{B}}{\left( l \right)} } }$和${\tau_k^{{\text{A}} \left( l \right)} }$; (5) 更新吞吐量$R_{{\text{sum}}}^{\left( l \right)}$; (6) end while; (7) 输出$\tau _k^{\rm{B}}$, $ \tau _k^{\text{A}} $, $ {\beta _k} $, $ {p_k} $ -
[1] XU Yongjun, GUI Guan, GACANIN H, et al. A survey on resource allocation for 5G heterogeneous networks: Current research, future trends, and challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2021, 23(2): 668–695. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2021.3059896. [2] XU Yongjun, GU Bowen, HU R Q, et al. Joint computation offloading and radio resource allocation in MEC-based wireless-powered backscatter communication networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(6): 6200–6205. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3077094. [3] 张晓茜, 徐勇军. 面向零功耗物联网的反向散射通信综述[J]. 通信学报, 2022, 43(11): 199–212. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2022199.ZHANG Xiaoxi and XU Yongjun. Survey on backscatter communication for zero-power IoT[J]. Journal on Communications, 2022, 43(11): 199–212. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2022199. [4] 徐勇军, 杨浩克, 李国军, 等. 多标签无线供电反向散射通信网络能效优化算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(10): 3492–3498. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210772.XU Yongjun, YANG Haoke, LI Guojun, et al. Energy-efficient optimization algorithm in multi-tag wireless-powered backscatter communication networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(10): 3492–3498. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210772. [5] 徐勇军. 下垫式认知无线电网络动态资源分配问题研究[D]. [博士论文]. 吉林大学, 2015.XU Yongjun. Research on dynamic resource allocation for underlay cognitive radio networks[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation]. Jilin University, 2015. [6] LI Xingwang, ZHENG Yike, KHAN W U, et al. Physical layer security of cognitive ambient backscatter communications for green internet-of-things[J]. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, 2021, 5(3): 1066–1076. doi: 10.1109/TGCN.2021.3062060. [7] LI Xingwang, WANG Qunshu, ZENG Ming, et al. Physical-layer authentication for ambient backscatter-aided NOMA symbiotic systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2023, 71(4): 2288–2303. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2023.3245659. [8] XU Yongjun, XIE Hao, LI Dong, et al. Energy-efficient beamforming for heterogeneous industrial IoT networks with phase and distortion noises[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022, 18(11): 7423–7434. doi: 10.1109/TII.2022.3158612. [9] LI Xingwang, LIU Huiling, LI Geng, et al. Effective capacity analysis of AmBC-NOMA communication systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71(10): 11257–11261. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3186871. [10] JAFARI R and FAPOJUWO A O. Maximizing secondary users’ sum-throughput in an in-band full-duplex cognitive wireless powered backscatter communication network[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2022, 16(3): 4082–4093. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2021.3124097. [11] XIAO Sa, GUO Huayan, and LIANG Yingchang. Resource allocation for full-duplex-enabled cognitive backscatter networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(6): 3222–3235. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2912203. [12] LYU Bin, GUO Haiyan, YANG Zhen, et al. Throughput maximization for hybrid backscatter assisted cognitive wireless powered radio networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2018, 5(3): 2015–2024. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2820180. [13] KANG Xin, LIANG Yingchang, and YANG Jing. Riding on the primary: A new spectrum sharing paradigm for wireless-powered IoT devices[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2018, 17(9): 6335–6347. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2018.2859389. [14] ZHUANG Yuandong, LI Xi, JI Hong, et al. Optimal resource allocation for RF-powered underlay cognitive radio networks with ambient backscatter communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(12): 15216–15228. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3037152. [15] KISHORE R, GURUGOPINATH S, SOFOTASIOS P C, et al. Opportunistic ambient backscatter communication in RF-powered cognitive radio networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2019, 5(2): 413–426. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2019.2907090. [16] ZHANG Yu, GAO Feifei, FAN Lisheng, et al. Secure communications for multi-tag backscatter systems[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2019, 8(4): 1146–1149. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2019.2909199. [17] WANG Pu, WANG Ning, DABAGHCHIAN M, et al. Optimal resource allocation for secure multi-user wireless powered backscatter communication with artificial noise[C]// IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Paris, France, 2019: 460–468. [18] XU Yongjun, GU Bowen, and LI Dong. Robust energy-efficient optimization for secure wireless-powered backscatter communications with a non-linear EH model[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2021, 25(10): 3209–3213. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2021.3097737. [19] XU Yongjun, XIE Hao, WU Qingqing, et al. Robust max-min energy efficiency for RIS-aided HetNets with distortion noises[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2022, 70(2): 1457–1471. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2022.3141798. [20] YE Yinghui, SHI Liqin, CHU Xiaoli, et al. Mutualistic cooperative ambient backscatter communications under hardware impairments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2022, 70(11): 7656–7668. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2022.3201119. [21] XU Yongjun, YANG Meng, YANG Yang, et al. Max-min energy-efficient optimization for cognitive heterogeneous networks with spectrum sensing errors and channel uncertainties[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2022, 11(6): 1113–1117. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2021.3130632. -





 下载:
下载:
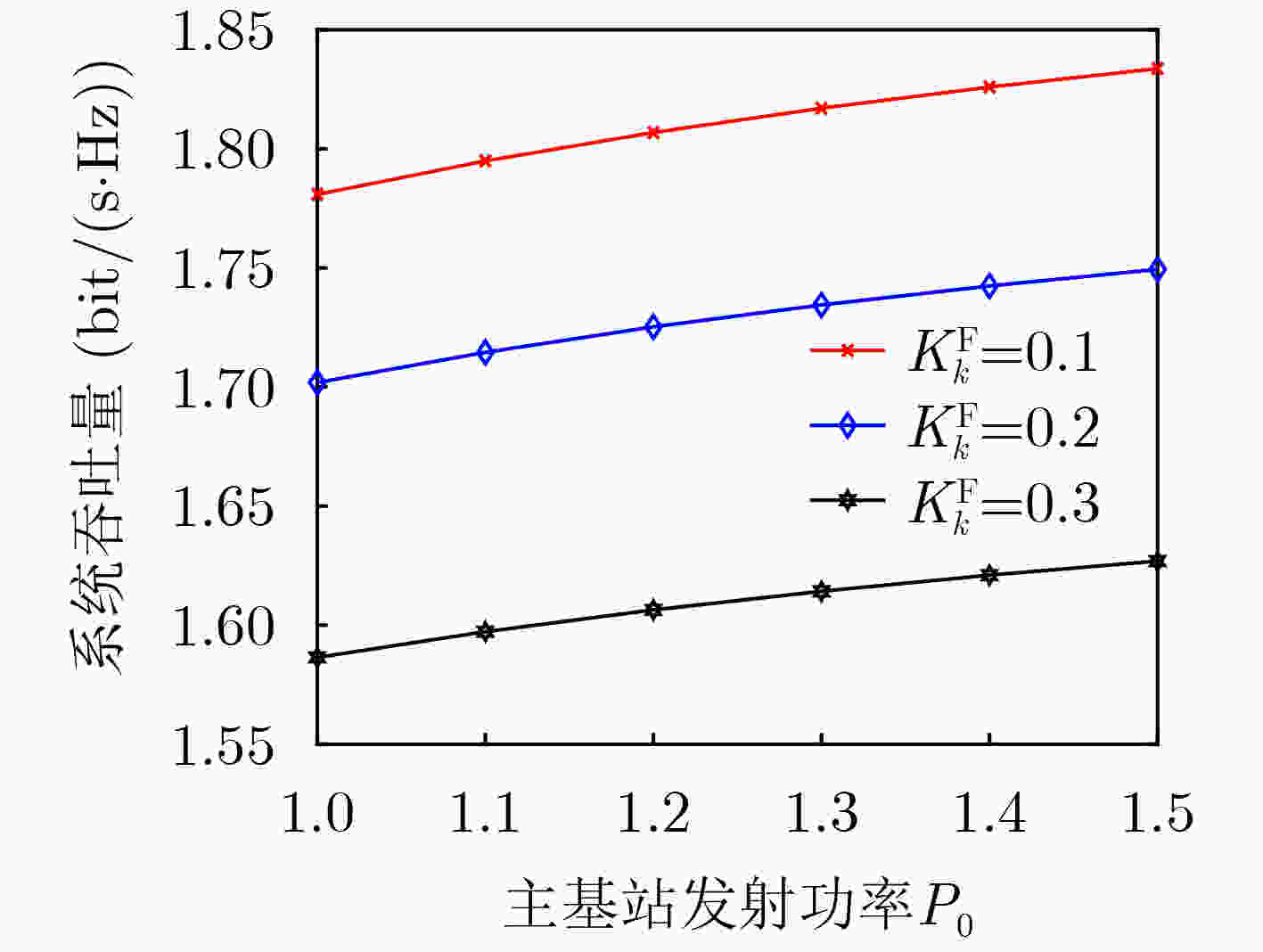
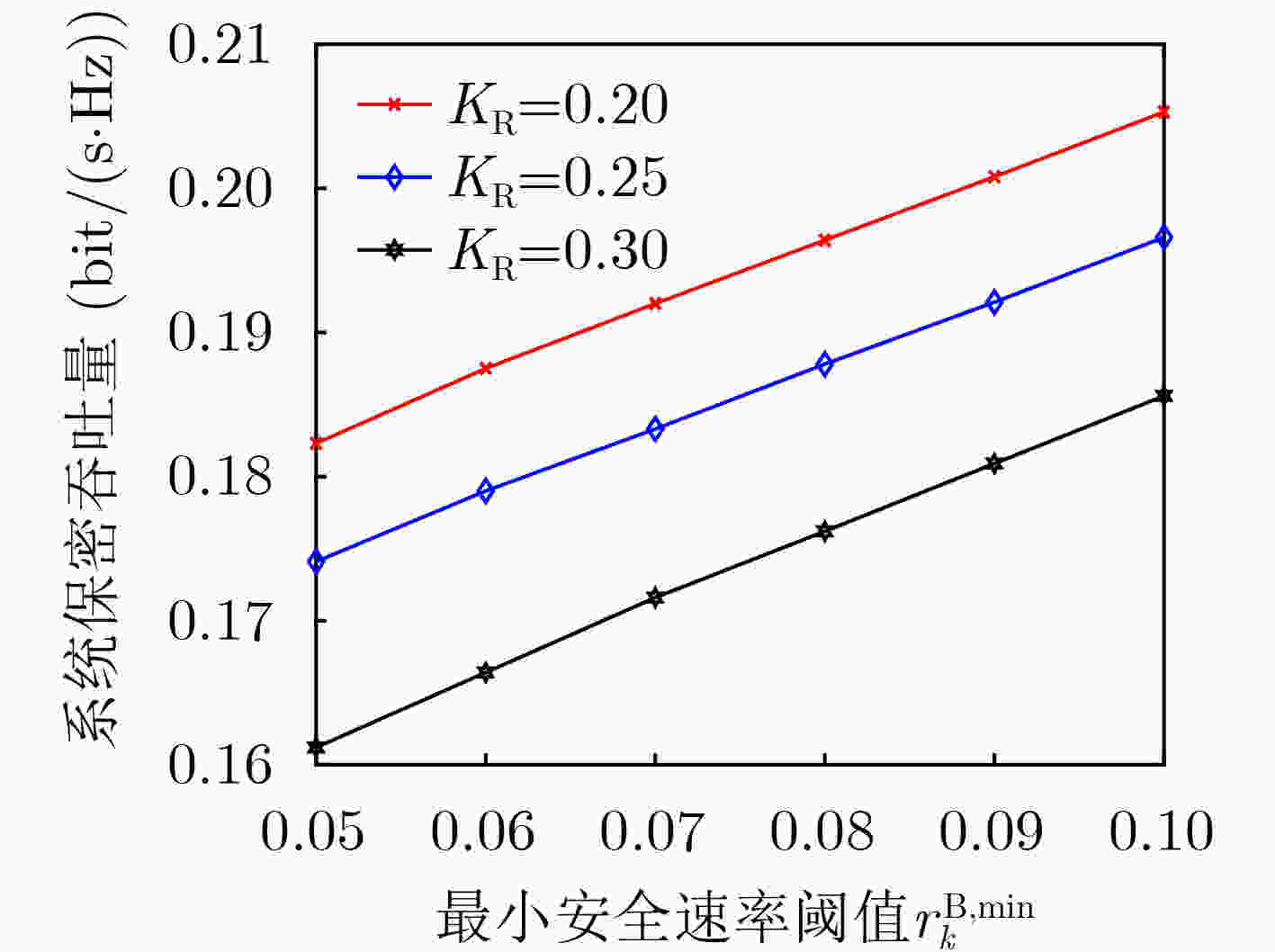

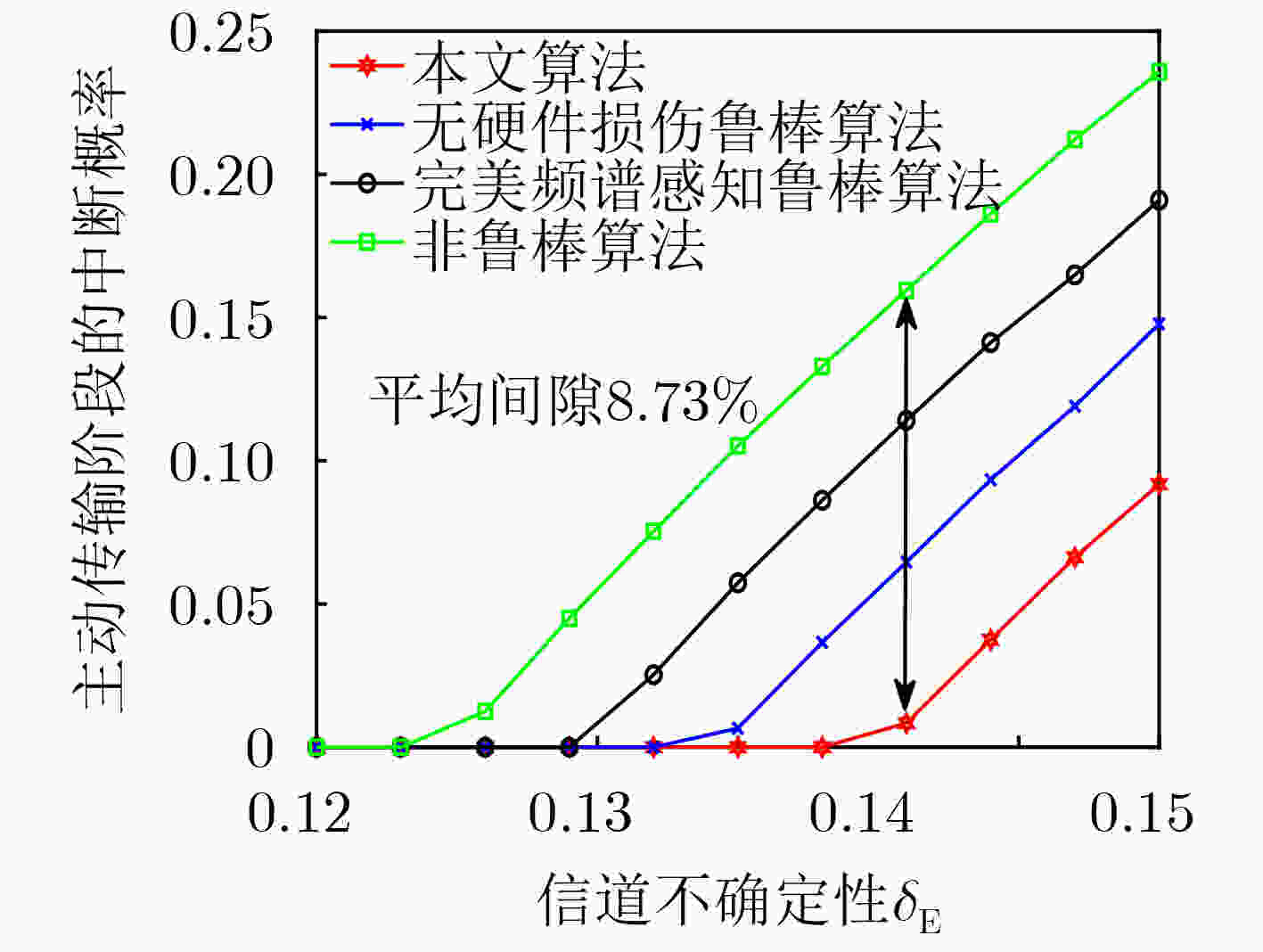


 下载:
下载:
