Parameter Estimation of Surface Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Signals Based on Total Least Squares-Estimation of Signal Parameters via Rotational Invariance Technique
-
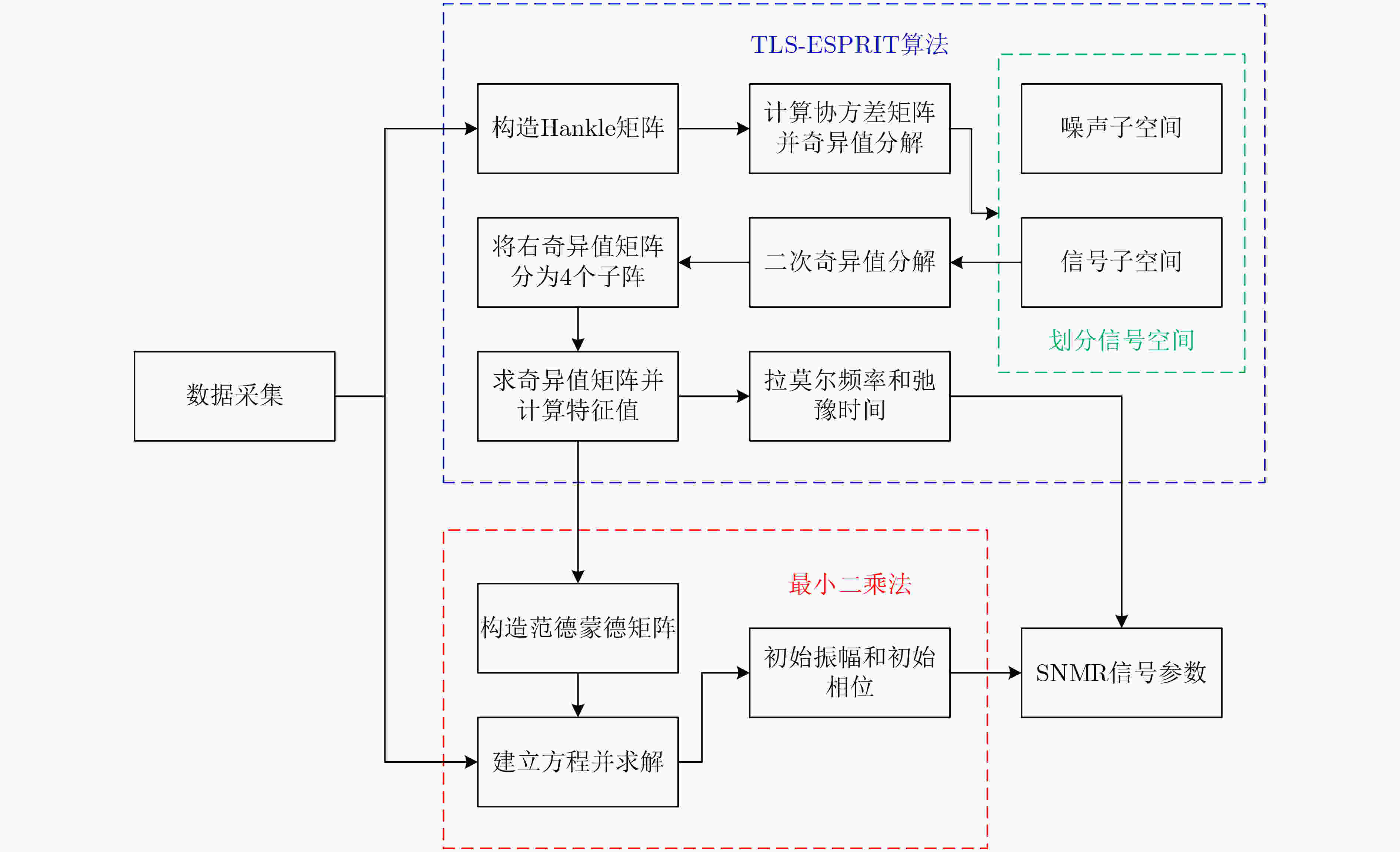
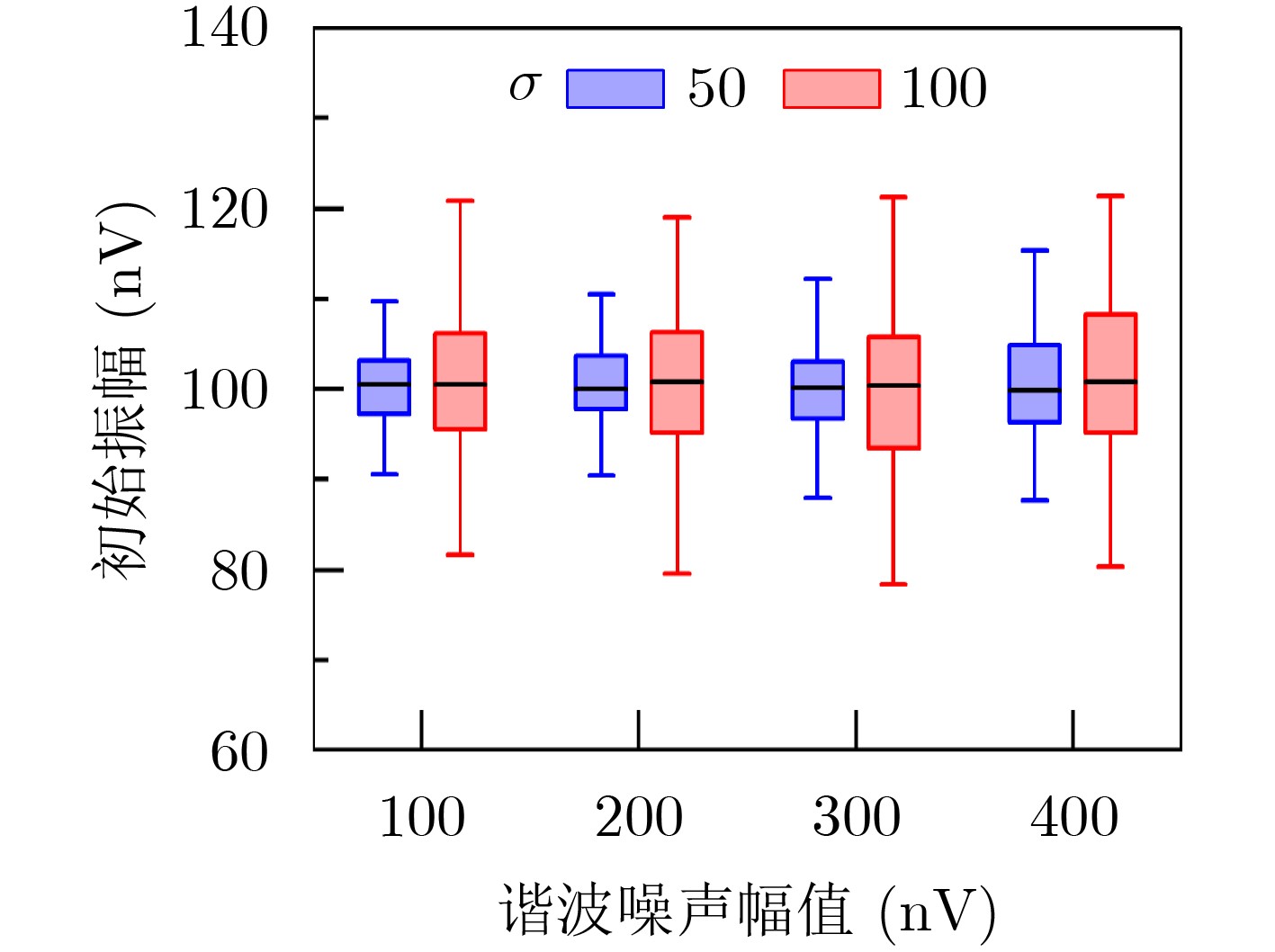
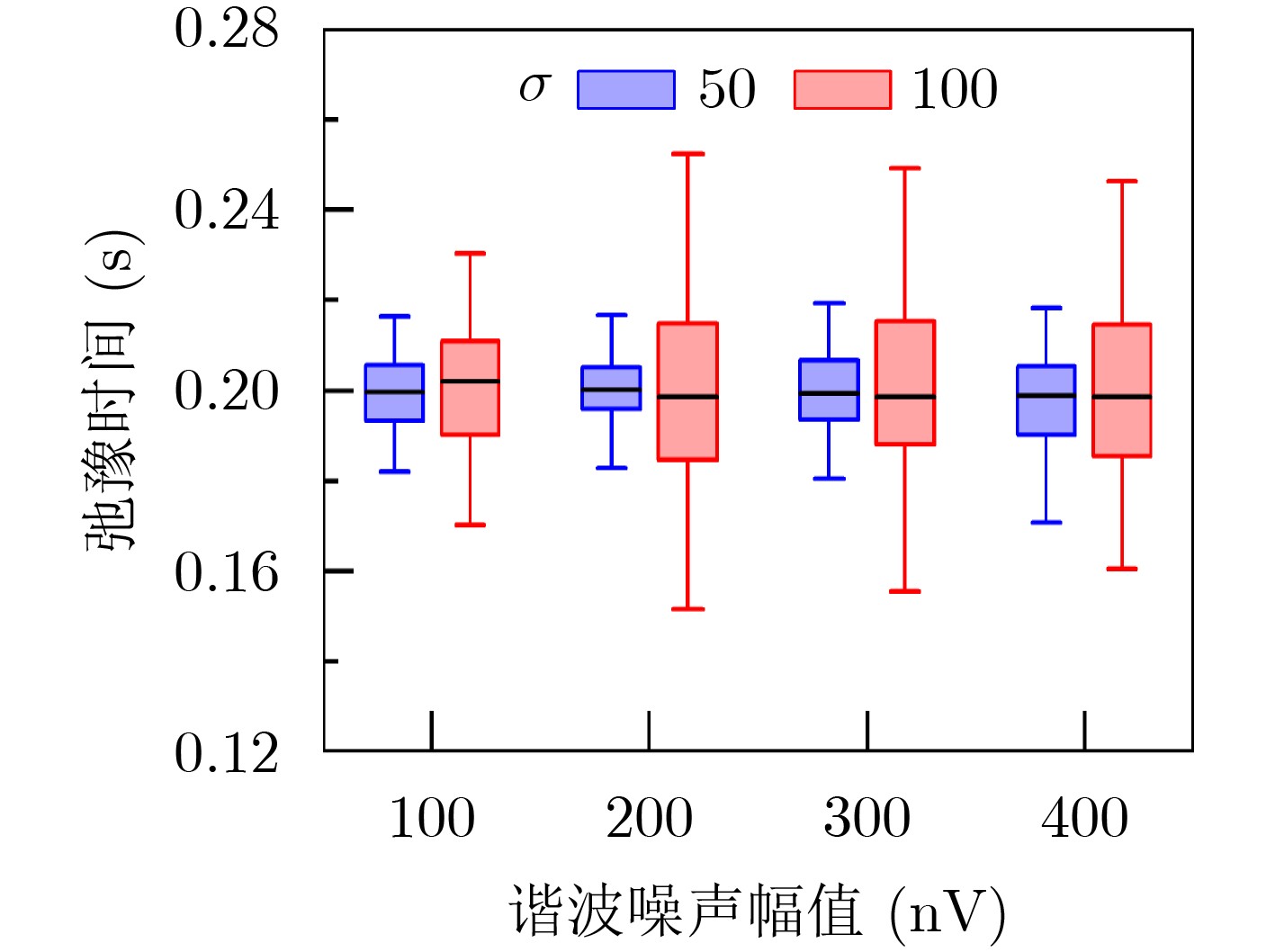
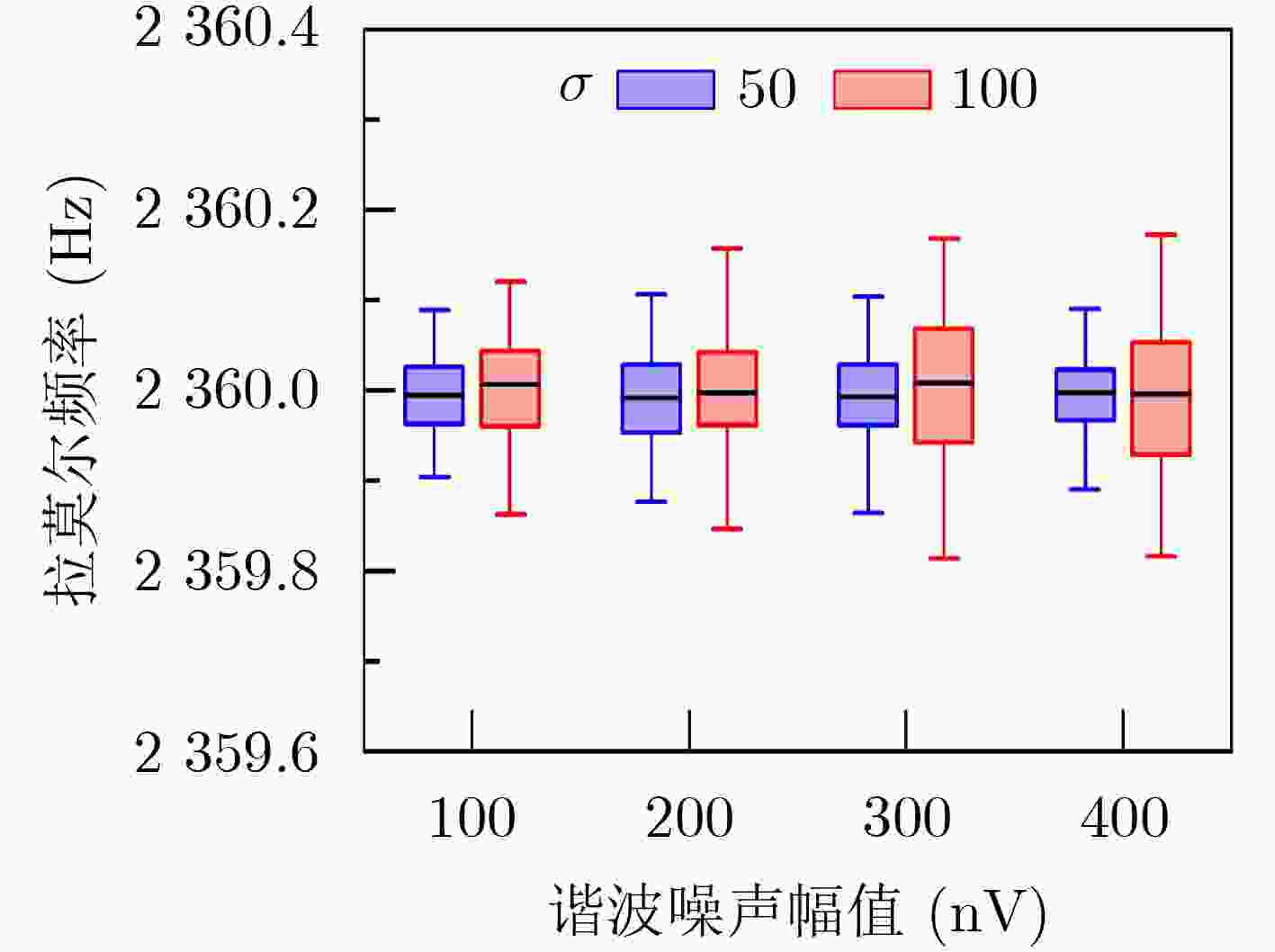
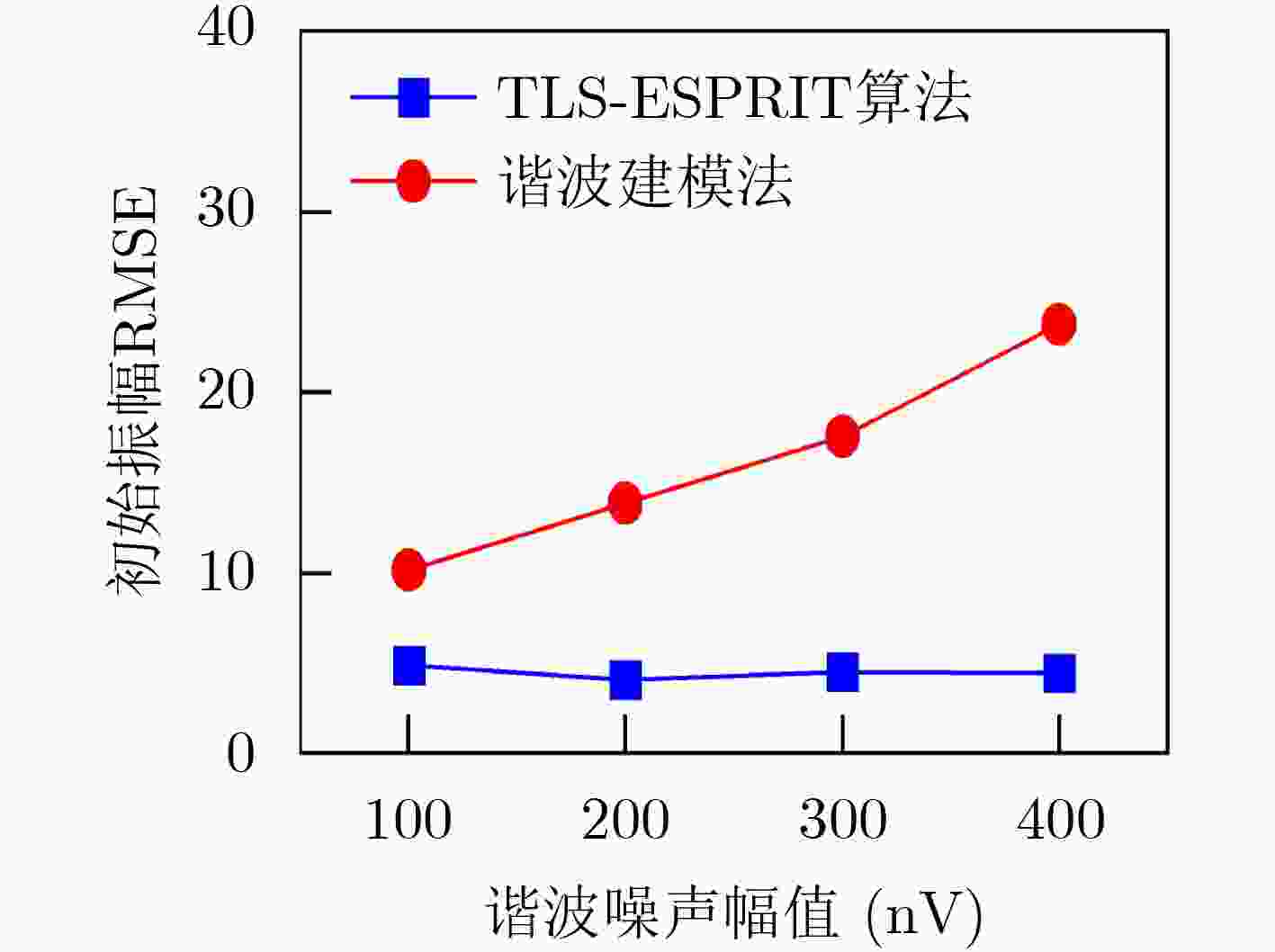
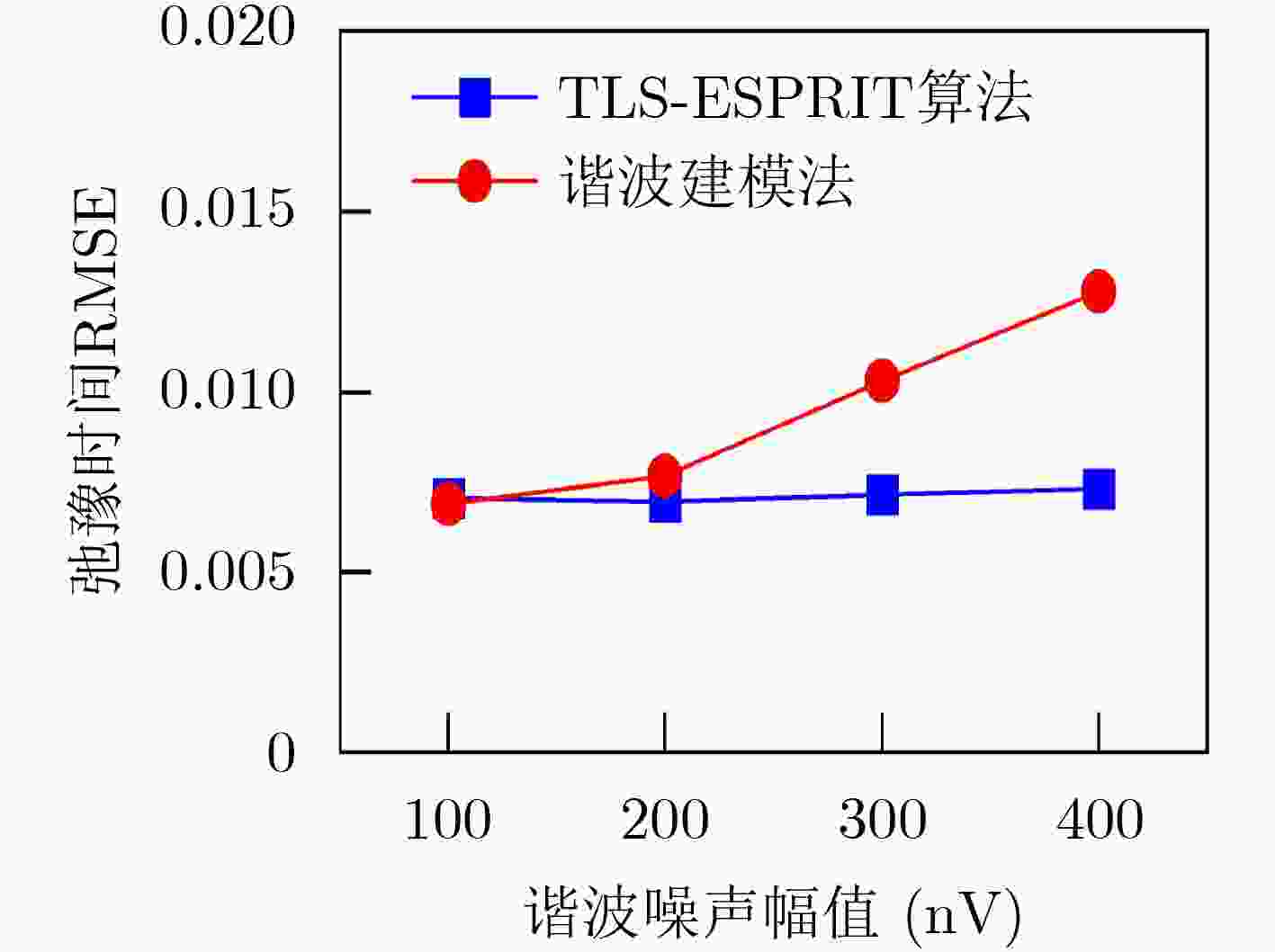
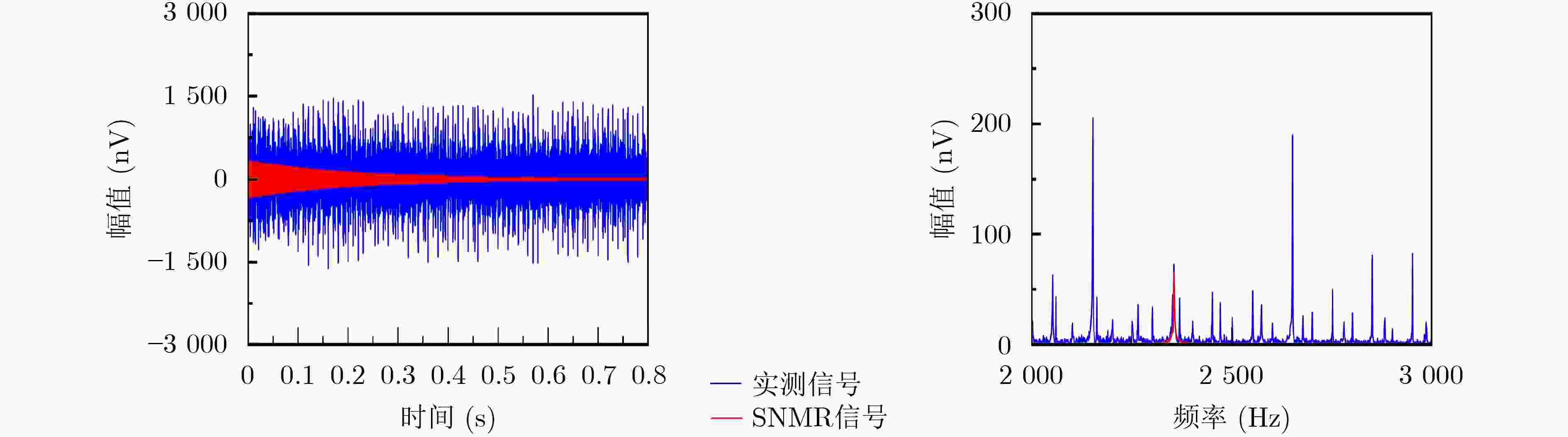
摘要: 在地表核磁共振(SNMR)找水系统中,根据SNMR信号的参数能够预估地下含水层的储水量、导电性以及孔隙结构等信息。然而在实际应用中探测现场采集的SNMR信号十分微弱,易受到环境噪声干扰,导致无法直接获取SNMR信号的参数。针对这一问题,该文提出基于总体最小二乘-旋转不变法(TLS-ESPRIT)的地表核磁共振信号参数估计方法。基于谐波噪声与SNMR信号的相似信号特征构成一个由多个正弦衰减信号叠加的混合信号模型,使用TLS-ESPRIT将混合信号参数提取问题转换为旋转不变矩阵的广义特征值求解,从而获得SNMR信号的拉莫尔频率和弛豫时间,并结合最小二乘法求得其初始振幅和相位。仿真信号和实测信号实验结果表明此方法能够估计出混有随机噪声和工频谐波噪声的SNMR信号的参数,相比传统的谐波建模方法,在参数提取精度上效果更好。
-
关键词:
- 地表核磁共振 /
- 总体最小二乘-旋转不变法 /
- 谐波噪声
Abstract: In the Surface Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (SNMR) water searching system, the parameters of SNMR signals can be used to predict the water storage, electrical conductivity, pore structure of underground aquifer. However, the SNMR signals collected on site are very weak in practical application, which is easy to be interfered by environmental noise, resulting in the inability to directly obtain the parameters of SNMR signal. To solve this problem, an estimation method of SNMR signal parameters based on Total Least Squares-Estimation of Signal Parameters via Rotational Invariance Technique (TLS-ESPRIT) is proposed in this paper. Based on the similar signal characteristics of harmonic noise and SNMR signals, a mixed signal model consisting of multiple sinusoidal attenuation signals is constructed. TLS-ESPRIT is used to transform the problem of extracting mixed signal parameters into a generalized eigenvalue solution of a rotation invariant matrix, in order to obtain the Lamor frequency and the relaxation time of the SNMR signal, and its initial amplitude and phase are obtained by combining the least squares method. The experimental results of simulated signal and measured signal show that the proposed method can estimate the parameters of SNMR signal mixed with random noise and power frequency harmonic noise. Compared with the traditional harmonic modeling method, the parameter extraction accuracy is better. -
表 1 SNMR信号参数实际值以及使用TLS-ESPRIT算法求得的参数估计值
SNMR信号参数实际值 TLS-ESPRIT算法的估计值 $ {E_0} $(nV) $ T_2^* $(s) $ {f_L} $(Hz) $ {E_0} $(nV) $ T_2^* $(s) $ {f_L} $(Hz) 1 400 0.05 2355 382.71 0.0524 2354.853 2 400 0.1 2355 368.22 0.1079 2354.967 3 400 0.2 2355 442.45 0.2007 2355.061 4 400 0.3 2355 363.39 0.2936 2355.036 5 400 0.4 2355 424.78 0.4280 2355.026 -
[1] TRUSHKIN D V, SHUSHAKOV O A, and LEGCHENKO A V. The potential of a noise-reducing antenna for surface NMR groundwater surveys in the earth’s magnetic field[J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 1994, 42(8): 855–862. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2478.1994.tb00245.x. [2] RANGEL R C, PARSEKIAN A D, FARQUHARSON L M, et al. Geophysical observations of Taliks below drained lake basins on the arctic coastal plain of Alaska[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 2021, 126(3): e2020JB020889. doi: 10.1029/2020JB020889. [3] LI Mengna, ZENG Yijian, LUBCZYNSKI M W, et al. A first investigation of hydrogeology and hydrogeophysics of the Maqu catchment in the Yellow River source region[J]. Earth System Science Data, 2021, 13(10): 4727–4757. doi: 10.5194/essd-13-4727-2021. [4] LU Kai, LI Fan, PAN Jianwei, et al. Using electrical resistivity tomography and surface nuclear magnetic resonance to investigate cultural relic preservation in Leitai, China[J]. Engineering Geology, 2021, 285: 106042. doi: 10.1016/J.ENGGEO.2021.106042. [5] BEHROOZMAND A A, KEATING K, and AUKEN E. A review of the principles and applications of the NMR technique for near-surface characterization[J]. Surveys in Geophysics, 2015, 36(1): 27–85. doi: 10.1007/s10712-014-9304-0. [6] KEATING K, WALSH D O, and GRUNEWALD E. The effect of magnetic susceptibility and magnetic field strength on porosity estimates determined from low-field nuclear magnetic resonance[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2020, 179: 104096. doi: 10.1016/j.jappgeo.2020.104096. [7] KREMER T, IRONS T, MÜLLER-PETKE M, et al. Review of acquisition and signal processing methods for electromagnetic noise reduction and retrieval of surface nuclear magnetic resonance parameters[J]. Surveys in Geophysics, 2022, 43(4): 999–1053. doi: 10.1007/S10712-022-09695-3. [8] LEGCHENKO A and VALLA P. A review of the basic principles for proton magnetic resonance sounding measurements[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2002, 50(1/2): 3–19. doi: 10.1016/S0926-9851(02)00127-1. [9] COSTABEL S and MÜLLER-PETKE M. Despiking of magnetic resonance signals in time and wavelet domains[J]. Near Surface Geophysics, 2014, 12(2): 185–198. doi: 10.3997/1873-0604.2013027. [10] 万玲, 张扬, 林君, 等. 基于能量运算的磁共振信号尖峰噪声抑制方法[J]. 地球物理学报, 2016, 59(6): 2290–2301. doi: 10.6038/cjg20160631.WAN Ling, ZHANG Yang, LIN Jun, et al. Spikes removal of magnetic resonance sounding data based on energy calculation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2016, 59(6): 2290–2301. doi: 10.6038/cjg20160631. [11] LEGCHENKO A and VALLA P. Removal of power-line harmonics from proton magnetic resonance measurements[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2003, 53(2/3): 103–120. doi: 10.1016/S0926-9851(03)00041-7. [12] LARSEN J J, DALGAARD E, and AUKEN E. Noise cancelling of MRS signals combining model-based removal of powerline harmonics and multichannel Wiener filtering[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2014, 196(2): 828–836. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggt422. [13] 田宝凤, 朱慧, 易晓峰, 等. 基于谐波建模和自相关的磁共振信号消噪与提取方法研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2018, 61(2): 767–780. doi: 10.6038/cjg2018L0091.TIAN Baofeng, ZHU Hui, YI Xiaofeng, et al. Denoising and extraction method of magnetic resonance sounding signal based on adaptive harmonic modeling and autocorrelation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2018, 61(2): 767–780. doi: 10.6038/cjg2018L0091. [14] 庄双勇, 赵伟, 赵东芳, 等. 一种基于滑窗TLS-ESPRIT算法的超谐波动态分析方法[J]. 计量学报, 2020, 41(4): 475–483. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1158.2020.04.014.ZHUANG Shuangyong, ZHAO Wei, ZHAO Dongfang, et al. A supraharmonics dynamic analysis method based on sliding-window TLS-ESPRIT algorithm[J]. Acta Metrologica Sinica, 2020, 41(4): 475–483. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1158.2020.04.014. [15] CHEN Jian, JIN Tao, MOHAMED M A, et al. An adaptive TLS-ESPRIT algorithm based on an S-G filter for analysis of low frequency oscillation in wide area measurement systems[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 47644–47654. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2908629. [16] SAMAL S K and SUBUDHI B. New signal subspace approach to estimate the inter-area oscillatory modes in power system using TLS-ESPRIT algorithm[J]. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution, 2019, 13(18): 4123–4140. doi: 10.1049/iet-gtd.2018.6401. [17] 张硕, 杨君, 葛鹏程, 等. 基于Hankel矩阵改进的TLS-ESPRIT多频带融合处理[J]. 电光与控制, 2022, 29(9): 90–95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2022.09.018.ZHANG Shuo, YANG Jun, GE Pengcheng, et al. TLS-ESPRIT multiband fusion processing based on hankel matrix improvement[J]. Electronics Optics &Control, 2022, 29(9): 90–95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2022.09.018. [18] 张小宽, 郑舒予, 奚之飞, 等. 基于改进LS-ESPRIT算法的GTD模型参数估计与RCS重构[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(10): 2493–2499. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190747.ZHANG Xiaokuan, ZHENG Shuyu, XI Zhifei, et al. GTD model parameters estimation and RCS reconstruction based on the improved LS-ESPRIT algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(10): 2493–2499. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190747. [19] GRUNEWALD E, KNIGHT R, and WALSH D. Advancement and validation of surface nuclear magnetic resonance spin-echo measurements of T2[J]. Geophysics, 2014, 79(2): EN15–EN23. doi: 10.1190/geo2013-0105.1. [20] SRIVASTAVA A K, TIWARI A N, and SINGH S N. Harmonic/interharmonic estimation using standard deviation assisted ESPRIT method[J]. COMPEL:The International Journal for Computation and Mathematics in Electrical and Electronic Engineering, 2021, 40(6): 1067–1083. doi: 10.1108/COMPEL-03-2021-0108. -





 下载:
下载:
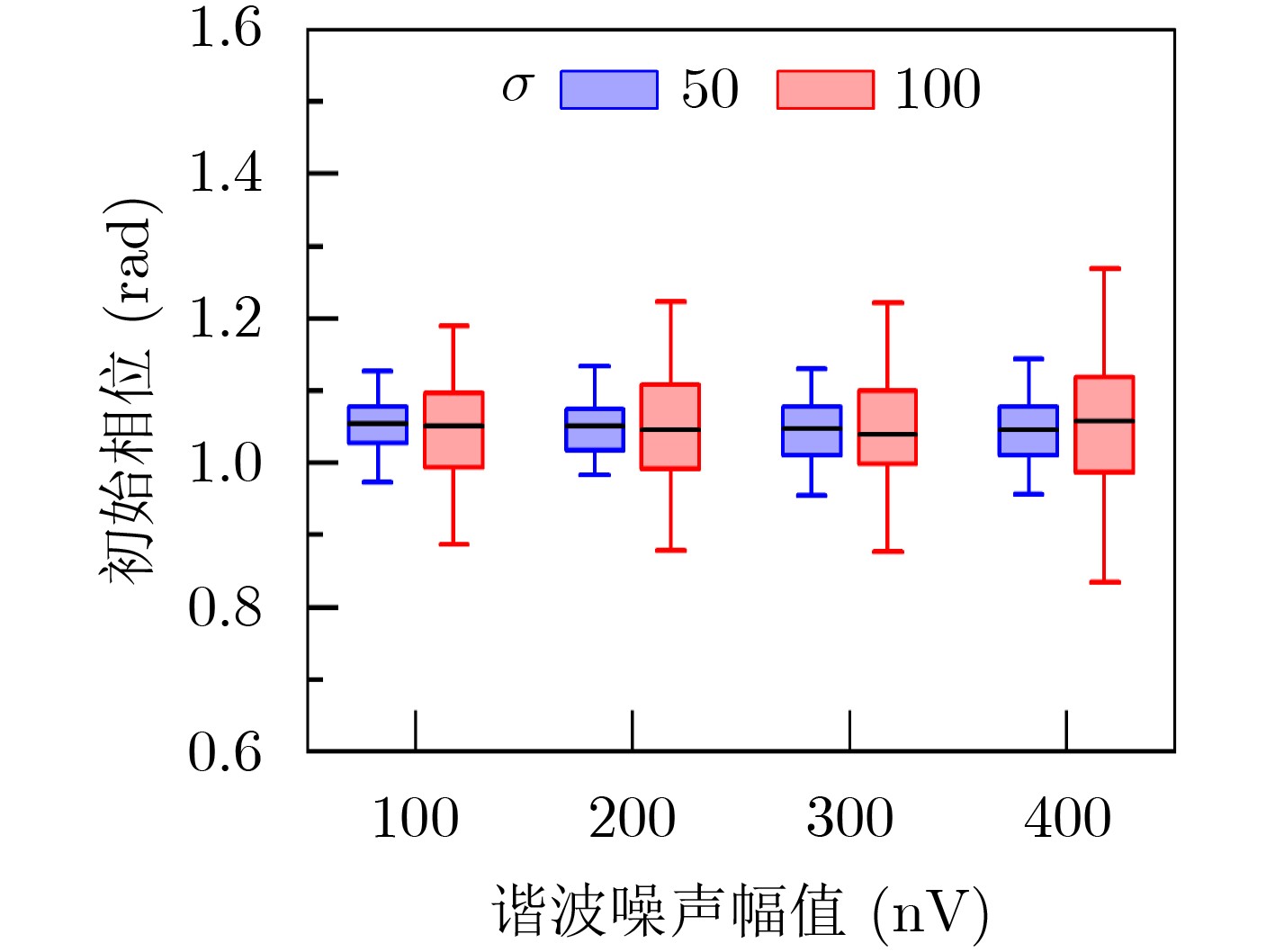
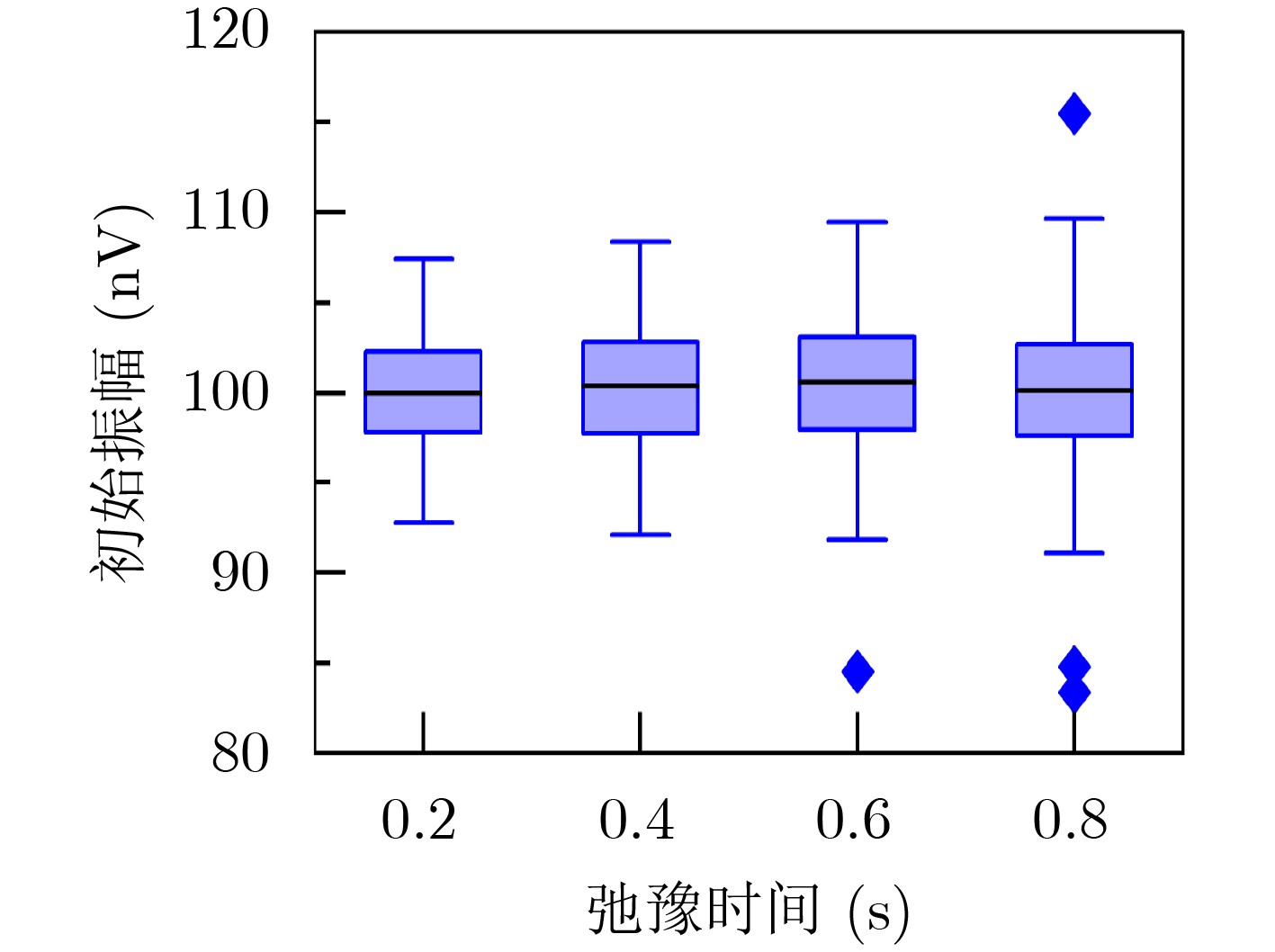
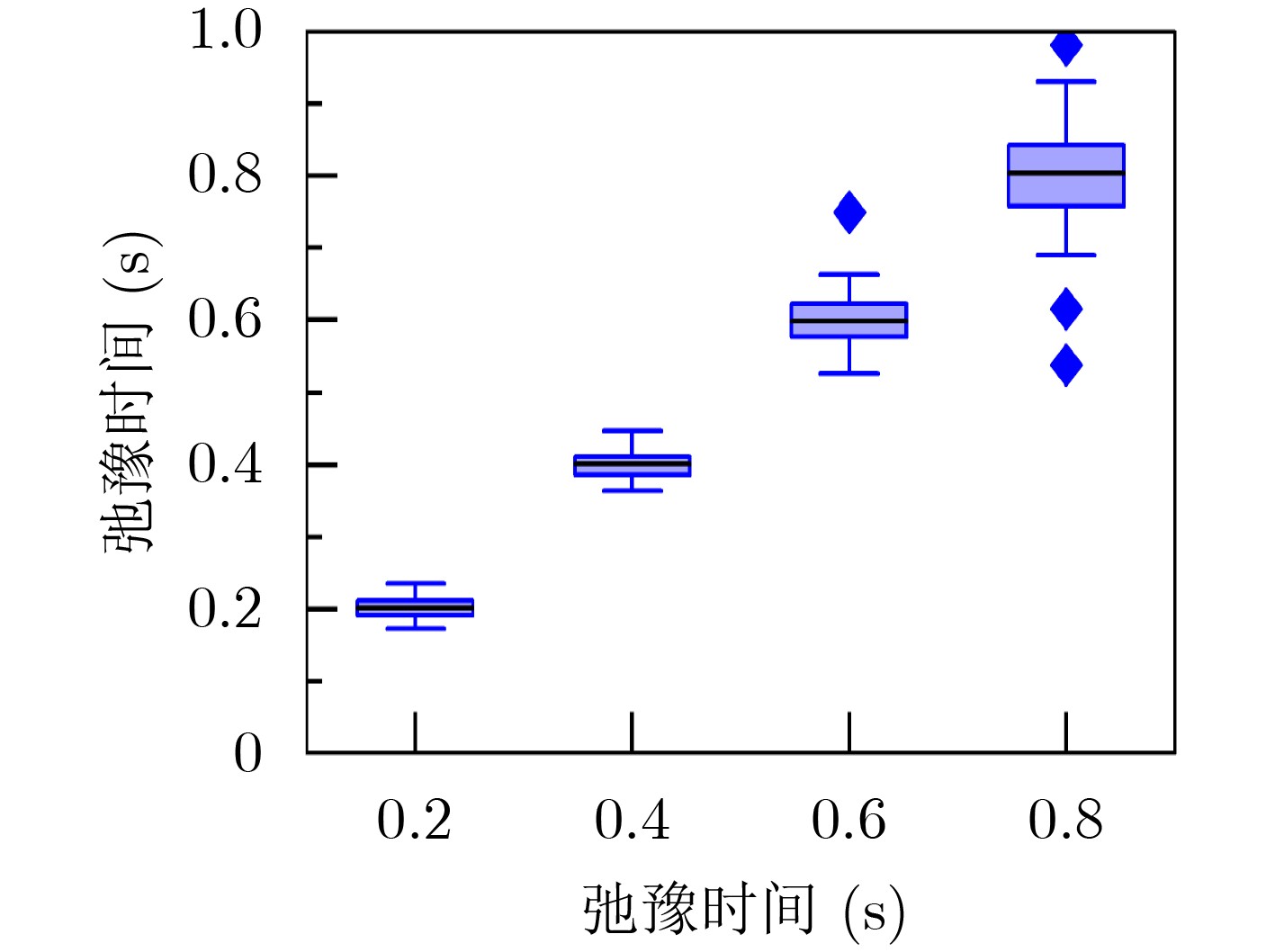

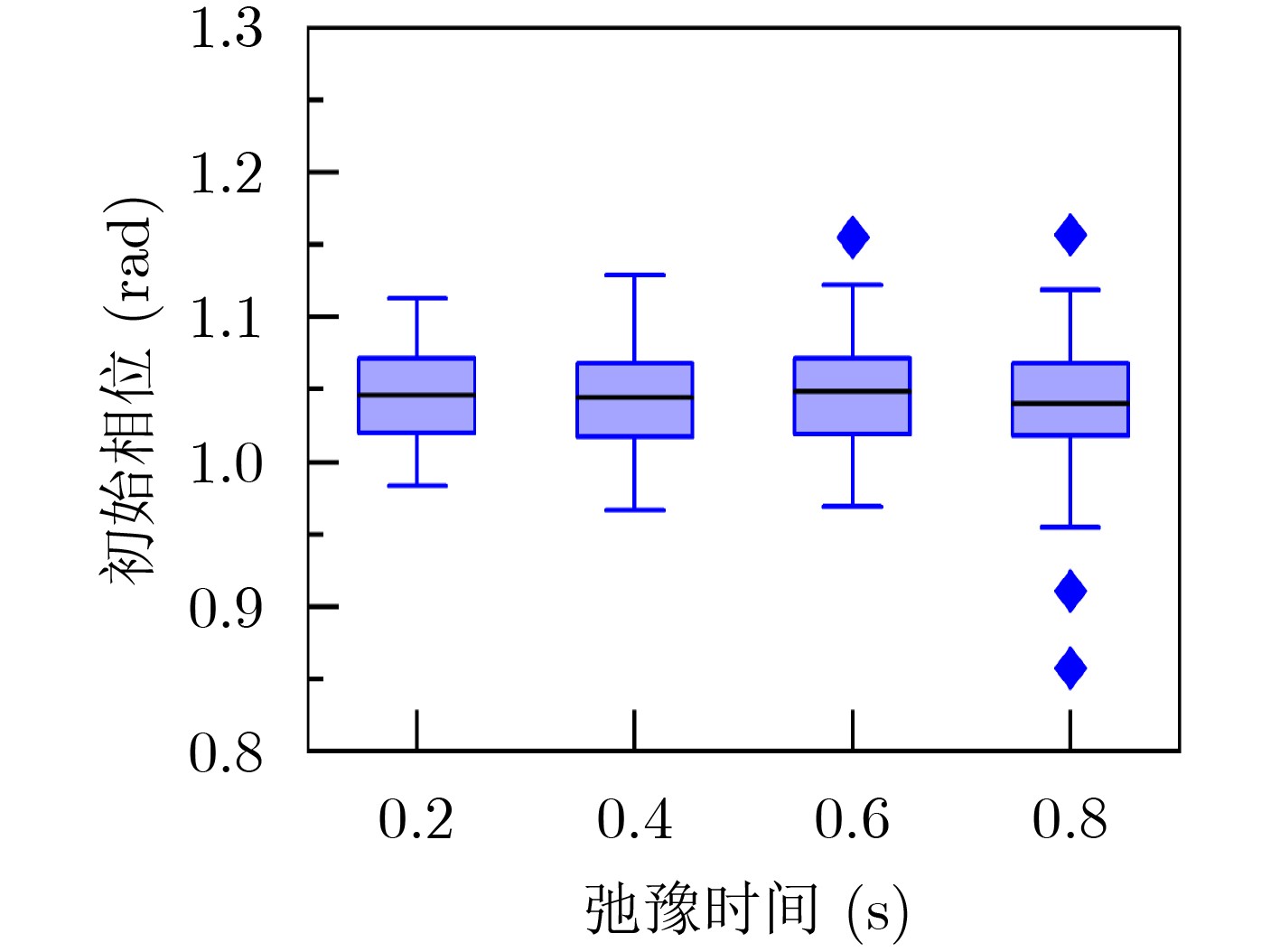


 下载:
下载:
