Recognition of Basketball Tactics Based on Vision Transformer and Track Filter
-
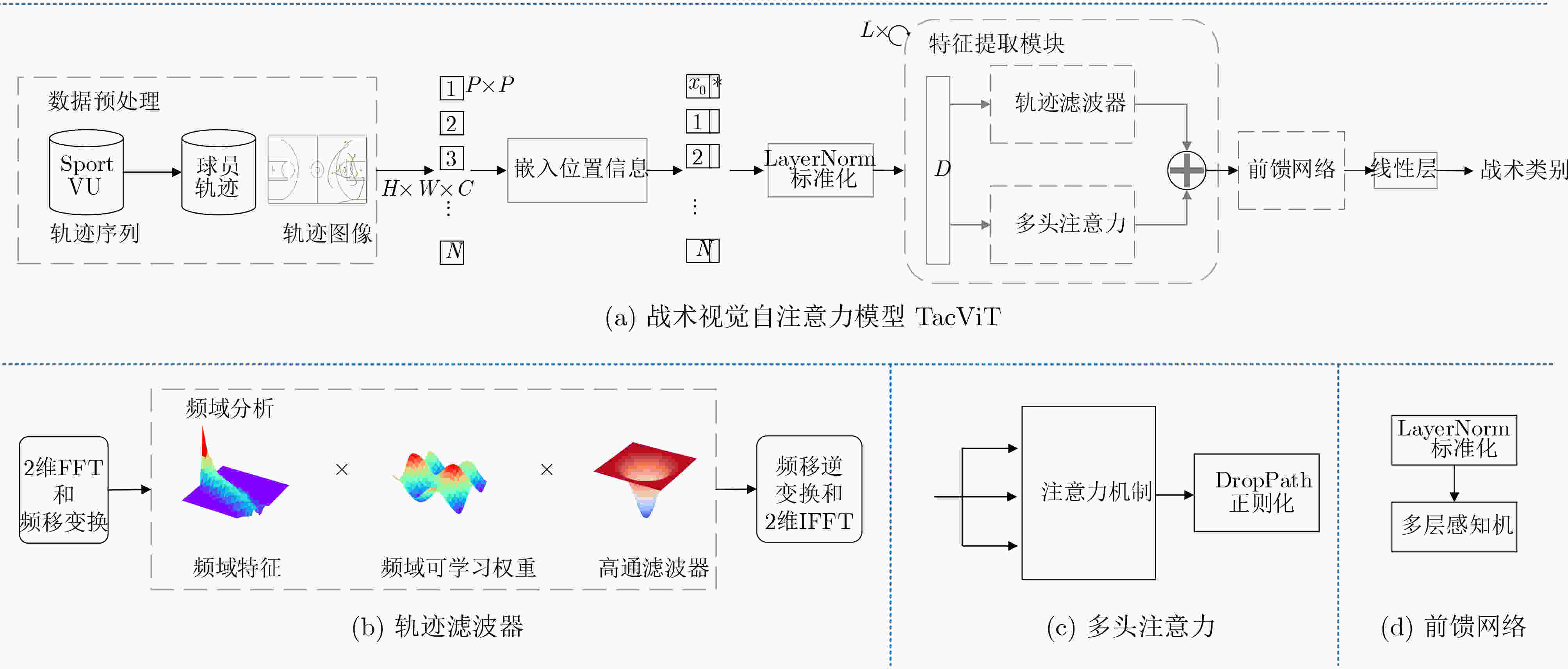
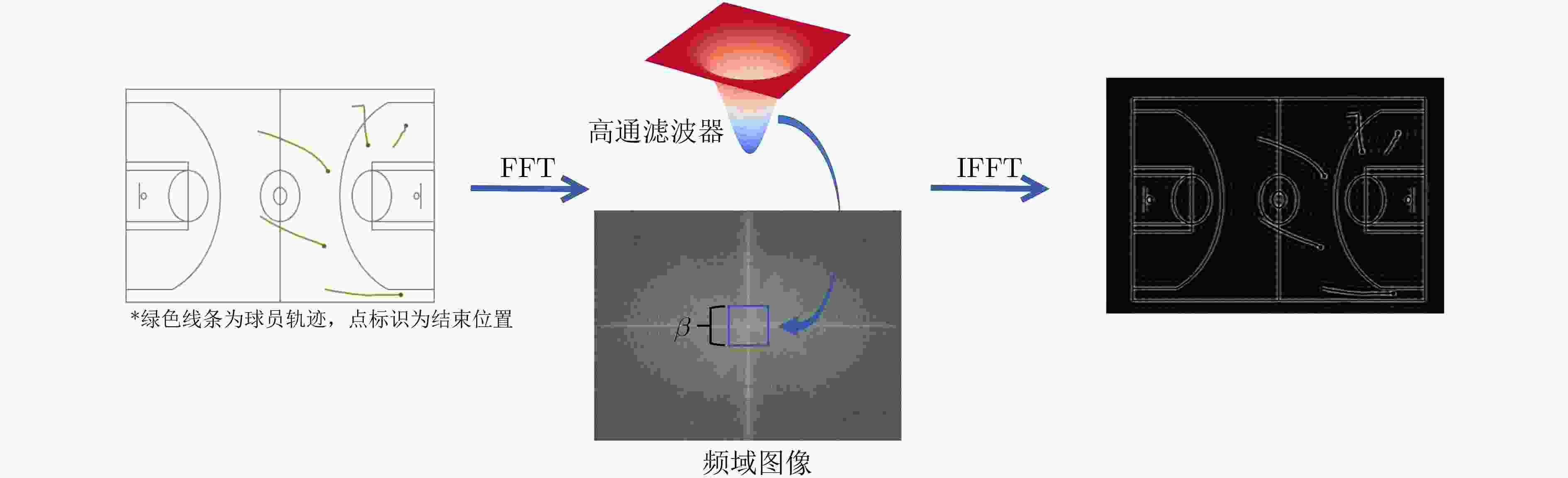
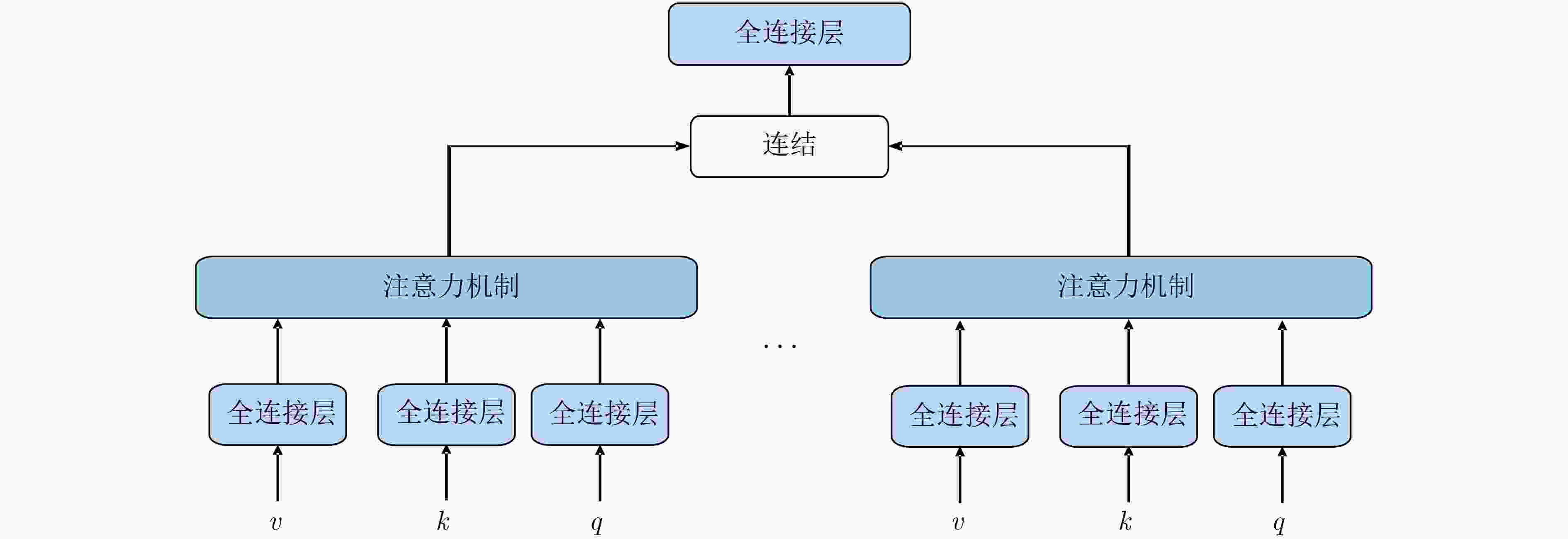
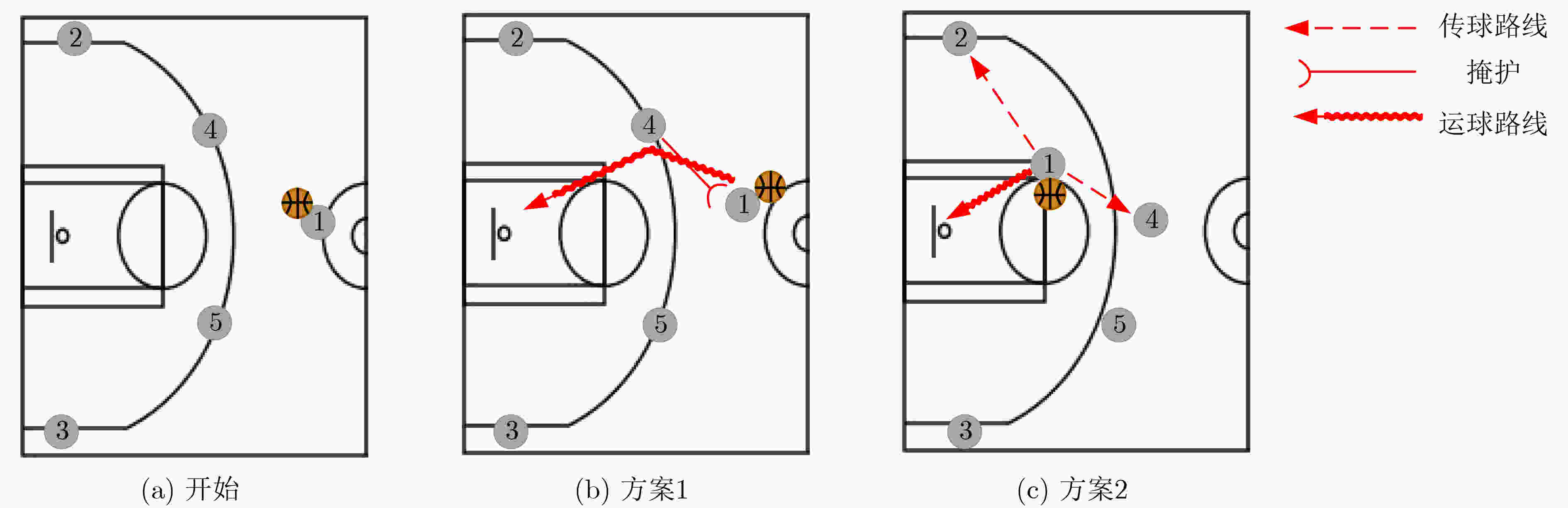
摘要: 通过机器学习分析球员轨迹数据获得进攻或防守战术,是篮球视频内容理解的关键组成部分。传统机器学习方法需要人为设定特征变量,灵活性大大降低,因此如何自动获取可用于战术识别的特征信息成为关键问题。为此,该文基于美国职业篮球联赛(NBA)比赛中球员轨迹数据设计了一个篮球战术识别模型(TacViT),该模型以视觉自注意力模型(ViT)作为主干网络,利用多头注意力模块提取丰富的全局轨迹特征信息,同时并入轨迹滤波器来加强球场线与球员轨迹之间的特征信息交互,增强球员位置特征表示,其中轨迹滤波器以对数线性复杂度学习频域中的长期空间相关性。该文将运动视觉系统(SportVU)的序列数据转化为轨迹图,自建篮球战术数据集(PlayersTrack),在该数据集上的实验表明,TacViT的准确率达到了82.5%,相对未做更改的视觉自注意力S模型 (ViT-S),精度上提升了16.7%。Abstract: The analysis of player trajectory data using machine learning to obtain offensive or defensive tactics is a crucial component of understanding basketball video content. Traditional machine learning methods require the setting of feature variables manually, significantly reducing flexibility. Therefore, the key issue is how to automatically obtain feature information that can be used for tactic recognition. To address this issue, a basketball Tactic Vision Transformer (TacViT) recognition model is proposed based on player trajectory data from the National Basketball Association (NBA) games. The proposed model adopts Vision Transformer (ViT) as the backbone network and multi-head attention modules to extract rich global trajectory feature information. Trajectory filters are also incorporated in order to not only enhance the feature interaction between the court lines and player trajectories, but also strengthen the representation of player position features in this study. The trajectory filters learn the long-term spatial correlations in the frequency domain with log-linear complexity. A self-built basketball tactic dataset (PlayersTrack) is created from the sequence data of the Sport Vision System (SportVU), which are converted into trajectory graphs in this work. The experiments on this dataset showed that the accuracy of TacViT reached 82.5%, which is a 16.7% improvement over the accuracy of the Vision Transformer S model (ViT-S) without modifications.
-
表 1 混淆矩阵正确率
“牛角” “挡拆” “二三联防” “边线球” “牛角” 0.86 0.08 0 0.06 “挡拆” 0.12 0.76 0.06 0.04 “二三联防” 0 0.10 0.90 0 “边线球” 0.04 0.10 0.11 0.75 表 2 与当前的主流网络对比
-
[1] PERŠE M, KRISTAN M, KOVAČIČ S, et al. A trajectory-based analysis of coordinated team activity in a basketball game[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2009, 113(5): 612–621. doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2008.03.001. [2] YUE Qiang and WEI Chao. Innovation of human body positioning system and basketball training system[J]. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, 2022, 2022: 2369925. doi: 10.1155/2022/2369925. [3] MILLER A C and BORNN L. Possession sketches: Mapping NBA strategies[C]. The 2017 MIT Sloan Sports Analytics Conference, Boston, USA, 2017. [4] TIAN Changjia, DE SILVA V, CAINE M, et al. Use of machine learning to automate the identification of basketball strategies using whole team player tracking data[J]. Applied Sciences, 2019, 10(1): 24. doi: 10.3390/app10010024. [5] MCINTYRE A, BROOKS J, GUTTAG J, et al. Recognizing and analyzing ball screen defense in the NBA[C]. The MIT Sloan Sports Analytics Conference, Boston, USA, 2016: 11–12. [6] WANG K C and ZEMEL R. Classifying NBA offensive plays using neural networks[C]. MIT Sloan Sports Analytics Conference, Boston, USA, 2016. [7] CHEN H T, CHOU C L, FU T S, et al. Recognizing tactic patterns in broadcast basketball video using player trajectory[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2012, 23(6): 932–947. doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2012.06.003. [8] TSAI T Y, LIN Y Y, LIAO H Y M, et al. Recognizing offensive tactics in broadcast basketball videos via key player detection[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Beijing, China, 2017: 880–884. [9] TSAI T Y, LIN Y Y, JENG S K, et al. End-to-end key-player-based group activity recognition network applied to basketball offensive tactic identification in limited data scenarios[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 104395–104404. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3098840. [10] CHEN C H, LIU T L, WANG Y S, et al. Spatio-temporal learning of basketball offensive strategies[C]. The 23rd ACM international conference on Multimedia, Brisbane, Australia, 2015: 1123–1126. [11] BORHANI Y, KHORAMDEL J, and NAJAFI E. A deep learning based approach for automated plant disease classification using vision transformer[J]. Scientific Reports, 2022, 12(1): 11554. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-15163-0. [12] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. The 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. [13] VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]. The 31st International Conference onAdvances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 6000–6010. [14] LI Shaohua, XUE Kaiping, ZHU Bin, et al. FALCON: A Fourier transform based approach for fast and secure convolutional neural network predictions[C]. The 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 8702–8711. [15] DING Caiwen, LIAO Siyu, WANG Yanzhi, et al. CirCNN: Accelerating and compressing deep neural networks using block-circulant weight matrices[C]. The 50th Annual IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture, Cambridge, USA, 2017: 395–408. [16] DOSOVITSKIY A, BEYER L, KOLESNIKOV A, et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale[C]. The 9th International Conference on Learning Representations, Vienna, Austria, 2021. [17] WU Kan, PENG Houwen, CHEN Minghao, et al. Rethinking and improving relative position encoding for vision transformer[C]. Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 10013–10021. [18] HSIEH H Y, CHEN C Y, WANG Y S, et al. BasketballGAN: Generating basketball play simulation through sketching[C]. The 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Chengdu, China, 2019: 720–728. [19] HAN Kai, XIAO An, WU Enhua, et al. Transformer in transformer[C]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2021: 15908–15919. [20] CHEN C F R, FAN Quanfu, and PANDA R. CrossViT: Cross-attention multi-scale vision transformer for image classification[C]. The 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Montreal, Canada, 2021: 347–356. [21] STSTS. PERFORMANCE ANAL YSIS POWERED BYAI[OL]. https://www.statsperform.com/team-performance. 2022.7. [22] RAO Yongming, ZHAO Wenliang, ZHU Zheng, et al. Global filter networks for image classification[C]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 34: Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2021, 2021: 980–993. [23] LIU Ze, LIN Yutong, CAO Yue, et al. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows[C]. The 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 9992–10002. [24] TOUVRON H, CORD M, DOUZE M, et al. Training data-efficient image transformers & distillation through attention[C]. The 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, Vienna, Austria, 2021: 10347–10357. [25] TOUVRON H, BOJANOWSKI P, CARON M, et al. ResMLP: Feedforward networks for image classification with data-efficient training[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(4): 5314–5321. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3206148. -





 下载:
下载:
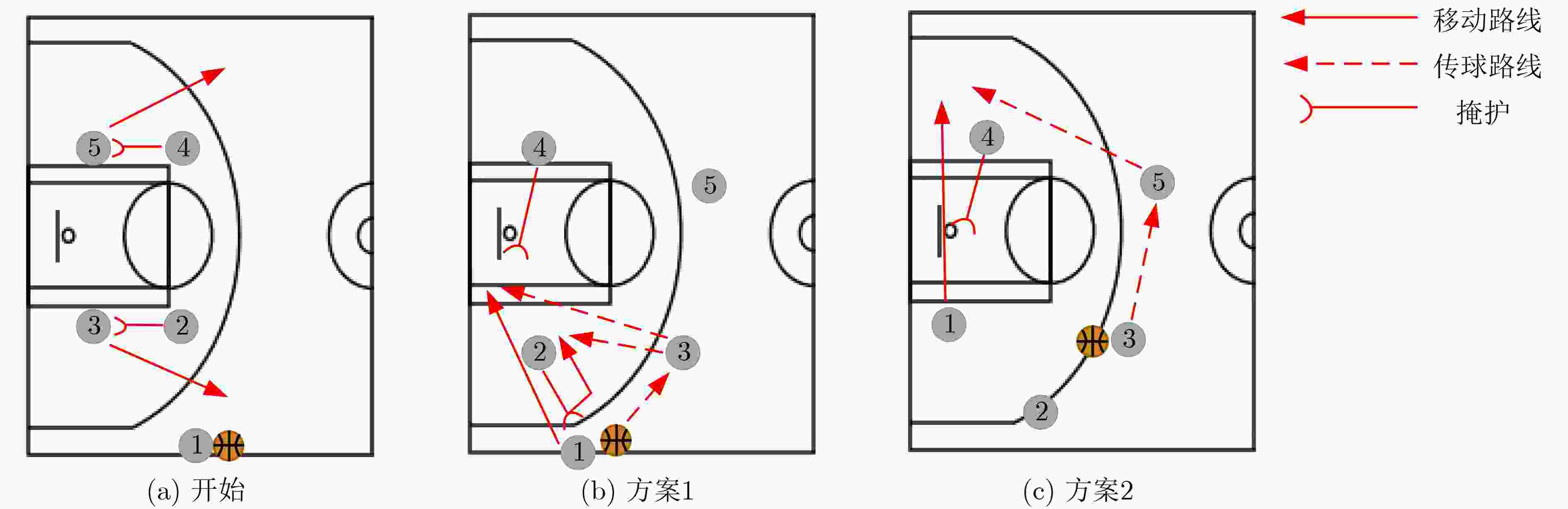
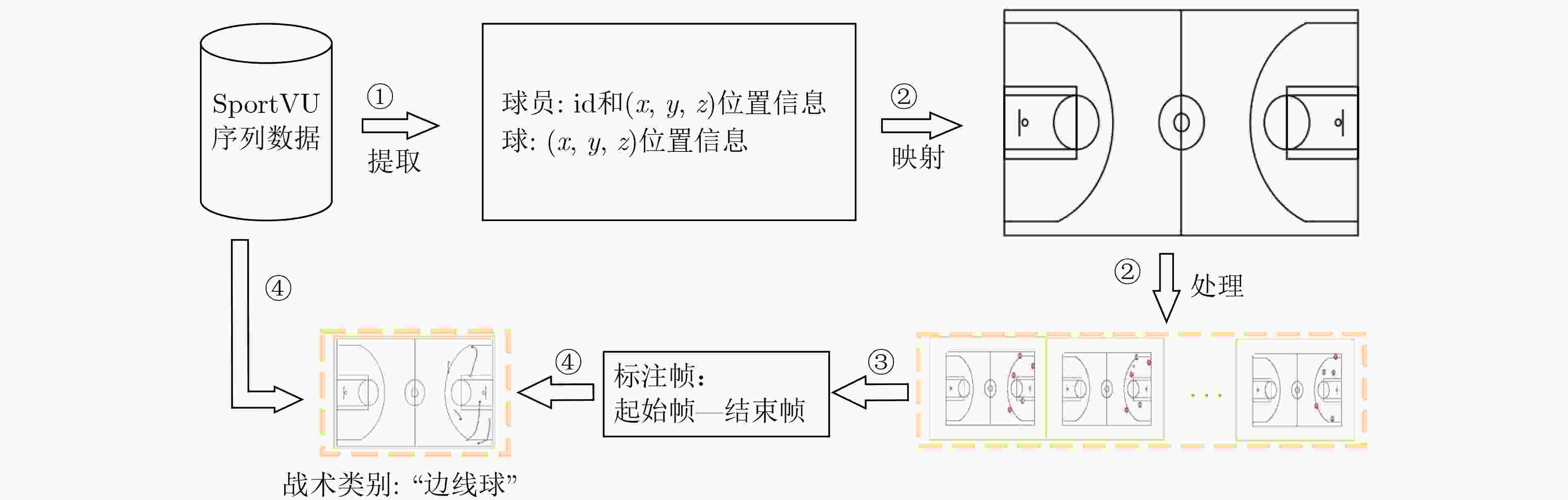
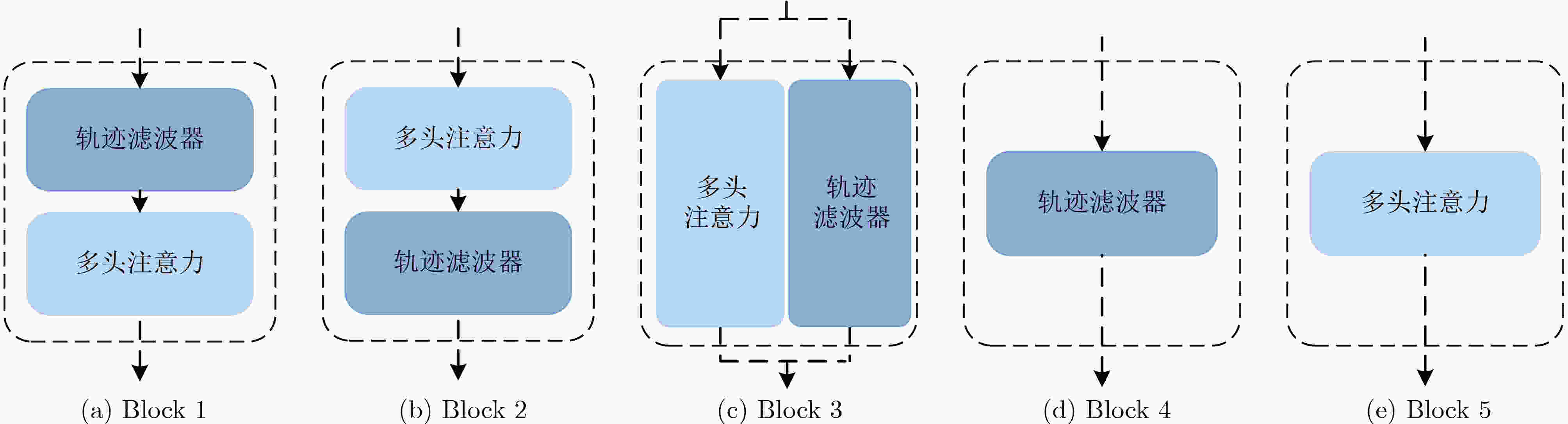
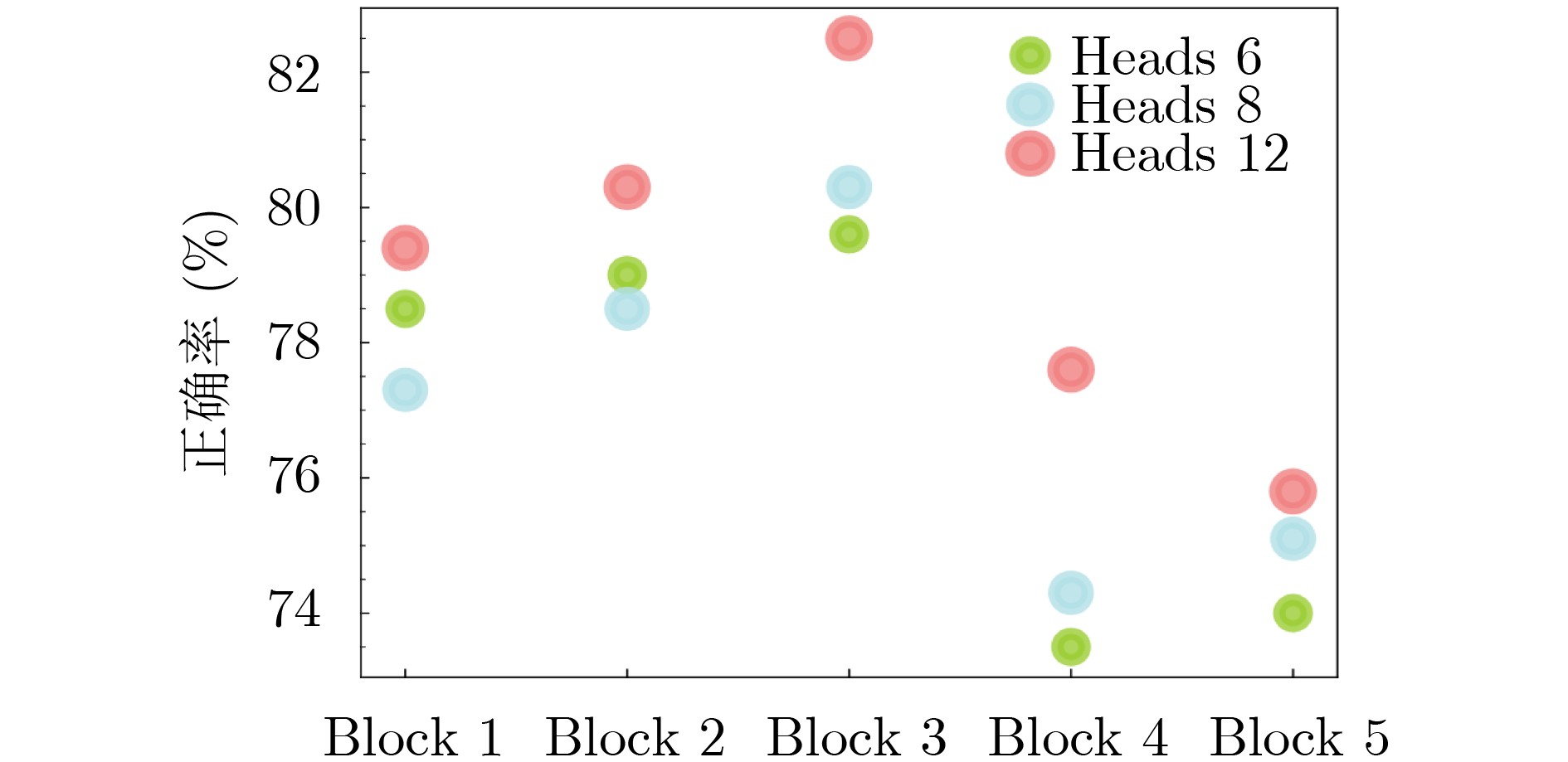


 下载:
下载:
