Low Light Image Enhancement With Adaptive Light Initialization
-
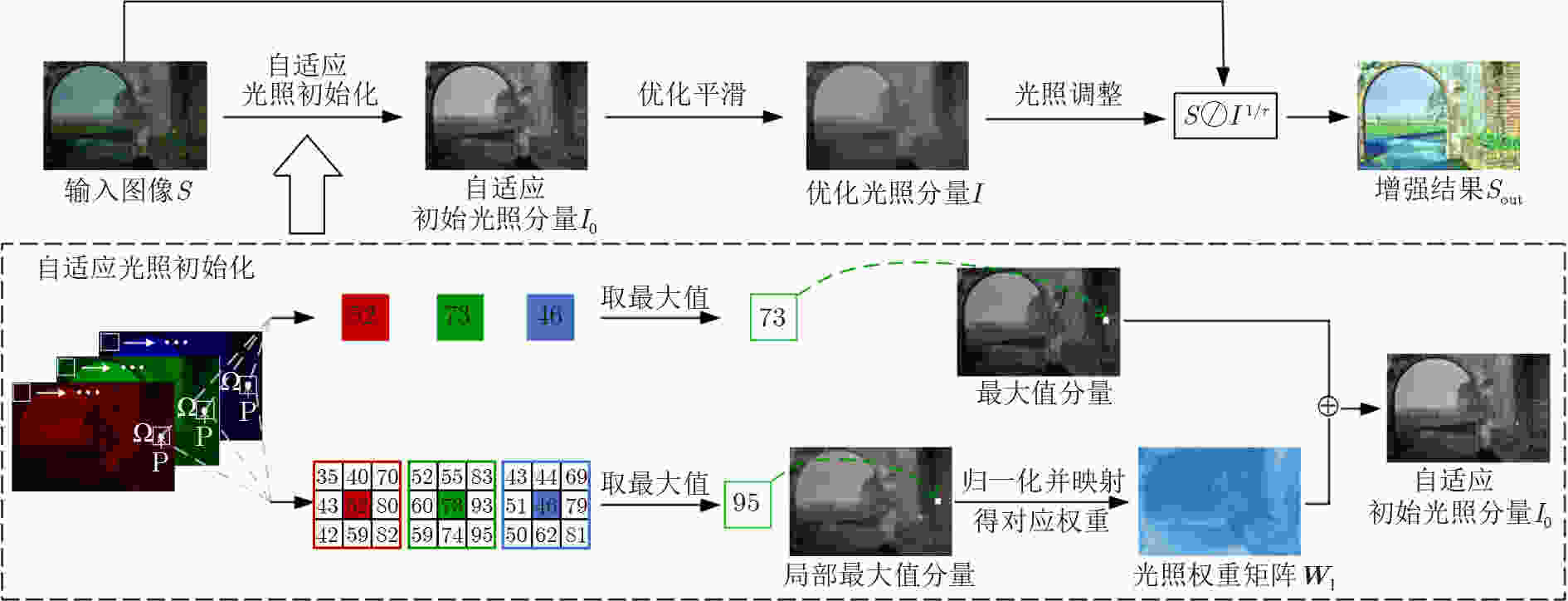
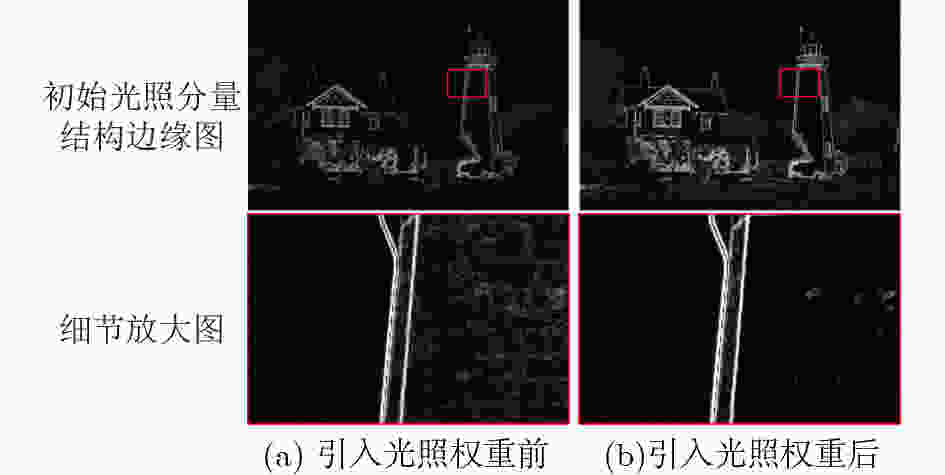
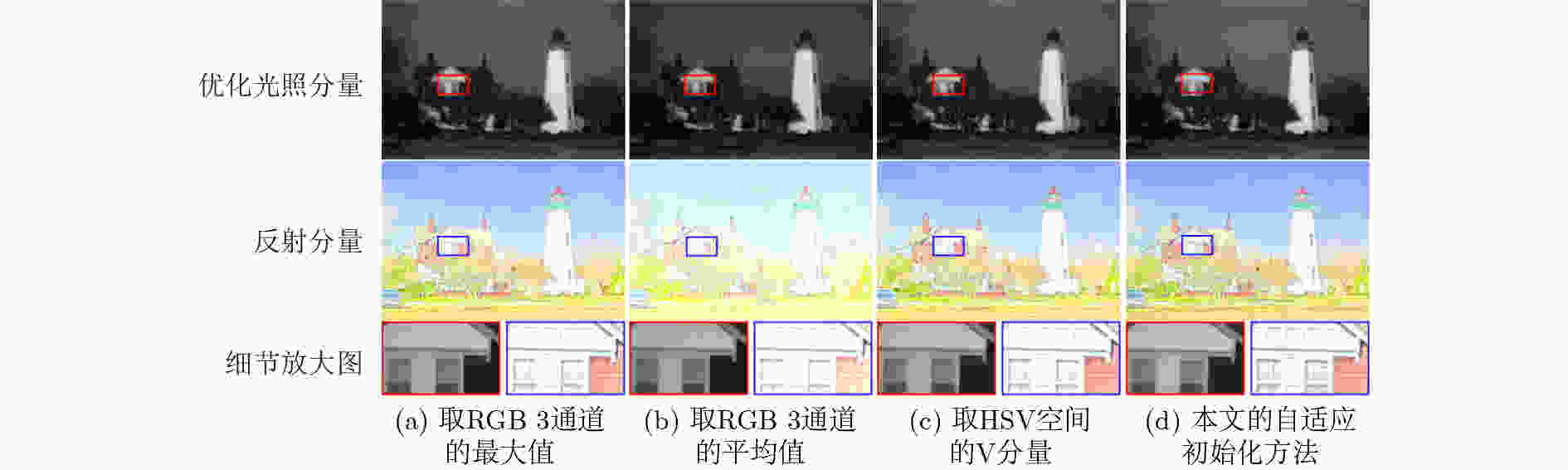
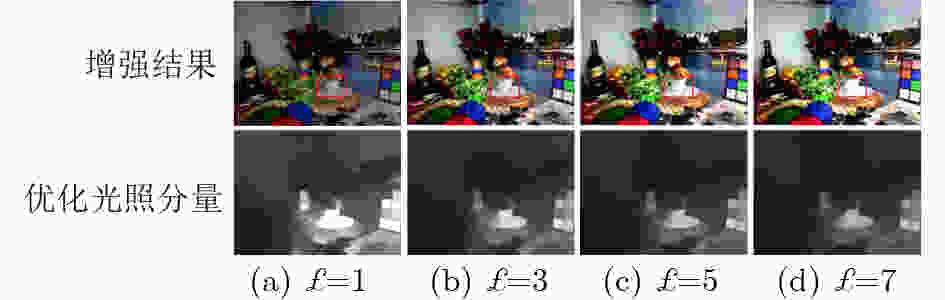
摘要: 由于光照分量分解估计的高度不确定性,如何准确估计图像的光照分量一直是基于Retinex模型的图像增强方法需要解决的难题。该文提出一个简单有效的方法,准确估计图像的初始光照分量,进而实现弱光图像增强。具体地,首先根据输入图像得到其对应的光照权重矩阵,以指导光照分量的自适应初始化估计;随后在光照结构约束下,对初始光照分量优化估计,并进一步执行非线性光照调整;最终结合Retinex模型得到增强结果。实验表明,该方法不仅能够实现准确的图像分解估计,而且与现有的弱光图像增强方法相比,该文所提方法在多个数据集上的主观视觉效果和客观评价指标都有更好的表现,同时也保持着良好的运行效率。Abstract: Due to the high uncertainty in the estimation of the light component decomposition, how to accurately estimate the light component of an image has been a challenge to be addressed by image enhancement methods based on the Retinex model. An effective method is proposed to accurately estimate the initial illumination component in this paper. Specifically, the corresponding illumination weight matrices for different inputs are obtained to guide the adaptive initialization estimation, subsequently the estimation of the initial illumination components are optimized under the constraints of the illumination structure, and the non-linear illumination adjustment be performed on them. Finally, the Retinex be combined to obtain the enhanced images. Experiments show that our method not only achieves accurate image decomposition estimation, but also performs better in terms of both subjective visual effects and objective evaluation metrics on multiple datasets while maintaining good operational efficiency compared with existing methods for low-light image enhancement.
-
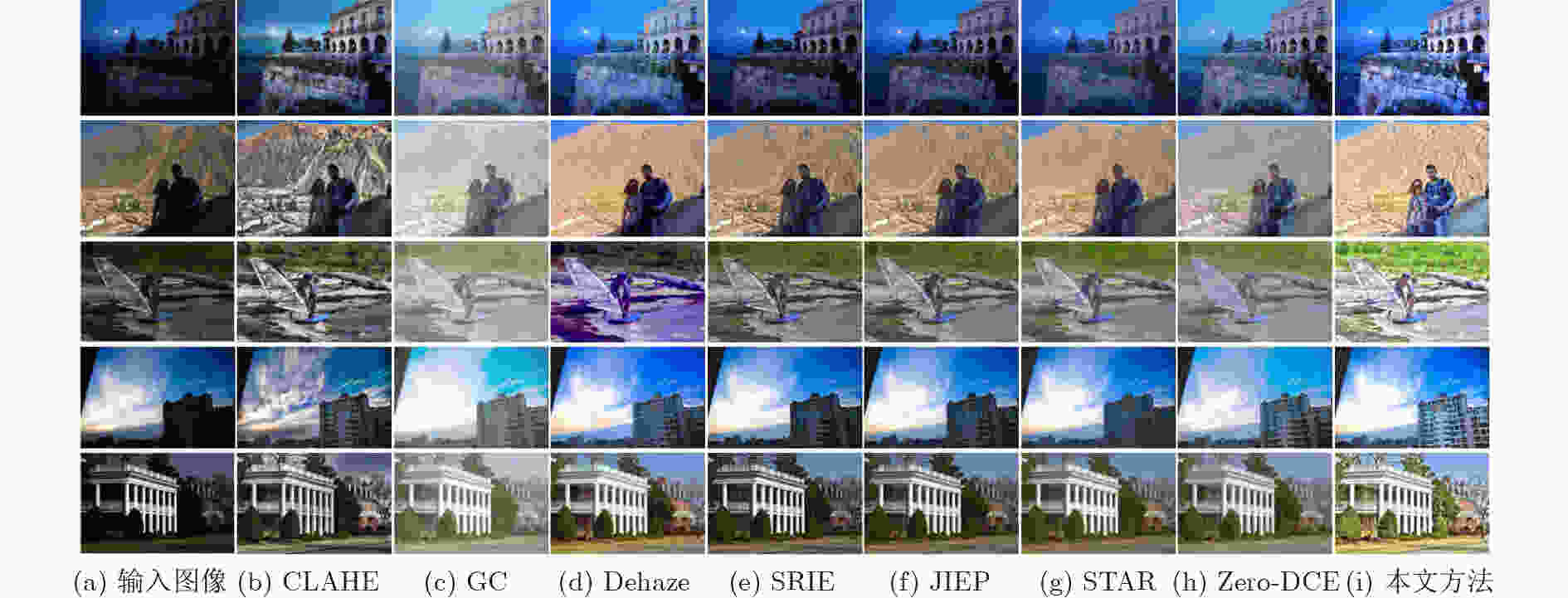
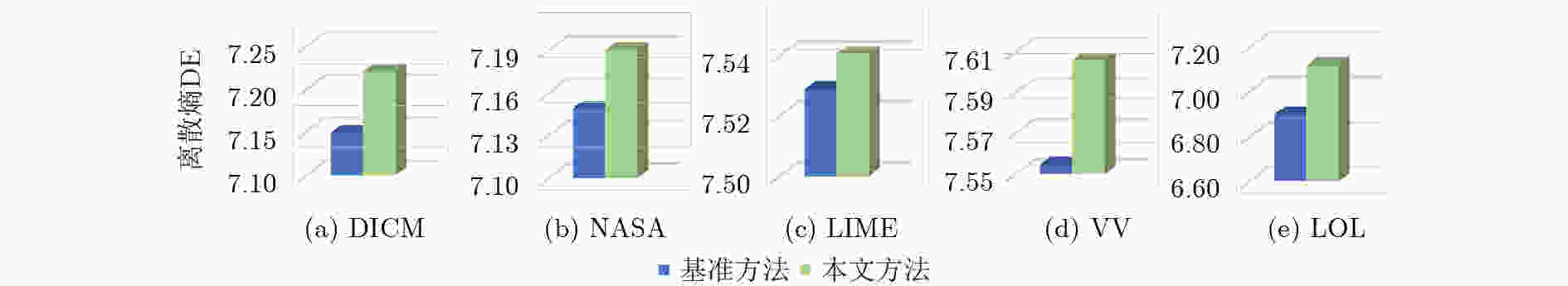
表 1 不同方法在各数据集上DE↑的平均值
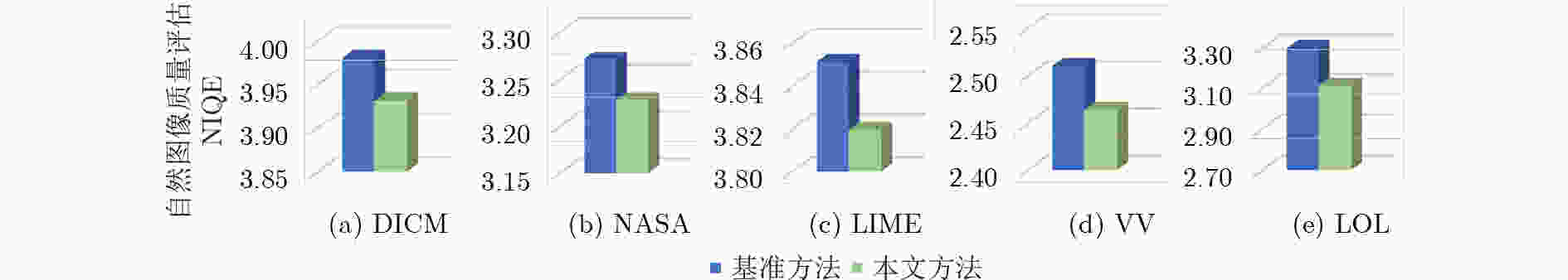
数据集 CLAHE GC Dehaze SRIE JIEP STAR Zero-DCE 本文方法 DICM 7.028 2 6.514 6 7.068 4 7.028 9 7.069 8 6.988 7 7.029 2 7.218 8 NASA 6.952 0 6.580 2 6.907 2 7.101 2 7.072 8 6.935 9 6.629 8 7.186 9 LIME 7.050 0 6.769 7 7.074 7 6.854 8 6.902 8 6.783 4 7.017 4 7.533 8 VV 7.277 4 7.017 6 7.344 6 7.348 2 7.361 8 7.272 4 7.433 2 7.605 1 LOL 6.713 2 6.465 2 6.836 4 6.840 7 6.799 0 6.683 9 7.051 8 7.118 7 表 2 不同方法在各数据集上NIQE↓的平均值
数据集 CLAHE GC Dehaze SRIE JIEP STAR Zero-DCE 本文方法 DICM 3.970 3 4.061 4 4.210 3 4.214 6 4.049 5 4.339 5 3.724 7 3.851 5 NASA 3.306 8 3.947 1 3.381 9 3.511 9 3.374 5 3.701 1 4.289 2 3.234 1 LIME 4.018 9 4.110 2 4.140 7 3.885 9 3.946 3 4.015 1 3.762 0 3.813 8 VV 2.851 4 2.737 1 3.076 3 2.725 8 2.646 3 2.822 3 3.084 4 2.471 4 LOL 3.670 2 3.441 0 3.536 1 3.400 2 3.342 9 3.471 5 3.294 0 3.114 8 表 3 不同方法增强图像的运行时间平均值(s)
方法 CLAHE GC Dehaze SRIE 时间 0.17 0.22 1.57 15.26 方法 JIEP STAR Zero-DCE 本文方法 时间 20.43 23.52 2.81 8.96 -
[1] BI Xiuli, HU Jinwu, XIAO Bin, et al. IEMask R-CNN: Information-enhanced Mask R-CNN[J]. IEEE Transactions on Big Data, 2023, 9(2): 688–700. doi: 10.1109/TBDATA.2022.3187413. [2] LAND E H. The retinex theory of color vision[J]. Scientific American, 1977, 237(6): 108–129. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican1277-108. [3] LAND E H and MCCANN J J. Lightness and retinex theory[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1971, 61(1): 1–11. doi: 10.1364/JOSA.61.000001. [4] SMITHA A, FEBIN I P, and JIDESH P. A retinex based non-local total generalized variation framework for OCT image restoration[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2022, 71: 103234. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.103234. [5] LIU Risheng, MA Long, ZHANG Jiaao, et al. Retinex-inspired unrolling with cooperative prior architecture search for low-light image enhancement[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 10556–10565. [6] JOBSON D J, RAHMAN Z, and WOODELL G A. Properties and performance of a center/surround retinex[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1997, 6(3): 451–462. doi: 10.1109/83.557356. [7] JOBSON D J, RAHMAN Z, and WOODELL G A. A multiscale retinex for bridging the gap between color images and the human observation of scenes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1997, 6(7): 965–976. doi: 10.1109/83.597272. [8] KIMMEL R, ELAD M, SHAKED D, et al. A variational framework for retinex[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2003, 52(1): 7–23. doi: 10.1023/A:1022314423998. [9] FU Xueyang, ZENG Delu, HUANG Yue, et al. A weighted variational model for simultaneous reflectance and illumination estimation[C]. The 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 2782–2790. [10] XU Jun, HOU Yingkun, REN Dongwei, et al. STAR: A structure and texture aware retinex model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 5022–5037. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.2974060. [11] CAI Bolun, XU Xianming, GUO Kailing, et al. A joint intrinsic-extrinsic prior model for retinex[C]. The 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 4020–4029. [12] GUO Xiaojie, LI Yu, and LING Haibin. LIME: Low-light image enhancement via illumination map estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(2): 982–993. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2639450. [13] LI Mading, LIU Jiaying, YANG Wenhan, et al. Structure-revealing low-light image enhancement via robust retinex model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(6): 2828–2841. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2810539. [14] CAO Gang, HUANG Lihui, TIAN Huawei, et al. Contrast enhancement of brightness-distorted images by improved adaptive gamma correction[J]. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 2018, 66: 569–582. doi: 10.1016/j.compeleceng.2017.09.012. [15] WANG Ruixing, ZHANG Qing, FU C W, et al. Underexposed photo enhancement using deep illumination estimation[C]. The 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 6842–6850. [16] REN Xutong, YANG Wenhan, CHENG Wenhuang, et al. LR3M: Robust low-light enhancement via low-rank regularized retinex model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 5862–5876. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.2984098. [17] NASA. Retinex image processing[EB/OL]. https://dragon.larc.nasa.gov/retinex/pao/news, 2001. [18] VONIKAKIS V, ANDREADIS I, and GASTERATOS A. Fast centre–surround contrast modification[J]. IET Image Processing, 2008, 2(1): 19–34. doi: 10.1049/iet-ipr:20070012. [19] LEE C, LEE C, and KIM C S. Contrast enhancement based on layered difference representation of 2D histograms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2013, 22(12): 5372–5384. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2013.2284059. [20] WEI Chen, WANG Wenjing, YANG Wenhan, et al. Deep retinex decomposition for low-light enhancement[C]. British Machine Vision Conference 2018, Newcastle, UK, 2018: 155. [21] YE Zhengmao, MOHAMADIAN H, and YE Yongmao. Discrete entropy and relative entropy study on nonlinear clustering of underwater and arial images[C]. 2007 IEEE International Conference on Control Applications, Singapore, 2007: 313–318. [22] HAUTIÈRE N, TAREL J P, AUBERT D, et al. Blind contrast enhancement assessment by gradient ratioing at visible edges[J]. Image Analysis and Stereology, 2008, 27(2): 87–95. doi: 10.5566/ias.v27.p87-95. [23] REZA A M. Realization of the contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization (CLAHE) for real-time image enhancement[J]. Journal of VLSI Signal Processing Systems for Signal, Image and Video Technology, 2004, 38(1): 35–44. doi: 10.1023/B:VLSI.0000028532.53893.82. [24] RAHMAN S, RAHMAN M, ABDULLAH-AL-WADUD M, et al. An adaptive gamma correction for image enhancement[J]. EURASIP Journal on Image and Video Processing, 2016, 2016(1): 35. doi: 10.1186/s13640-016-0138-1. [25] DONG Xuan, WANG Guan, PANG Yi, et al. Fast efficient algorithm for enhancement of low lighting video[C]. 2011 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, Barcelona, 2011: 1–6. [26] LI Chongyi, GUO Chunle, and LOY C C. Learning to enhance low-light image via zero-reference deep curve estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(8): 4225–4238. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3063604. -






 下载:
下载:

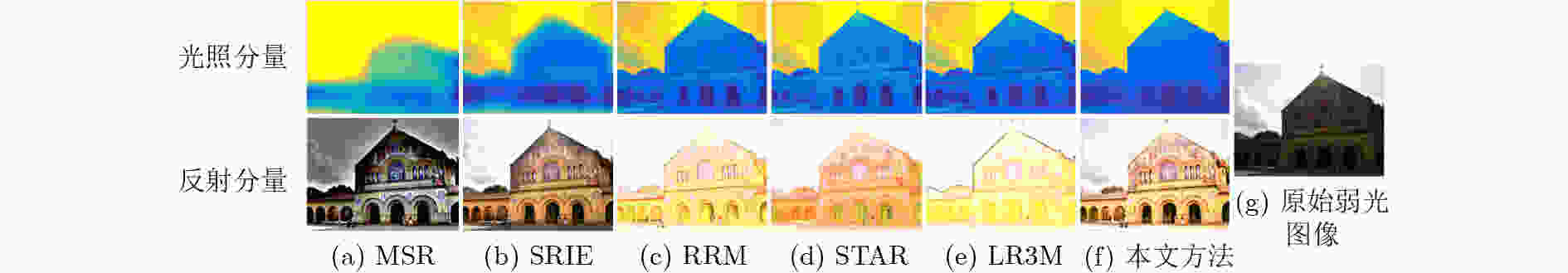


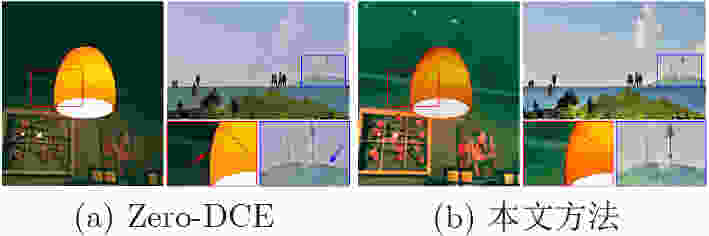


 下载:
下载:
