3D Hilbert Space Filling Curve Encoding and Decoding Algorithms Based on Efficient Prefix Reduction
-
摘要: 3维Hilbert空间填充曲线(3D HSFC)的编码和解码效率对空间查询处理、图像处理等领域的应用举足轻重。现有的3维编解码算法独立编解码每一个点,忽略了Hilbert曲线的局部保持特性。为了提高编解码效率,该文设计了高效的3D状态视图,并提出一种新的前缀约简的3D HSFC编码算法(PR-3HE)和前缀约简3D HSFC解码算法(PR-3HD),这两个算法通过公共前缀的定义和识别、公共前缀约简及多种优化技术来最小化需要编码的阶数,从而提高3D HSFC的编解码效率。理论上证明:当编码或解码一个$k$阶的窗体(窗体内总共含有${2^k} \times {2^k} \times {2^k}$个点)时,PR-3HE平均每个点的编码阶数不超过2,PR-3HD平均解码阶数不超过8/7。相对于传统的基于迭代的方法,编解码时间复杂度从$O(k)$降低到了$O(1)$。实验结果表明,该文算法在模拟数据集和真实数据集上的表现显著优于现有算法。
-
关键词:
- 3维Hilbert空间填充曲线 /
- 3维状态视图 /
- 前缀约简 /
- 3D HSFC编码算法 /
- 3D HSFC解码算法
Abstract: The encoding and decoding efficiency of 3D Hilbert Space Filling Curve (3D HSFC) is key for the application of spatial query processing, image processing. The existing 3D encoding and decoding algorithms encode and decode each point independently, ignoring the local preservation characteristic of Hilbert curve. To improve the efficiency of encoding and decoding, an efficient 3D state view is designed in this paper, and a new Prefix Reduction 3D HSFC Encoding Algorithm (PR-3HE) and Prefix Reduction 3D HSFC Decoding Algorithm (PR-3HD) are proposed. These two algorithms minimize the orders to be processed through the definition and identification of common prefix, common prefix reduction and various optimization techniques, thus improving 3D HSFC encoding and decoding efficiency. Theoretical proof is provided in this paper, demonstrating that when encoding or decoding a k-order window (all ${2^k} \times {2^k} \times {2^k}$ points in a window), PR-3HE passively encodes no more than 2 orders for each coordinate on average, while PR-3HD passively decodes no more than 8/7 orders for each Hilbert code on average. The encoding and decoding time complexity can be reduced from $O(k)$ to $O(1)$. Experimental results show on both synthetic and real dataset the benefits of our algorithms over the other counterparts. -
表 1 CHM
状态 000 001 010 011 100 101 110 111 0 0 1 3 2 7 6 4 5 1 0 1 7 6 3 2 4 5 2 0 3 1 2 7 4 6 5 3 0 7 1 6 3 4 2 5 4 0 3 7 4 1 2 6 5 5 0 7 3 4 1 6 2 5 6 2 1 3 0 5 6 4 7 7 6 1 7 0 5 2 4 3 8 2 3 1 0 5 4 6 7 9 6 7 1 0 5 4 2 3 10 4 3 7 0 5 2 6 1 11 4 7 3 0 5 6 2 1 12 2 1 5 6 3 0 4 7 13 6 1 5 2 7 0 4 3 14 2 3 5 4 1 0 6 7 15 6 7 5 4 1 0 2 3 16 4 3 5 2 7 0 6 1 17 4 7 5 6 3 0 2 1 18 2 5 1 6 3 4 0 7 19 6 5 1 2 7 4 0 3 20 2 5 3 4 1 6 0 7 21 6 5 7 4 1 2 0 3 22 4 5 3 2 7 6 0 1 23 4 5 7 6 3 2 0 1 表 2 CSM
状态 000 001 010 011 100 101 110 111 0 5 1 13 0 13 22 5 0 1 3 0 7 23 7 1 3 1 2 4 19 3 2 19 4 16 2 3 1 9 2 17 9 1 3 3 4 2 21 21 2 5 4 10 4 5 0 15 15 0 4 11 5 5 6 6 7 12 11 6 20 11 12 7 21 6 1 9 7 7 9 1 8 8 18 9 10 8 10 14 18 9 15 3 8 7 9 7 9 3 10 8 23 23 8 10 10 4 11 11 6 17 17 6 11 5 11 10 12 12 13 12 18 6 17 17 6 13 19 12 13 13 0 15 15 0 14 14 20 14 16 15 16 8 20 15 9 5 15 13 14 13 15 5 16 14 22 16 16 22 14 2 17 17 12 11 17 3 11 12 17 16 18 18 18 19 12 8 23 23 8 19 13 19 18 19 2 21 21 2 20 20 20 14 22 21 6 22 14 21 7 21 4 19 20 21 19 4 22 20 22 16 22 16 0 20 23 23 18 23 10 1 10 23 18 22 算法1 PR-3HE 输入:${H_p}$:$p$的编码;$|{P_{p,q}}|$:$p$和$q$的公共前缀长度; $q$:当前点;$r$:后邻点;$k$:阶数 输出:${H_q}$:当前点$q$的Hilbert编码;$|{P_{p,r} }|$:$q$和$r$的公共前缀
长度;1. ${H_q}$←$ \overrightarrow {H_p^{|{P_{p,q}}|}} $ 2. $|{P_{p,r}}|$←计算q和r的最大公共前缀长度 3. $s$←$ M[\text{|}{P}_{p,q}|+1] $ 4. FOR $i$←$ \text{|}{P}_{p,q}| $+1 to $k$ 5. ${H_q} = {H_q} < <3|{ { {\rm{CHM} }[s][x} }_q^i][y_q^i][z_q^i]$ 6. $s = {\text{CSM}}[s][x_q^i][y_q^i][z_q^i]$ 7. IF $i <= |{P_{q,r} }|$ 8. $M[i + 1] = s$ 9. END IF 10. END FOR 表 3 HCM
状态 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 000 001 011 010 110 111 101 100 1 000 001 101 100 110 111 011 010 2 000 010 011 001 101 111 110 100 3 000 010 110 100 101 111 011 001 4 000 100 101 001 011 111 110 010 5 000 100 110 010 011 111 101 001 6 011 001 000 010 110 100 101 111 7 011 001 101 111 110 100 000 010 8 011 010 000 001 101 100 110 111 9 011 010 110 111 101 100 000 001 10 011 111 101 001 000 100 110 010 11 011 111 110 010 000 100 101 001 12 101 001 000 100 110 010 011 111 13 101 001 011 111 110 010 000 100 14 101 100 000 001 011 010 110 111 15 101 100 110 111 011 010 000 001 16 101 111 011 001 000 010 110 100 17 101 111 110 100 000 010 011 001 18 110 010 000 100 101 001 011 111 19 110 010 011 111 101 001 000 100 20 110 100 000 010 011 001 101 111 21 110 100 101 111 011 001 000 010 22 110 111 011 010 000 001 101 100 23 110 111 101 100 000 001 011 010 表 4 HSM
状态 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 5 1 0 13 5 0 22 13 1 3 0 1 7 3 1 23 7 2 4 3 2 19 4 2 16 19 3 1 2 3 9 1 3 17 9 4 2 5 4 21 2 4 10 21 5 0 4 5 15 0 5 11 15 6 11 7 6 12 11 6 20 12 7 9 6 7 1 9 7 21 1 8 10 9 8 18 10 8 14 18 9 7 8 9 3 7 9 15 3 10 8 11 10 23 8 10 4 23 11 6 10 11 17 6 11 5 17 12 17 13 12 6 17 12 18 6 13 15 12 13 0 15 13 19 0 14 16 15 14 20 16 14 8 20 15 13 14 15 5 13 15 9 5 16 14 17 16 22 14 16 2 22 17 12 16 17 11 12 17 3 11 18 23 19 18 8 23 18 12 8 19 21 18 19 2 21 19 13 2 20 22 21 20 14 22 20 6 14 21 19 20 21 4 19 21 7 4 22 20 23 22 16 20 22 0 16 23 18 22 23 10 18 23 1 10 算法2 PR-3HD 输入:${X_p}$, ${Y_p}$,${Z_p}$:$p$的坐标分量;$|{P_{Hp,Hq} }|$:$Hp$和$Hq$的最大公共前
缀长度;${H_q}$, ${H_r}$:$q$和$r$的Hilbert编码;$k$:阶数输出:$q$的坐标分量;$|{P_{Hq,Hr} }|$:$Hq$和$Hr$的最大公共前缀长度; 1. ${X_q}$,${Y_q}$,${Z_q}$←$(\overleftarrow{X_p^{ {\text{|} }{P_{ {H_p},{H_q} } }|} },\overleftarrow{Y_p^{ {\text{|} }{P_{ {H_p},{H_q} } }|}},\overleftarrow{Z_p^{ {\text{|} }{P_{ {H_p},{H_q} } }|}})$ 2. $ {\text{|}}{P_{{H_q},{H_r}}}| $←计算Hq和Hr的最大公共前缀长度 3. $s$←$ M{\text{[|}}{P_{{H_p},{H_q}}}| + 1] $ 4. FOR $i$←$ {\text{|}}{P_{{H_p},{H_q}}}| $+1 to $k$ 5. $x_q^iy_q^iz_q^i = {\text{HCM}}[s][H_q^i]$ 6. ${X_q} = {X_q} < < 1|x_q^i$ 7. ${Y_q} = {Y_q} < < 1|y_q^i$ 8. ${Z_q} = {Z_1} << 1|z_q^i$ 9. $s = {\text{HSM}}[s][H_q^i]$ 10. IF $i <= |{P_{ {H_q},{H_r} } }|$ 11. $M[i + 1] = s$ 12. END IF 13. END FOR -
[1] YAO Zhixin, ZHANG Jianqin, LI Taizeng, et al. A trajectory big data storage model incorporating partitioning and spatio-temporal multidimensional hierarchical organization[J]. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 2022, 11(12): 621. doi: 10.3390/ijgi11120621. [2] LIU Zhaoman, WU Lei, MENG Weizhi, et al. Accurate range query with privacy preservation for outsourced location-based service in IOT[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(18): 14322–14337. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3068566. [3] ZHANG Xuncai, WANG Lingfei, ZHOU Zheng, et al. A chaos-based image encryption technique utilizing Hilbert curves and H-fractals[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 74734–74746. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2921309. [4] CHEN Jiafeng, YU Lu, and WANG Wenyi. Hilbert space filling curve based scan-order for point cloud attribute compression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022, 31: 4609–4621. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2022.3186532. [5] 贾连印, 陈明鲜, 李孟娟, 等. 基于状态视图的高效Hilbert编码和解码算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(6): 1494–1501. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190501.JIA Lianyin, CHEN Mingxian, LI Mengjuan, et al. State view based efficient Hilbert encoding and decoding algorithms[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(6): 1494–1501. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190501. [6] BÖHM C, PERDACHER M, and PLANT C. A novel Hilbert curve for cache-locality preserving loops[J]. IEEE Transactions on Big Data, 2021, 7(2): 241–254. doi: 10.1109/TBDATA.2018.2830378. [7] 贾连印, 孔明, 王维晨, 等. 数据偏斜分布下的二维Hilbert编解码算法[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 62(9): 1426–1434. doi: 10.16511/j.cnki.qhdxxb.2021.21.043.JIA Lianyin, KONG Ming, WANG Weichen, et al. 2-D Hilbert encoding and decoding algorithms on skewed data[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology), 2022, 62(9): 1426–1434. doi: 10.16511/j.cnki.qhdxxb.2021.21.043. [8] 李绍俊, 钟耳顺, 王少华, 等. 基于状态转移矩阵的Hilbert码快速生成算法[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2014, 16(6): 846–851. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1047.2014.00846.LI Shaojun, ZHONG Ershun, WANG Shaohua, et al. An algorithm for Hilbert ordering code based on state-transition matrix[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 2014, 16(6): 846–851. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1047.2014.00846. [9] HAVERKORT H. How many three-dimensional Hilbert curves are there?[J]. Journal of Computational Geometry, 2017, 8(1): 206–281. doi: 10.20382/jocg.v8i1a10. [10] WEISSENBÖCK J, FRÖHLER B, GRÖLLER E, et al. Dynamic volume lines: Visual comparison of 3D volumes through space-filling curves[J]. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2019, 25(1): 1040–1049. doi: 10.1109/TVCG.2018.2864510. [11] WU Yuhao, CAO Xuefeng, and AN Zipeng. A spatiotemporal trajectory data index based on the Hilbert curve code[C]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Beijing, China, 2020: 012005. [12] TSINGANOS P, CORNELIS B, CORNELIS J, et al. Hilbert sEMG data scanning for hand gesture recognition based on deep learning[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2021, 33(7): 2645–2666. doi: 10.1007/s00521-020-05128-7. [13] 陈晓宏, 储飞黄, 方胜良, 等. 基于剖分网格改进A*算法的航迹规划研究[J]. 电光与控制, 2022, 29(7): 17–21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2022.07.004.CHEN Xiaohong, CHU Feihuang, FANG Shengliang, et al. Trajectory planning based on A* algorithm improved by subdivision grid[J]. Electronics Optics &Control, 2022, 29(7): 17–21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2022.07.004. [14] MOORE D. Fast Hilbert curve generation, sorting, and range queries[EB/OL]. https://github.com/Cheedoong/hilbert, 2021. [15] 李晨阳, 张杨, 冯玉才. N维Hilbert编码的计算[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2006, 18(7): 1032–1038. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-9775.2006.07.024.LI Chenyang, ZHANG Yang, and FENG Yucai. Calculation of N-dimensional Hilbert codes[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design &Computer Graphics, 2006, 18(7): 1032–1038. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-9775.2006.07.024. [16] ZHANG Jian and KAMATA S I. A generalized 3-D Hilbert scan using look-up tables[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2012, 23(3): 418–425. doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2011.12.005. [17] JIA Lianyin, LIANG Binbin, LI Mengjuan, et al. Efficient 3D Hilbert curve encoding and decoding algorithms[J]. Chinese Journal of Electronics, 2022, 31(2): 277–284. doi: 10.1049/cje.2020.00.171. [18] ZHENG Yu, XIE Xing, and MA Weiying. GeoLife: A collaborative social networking service among user, location and trajectory[J]. IEEE Data Engineering Bulletin, 2010, 33(2): 32–39. -





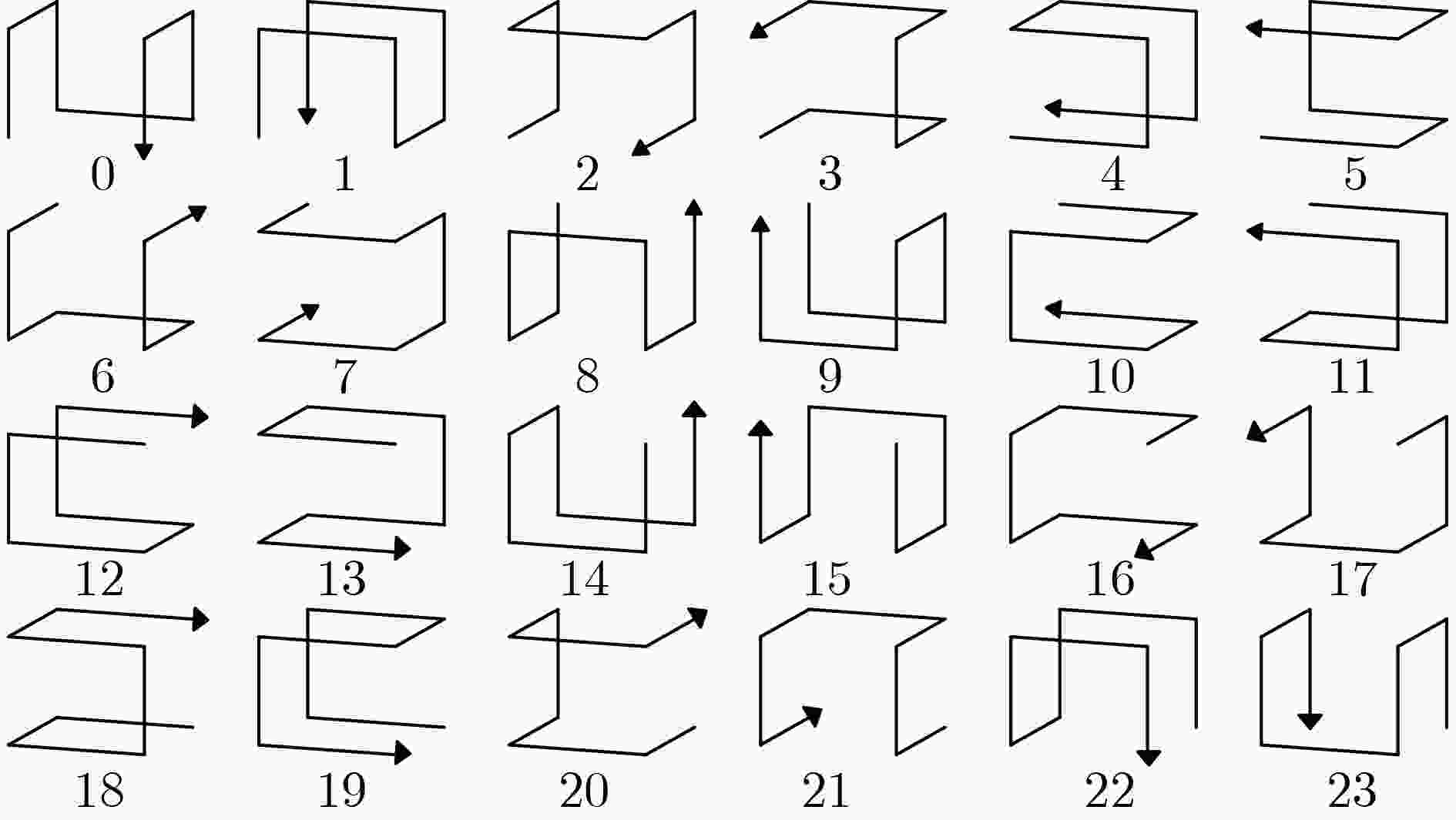
 下载:
下载:
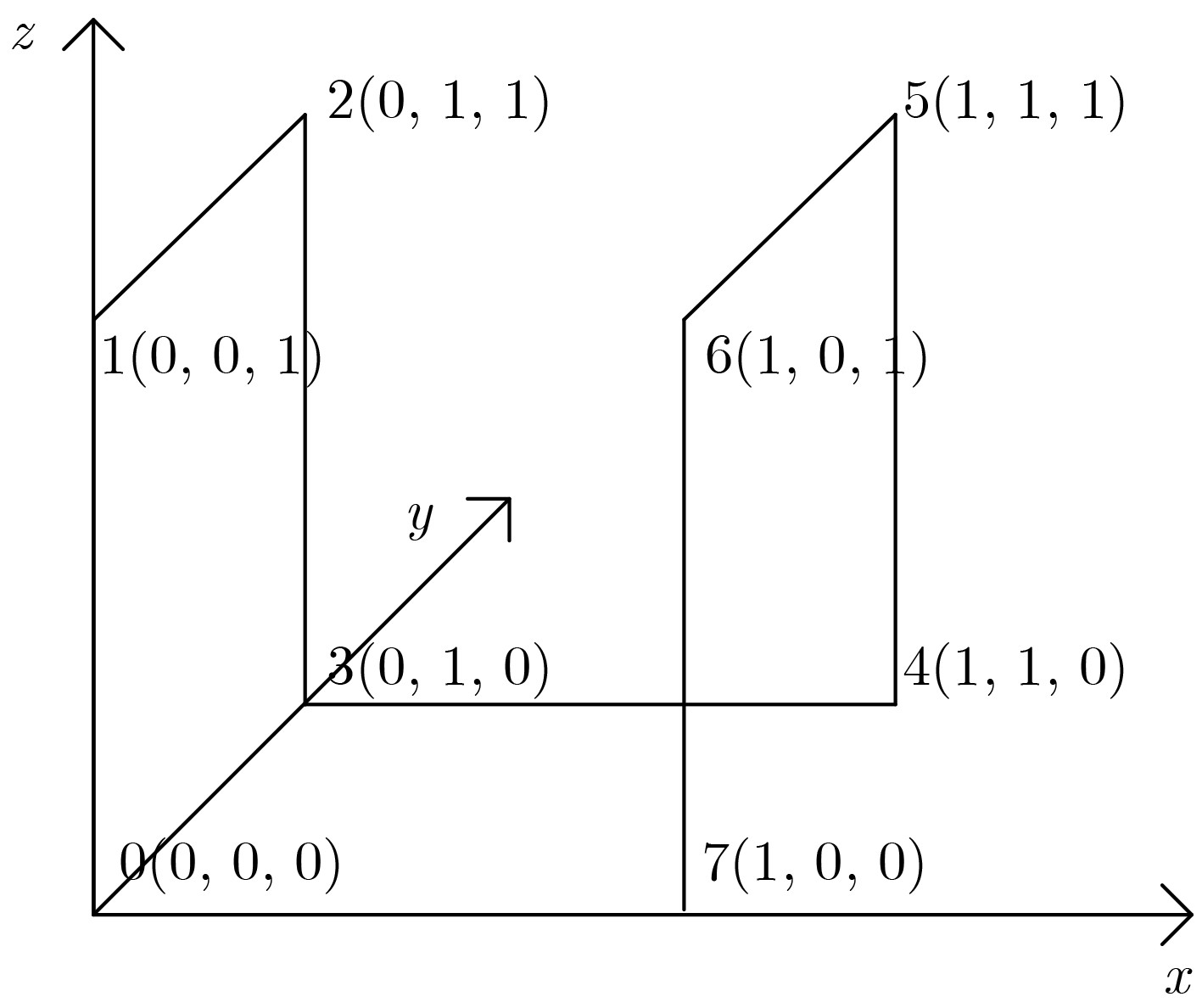
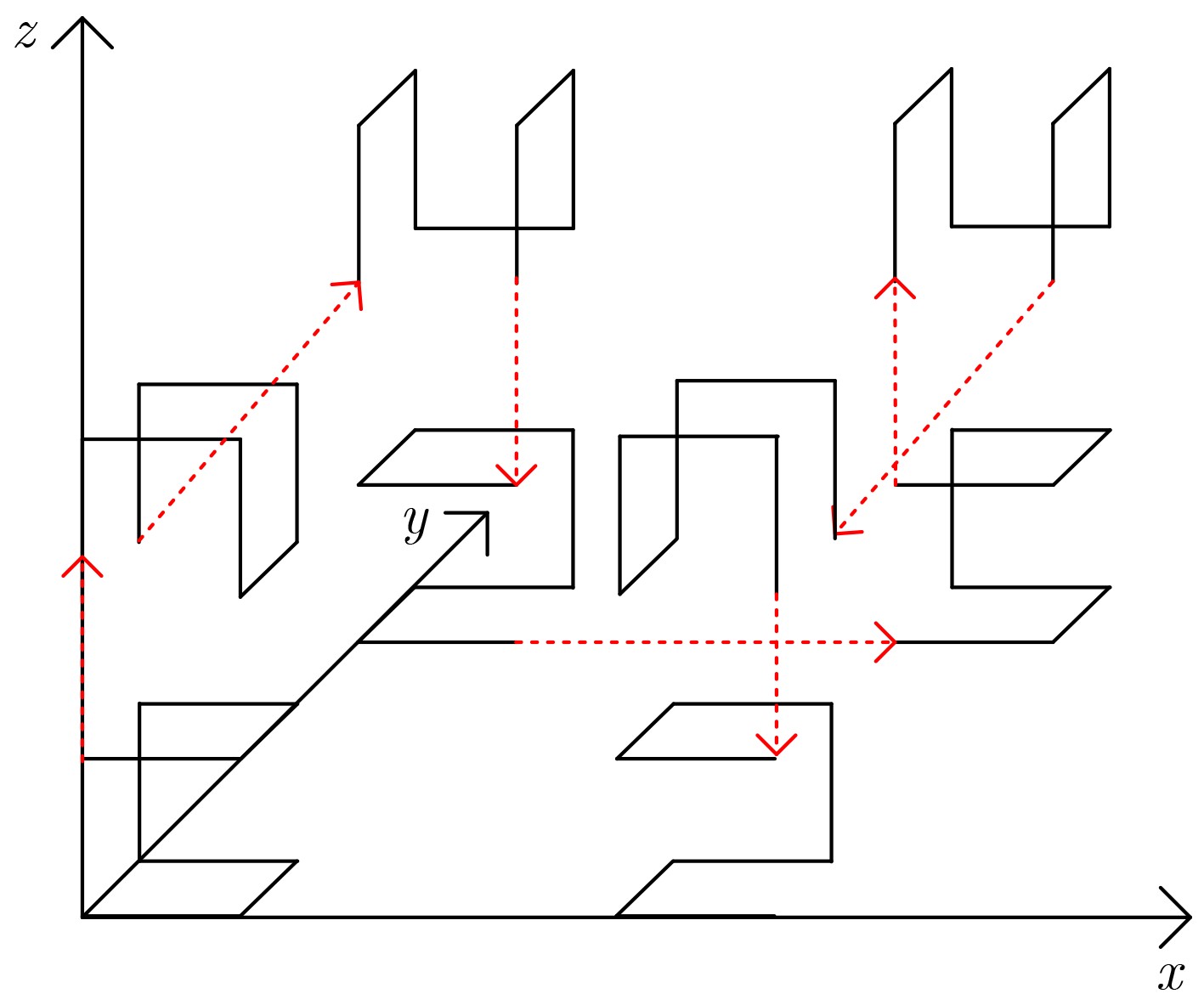

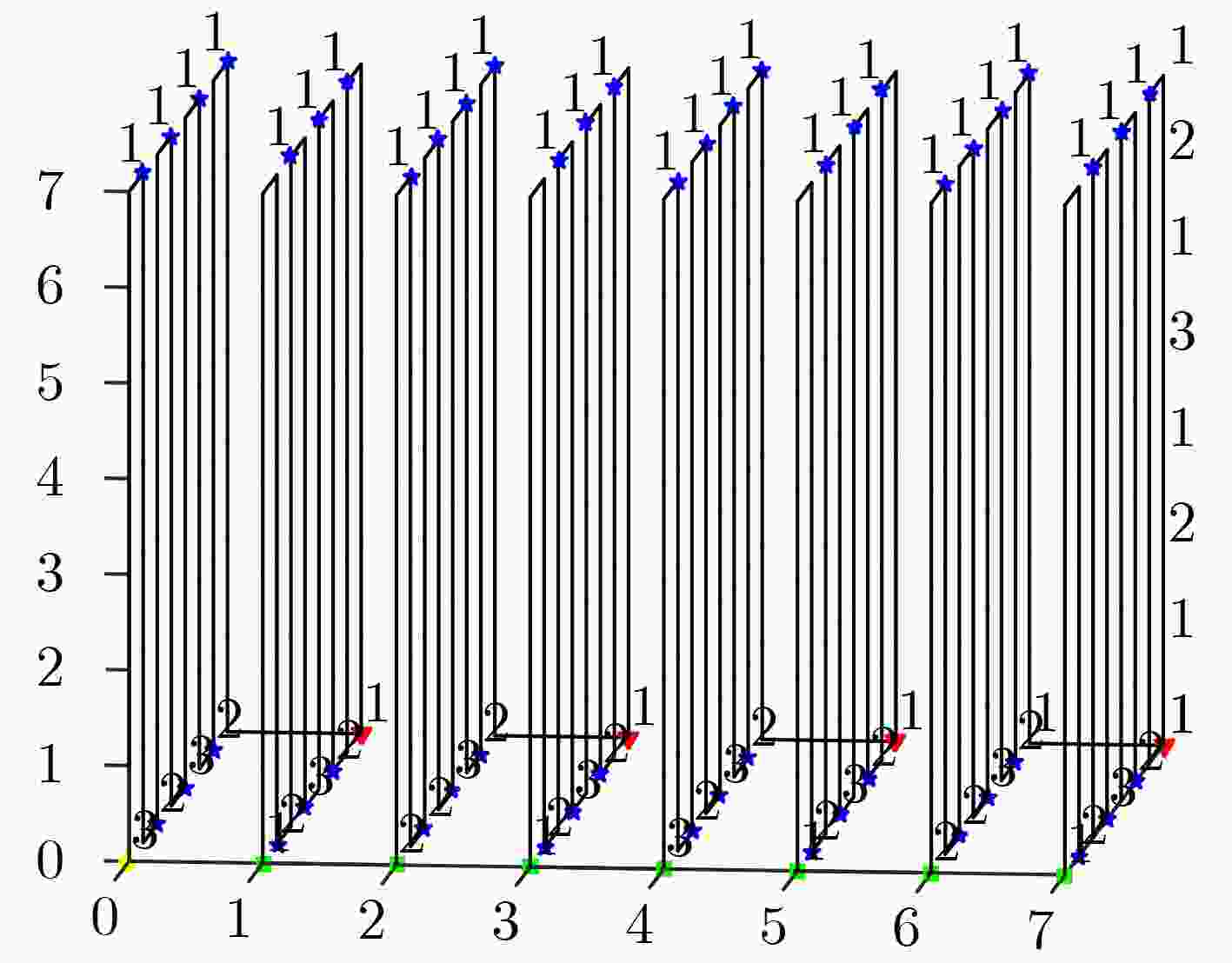

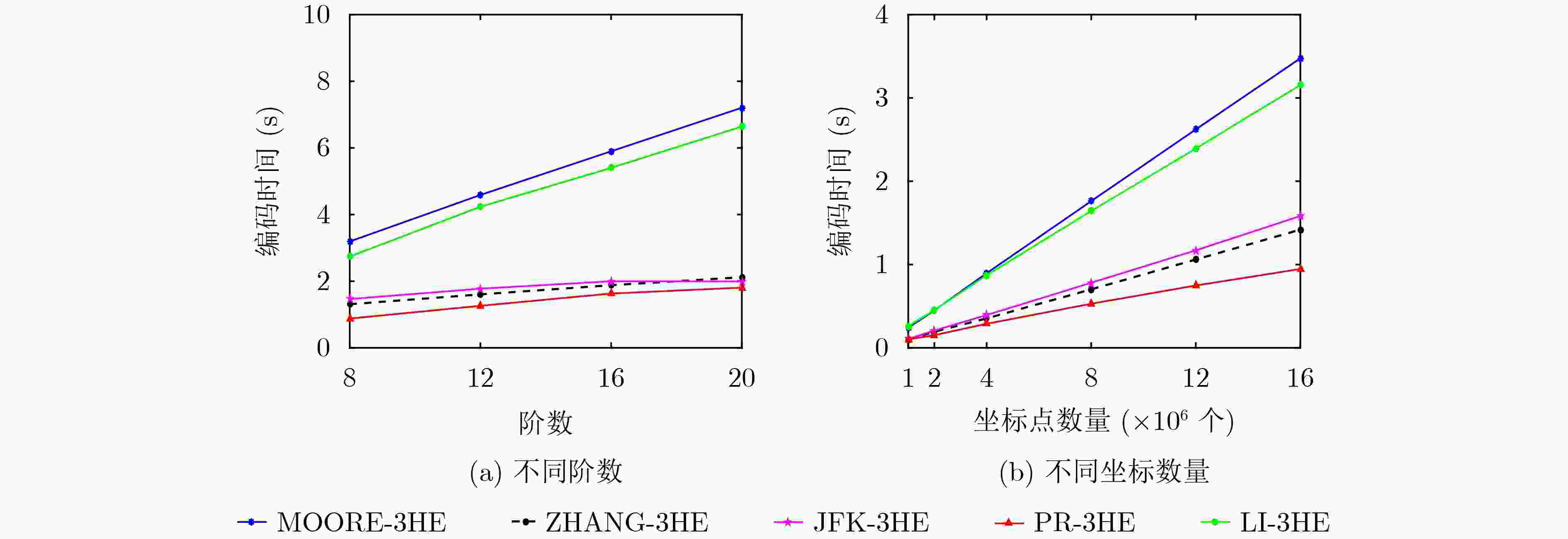
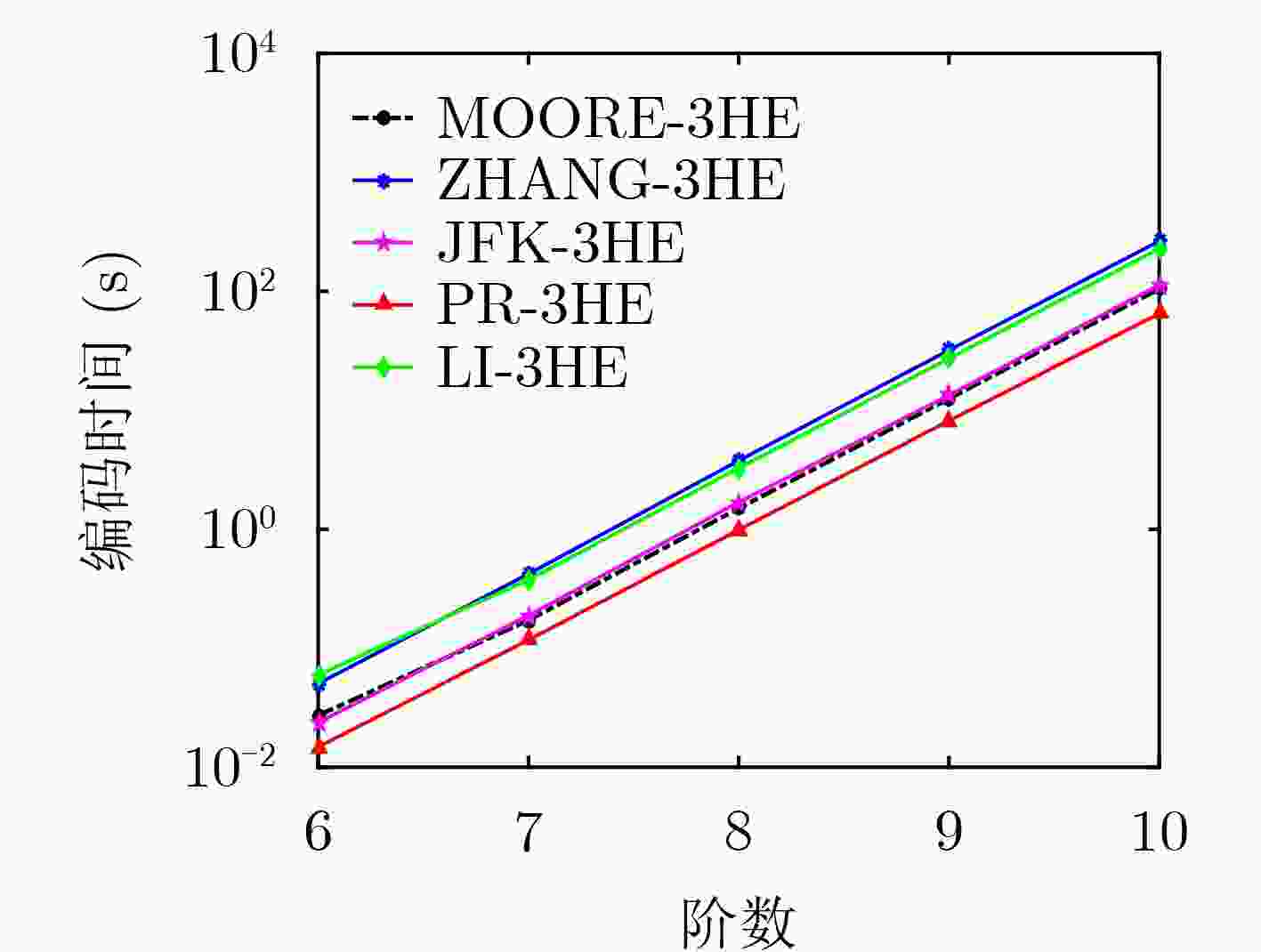
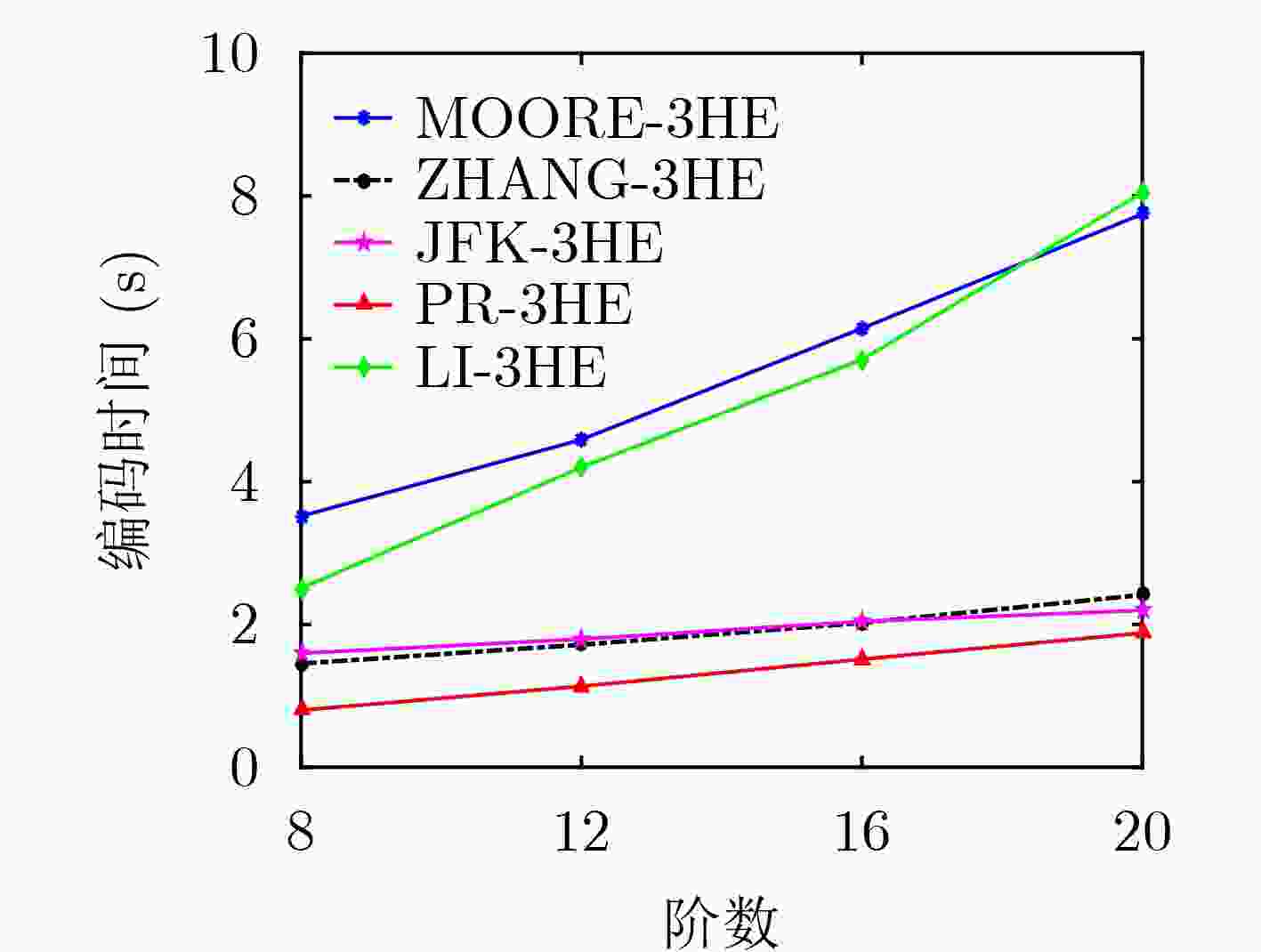
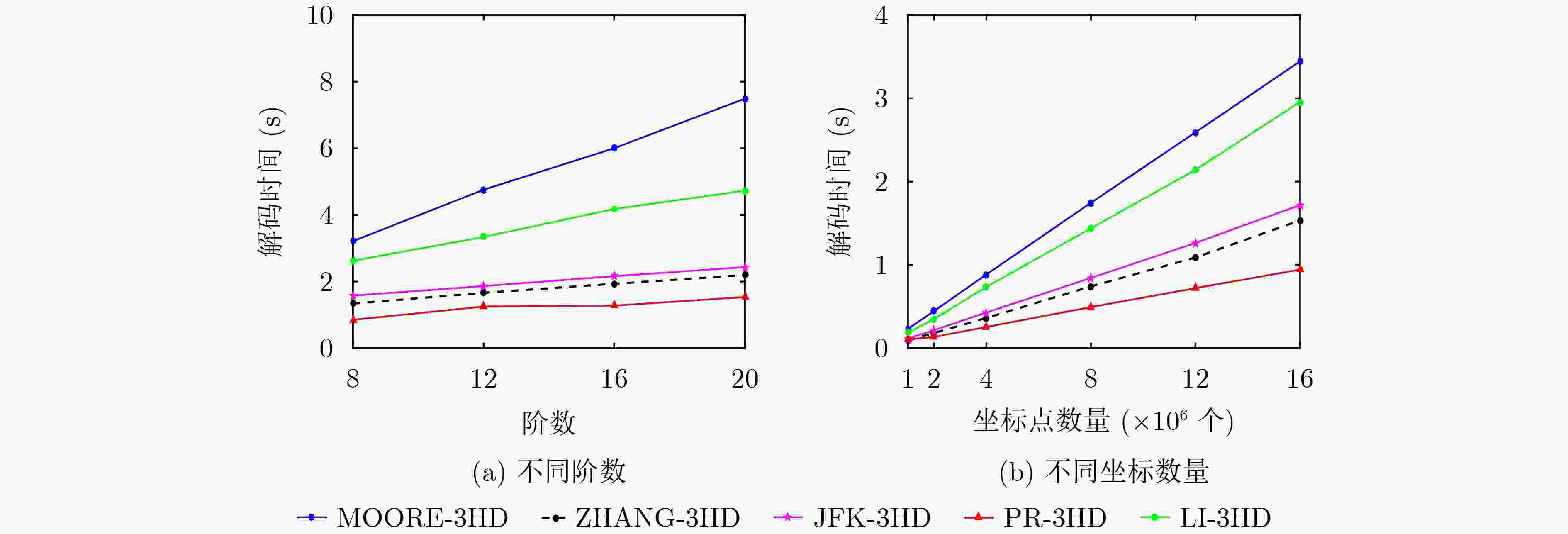
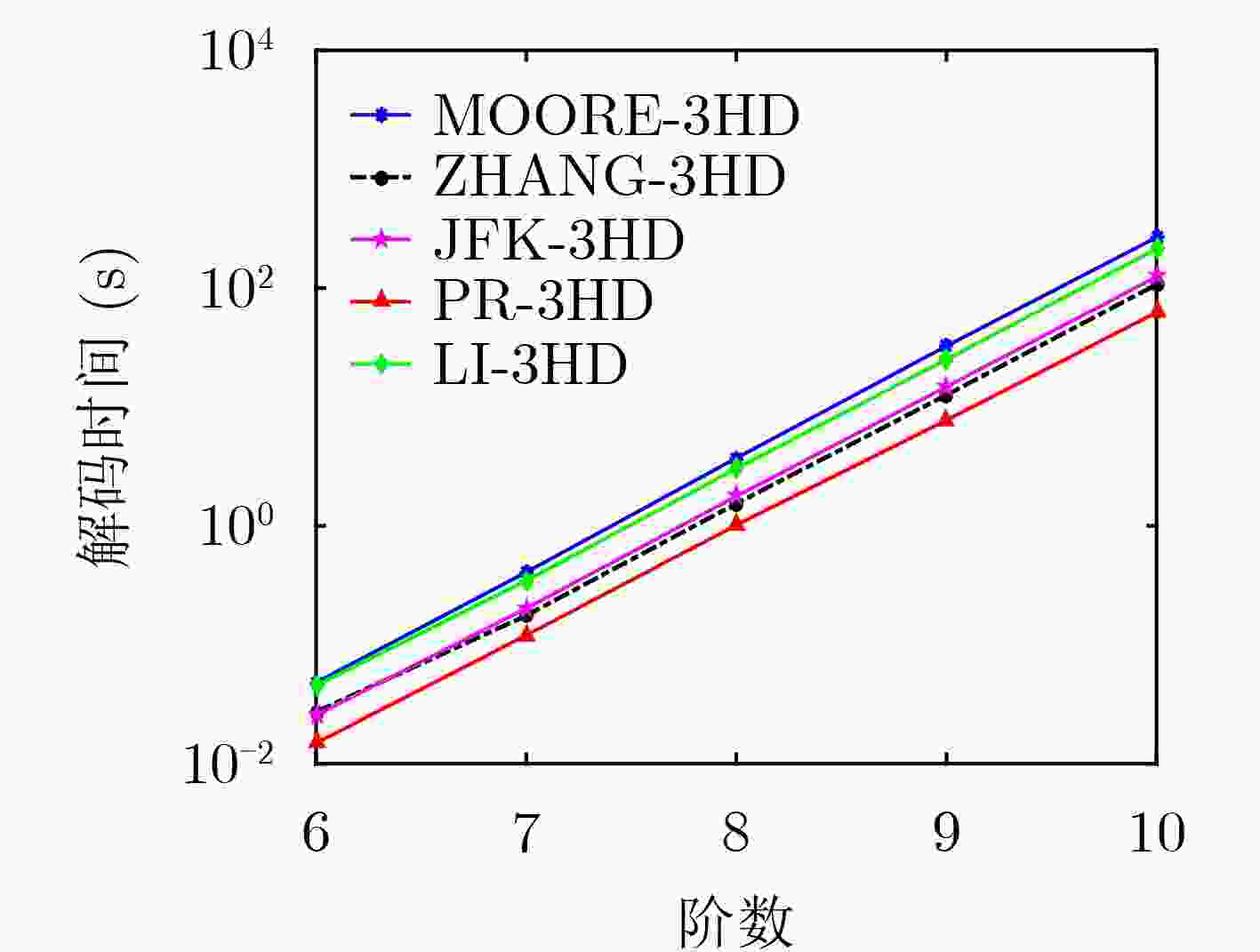
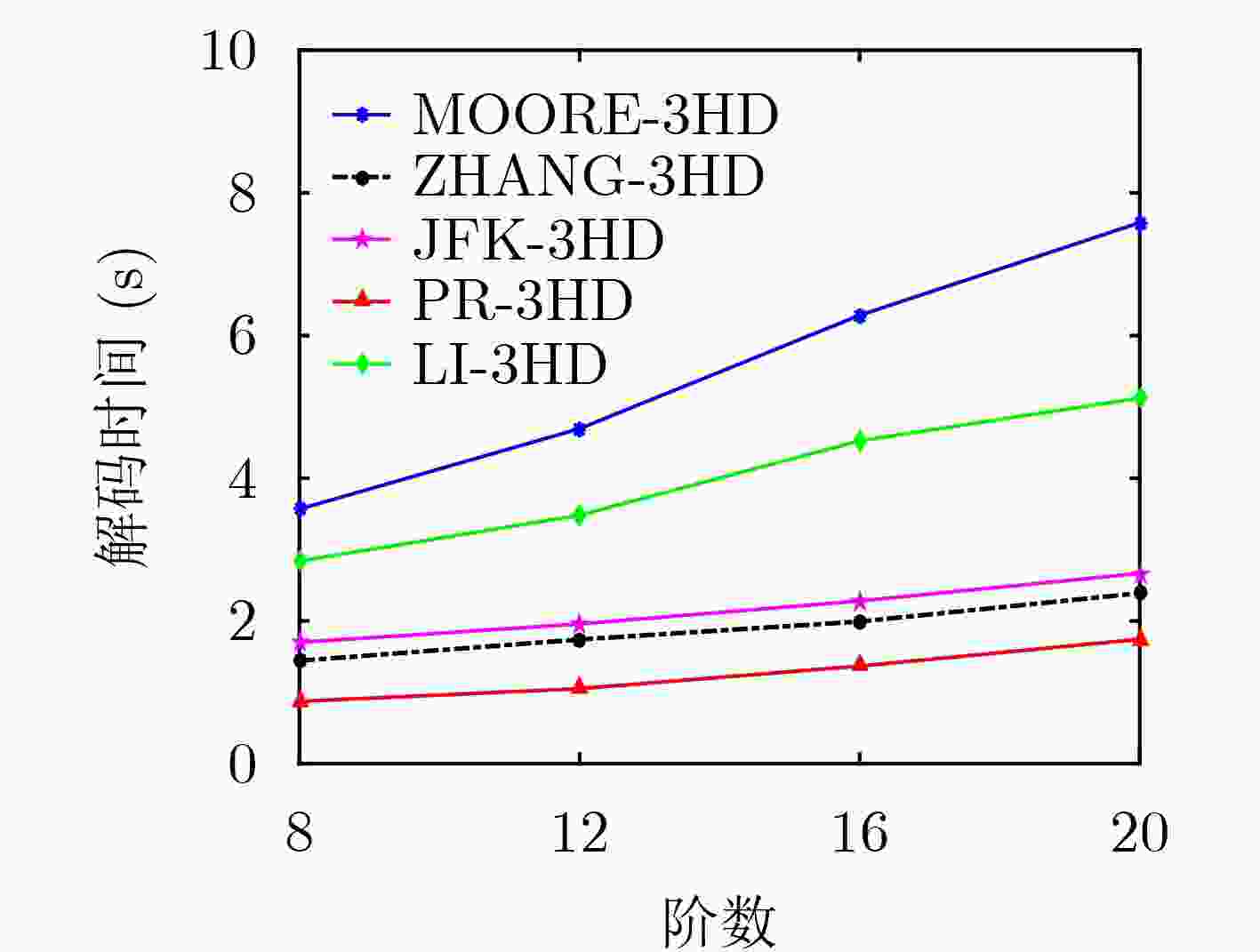


 下载:
下载:
