Spiking Neural Network for Object Detection Based on Dual Error
-
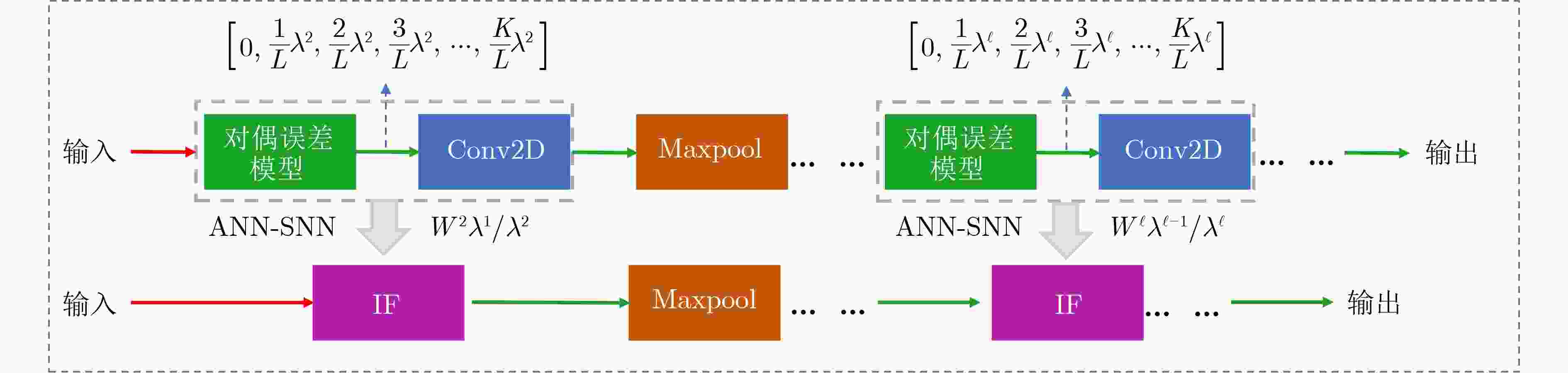
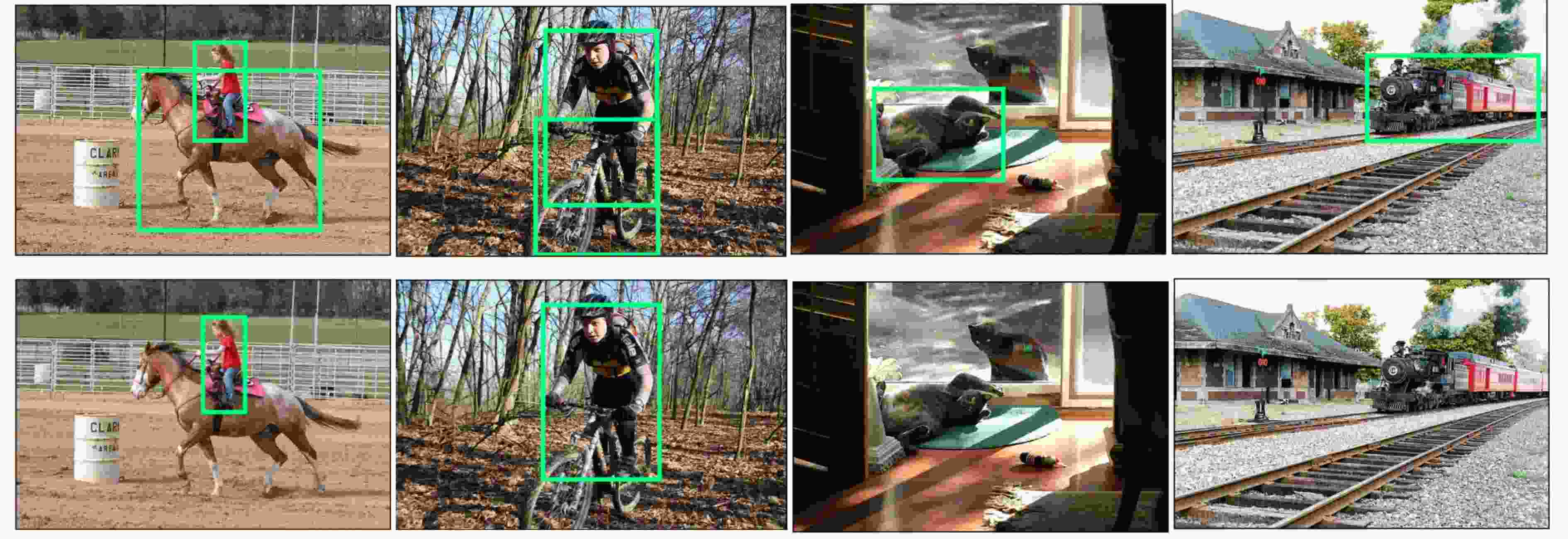
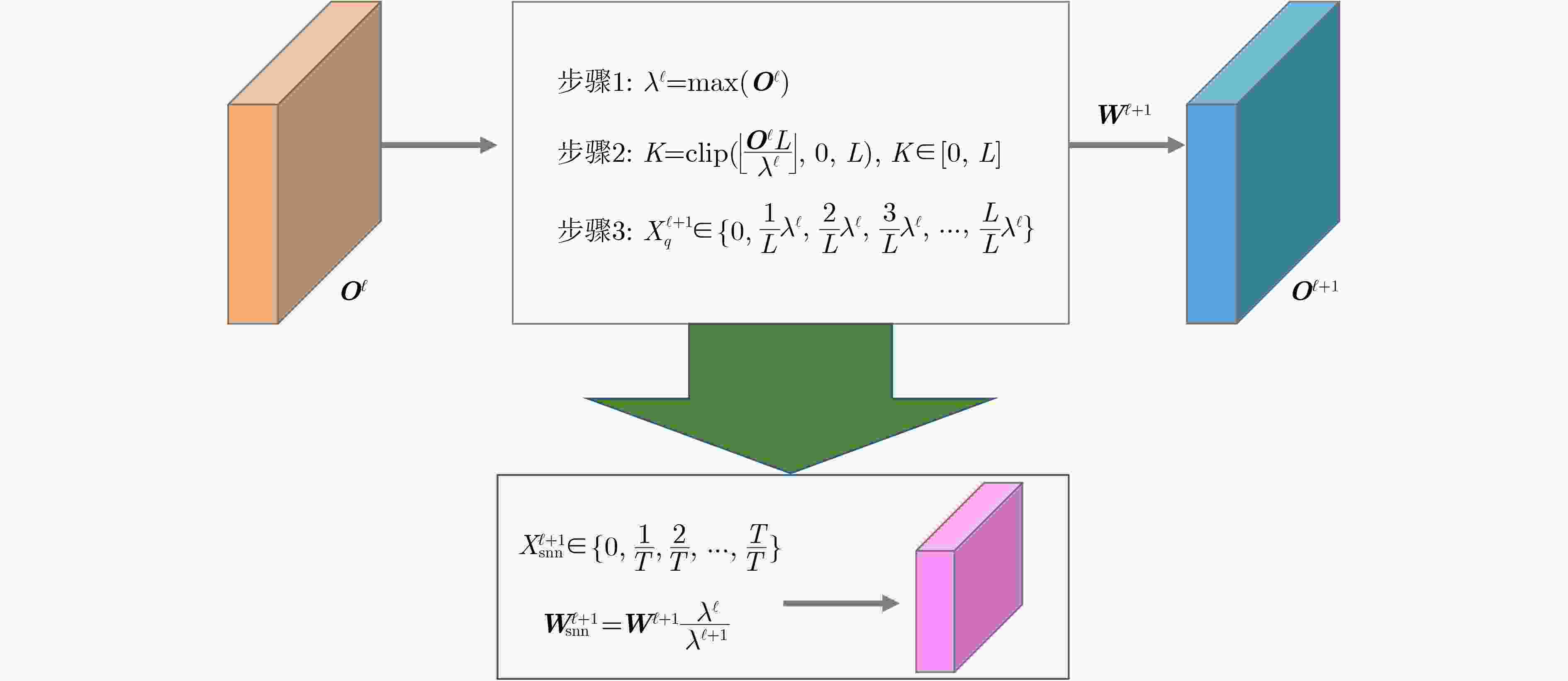
摘要: 脉冲神经网络(SNN)是一种模拟大脑神经元动力学的低功耗神经网络,为高计算效率、低能源消耗环境部署目标检测任务提供了可行的解决方案。由于脉冲的不可微性质导致SNN训练困难,一种有效的解决方法是将预训练的人工神经网络(ANN)转换为SNN来提高推理能力。然而,转换后的SNN 经常遇到性能下降和高延迟的问题,无法满足目标检测任务对高精度定位的要求。该文针对ANN转SNN过程中产生的误差问题,引入对偶误差模型降低转换性能损失。首先,该文分析误差产生原因,构建对偶误差模型来模拟ANN到SNN转换误差。进一步地,将对偶误差模型引入到ANN训练过程,使转换前后的模型在训练和推理过程中误差保持一致,从而降低模型的转换性能损失。最后,利用轻量化检测算法YOLO在数据集PASCAL VOC和 MS COCO上验证了对偶误差模型的有效性。Abstract: A Spiking Neural Network (SNN) is a low-power neural network that simulates the dynamics of neurons in the brain, providing a feasible solution for deploying object detection tasks in high computational efficiency and low energy consumption environments. Due to the non-differentiable nature of spikes, SNN training is difficult, and a practical solution is to convert pre-trained Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) into SNNs to improve inference ability. However, the converted SNN often suffers from performance degradation and high latency, which can not meet the high-precision localization requirements for object detection tasks. A dual error is introduced to reduce the loss of conversion performance. To simulate the ANN to SNN conversion error, the causes of errors are analyzed, and a dual error model is built. Further, the dual error model is introduced into the ANN training process so that the errors of the models before and after conversion remain consistent during training and testing, thereby reducing the loss of conversion performance. Finally, the lightweight detection algorithm YOLO is used to verify the effectiveness of the dual error model on the PASCAL VOC and MS COCO datasets.
-
Key words:
- Spiking Neural Network (SNN) /
- Object detection /
- Conversion error /
- Dual error model
-
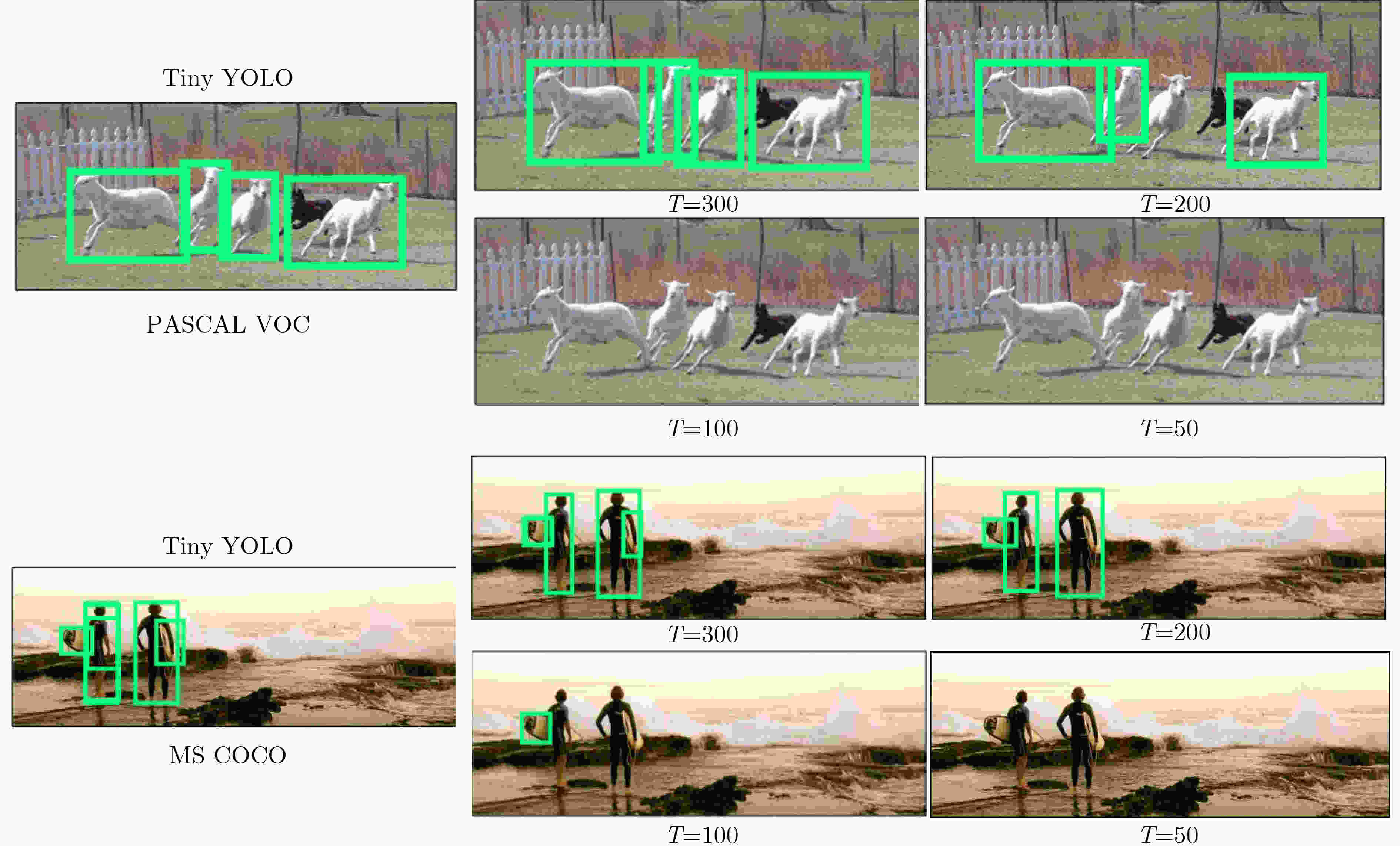
表 1 MS COCO和PASCAL VOC数据集上mAP实验结果(%)
模型 ANN SNN COCO VOC COCO VOC Tiny YOLO 26.24 53.01 – – Spiking YOLO(T =5000) 26.24 53.01 25.66 51.83 本文方法(T =300) 38.70 54.50 30.81 51.70 表 2 不同时间步长在两个数据集上mAP的结果(%)
T COCO VOC 300 30.81 51.70 200 25.60 49.30 100 0.13 31.20 50 0.00 0.06 表 3 对偶误差消融实验mAP(%)
模型 COCO VOC w\o DE-SNN(T=300) 28.86 50.23 w\o DE-SNN(T=200) 23.16 48.63 DE-SNN(T=300) 30.81 51.70 DE-SNN(T=200) 25.60 49.30 -
[1] DING Xiaohan, ZHANG Xiangyu, MA Ningning, et al. RepVGG: Making VGG-style ConvNets great again[C]. The 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 13728–13737. [2] GUO Yiwen, YAO Anbang, and CHEN Yurong. Dynamic network surgery for efficient DNNs[C]. The 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 2016. [3] GOU Jianping, YU Baosheng, MAYBANK S J, et al. Knowledge distillation: A survey[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2021, 129(6): 1789–1819. doi: 10.1007/s11263-021-01453-z [4] WANG Lin and YOON K J. Knowledge distillation and student-teacher learning for visual intelligence: A review and new outlooks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 44(6): 3048–3068. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3055564 [5] 曲志昱, 李根, 邓志安. 基于知识蒸馏与注意力图的雷达信号识别方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(9): 3170–3177. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210695QU Zhiyu, LI Gen, DENG Zhian. Radar signal recognition method based on knowledge distillation and attention map[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(9): 3170–3177. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210695 [6] GONG Yanchao, YANG Kaifang, LIU Ying, et al. Quantization parameter cascading for surveillance video coding considering all inter reference frames[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 5692–5707. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3087413 [7] JI Mengyu, PENG Gaoliang, LI Sijue, et al. A neural network compression method based on knowledge-distillation and parameter quantization for the bearing fault diagnosis[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2022, 127: 109331. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2022.109331 [8] AKOPYAN F, SAWADA J, CASSIDY A, et al. TrueNorth: Design and tool flow of a 65 mW 1 million neuron programmable neurosynaptic chip[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2015, 34(10): 1537–1557. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2015.2474396 [9] MA Songchen, PEI Jing, ZHANG Weihao, et al. Neuromorphic computing chip with spatiotemporal elasticity for multi-intelligent-tasking robots[J]. Science Robotics, 2022, 7(67): eabk2948. doi: 10.1126/scirobotics.abk2948 [10] MA De, SHEN Juncheng, GU Zonghua, et al. Darwin: A neuromorphic hardware co-processor based on spiking neural networks[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2017, 77: 43–51. doi: 10.1016/j.sysarc.2017.01.003 [11] BU Tong, FANG Wei, DING Jianhao, et al. Optimal ANN-SNN conversion for high-accuracy and ultra-low-latency spiking neural networks[C]. The Tenth International Conference on Learning Representations, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2022. [12] CAO Yongqiang, CHEN Yang, and KHOSLA D. Spiking deep convolutional neural networks for energy-efficient object recognition[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 113(1): 54–66. doi: 10.1007/s11263-014-0788-3 [13] SUN Wei, DAI Liang, ZHANG Xiaorui, et al. RSOD: Real-time small object detection algorithm in UAV-based traffic monitoring[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2022, 52(8): 8448–8463. doi: 10.1007/s10489-021-02893-3 [14] WU Peirong, LIU Airong, FU Jiyang, et al. Autonomous surface crack identification of concrete structures based on an improved one-stage object detection algorithm[J]. Engineering Structures, 2022, 272: 114962. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2022.114962 [15] KIM S, PARK S, NA B, et al. Spiking-YOLO: Spiking neural network for energy-efficient object detection[C]. The Thirty-Fourth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, USA, 2020: 11270–11277. [16] SENGUPTA A, YE Yuting, WANG R, et al. Going deeper in spiking neural networks: VGG and residual architectures[J]. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2019, 13: 95. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00095 [17] ZHANG Tielin, ZENG Yi, ZHAO Dongcheng, et al. A plasticity-centric approach to train the non-differential spiking neural networks[C]. The Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, USA, 2018: 77. [18] 杨静, 吉晓阳, 李少波, 等. 具有正则化约束的脉冲神经网络机器人触觉物体识别方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(7): 2595–2604.YANG Jing, JI Xiaoyang, LI Shaobo, et al. Spiking neural network robot tactile object recognition method with regularization constraints[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(7): 2595–2604. [19] MASQUELIER T and THORPE S J. Learning to recognize objects using waves of spikes and spike timing-dependent plasticity[C]. The 2010 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Barcelona, Spain, 2010: 1–8. [20] BOHTE S M, KOK J N, and LA POUTRÉ J A. SpikeProp: Backpropagation for networks of spiking neurons[C]. The 30th European Symposium on Artificial Neural Networks, Bruges, Belgium, 2000: 419–424. [21] HEBB D O. The effect of early and late brain injury upon test scores, and the nature of normal adult intelligence[J]. Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society, 1942, 85(3): 275–292. [22] CAPORALE N and DAN Yang. Spike timing-dependent plasticity: A Hebbian learning rule[J]. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 2008, 31: 25–46. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.31.060407.125639 [23] GERSTNER W. A Framework for Spiking Neuron Models: The Spike Response Model[M]. Handbook of Biological Physics, 2001, 4: 469–516. [24] GHAHARI A and ENDERLE J D. A neuron-based time-optimal controller of horizontal saccadic eye movements[J]. International Journal of Neural Systems, 2014, 24(6): 1450017. doi: 10.1142/S0129065714500178 [25] DIEHL P U, NEIL D, BINAS J, et al. Fast-classifying, high-accuracy spiking deep networks through weight and threshold balancing[C]. 2015 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Killarney, Ireland, 2015: 1–8. [26] FANG Wei, YU Zhaofei, CHEN Yanqi, et al. Deep residual learning in spiking neural networks[C/OL]. The 35th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2021: 21056–21069. [27] HAN Bing and ROY K. Deep spiking neural network: Energy efficiency through time based coding[C]. The 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 388–404. [28] HU Yangfan, TANG Huajin, and PAN Gang. Spiking deep residual networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(8): 5200–5205. [29] BU Tong, DING Jianhao, YU Zhaofei, et al. Optimized potential initialization for low-latency spiking neural networks[C]. The AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Palo Alto, USA, 2022: 11–20. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
