Cross-modal Audiovisual Separation Based on U-Net Network Combining Optical Flow Algorithm and Attention Mechanism
-
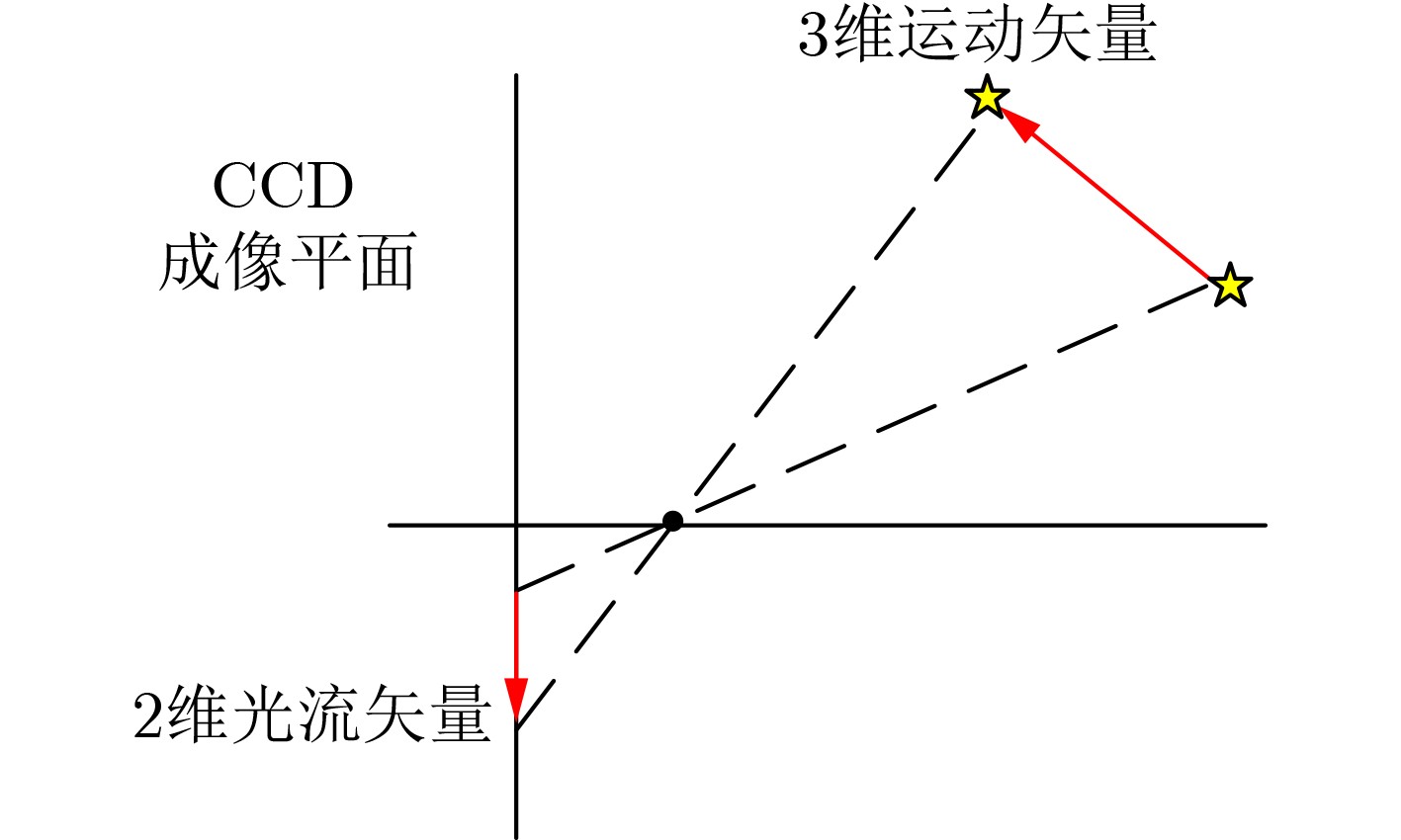
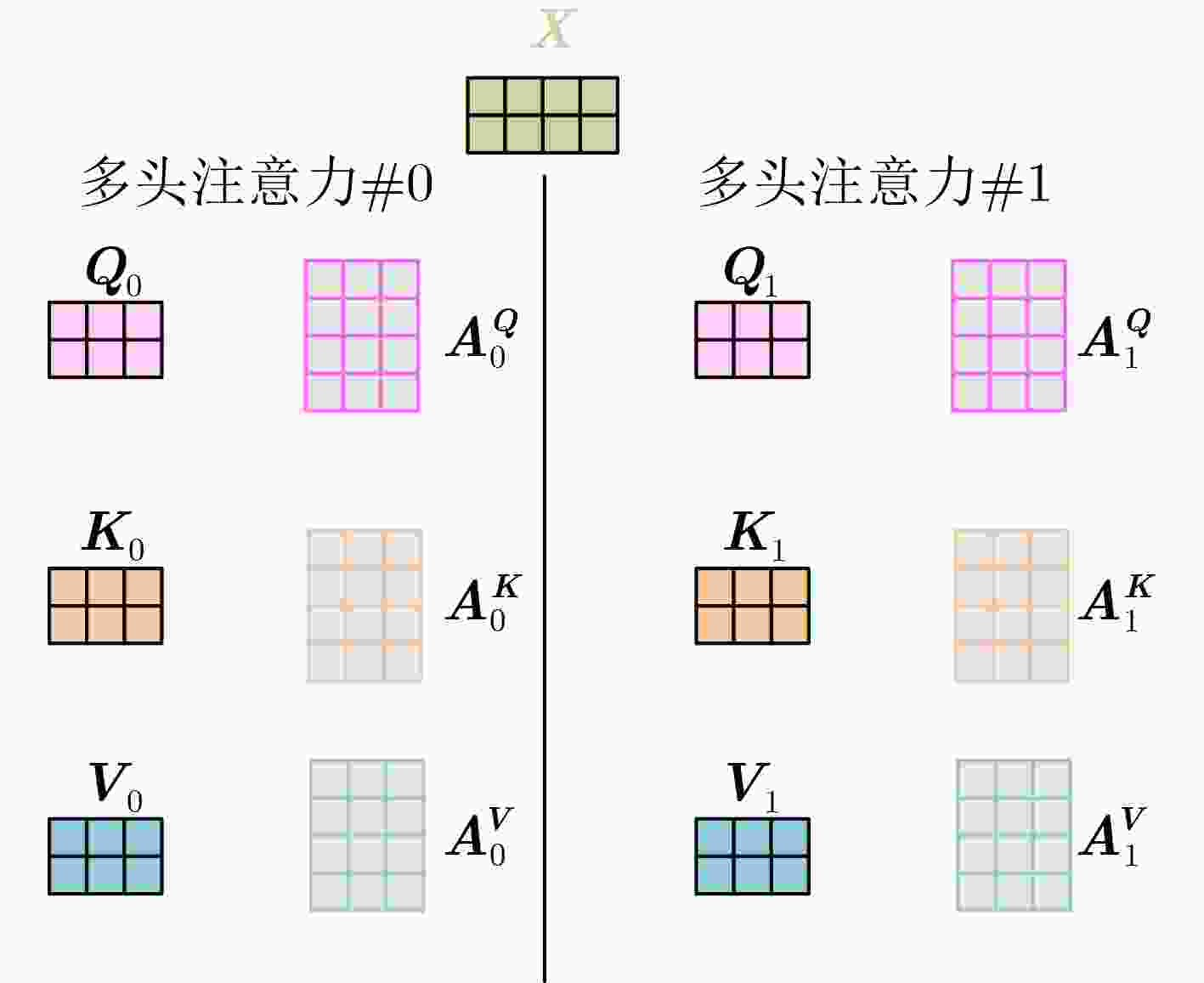
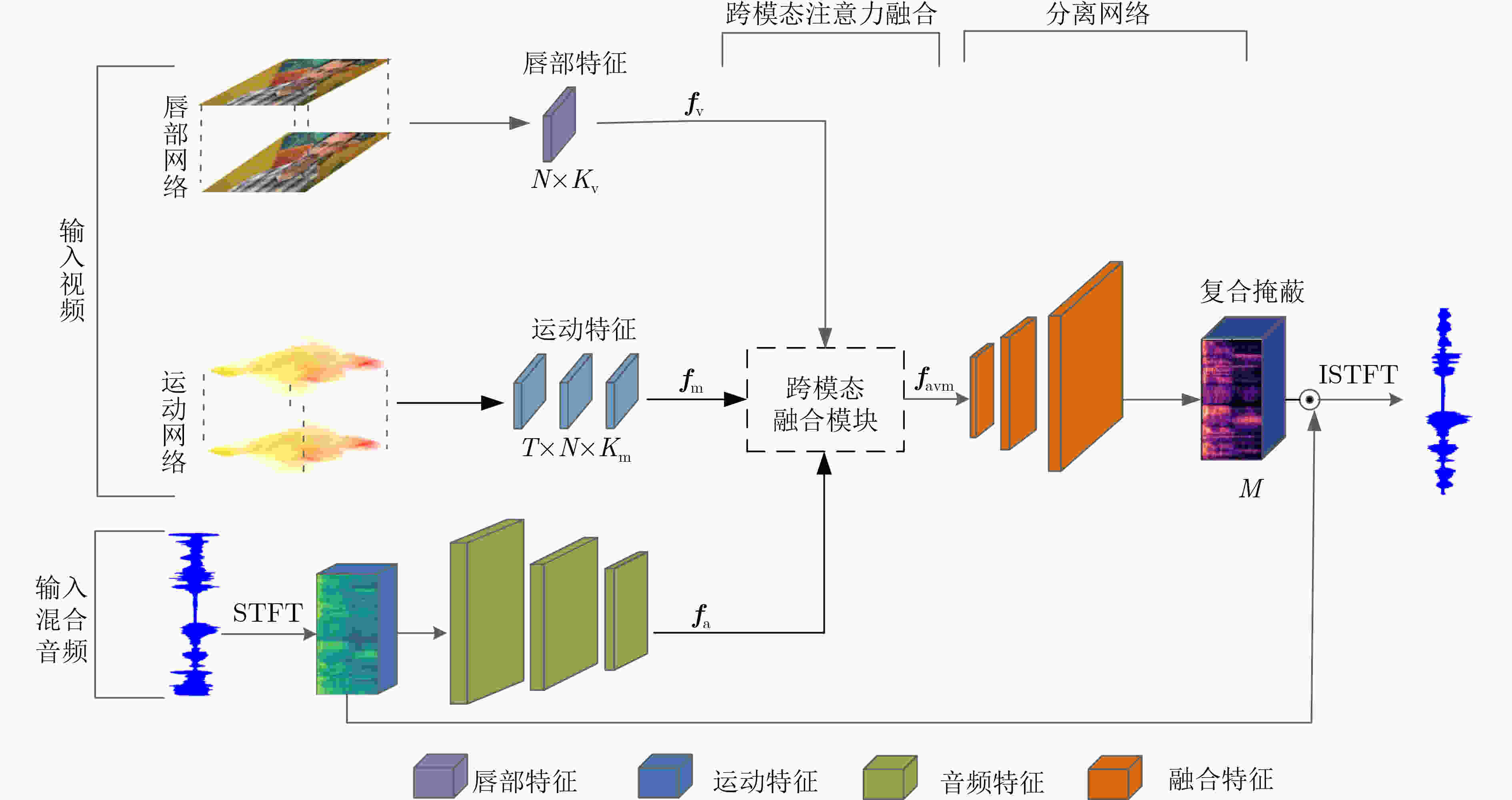
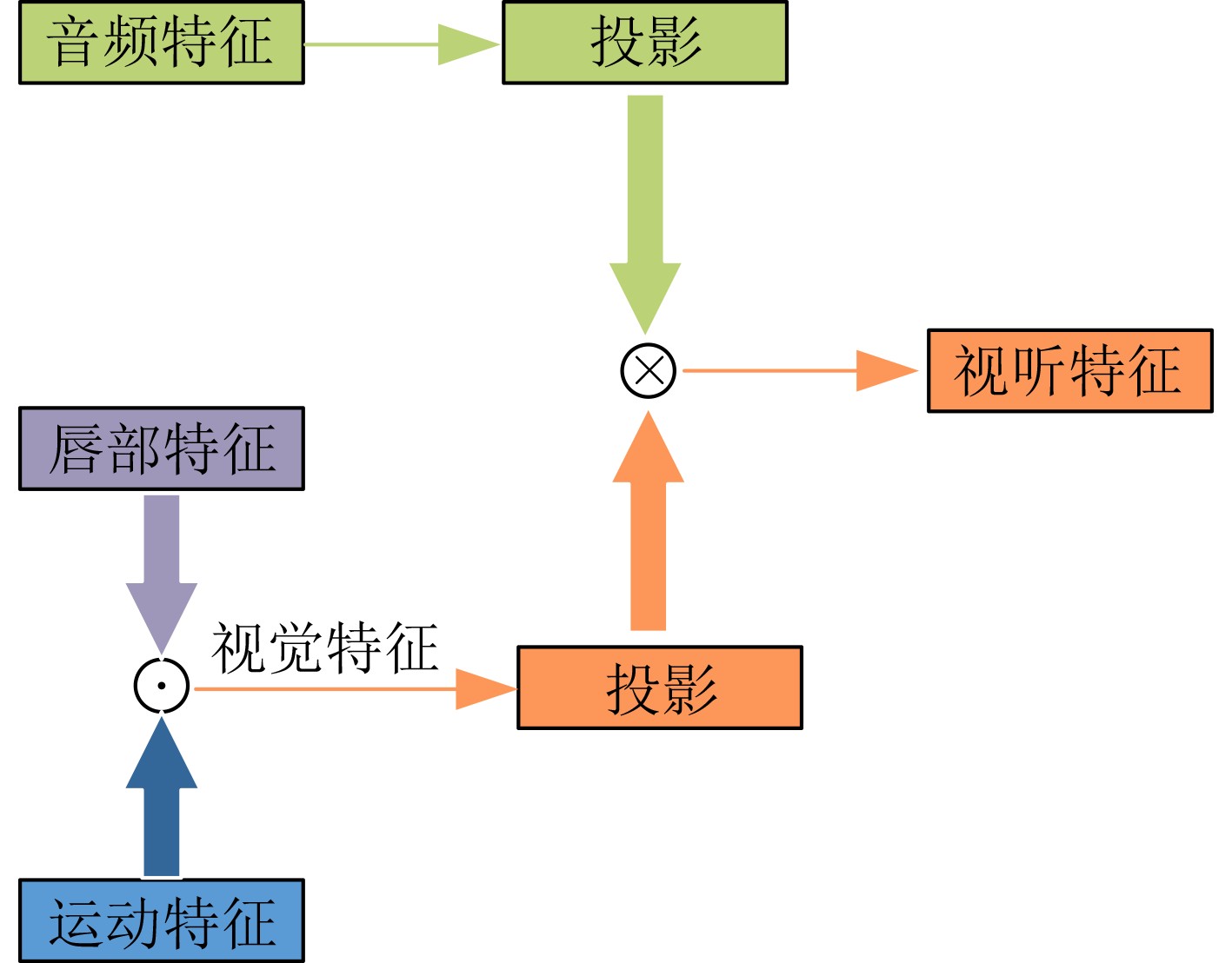
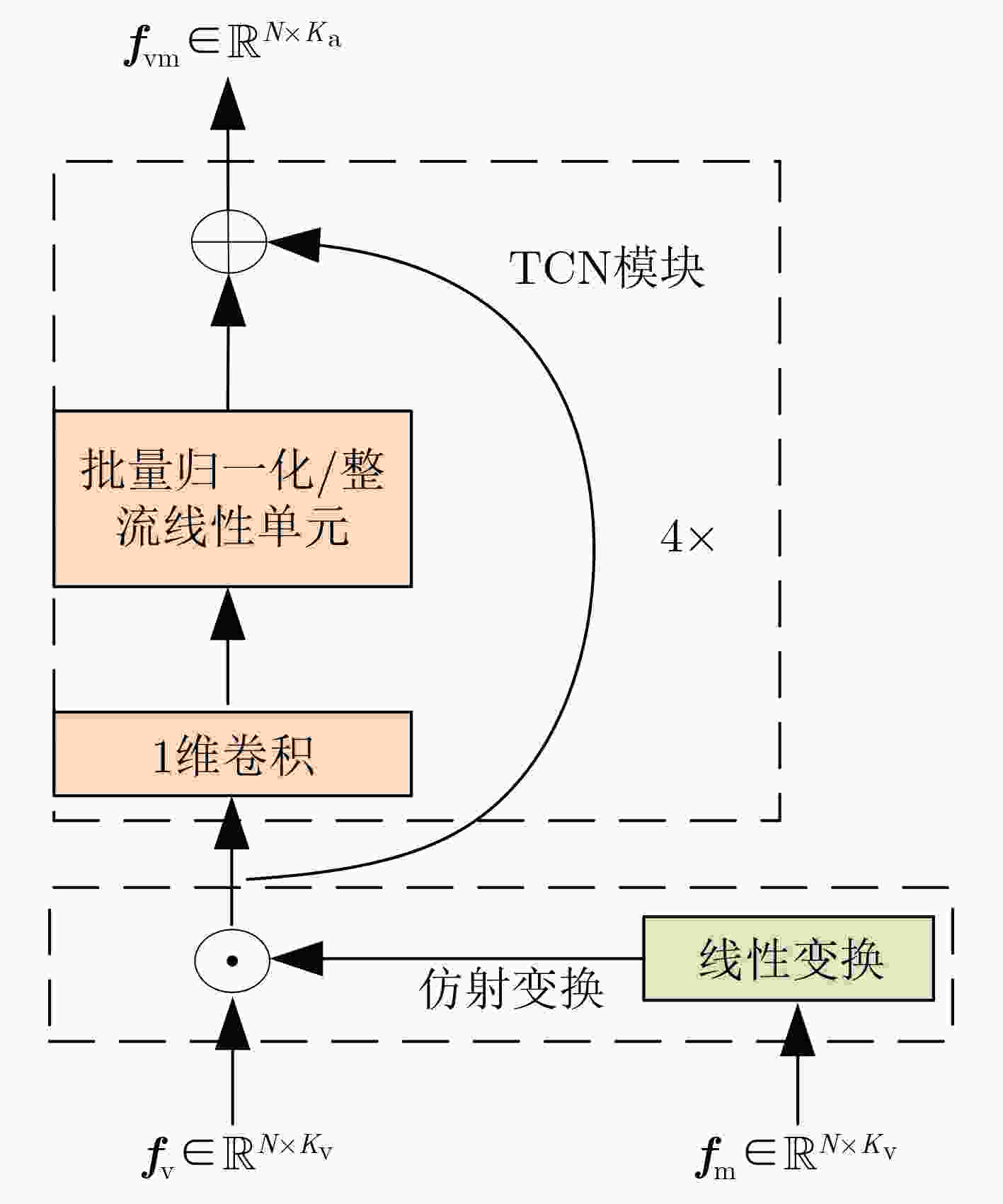
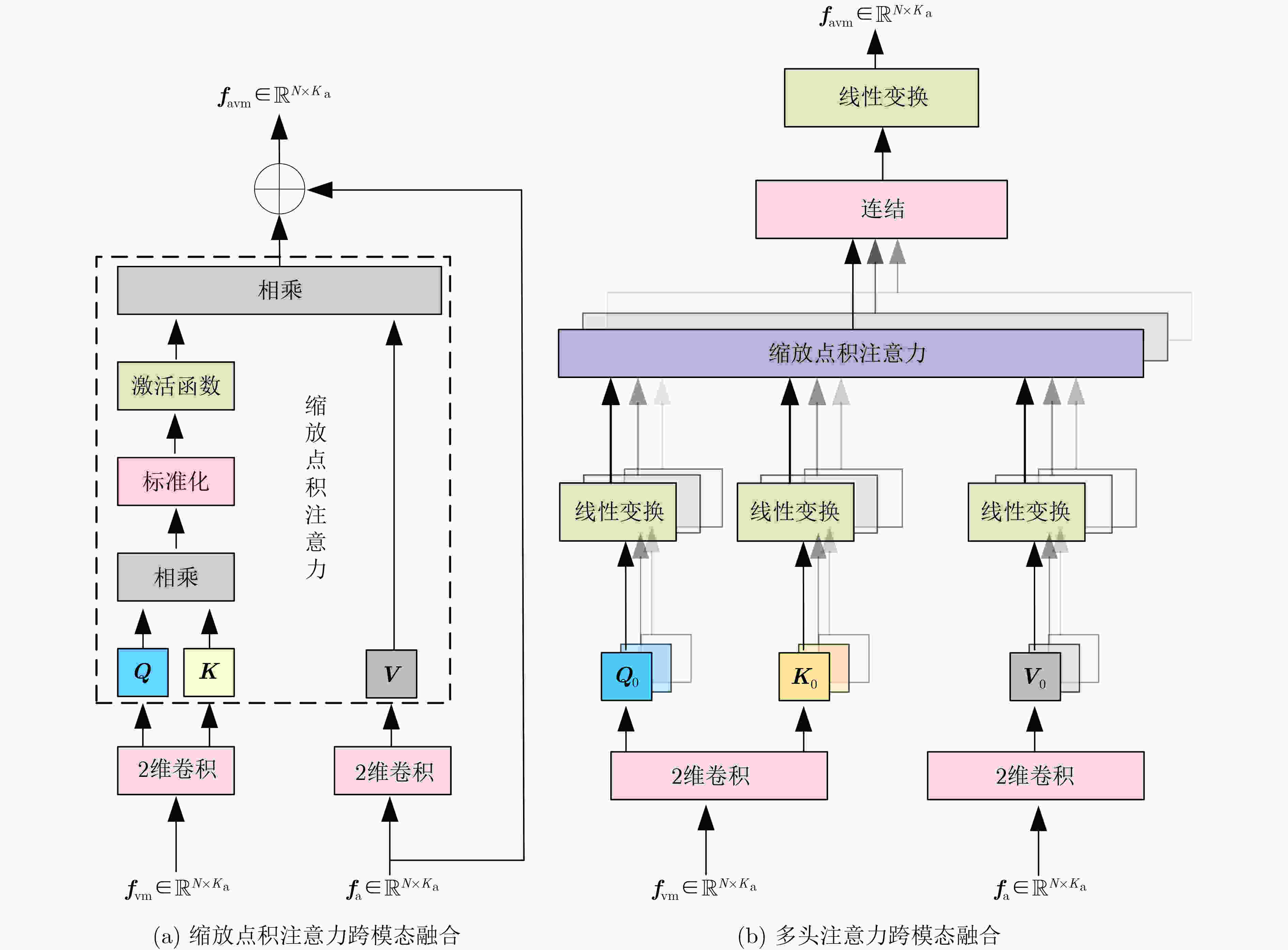
摘要: 目前多数的视听分离模型,大多是基于视频特征和音频特征简单拼接,没有充分考虑各个模态的相互关系,导致视觉信息未被充分利用,该文针对此问题提出了新的模型。该文充分考虑视觉特征、音频特征之间的相互联系,采用多头注意力机制,结合稠密光流(Farneback)算法和U-Net网络,提出跨模态融合的光流-视听语音分离(Flow-AVSS)模型。该模型通过Farneback算法和轻量级网络ShuffleNet v2分别提取运动特征和唇部特征,然后将运动特征与唇部特征进行仿射变换,经过时间卷积模块(TCN)得到视觉特征。为充分利用到视觉信息,在进行特征融合时采用多头注意力机制,将视觉特征与音频特征进行跨模态融合,得到融合视听特征,最后融合视听特征经过U-Net分离网络得到分离语音。利用客观语音质量评估(PESQ)、短时客观可懂度(STOI)及源失真比(SDR)评价指标,在AVspeech数据集进行实验测试。研究表明,该文所提方法与纯语音分离网络和仅采用特征拼接的视听分离网络相比,性能上分别提高了2.23 dB和1.68 dB。由此表明,采用跨模态注意力进行特征融合,能更加充分利用各个模态相关性,增加的唇部运动特征,能有效提高视频特征的鲁棒性,提高分离效果。Abstract: Most of the current audiovisual separation models are mostly based on simple splicing of video features and audio features, without fully considering the interrelationship of each modality, resulting in the underutilization of visual information, a new model is proposed to address this issue. Hence, in this paper, the interrelationship of each modality is taken into consideration. In addition, a multi-headed attention mechanism is used to combine the Farneback algorithm and the U-Net network to propose a cross-modal fusion optical Flow-Audio Visual Speech Separation (Flow-AVSS) model. The motion features and lip features are respectively extracted by the Farneback algorithm and the lightweight network ShuffleNet v2. Furthermore, the motion features are affine transformed with the lip features, and the visual features are obtained by the Temporal CoNvolution module (TCN). In order to utilize sufficiently the visual information, the multi-headed attention mechanism is used in the feature fusion to fuse the visual features with the audio features across modalities. Finally, the fused audio-visual features are passed through the U-Net separation network to obtain the separated speech. Using Perceptual Evaluation of Speech Quality (PESQ), Short-Time Objective Intelligibility (STOI), and Source-to-Distortion Ratio (SDR) evaluation metrics, experimental tests are conducted on the AVspeech dataset. It is shown that the performance of the proposed method is improved by 2.23 dB and 1.68 dB compared with the pure speech separation network or the audio-visual separation network based on feature splicing. Thus, it is indicated that the feature fusion based on the cross-modal attention can make fuller use of the individual modal correlations. Besides, the increased lip motion features can effectively improve the robustness of video features and improve the separation effect.
-
表 1 语音分离的性能评估(dB)
-
[1] WANG Deliang and BROWN G J. Computational Auditory Scene Analysis: Principles, Algorithms, and Applications[M]. Hoboken: Wiley, 2006: 1–14. [2] SCHMIDT M N and OLSSON R K. Single-channel speech separation using sparse non-negative matrix factorization[C]. The INTERSPEECH 2006, Pittsburgh, USA, 2006. [3] ZHOU Weili, ZHU Zhen, and LIANG Peiying. Speech denoising using Bayesian NMF with online base update[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2019, 78(11): 15647–15664. doi: 10.1007/s11042-018-6990-5 [4] SUN Lei, DU Jun, DAI Lirong, et al. Multiple-target deep learning for LSTM-RNN based speech enhancement[C]. 2017 Hands-free Speech Communications and Microphone Arrays, San Francisco, USA, 2017: 136–140. [5] HERSHEY J R, CHEN Zhuo, ROUX J L, et al. Deep clustering: Discriminative embeddings for segmentation and separation[C]. 2016 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Shanghai, China, 2016: 31–35. [6] YU Dong, KOLBÆK M, TAN Zhenghua, et al. Permutation invariant training of deep models for speaker-independent multi-talker speech separation[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, New Orleans, USA, 2017: 241–245. [7] GOLUMBIC E Z, COGAN G B, SCHROEDER C E, et al. Visual input enhances selective speech envelope tracking in auditory cortex at a “cocktail party”[J]. The Journal of Neuroscience, 2013, 33(4): 1417–1426. doi: 10.1523/jneurosci.3675-12.2013 [8] SUSSMAN E S. Integration and segregation in auditory scene analysis[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2005, 117(3): 1285–1298. doi: 10.1121/1.1854312 [9] TAO Ruijie, PAN Zexu, DAS R K, et al. Is someone speaking?: Exploring long-term temporal features for audio-visual active speaker detection[C]. The ACM Multimedia Conference, Chengdu, China, 2021: 3927–3935. [10] LAKHAN A, MOHAMMED M A, KADRY S, et al. Federated Learning-Aware Multi-Objective Modeling and blockchain-enable system for IIoT applications[J]. Computers and Electrical Engineering, 2022, 100: 107839. doi: 10.1016/j.compeleceng.2022.107839 [11] MORGADO P, LI Yi, and VASCONCELOS N. Learning representations from audio-visual spatial alignment[C]. The 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2020: 397. [12] GABBAY A, EPHRAT A, HALPERIN T, et al. Seeing through noise: Visually driven speaker separation and enhancement[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Calgary, Canada, 2018: 3051–3055. [13] AFOURAS T, CHUNG J S, and ZISSERMAN A. The conversation: Deep audio-visual speech enhancement[C]. The 19th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association, Hyderabad, India, 2018: 3244–3248. [14] EPHRAT A, MOSSERI I, LANG O, et al. Looking to listen at the cocktail party: A speaker-independent audio-visual model for speech separation[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2018, 37(4): 112. doi: 10.1145/3197517.3201357 [15] GAO Ruohan and GRAUMAN K. VisualVoice: Audio-visual speech separation with cross-modal consistency[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 15490–15500. [16] XIONG Junwen, ZHANG Peng, XIE Lei, et al. Audio-visual speech separation based on joint feature representation with cross-modal attention[J]. arXiv preprint arVix: 2203.02655, 2022. [17] 杨子龙, 朱付平, 田金文, 等. 基于显著性与稠密光流的红外船只烟幕检测方法研究[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2021, 50(7): 20200496. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20200496YANG Zilong, ZHU Fuping, TIAN Jinwen, et al. Ship smoke detection method based on saliency and dense optical flow[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2021, 50(7): 20200496. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20200496 [18] 田佳莉. 基于多特征的考场异常行为识别研究[D]. [硕士论文], 沈阳工业大学, 2021.TIAN Jiali. Research on abnormal behavior recognition of examination room based on multi-features[D]. [Master dissertation], Shenyang University of Technology, 2021. [19] 欧阳玉梅. 基于稠密光流算法的运动目标检测的Python实现[J]. 现代电子技术, 2021, 44(1): 78–82. doi: 10.16652/j.issn.1004-373x.2021.01.017OUYANG Yumei. DOF algorithm based moving object detection programmed by Python[J]. Modern Electronics Technique, 2021, 44(1): 78–82. doi: 10.16652/j.issn.1004-373x.2021.01.017 [20] MA Ningning, ZHANG Xiangyu, ZHENG Haitao, et al. ShuffleNet V2: Practical guidelines for efficient CNN architecture design[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 116–131. [21] CARREIRA J and ZISSERMAN A. Quo vadis, action recognition? A new model and the kinetics dataset[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 4724–4733. [22] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, and BROX T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]. The 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 2015: 234–241. [23] PEREZ E, STRUB F, DE VRIES H, et al. FiLM: Visual reasoning with a general conditioning layer[C]. The Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, USA, 2018: 3942–3951. [24] BAI Shaojie, KOLTER J Z, and KOLTUN V. An empirical evaluation of generic convolutional and recurrent networks for sequence modeling[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1803.01271, 2018. [25] VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 6000–6010. [26] THIEDE T, TREURNIET W, BITTO R, et al. PEAQ - The ITU standard for objective measurement of perceived audio quality[J]. Journal of the Audio Engineering Society, 2000, 48(1): 3–29. [27] TAAL C H, HENDRIKS R C, HEUSDENS R, et al. An algorithm for intelligibility prediction of time–frequency weighted noisy speech[J]. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2011, 19(7): 2125–2136. doi: 10.1109/TASL.2011.2114881 [28] LE ROUX J, WISDOM S, ERDOGAN H, et al. SDR-half-baked or well done?[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Brighton, UK, 2019: 626–630. [29] LUO Y and MESGARANI N. Conv-TasNet: Surpassing ideal time-frequency magnitude masking for speech separation[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2019, 27(8): 1256–1266. doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2019.2915167 -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
