An Image Fusion Algorithm Based on Ant Lion Optimized Maximum Entropy Segmentation and Guided Filtering
-
摘要:
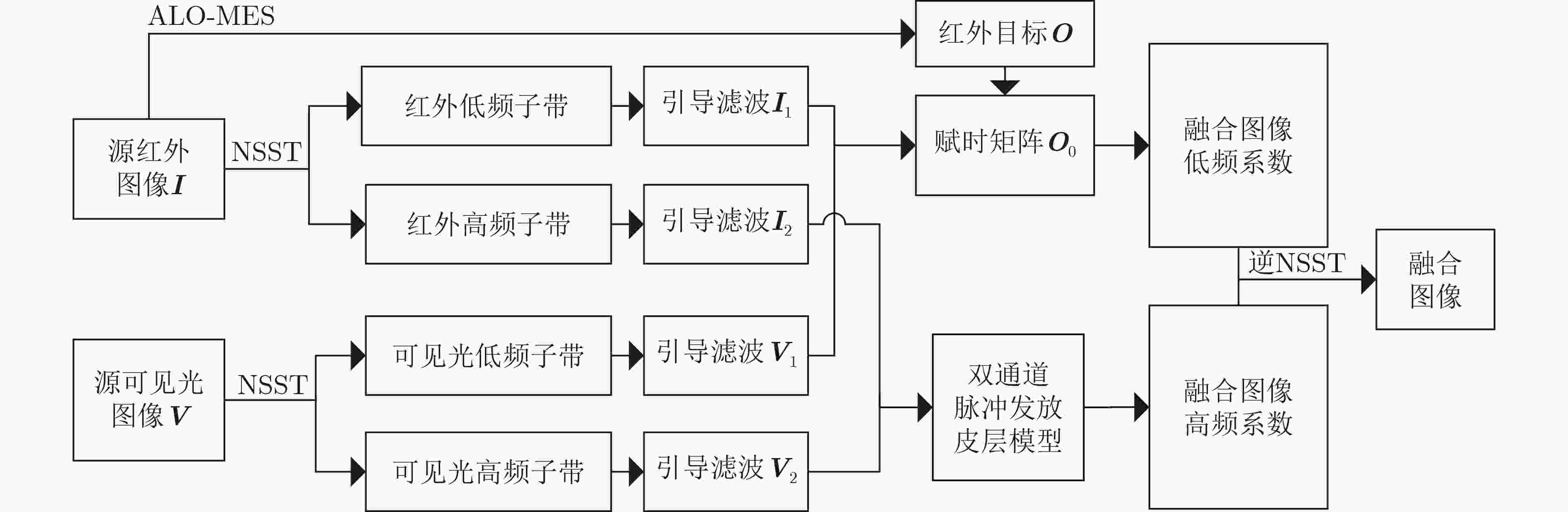
传统红外与可见光图像融合算法中易出现目标提取不够充分、细节丢失等问题,导致融合效果不理想,从而无法应用于目标检测、跟踪或识别等领域。因此,该文提出一种基于蚁狮优化算法(ALO)改进的最大香农(Shannon)熵分割法结合引导滤波的红外与可见光图像融合方法。首先,使用蚁狮最大熵分割法(ALO-MES)对红外图像进行目标提取,然后,对红外和可见光图像使用非下采样剪切波变换(NSST),并对获得的低频和高频分量进行引导滤波。由提取的目标图像与增强后的红外和可见光低频分量通过低频融合规则得到低频融合系数,增强后的高频分量通过双通道脉冲发放皮层模型(DCSCM)得到高频融合系数,最后经NSST逆变换得到融合图像。实验结果表明,所提算法能够得到目标明确、背景信息清晰的融合图像。
-
关键词:
- 图像融合 /
- 蚁狮优化算法 /
- 最大Shannon熵分割 /
- 引导滤波 /
- 双通道脉冲发放皮层模型
Abstract:Traditional fusion algorithms of infrared and visible images often have defects such as insufficient target extraction and loss of details, which lead to unsatisfactory fusion effects, and the fused image can not be applied to target detection, tracking or recognition. Therefore, a fusion method of infrared and visible images based on guided filtering and improved maximum Shannon entropy segmentation method using Ant Lion Optimization algorithm (ALO) is proposed. First, Ant Lion Optimized Maximum Entropy Segmentation (ALO-MES) algorithm is used to extract the target from infrared image. Then, the Non-Subsampled Shearlet Transform (NSST) is performed on the infrared and visible images to obtained the low frequency and high frequency sub-bands, and conduct guided filtering for obtained sub-bands. The low-frequency fusion coefficient is obtained from the extracted target image and the enhanced infrared and visible low-frequency components through the fusion rule based on ALO-MES. And the high-frequency fusion coefficient is obtained by the enhanced high-frequency sub-bands components through Dual-Channel Spiking Cortical Model (DCSCM). Finally, the fusion image is obtained by inverse NSST transform. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can get fusion image with clear target and background information.
-
表 1 4种图像分割算法对比
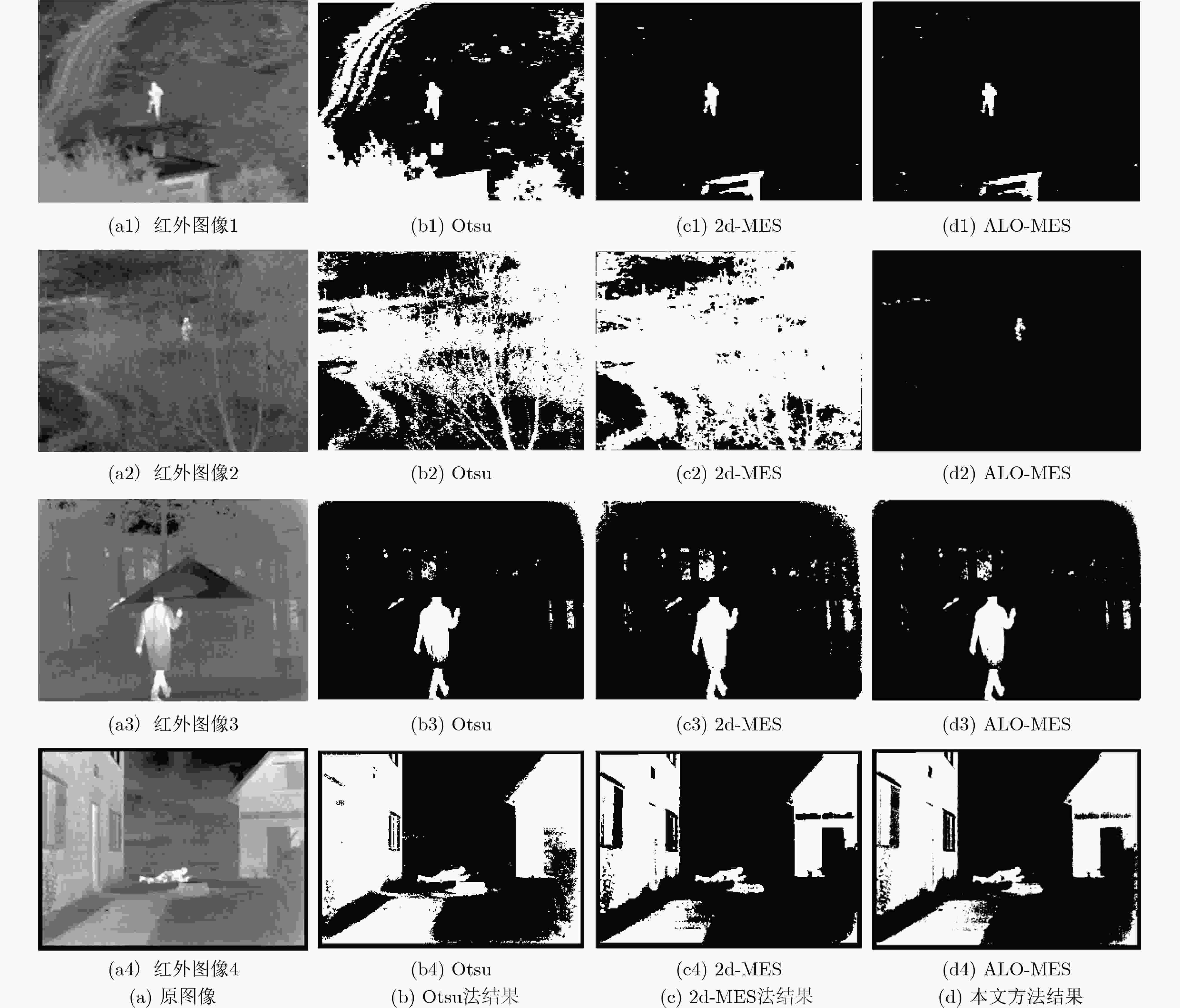
算法 Iter(1)/ Th(1) Iter(2)/ Th(2) Iter(3)/ Th(3) AV-Iter AV-Time(ms) MES 1/155 1/155 1/155 1.0 134 PSO-MES 2/154 2/157 2/168 2.0 93 FA-MES 2/154 3/155 3/155 2.6 109 ALO-MES 2/155 1/155 2/155 1.6 43 表 2 5组融合图像客观评价指标
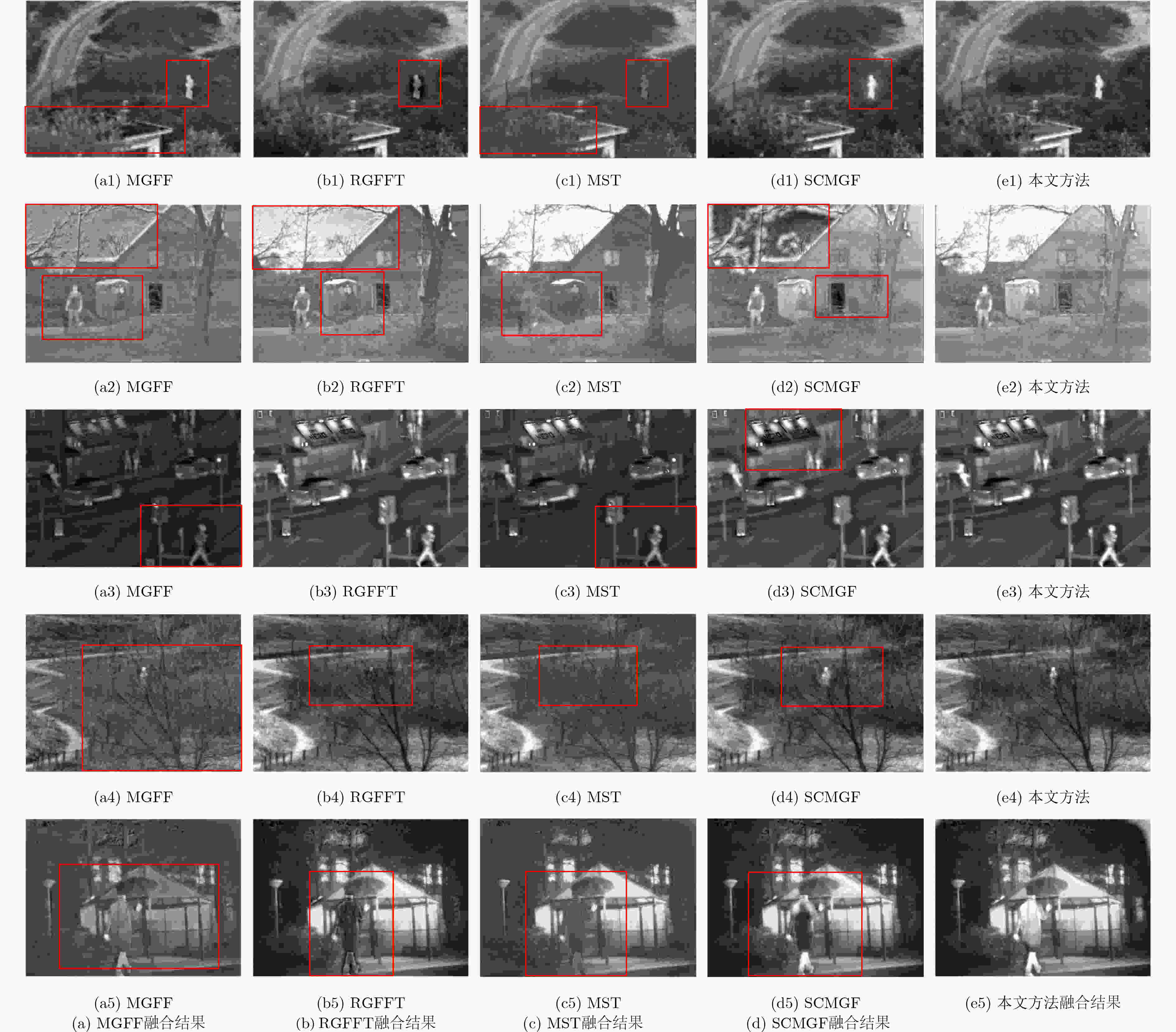
实验图像组 算法 AG STD MI EN QAB/F SSIM man MGFF 5.7765 32.0072 1.5041 6.8010 0.4201 0.5480 RGFFT 5.6651 39.3142 3.0086 7.1654 0.4781 0.5105 MST 5.5076 33.1331 2.8316 6.6562 0.4402 0.5192 SCMGF 5.4963 39.4170 3.4252 7.1643 0.4772 0.5186 本文 5.7943 39.5754 2.6810 7.1687 0.4336 0.5314 meeting MGFF 5.6886 31.5410 1.4270 6.8607 0.4759 0.1299 RGFFT 5.2517 45.9761 2.3598 6.9519 0.4546 0.4904 MST 5.3389 54.6009 4.2285 6.7975 0.5562 0.4873 SCMGF 5.6384 36.4719 1.8304 7.1768 0.4375 0.4795 本文 5.4586 46.1790 2.4660 6.9586 0.4770 0.4978 traffic MGFF 4.4707 31.8944 1.8872 6.5396 0.5653 0.4394 RGFFT 4.5027 35.8259 4.3799 6.7687 0.6721 0.4747 MST 4.1413 29.7569 2.6295 6.2525 0.5575 0.4219 SCMGF 4.2004 35.1244 2.7851 6.7725 0.5175 0.4054 本文 4.5927 37.5240 3.4377 6.7793 0.6081 0.4712 tree MGFF 7.7364 26.4433 0.9584 0.9584 0.3706 0.5471 RGFFT 7.0601 40.4418 4.1932 7.1627 0.5510 0.5181 MST 7.2675 35.5588 2.6991 6.7720 0.4449 0.5409 SCMGF 6.8891 40.1562 3.2675 7.1576 0.4772 0.5272 本文 7.4905 40.4902 2.8634 7.1664 0.4279 0.5537 Kaptein MGFF 6.0267 35.4698 1.5254 6.6835 0.4707 0.5218 RGFFT 5.9171 56.9160 3.4177 7.2780 0.5115 0.4509 MST 5.8412 47.7283 3.2752 6.6078 0.5063 0.4955 SCMGF 5.7244 58.6063 4.5781 7.2761 0.5273 0.4796 本文 6.1993 61.2249 3.4664 7.3985 0.4888 0.4888 -
[1] 张介嵩, 黄影平, 张瑞. 基于CNN的点云图像融合目标检测[J]. 光电工程, 2021, 48(5): 200418. doi: 10.12086/oee.2021.200418ZHANG Jiesong, HUANG Yingping, and ZHANG Rui. Fusing point cloud with image for object detection using convolutional neural networks[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2021, 48(5): 200418. doi: 10.12086/oee.2021.200418 [2] ZHOU Zhiqiang, WANG Bo, LI Sun, et al. Perceptual fusion of infrared and visible images through a hybrid multi-scale decomposition with Gaussian and bilateral filters[J]. Information Fusion, 2016, 30: 15–26. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2015.11.003 [3] 谭威, 宋闯, 赵佳佳, 等. 基于多层级图像分解的图像融合算法[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2022, 51(8): 20210681. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20210681TAN Wei, SONG Chuang, ZHAO Jiajia, et al. Multi-layer image decomposition-based image fusion algorithm[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2022, 51(8): 20210681. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20210681 [4] 戴进墩, 刘亚东, 毛先胤, 等. 基于FDST和双通道PCNN的红外与可见光图像融合[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2019, 48(2): 0204001. doi: 10.3788/IRLA201948.0204001DAI Jindun, LIU Yadong, MAO Xianyin, et al. Infrared and visible image fusion based on FDST and dual-channel PCNN[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2019, 48(2): 0204001. doi: 10.3788/IRLA201948.0204001 [5] LIU Wei and WANG Zengfu. A novel multi-focus image fusion method using multiscale shearing non-local guided averaging filter[J]. Signal Processing, 2020, 166: 107252. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2019.107252 [6] ZHANG Qiang, LIU Yi, BLUM R S, et al. Sparse representation based multi-sensor image fusion for multi-focus and multi-modality images: A review[J]. Information Fusion, 2018, 40: 57–75. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2017.05.006 [7] ZHOU Huabing, HOU Jilei, ZHANG Yanduo, et al. Unified gradient- and intensity-discriminator generative adversarial network for image fusion[J]. Information Fusion, 2022, 88: 184–201. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2022.07.016 [8] 朱浩然, 刘云清, 张文颖. 基于对比度增强与多尺度边缘保持分解的红外与可见光图像融合[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(6): 1294–1300. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170956ZHU Haoran, LIU Yunqing, and ZHANG Wenying. Infrared and visible image fusion based on contrast enhancement and multi-scale edge-preserving decomposition[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(6): 1294–1300. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170956 [9] MA Jiayi, TANG Linfeng, XU Meilong, et al. STDFusionNet: An infrared and visible image fusion network based on salient target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2021, 70: 5009513. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2021.3075747 [10] 陈永, 张娇娇, 王镇. 多尺度密集连接注意力的红外与可见光图像融合[J]. 光学 精密工程, 2022, 30(18): 2253–2266. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223018.2253CHEN Yong, ZHANG Jiaojiao, and WANG Zhen. Infrared and visible image fusion based on multi-scale dense attention connection network[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2022, 30(18): 2253–2266. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223018.2253 [11] XU Meilong, TANG Linfeng, ZHANG Hao, et al. Infrared and visible image fusion via parallel scene and texture learning[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2022, 132: 108929. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2022.108929 [12] MIRJALILI S. The ant lion optimizer[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2015, 83: 80–98. doi: 10.1016/j.advengsoft.2015.01.010 [13] KAPUR J N, SAHOO P K, and WONG A K C. A new method for gray-level picture thresholding using the entropy of the histogram[J]. Computer Vision, Graphics, and Image Processing, 1985, 29(3): 273–285. doi: 10.1016/0734-189X(85)90125-2 [14] ABUALIGAH L, SHEHAB M, ALSHINWAN M, et al. Ant lion optimizer: A comprehensive survey of its variants and applications[J]. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering, 2021, 28(3): 1397–1416. doi: 10.1007/s11831-020-09420-6 [15] 吴一全, 王志来. 基于目标提取与引导滤波增强的红外与可见光图像融合[J]. 光学学报, 2017, 37(8): 0810001. doi: 10.3788/AOS201737.0810001WU Yiquan and WANG Zhilai. Infrared and visible image fusion based on target extraction and guided filtering enhancement[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2017, 37(8): 0810001. doi: 10.3788/AOS201737.0810001 [16] 绽琨. 脉冲发放皮层模型及其应用[D]. [博士论文], 兰州大学, 2010.ZHAN Kun. Spiking cortical model and its applications[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Lanzhou University, 2010. [17] TOET A. TNO image fusion dataset[EB/OL]. http://dx. doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.1008029, 2014. [18] 付阿利, 雷秀娟. 基于改进PSO算法的最大熵阈值图像分割[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2008, 44(29): 174–176,187. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2008.29.049FU Ali and LEI Xiujuan. Maximum-entropy thresholding image segmentation method based on improved PSO algorithm[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2008, 44(29): 174–176,187. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2008.29.049 [19] 吴鹏. 萤火虫算法优化最大熵的图像分割方法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2014, 50(12): 115–119. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1312-0178WU Peng. Image segmentation method based on firefly algorithm and maximum entropy method[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2014, 50(12): 115–119. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1312-0178 [20] BAVIRISETTI D P, XIAO Gang, ZHAO Junhao, et al. Multi-scale guided image and video fusion: A fast and efficient approach[J]. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 2019, 38(12): 5576–5605. doi: 10.1007/s00034-019-01131-z [21] 巩稼民, 吴成超, 郭刘飞, 等. 基于RGF改进显著性检测与SCM相结合的图像融合[J]. 激光与红外, 2022, 52(8): 1251–1258. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2022.08.023GONG Jiamin, WU Chengchao, GUO Liufei, et al. Image fusion based on RGF improved significance detection and SCM[J]. Laser &Infrared, 2022, 52(8): 1251–1258. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2022.08.023 [22] CHEN Jun, LI Xuejiao, LUO Linbo, et al. Infrared and visible image fusion based on target-enhanced multiscale transform decomposition[J]. Information Sciences, 2020, 508: 64–78. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2019.08.066 [23] 巩稼民, 吴艺杰, 刘芳, 等. 基于NSST域结合SCM与引导滤波的图像融合[J]. 光电子·激光, 2021, 32(7): 719–727. doi: 10.16136/j.joel.2021.07.0482GONG Jiamin, WU Yijie, LIU Fang, et al. Image fusion based on nonsubsampled shearlet transform domain combined with spiking cortical model and guided filtering[J]. Journal of Optoelectronics·Laser, 2021, 32(7): 719–727. doi: 10.16136/j.joel.2021.07.0482 -





 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:
