| [1] |
何庆华, 彭承琳, 吴宝明. 脑机接口技术研究方法[J]. 重庆大学学报:自然科学版, 2002, 25(12): 106–109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-582X.2002.12.030HE Qinghua, PENG Chenglin, and WU Baoming. Research methods of brain-computer interface technology[J]. Journal of Chongqing University:Natural Science Edition, 2002, 25(12): 106–109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-582X.2002.12.030
|
| [2] |
XU Minpeng, HAN Jin, WANG Yijun, et al. Implementing over 100 command codes for a high-speed hybrid brain-computer interface using concurrent P300 and SSVEP features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2020, 67(11): 3073–3082. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2020.2975614
|
| [3] |
XU Minpeng, XIAO Xiaolin, WANG Yijun, et al. A brain-computer interface based on miniature-event-related potentials induced by very small lateral visual stimuli[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2018, 65(5): 1166–1175. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2018.2799661
|
| [4] |
MENG Jiayuan, XU Minpeng, WANG Kun, et al. Separable EEG features induced by timing prediction for active brain-computer interfaces[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(12): 3588. doi: 10.3390/s20123588
|
| [5] |
张力新, 张珊珊, 王坤, 等. 运动相关思维诱发脑电信息解码与应用综述[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2019, 40(1): 1–11. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.J1804309ZHANG Lixin, ZHANG Shanshan, WANG Kun, et al. Review on the decoding and application of electroencephalography information induced by motor-related mental activity[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2019, 40(1): 1–11. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.J1804309
|
| [6] |
NG A K, ANG K K, TEE K P, et al. Optimizing low-frequency common spatial pattern features for multi-class classification of hand movement directions[C]. 2013 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Osaka, Japan, 2013: 2780–2783.
|
| [7] |
ROBINSON N, GUAN Cuntai, VINOD A P, et al. Multi-class EEG classification of voluntary hand movement directions[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2013, 10(5): 056018. doi: 10.1088/1741-2560/10/5/056018
|
| [8] |
YUAN Han, PERDONI C, and HE Bin. Relationship between speed and EEG activity during imagined and executed hand movements[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2010, 7(2): 026001. doi: 10.1088/1741-2560/7/2/026001
|
| [9] |
JOCHUMSEN M, NIAZI I K, MRACHACZ-KERSTING N, et al. Detection and classification of movement-related cortical potentials associated with task force and speed[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2013, 10(5): 056015. doi: 10.1088/1741-2560/10/5/056015
|
| [10] |
YIN Xuxian, XU Baolei, JIANG Changhao, et al. A hybrid BCI based on EEG and fNIRS signals improves the performance of decoding motor imagery of both force and speed of hand clenching[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2015, 12(3): 036004. doi: 10.1088/1741-2560/12/3/036004
|
| [11] |
YIN Xuxian, XU Baolei, JIANG Changhao, et al. NIRS-based classification of clench force and speed motor imagery with the use of empirical mode decomposition for BCI[J]. Medical Engineering & Physics, 2015, 37(3): 280–286. doi: 10.1016/j.medengphy.2015.01.005
|
| [12] |
李玉, 熊馨, 李昭阳, 等. 基于功能性近红外光谱识别右脚三种想象动作研究[J]. 生物医学工程学杂志, 2020, 37(2): 262–270. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.201905001LI Yu, XIONG Xin, LI Zhaoyang, et al. Recognition of three different imagined movement of the right foot based on functional near-infrared spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2020, 37(2): 262–270. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.201905001
|
| [13] |
WANG Kun, XU Minpeng, WANG Yijun, et al. Enhance decoding of pre-movement EEG patterns for brain-computer interfaces[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2020, 17(1): 016033. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ab598f
|
| [14] |
EDELMAN B J, BAXTER B, and HE Bin. EEG source imaging enhances the decoding of complex right-hand motor imagery tasks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2016, 63(1): 4–14. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2015.2467312
|
| [15] |
MILLER K J, ZANOS S, FETZ E E, et al. Decoupling the cortical power spectrum reveals real-time representation of individual finger movements in humans[J]. Journal of Neuroscience, 2009, 29(10): 3132–3137. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5506-08.2009
|
| [16] |
XIAO Ran and DING Lei. Evaluation of EEG features in decoding individual finger movements from one hand[J]. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, 2013, 2013: 243257. doi: 10.1155/2013/243257
|
| [17] |
SALEHI S S M, MOGHADAMFALAHI M, QUIVIRA F, et al. Decoding complex imagery hand gestures[C]. 2017 39th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Jeju, Korea, 2017: 2968–2971.
|
| [18] |
MWATA-VELU T, AVINA-CERVANTES J G, CRUZ-DUARTE J M, et al. Imaginary finger movements decoding using empirical mode decomposition and a stacked BiLSTM architecture[J]. Mathematics, 2021, 9(24): 3297. doi: 10.3390/MATH9243297
|
| [19] |
LIU Kunjia, YU Yang, LIU Yadong, et al. EEG-based motor imagery differing in task complexity[C]. 7th International Conference on Intelligence Science and Big Data Engineering, Dalian, China, 2017: 608–618.
|
| [20] |
CHEN Zhitang, WANG Zhongpeng, WANG Kun, et al. Recognizing motor imagery between hand and forearm in the same limb in a hybrid brain computer interface paradigm: An online study[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 59631–59639. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2915614
|
| [21] |
MOHAMED A K, MARWALA T, and JOHN L R. Single-trial EEG discrimination between wrist and finger movement imagery and execution in a sensorimotor BCI[C]. 2011 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, USA, 2011: 6289–6293.
|
| [22] |
KANDEL E R, SCHWARTZ J H, and JESSELL T M. Principles of Neural Science[M]. 4th ed. New York, USA: McGraw-Hill, 2000.
|
| [23] |
WANG Jiarong, BI Luzheng, and FEI Weijie. Using non-linear dynamics of EEG signals to classify primary hand movement intent under opposite hand movement[J]. Frontiers in Neurorobotics, 2022, 16: 845127. doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2022.845127
|
| [24] |
BENZY V K, VINOD A P, SUBASREE R, et al. Motor imagery hand movement direction decoding using brain computer interface to aid stroke recovery and rehabilitation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2020, 28(12): 3051–3062. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2020.3039331
|
| [25] |
CHOUHAN T, ROBINSON N, VINOD A P, et al. Wavlet phase-locking based binary classification of hand movement directions from EEG[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2018, 15(6): 066008. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/aadeed
|
| [26] |
SOSNIK R and BEN ZUR O. Reconstruction of hand, elbow and shoulder actual and imagined trajectories in 3D space using EEG slow cortical potentials[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2020, 17(1): 016065. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ab59a7
|
| [27] |
MONDINI V, KOBLER R J, SBURLEA A I, et al. Continuous low-frequency EEG decoding of arm movement for closed-loop, natural control of a robotic arm[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2020, 17(4): 046031. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/aba6f7
|
| [28] |
ROBINSON N, CHESTER W J, and SMITHA K G. Use of mobile EEG in decoding hand movement speed and position[J]. IEEE Transactions on Human-Machine Systems, 2021, 51(2): 120–129. doi: 10.1109/THMS.2021.3056274
|
| [29] |
CRAMER S C, WEISSKOFF R M, SCHAECHTER J D, et al. Motor cortex activation is related to force of squeezing[J]. Human Brain Mapping, 2002, 16(4): 197–205. doi: 10.1002/hbm.10040
|
| [30] |
WANG Kun, WANG Zhongpeng, GUO Yi, et al. A brain-computer interface driven by imagining different force loads on a single hand: An online feasibility study[J]. Journal of Neuroengineering and Rehabilitation, 2017, 14(1): 93. doi: 10.1186/s12984-017-0307-1
|
| [31] |
FU Yunfa, CHEN Jian, and XIONG Xin. Calculation and analysis of microstate related to variation in executed and imagined movement of force of hand clenching[J]. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, 2018, 2018: 9270685. doi: 10.1155/2018/9270685
|
| [32] |
XIONG Xin, FU Yunfa, CHEN Jian, et al. Single-trial recognition of imagined forces and speeds of hand clenching based on brain topography and brain network[J]. Brain Topography, 2019, 32(2): 240–254. doi: 10.1007/s10548-018-00696-3
|
| [33] |
USAMA N, KUNZ LEERSKOV K, NIAZI I K, et al. Classification of error-related potentials from single-trial EEG in association with executed and imagined movements: A feature and classifier investigation[J]. Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing, 2020, 58(11): 2699–2710. doi: 10.1007/s11517-020-02253-2
|
| [34] |
FARABBI A, ALOIA V, and MAINARDI L. ARX-based EEG data balancing for error potential BCI[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2022, 19(3): 036023. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ac6d7f
|
| [35] |
KUMAR A, GAO Lin, PIROGOVA E, et al. A review of error-related potential-based brain-computer interfaces for motor impaired people[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 142451–142466. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2944067
|
| [36] |
LOPES-DIAS C, SBURLEA A I, and MÜLLER-PUTZ G R. Online asynchronous decoding of error-related potentials during the continuous control of a robot[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 17596. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-54109-x
|
| [37] |
ZHANG Huaijian, CHAVARRIAGA R, GHEORGHE L, et al. Inferring driver's turning direction through detection of error related brain activity[C]. 2013 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Osaka, Japan, 2013: 2196–2199.
|
| [38] |
ITURRATE I, GRIZOU J, OMEDES J, et al. Exploiting task constraints for self-calibrated brain-machine interface control using error-related potentials[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(7): e0131491. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131491
|
| [39] |
EHRLICH S K and CHENG G. Human-agent co-adaptation using error-related potentials[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2018, 15(6): 066014. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/aae069
|
| [40] |
KREILINGER A, NEUPER C, PFURTSCHELLER G, et al. Implementation of error detection into the graz-brain-computer interface, the interaction error potential[C]. Assistive Technology from Adapted Equipment to Inclusive Environments, Florenz, Italy, 2009: 195–199.
|
| [41] |
PARASHIVA P K and VINOD A P. Improving direction decoding accuracy during online motor imagery based brain-computer interface using error-related potentials[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2022, 74: 103515. doi: 10.1016/J.BSPC.2022.103515
|
| [42] |
BHATTACHARYYA S, KONAR A, and TIBAREWALA D N. Motor imagery, P300 and error-related EEG-based robot arm movement control for rehabilitation purpose[J]. Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing, 2014, 52(12): 1007–1017. doi: 10.1007/s11517-014-1204-4
|
| [43] |
NOURMOHAMMADI A, JAFARI M, and ZANDER T O. A survey on unmanned aerial vehicle remote control using brain-computer interface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Human-Machine Systems, 2018, 48(4): 337–348. doi: 10.1109/THMS.2018.2830647
|
| [44] |
OSBORN L E, DING Keqin, HAYS M A, et al. Sensory stimulation enhances phantom limb perception and movement decoding[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2020, 17(5): 056006. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/abb861
|
| [45] |
MENG Jianjun, ZHANG Shuying, BEKYO A, et al. Noninvasive electroencephalogram based control of a robotic arm for reach and grasp tasks[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 38565. doi: 10.1038/srep38565
|
| [46] |
韩锦, 董博文, 刘邈, 等. 基于P300-SSVEP的双人协同脑-控机械臂汉字书写系统[J]. 数据采集与处理, 2022, 37(6): 1401–1411. doi: 10.16337/j.1004-9037.2022.06.020HAN Jin, DONG Bowen, LIU Miao, et al. Two-person collaborative brain-controlled robotic arm system for writing Chinese character using P300 and SSVEP features[J]. Journal of Data Acquisition and Processing, 2022, 37(6): 1401–1411. doi: 10.16337/j.1004-9037.2022.06.020
|
| [47] |
EDELMAN B J, MENG Jianjun, SUMA D, et al. Noninvasive neuroimaging enhances continuous neural tracking for robotic device control[J]. Science Robotics, 2019, 4(31): eaaw6844. doi: 10.1126/scirobotics.aaw6844
|
| [48] |
KOBLER R J, SBURLEA A I, and MÜLLER-PUTZ G R. Tuning characteristics of low-frequency EEG to positions and velocities in visuomotor and oculomotor tracking tasks[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 17713. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-36326-y
|
| [49] |
WALDERT S, PISTOHL T, BRAUN C, et al. A review on directional information in neural signals for brain-machine interfaces[J]. Journal of Physiology-Paris, 2009, 103(3/5): 244–254. doi: 10.1016/j.jphysparis.2009.08.007
|
| [50] |
HONG Jian and PARK J H. Efficacy of neuro-feedback training for PTSD symptoms: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research And Public Health, 2022, 19(20): 13096. doi: 10.3390/IJERPH192013096
|
| [51] |
BIASIUCCI A, LEEB R, ITURRATE I, et al. Brain-actuated functional electrical stimulation elicits lasting arm motor recovery after stroke[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 2421. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04673-z
|
| [52] |
BARSOTTI M, LEONARDIS D, LOCONSOLE C, et al. A full upper limb robotic exoskeleton for reaching and grasping rehabilitation triggered by MI-BCI[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, Singapore, 2015: 49–54.
|
| [53] |
LIU Jingyi, ABD-EL-BARR M, and CHI J H. Long-term training with a brain-machine interface-based gait protocol induces partial neurological recovery in paraplegic patients[J]. Neurosurgery, 2016, 79(6): N13–N14. doi: 10.1038/srep30383
|
| [54] |
QUANDT F and HUMMEL F C. The influence of functional electrical stimulation on hand motor recovery in stroke patients: A review[J]. Experimental & Translational Stroke Medicine, 2014, 6: 9. doi: 10.1186/2040-7378-6-9
|
| [55] |
YOO S S, LEE J H, O'LEARY H, et al. Neurofeedback fMRI-mediated learning and consolidation of regional brain activation during motor imagery[J]. International Journal of Imaging Systems and Technology, 2008, 18(1): 69–78. doi: 10.1002/ima.20139
|
| [56] |
XU Minpengg, HE Feng, JUNG T P, et al. Current challenges for the practical application of electroencephalography-based brain-computer interfaces[J]. Engineering, 2021, 7(12): 1710–1712. doi: 10.1016/j.eng.2021.09.011
|
| [57] |
LECUN Y, BENGIO Y, and HINTON G. Deep learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 521(7553): 436–444. doi: 10.1038/nature14539
|
| [58] |
XU Lichao, XU Minpeng, MA Zhen, et al. Enhancing transfer performance across datasets for brain-computer interfaces using a combination of alignment strategies and adaptive batch normalization[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2021, 18(4): 0460e5. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/AC1ED2
|





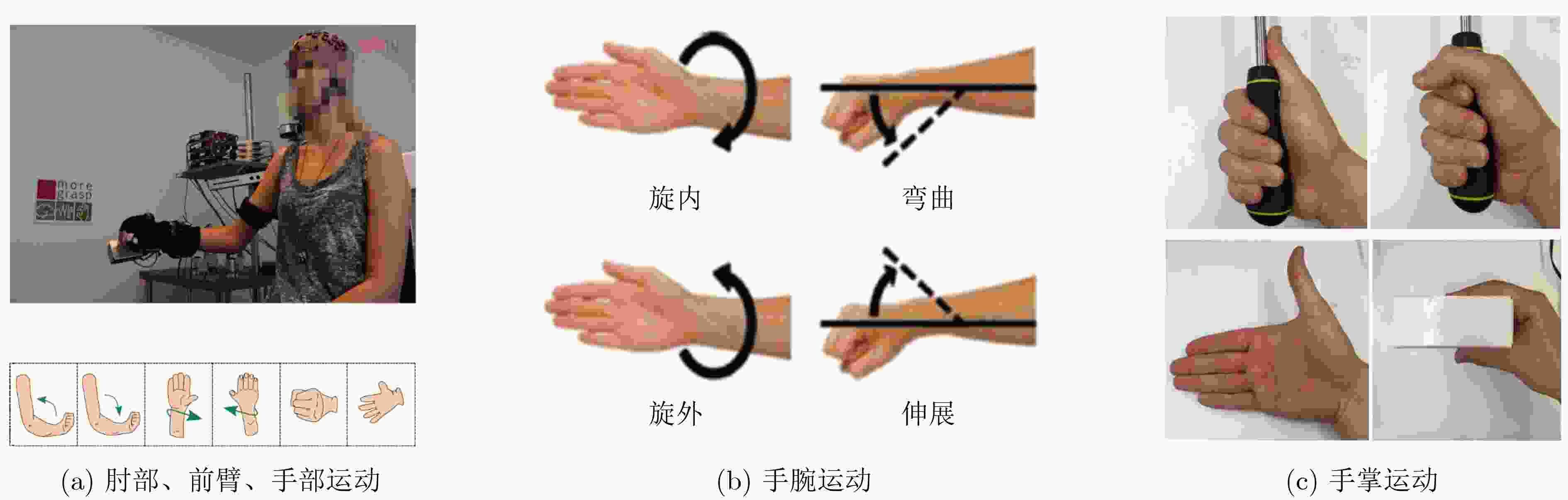
 下载:
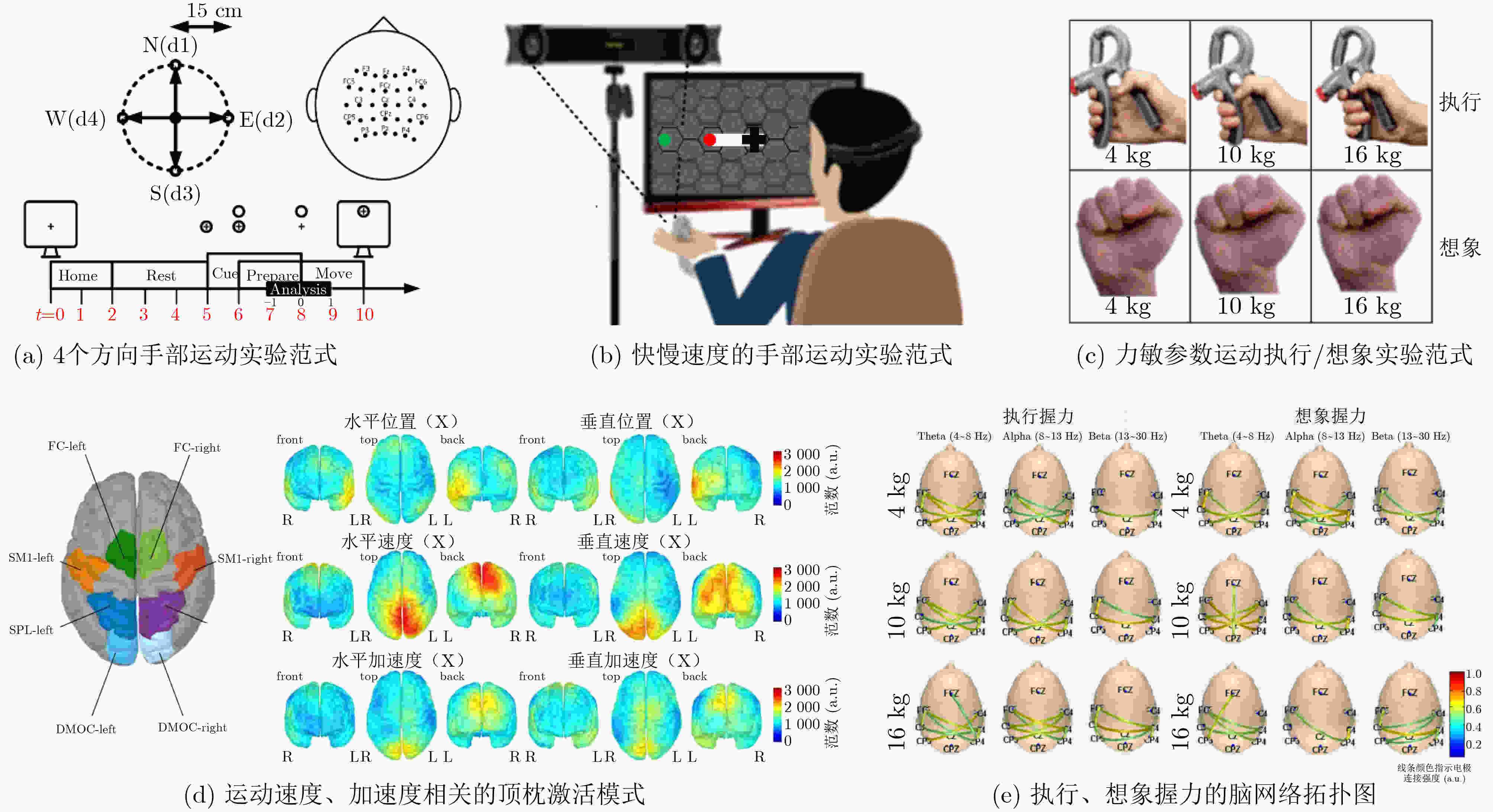
下载:
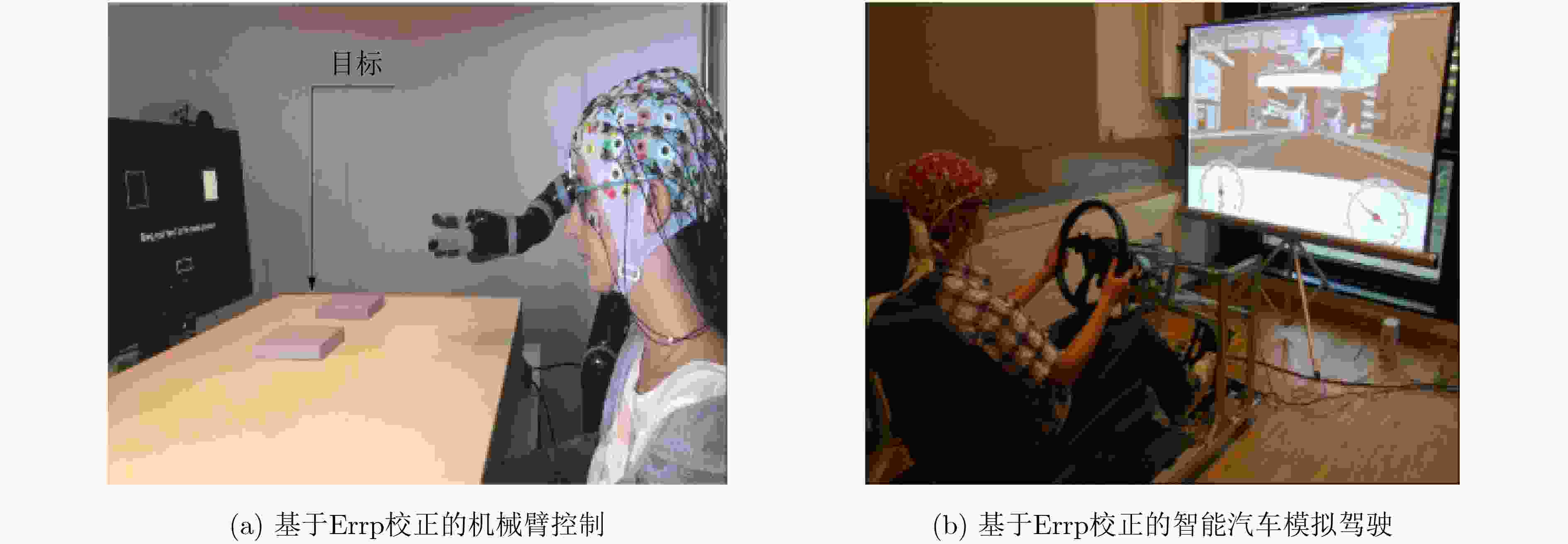


 下载:
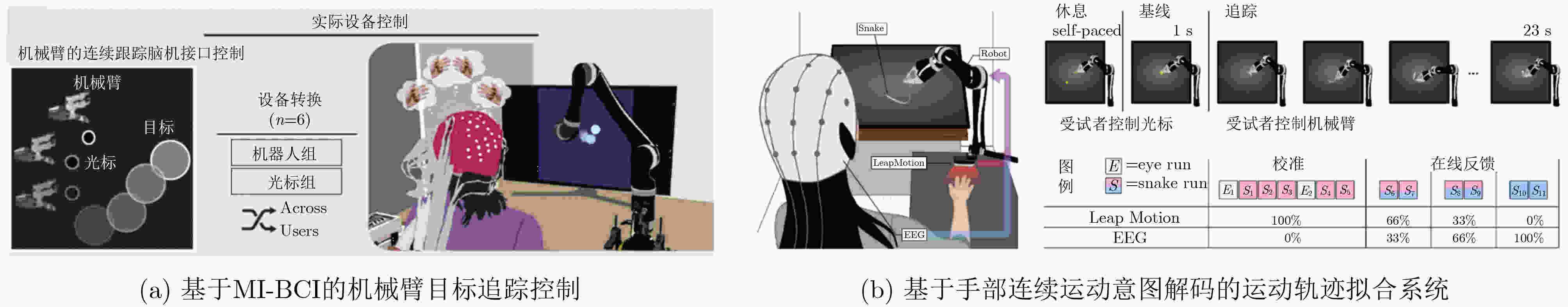
下载:
